IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Baikal-GVD: Underwater neutrino telescope
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Sci and Tech
In news
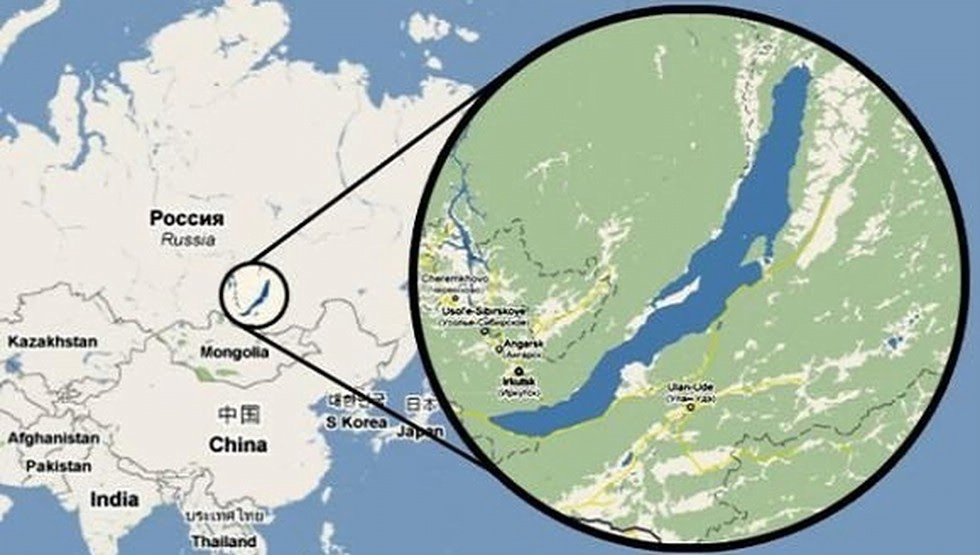
- Russian scientists launched one of the world’s biggest underwater neutrino telescopes called the Baikal-GVD (Gigaton Volume Detector) in the waters of Lake Baikail.
- Lake Baikal is the world’s deepest lake situated in Siberia.
Key takeaways
- Mission: To study in detail the fundamental particles called neutrinos and to possibly determine their sources.
- It is one of the three largest neutrino detectors in the world along with the IceCube at the South Pole and ANTARES in the Mediterranean Sea.
Important value additions
Lake Baikal
- Lake Baikal is a rift lake located in southern Siberia, Russia.
- It is the largest freshwater lake by volume in the world, containing 22 to 23% of the world’s fresh surface water.
- It is the seventh-largest lake in the world by surface area.
- Maximum depth: 1,642 m (5,387 ft)
- It is the world’s oldest (25–30 million years) and deepest lake.
- It has a long, crescent shape.
- The region to the east of Lake Baikal is referred to as Transbaikalia or as the Trans baikal.
- The loosely defined region around the lake itself is sometimes known as Baikalia.
- UNESCO declared Lake Baikal a World Heritage Site in 1996.
Launch of MyNEP2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – Education
In news
- “MyNEP2020” Platform of NCTE Web Portal was recently launched.
- Ministry: Ministry of Education
Key takeaways
- The platform seeks to invite suggestions from the stakeholders for preparing draft for development of National Professional Standards for Teachers (NPST) and National Mission for Mentoring Program membership (NMM).
- NPST and NMM are two major recommendations of NEP 2020.
- The platform will be operational from 1st April 2021 to 15th May 2021.
- For preparing the documents, NCTE will work in close consultation with individuals/organizations.
- Expert committee will extensively review the inputs collected during the consultation period and will finally formulate the Drafts for public review.
- Comments will then be used to prepare a final Draft for notification.
Do you know?
- National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE) is a statutory body of Indian government set up under the National Council for Teacher Education Act, 1993 in 1995 to formally oversee standards, procedures and processes in the Indian education system.
Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (SPACs)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Economy
In news
- Earlier this month, the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) issued an investor alert, which was the first warning of sorts for special purpose acquisition companies (SPACs).
Important value additions
- A SPAC, or a blank-cheque company, is an entity specifically set up with the objective of acquiring a firm in a particular sector.
- Aim: To raise money in an initial public offering (IPO), and at this point in time, it does not have any operations or revenues.
- Once the money is raised from the public, it is kept in an escrow account, which can be accessed while making the acquisition.
- If the acquisition is not made within two years of the IPO, the SPAC is delisted, and the money is returned to the investors.
- Certain market participants believe that, through a SPAC transaction, a private company can become a publicly-traded company with more certainty as to pricing and control over deal terms as compared to traditional IPOs.
Indian scenario:
- In India, renewable energy producer ReNew Power last month announced an agreement to merge with RMG Acquisition Corp II, a blank-cheque company.
- It became the first involving an Indian company during the latest boom in SPAC deals.
Committee formed to popularise the legacy of Anangpal II
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – I – History
In news
- The government has recently formed a committee to popularise the legacy of 11th-century Tomar king, Anangpal II.
