IASbaba's Press Information Bureau, UPSC Articles
GS-2
Government takes steps to ramp up availability of Amphotericin B – to fight Mucormycosis
(Topic: Health)
A sudden increase in demand has been observed in some states for Amphotericin B which is being actively prescribed by the physicians to patients suffering from Mucormycosis, a post COVID complication. The Government of India is therefore engaging with the manufacturers to ramp up production of the drug. The supply position is expected to improve with extra imports of this drug and increase in its production domestically.
Mucormycosis
- Mucormycosis is also called Black Fungus or Zygomycosis.
- It is a serious but rare fungal infection caused by a group of molds called mucormycetes.
- It occurs through inhalation, inoculation, or ingestion of spores from the environment.
- Mucormycosis does not spread between people or between people and animals.
- It usually occurs in people who have health problems or take medicines that lower the body’s ability to fight germs and sickness.
- Symptoms: One-sided facial swelling and numbness, headache, nasal or sinus congestion, black lesions on nasal bridge or upper inside of the mouth, fever, abdominal pain, nausea and gastrointestinal bleeding.
- It needs to be treated with prescription antifungal medicine.
- Often, mucormycosis requires surgery to cut away the infected tissue.
- There is no vaccine to prevent it.
- Early detection can prevent loss of eyesight, nose or jaw through clinical intervention.
Amphotericin B injection is used to treat serious and potentially life-threatening fungal infections.
- It is in a class of medications called antifungals.
- It works by slowing the growth of fungi that cause infection.
- It is typically given by injection into a vein.
- Amphotericin B was isolated from Streptomyces nodosus in 1955 and came into medical use in 1958.
- It is on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines.
Threefold increase in production of Remdesivir in the country
(Topic: Health)
Drugs such as Remdesivir are given to patients who have ‘moderate or moderate progressing towards severe’ COVID-19 infection.
How does it work?
Once the virus enters the human cell, it releases its genetic material, which is then copied using the body’s existing mechanism. At every stage of infection, various human proteins, virus proteins, and their interactions come into play. At the replication stage, the key viral protein, called RdRp, becomes the engine of the virus. Remdesivir acts by directly attacking RdRp. With Remdesivir replacing the ‘feeding’ material it needs, the virus fails to replicate further.
When should Remdesivir ideally be used?
Remdesivir was the first drug approved by the USFDA for treating the SARS-CoV-2 virus. It was claimed to be effective in the severe and critical stages of COVID-19. But, it was also understood to be ‘hepatotoxic’, damaging to the liver cells.
Practically viral replication ends in the first 1-7 days, complications that occur in critical and severe COVID-19 post 7-8 days are due to an inflammatory response (SIRS). So this drug ideally should be used in the early stages, between the second and tenth day when viral replication is happening.
What patients need to know
According to a WHO study, Remdesivir fails to prevent deaths among patients, but may reduce the length of hospital stay by 1-3 days. It should not be used on patients who are asymptomatic, mildly symptomatic or who are severely ill and have suffered multi-organ dysfunction. It can, however, be used between the second and tenth day of infection to improve its effectiveness among patients who have moderate or moderate progressing-towards-severe infection.
Liquid Medical Oxygen
(Topic: Health)
We know 65% of human body is oxygen. Yes, oxygen is vital for respiration, the process that transfers energy from glucose to cells. In fact, every cell in our body requires oxygen. When we breathe air in, oxygen molecules enter the lungs and pass through lung walls into our blood.
Oxygen is crucial for the treatment of patients with severe COVID-19, since the disease affects lung functioning. Shortness of breath or difficulty of breathing is one of the most common symptoms in patients with severe COVID-19. It also hampers the supply of oxygen to various parts of the body. They hence need oxygen therapy, to be supplied through medical oxygen.
One of the ways in which this oxygen can be supplied is through Liquid Medical Oxygen (LMO). LMO is nothing but high purity oxygen used for medical treatment, and is developed for use in the human body.
Why in liquid state
Due to its low melting and boiling points, oxygen is in a gaseous state at room temperature. Liquification enables storage in larger volume and easier transportation.
How Liquid Medical Oxygen is produced
There are several methods. The most common production method is separation of oxygen in what are known as Air Separation Units or ASUs. ASUs are basically plants that separate large volumes of gases. They use a method called Fractional Distillation Method to produce pure oxygen from atmospheric air, which consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen – 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and remaining 1% other gases including argon, carbon dioxide, neon, helium, and hydrogen.
In this method, gases from the air are separated into various components after cooling them into a liquid state and then liquid oxygen is extracted from it.
Atmospheric air is first cooled to -181°C. Oxygen liquifies at this point. Since, the boiling point of Nitrogen is -196°C, it remains in a gaseous state. But Argon has a boiling point similar to that of oxygen (–186°C) and hence a significant amount of Argon liquifies along with Oxygen.