Key takeaways
- Aim: To establish Anangpal II as the founder of Delhi.
- Headed by: Brij Bhushan Singh, BJP MP from UP’s Gonda
- Its proposals include building a statue of Anangpal II at the Delhi airport and building a museum dedicated to his legacy in Delhi.
- There is also a proposal to make Lal Kot an ASI-protected monument.
Important value additions
- Anangpal II was popularly known as Anangpal Tomar.
- He belonged to the Tomar dynasty that ruled parts of present-day Delhi and Haryana between the 8th and 12th centuries.
- He is credited to have established and populated Delhi during his reign in the 11th century.
- It was he who built Lal Kot fort and Anangtal Baoli.
- He was succeeded by his grandson Prithviraj Chauhan, who was defeated by the Ghurid forces in the Battle of Tarain (present-day Haryana) after which the Delhi Sultanate was established in 1192.
Upgradation of Kargil Zanskar road
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Infrastructure
In news
- Union Minister for Road Transport & Highways has approved a 780 Crore rupees project for upgradation of Kargil Zanskar road.
Key takeaways
- The 2 lane Kargil Zanskar NH 301 road is sanctioned under Engineering, Procurement and Construction (EPC) mode.
- Zanskar- Kargil road was declared National Highway in 2017.
- This road from Zanskar valley, also connects Suru valley, Sankoo valley of Kargil Ladakh with the Highway.
- It will be a key for economic development of the remote region of Ladakh.
Miscellaneous
Parosmia
-
Some people may experience parosmia as a symptom of COVID-19.
- Affected individuals experience “distortions of the sense of smell”.
- A person with parosmia can detect certain odours, but they might experience the smell of certain things as different and often unpleasant.
- For instance, to someone with parosmia, coffee may smell like burnt toast.
- Parosmia is a temporary condition and is not harmful.
- Some common triggers: Roasted, toasted or grilled foods, coffee, onions, chocolate, garlic and eggs.
- It is likely that parosmia manifests itself due to the damage caused to the olfactory neurons when “the delicate and complex structure in the nose is attacked by a virus.”
(Mains Focus)
EXECUTIVE/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Structure, organization and functioning of the Executive; Issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Prakash Singh Case: 2006 SC ruling on Police Reforms
Context: The recent allegations of lobbying by several IPS officers in Maharashtra and of ‘power brokers’ deciding on postings in nexus with the government shows that Political interference in police postings continues despite the landmark Prakash Singh judgment nearly decade-and-a-half ago
What is the SC’s Prakash Singh judgment on police reforms?
- Prakash Singh, who served as DGP of UP Police and Assam Police besides other postings, filed a PIL in the Supreme Court post retirement, in 1996, seeking police reforms. In 2006, the Supreme Court gave 7 directives with a view to bring in police reforms
- The Court put on record the deep rooted problems of politicization, lack of accountability mechanisms and systemic weaknesses that have resulted in poor all round performance and fomented present public dissatisfaction with policing.
The directives are –
- Setting up of State Security Commissions (SSC) – lays broad policy guidelines, evaluated performance of state police & ensures state government does not exercise unwarranted pressure
- Fixing the tenure (minimum of two years) and merit based transparent selection of the DGP
- A minimum tenure for the Inspector General of Police
- Separation of investigation and law and order functions
- Setting up of Police Establishment Boards– to decide transfers, postings, promotions and other service related matters of police officers of and below the rank of DySP and make recommendation with these matter of police officers above rank of DySP.
- Creating a Police Complaints Authority- to inquire into public complaints against police officers of and above the rank of DySP
- Forming a National Security Commission– at the union level to prepare a panel for selection and placement of Chiefs of the Central Police Organisations (CPO) with a minimum tenure of two years.
What has been the record of States implement SC directive?
- According to report by Commonwealth Human Rights Initiative (CHRI) notes that the efforts at implementing reforms remain slow, piecemeal and largely regressive. Not even one state was fully compliant with the apex court directives
- 18 states passed or amended their Police Acts in this time but not one fully matches legislative models.
- Not a single Union Territory is compliant with the directives, signalling the Central government’s non-compliance.
- Only six States provide security of tenure for their police chief and only 13 States have instituted an internal mechanism to enable the police leadership to make decisions on transfers and postings of State police officers without political interference
- The CHRI found that 26 out of 28 States have constituted an SSC either through Police Acts or government orders. While Telangana and Odisha are the only two States that have not established SSCs on paper, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka are the only States that make the recommendations of the SSC binding.
How State governments circumvent the SC directives to continue controlling the police?
- Piecemeal Changes: State legislations has been criticised for being “flawed” and only making piecemeal changes to save themselves from the ire of the Supreme Court that was pulling up states that had not followed its directives. It is also criticised that the state Acts were deliberately formulated in such a way that “it just gave legal garb to the status quo that existed before”.
- CM special powers retained: In Maharashtra Police Act of 2014, a section 22(N)(2) had been added that gave the CM special powers to transfer officers at any point in case of ‘administrative exigencies’. Thus, while the SC directive was that an officer should not be transferred before the given tenure, CM’s have used this section for mid-term transfer thereby maintaining control on transfers.