The resultant mixture of Oxygen and Argon is drained, decompressed and passed through a second low-pressure distillation vessel for further purification. We then get the output as final purified liquid oxygen, which is then transported using cryogenic containers.
What are cryogenic containers?
Cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures.
A cryogenic liquid is defined as a liquid with a normal boiling point below –90°C. Cryogenic liquid containers are specially designed for safe and economic transportation and storage of liquefied gases at cryogenic temperatures, lower than –90°C. These containers are highly insulated, in which liquid gases are stored at very low temperatures.
What is Pressure Swing Adsorption Technique?
Oxygen can also be produced non-cryogenically, in gaseous form, using selective adsorption. This method leverages the property that under high pressure, gases tend to be attracted to solid surfaces. The higher the pressure, the more the adsorption of gas.
If a gas mixture such as air is passed under pressure through a vessel containing an adsorbent bed of ‘zeolite’ that attracts nitrogen more strongly than oxygen, a part or all of the nitrogen will stay in the bed, and the gas exiting the vessel will be richer in oxygen, relative to the mixture entering the vessel.
Hospitals can also opt for on-site generation of oxygen by this method, where oxygen is produced from ambient air by concentrating it. Producing oxygen near hospitals has the additional advantage of eliminating need for transportation. In addition to the above sources of medical oxygen, there are also portable oxygen generators known as Oxygen Concentrators that can be used at home.
India-UK Virtual Summit
(Topic: International Relations)
UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson announced new UK-India trade and investment worth 1 billion pounds, including an investment of 240 million pounds by the Serum Institute of India for its vaccine business in Britain.
The key takeaways from the virtual summit between Indian Prime Minister and the UK Prime Minister –
A. The UK-India trade and investment package:
- The package includes over 533 million pounds of new Indian investment into the UK, in vital and growing sectors such as health and technology, British exports to India worth more than 446 million pounds, while 200 million pounds of these deals will support low carbon growth.
- The investments include 240 million pounds to be pumped in by the Serum Institute for its vaccine business in Britain, and a new sales office.
B. ‘Roadmap 2030′
- To elevate bilateral ties to a ‘Comprehensive Strategic Partnership’.
- It will pave the way for a deeper and stronger engagement over the next ten years in the key areas of people to people contacts, trade and economy, defence and security, climate action and health.
C. ‘Enhanced Trade Partnership’ (ETP)
- It sets an ambitious target of more than doubling bilateral trade by 2030.
- As part of the ETP, India and the UK agreed on a roadmap to negotiate a comprehensive and balanced FTA, including consideration of an Interim Trade Agreement for delivering early gains.
D. India-UK ‘Global Innovation Partnership’
- It aims to support the transfer of inclusive Indian innovations to select developing countries, starting with Africa
- Cabinet gives ex-post facto approval to MoU between India and UK on Global Innovation Partnership
E. A comprehensive partnership on migration and mobility
- It will facilitate greater opportunities for the mobility of students and professionals between the two countries.
- Cabinet approves MoU between India and United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland on Migration and Mobility Partnership
India-EU Leaders’ Meeting
(Topic: International Relations)
At the invitation of the President of the European Council, Indian Prime Minister participated in the India-EU Leaders’ Meeting.
Key takeaways
- The meeting was held in a hybrid format.
- Leaders of all the 27 EU Member States, President of the European Council and the European Commission participated.
- This is the first time that the EU hosted a meeting with India in the EU+27 format.
- It will further build on the momentum witnessed in the relationship since the 15th India-EU Summit in July 2020.
- During the meeting, the leaders exchanged views on three key thematic areas: i) foreign policy and security; ii) COVID-19, climate and environment; and iii) trade, connectivity and technology.
Do you know?
- India and the EU launched an ambitious and comprehensive ‘Connectivity Partnership’ which is focused on enhancing digital, energy, transport and people-to-people connectivity.
- India welcomed the EU’s decision to join CDRI.
- India and the EU also agreed to enhance bilateral cooperation on digital and emerging technologies such as 5G, AI, Quantum and High-Performance Computing including through the early operationalization of the Joint Task Force on AI and the Digital Investment Forum.
- A finance contract of Euro 150 million for the Pune Metro Rail Project was signed by the Ministry of Finance and European Investment Bank.
India participates in the 3rd Arctic Science Ministerial
(Topic: International Relations)
The first two meetings—ASM1 and ASM2—were held in the USA in 2016 and Germany in 2018, respectively. ASM is a global platform for discussing cooperation and research in the Arctic Region. The first Arctic Science Ministerial was held in the US in 2016 and the second one was in Germany in 2018. The third was jointly organized by Japan and Iceland and was held in Asia.
Objective: The Arctic Science Ministerial aims at providing opportunities to various stakeholders, which include indigenous communities, academia, policymakers, and governments, to enhance their collective understanding of the Arctic Region. It also emphasizes and engages in the constant monitoring and strengthening of observations.
India will continue to continue to play a positive role in deepening the shared understanding of the Arctic through research, observation, international cooperation, and capacity building.
- India shared its plans of contributing to the observing systems in the Arctic, both by remote-sensing or on-site.
- India will be deploying open ocean mooring in the Arctic Region. It will be for the long-term monitoring of the upper ocean variables and marine meteorological parameters.
- India talked about the growing evidence of a connection between the Indian Ocean and the Arctic region, which modulates the Indian Monsoon. It added that improving the understating of physical processes and measuring the impact of Arctic ice melt on India’s monsoon is significant.
- NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellite Mission: Informed that the launch of the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellite Mission, in collaboration with the United States is also underway. The mission by India and the US aims at conducting global measurements of the consequences and cause of the land surface changes with the use of advanced radar imaging.
- Contributions to the Sustained Arctic Observational Network (SAON) would continue. It is a joint activity of the International Arctic Science Committee (IASC) and the Arctic Council. The purpose is to support and strengthen the development of multinational engagement for sustained and coordinated pan-Arctic observing and data sharing systems.
India’s engagement with the Arctic dates back to 1920 with the signing of the Svalbard Treaty in Paris.
- India has had a permanent research station in the Arctic Region called Himadari at NyAlesund, Svalbard Area in Norway, since July 2008.
- It has also deployed a multi-sensor moored observatory known as IndARC in Kongsfjordan fjord since July 2014.
- India’s research in the Arctic Region is conducted, coordinated, and promoted by the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research, Goa. It comes under the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- Recently, India drafted a new Arctic policy that aims at expanding scientific research, sustainable tourism and exploration of mineral oil and gas in the Arctic region
GS-3
Agarbatti sector to bring back livelihoods for local communities
(Topic: Agriculture)
National Bamboo Mission has launched an MIS (Management Information Systems) based reporting platform for agarbatti stick production to collate the locations of stick making units, availability of raw material, functioning of the units, production capacity, marketing, etc.
With the help of this module, the linkages with the industry will be synergised better to enable seamlessly procurement from production units and information gaps can be plugged. All NBM States are in the process of documenting all the units to assess better how further support can be given for ‘Vocal for Local’ and ‘Make for the World’ since Indian agarbatti are much sought after in global markets.
National Bamboo Mission (NBM), Ministry of Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME), Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) schemes as well as States, together with industry partners have stepped up focused support to enable India to become Atma Nirbhar in the agarbatti sector, to bring back livelihoods for the local communities while at the same time modernising the sector too. The agarbatti sector traditionally provided large scale employment to the local workforce, which however dwindled due to various factors including the ingress of cheap imports of round sticks and raw batti.
A comprehensive study was carried out by NBM in 2019 following which policy measures taken by the Government of moving raw batti imports from free to restricted category in Aug 2019 and increasing import duty on round stick uniformly to 25% in June 2020 came as a boost to the domestic units.
Background of NBM
The restructured National Bamboo Mission (NBM) was launched in 2018-19 for holistic development of the bamboo sector through a cluster-based approach in a hub (industry) and spoke model to harness the opportunities by providing backward and forward linkages among the stakeholders – linking farmers to markets.
There is a huge potential to place Indian bamboo products in the domestic as well as global markets with the latest technologies, modern processing and by generating awareness on compliance requirements for destination countries. The Mission is streamlining its interventions to enhance domestic industrial activities as well as augmenting the farmer’s income with support from technical agencies and facilitative steps. Direct subsidy of 50% is given to farmers at Rs 1.00 lakh per ha, 100% to Government agencies and also to entrepreneurs for setting up various product development units, etc.
The Mission is presently being executed by 21 States, including all the 9 States of NER through the respective State Bamboo Missions. NBM is also advising States to make available quality planting material to the farmers out to carry out plantations of commercially required species, set up common facility centres and other post-harvest units in complete sync with the requirement of existing and sunrise industries for a win-win situation for farmers and Indian bamboo industry.
Ministry of Food Processing Industries issues guidelines for ‘Production Linked Incentive Scheme for the Food Processing Industry’
(Topic: Economy)
Government of India has approved a new Central Sector Scheme namely‘ Production Linked Incentive Scheme for Food Processing Industry’ for implementation during 2021-22 to 2026-27 with an outlay of Rs. 10,900 crore.
Objective: To support creation of global food manufacturing champions commensurate with India’s natural resource endowment and support Indian brands of food products in the international markets.
Ministry of Food Processing Industries is inviting applications for availing sales based incentives and grants for undertaking Branding & Marketing activities abroad under the scheme from three categories of Applicants:
- Category-I: Applicant under this category could undertake Branding & Marketing activities abroad also and apply for grant under the scheme with a common application.
- Category-II: SMEs Applicants manufacturing innovative/ organic products who apply for PLI Incentive based on Sales.
- Category-III: Applicants applying solely for grant for undertaking Branding & Marketing activities abroad
Cabinet approves Production Linked Incentive scheme “National Programme on Advanced Chemistry Cell Battery