- Ineffective Police Establishment Boards: Several senior officers, some of whom have been part of the five-member PEB, has told that the officers on the committee are ‘unofficially’ informed by the government about which officer would be preferred for which post. Among five officers, even if one or two do not agree, the majority usually sides with what the postings that the government of the day is interested in, thus rendering PEBs ineffective in its functioning
- Inefficient State Police Complaints Authority (SPCA): In those states in which it was set up, SPCA did receive complaints from public. However, SPCA was struggling to set up offices in rural areas. Several activists had alleged that the SPCA was toothless as it could recommend action against any officer found guilty (final decision rested with the government). Also, the body has struggled due to lack of staff members.
Conclusion
The court’s intention in Prakash Singh directive was to bring this internal decision-making firmly to the police leadership. Continued non-compliance with this directive will only further undermine the authority of the police leadership, affect the morale of officers and blur accountability.
Connecting the dots:
ELECTIONS/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Structure, organization and functioning of the Legislature; Issues and challenges pertaining to elections
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Electoral Bonds Scheme
Context: In the wake of the upcoming State elections, the Association of Democratic Reforms (ADR) has filed a petition in the Supreme Court, seeking a stay in the electoral bond.
The Supreme Court recently flagged its concern that political parties could misuse crores of rupees received as donations through electoral bonds to bankroll violent protests or even terror.
About Electoral Bonds Scheme
- Electoral Bond is a financial instrument for making donations to political parties.
- The bonds are issued in multiples of Rs. 1,000, Rs. 10,000, Rs. 1 lakh, Rs. 10 lakh and Rs. 1 crore without any maximum limit.
- State Bank of India is authorised to issue and encash these bonds, which are valid for fifteen days from the date of issuance.
- These bonds are redeemable in the designated account of a registered political party.
- The bonds are available for purchase by any person (who is a citizen of India or incorporated or established in India) for a period of ten days each in the months of January, April, July and October as may be specified by the Central Government.
- A person being an individual can buy bonds, either singly or jointly with other individuals. Donor’s name is not mentioned on the bond.
Misuse of Electoral Bonds as Pointed Out during SC case:
- Anonymity: Neither the donor (who could be an individual or a corporate) nor the political party is obligated to reveal whom the donation comes from.
- Asymmetry of information: Because the bonds are purchased through the SBI (Central PSU), the government is always in a position to know who the donor is. This asymmetry of information threatens to favour the scheme towards the political party that is ruling at the time.
- Control Over usage: The court asked the government whether there is any “control” over how these donations were used by political parties.
- Scheme facilitates kickbacks: Though the original purchase of bonds could be done using white money, somebody could anonymously re-purchase the bonds from the original buyer and drop it at a political party office. Nobody will know who purchased the bonds from the original buyer. The scheme facilitates kickbacks
- Possibility of Money Laundering: With doing away with all the safeguard that were present in Corporate donations to Political parties (through Companies Act), Indian, foreign and even shell companies can now donate to political parties without having to inform anyone of the contribution.
- Question on procedure followed: The scheme was brought in through amendments to finance bill as the government of the day did not have majority in the Rajya Sabha (that has less powers w.r.t finance bill)
Government’s Defence:
- Conditions for electoral bonds: Only parties registered under the Representation of the People Act could receive donations through electoral bonds, and that they should not have secured less than 1% of the votes polled in the previous elections.
- Tackles Menace of Black Money in Politics: The Electoral Bond Scheme promotes white money into political funding (thus disincentivising black money) as it insists on cheque and digital paper trails of transactions
- Election Commission of India’s Support: ECI was not opposed to the bonds but was only concerned about the aspect of anonymity. It also urged the court not to stay the bonds and said the scheme is one step forward compared to the old system of cash funding, which was unaccountable.
Way Forward
- Voters can also help bring in substantial changes by demanding awareness campaigns. If voters reject candidates and parties that overspend or bribe them, democracy would move a step higher.
- Electoral bonds have raised questions on the electoral legitimacy of the government and thus the whole electoral process has become questionable. In this context, the courts should act as an umpire and enforce the ground rules of democracy.
- It is essential that if democracy is to thrive, the role of money in influencing politics ought to be limited. Thus, it is imperative that the scheme of the electoral bonds should be revised.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 One of the three largest neutrino detectors in the world was recently launched at which of the following ml
- Lake Baikal
- South Pole
- Mediterranean Sea
- Dead Sea
Q.2 Where is Lake Baikal situated?
- Israel
- Russia
- Tajikistan
- Turkey
Q.3 Which of the following was one of the factors for establishment of Delhi Sultanate in 1192?
- Battle of Tarain
- Battle of Kili
- Battle of Amroha
- First Battle of Panipat
ANSWERS FOR 1st March 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
On changes in Hong Kong’s special status by China:
On Places of Worship Act:
On benefits of updated land records:











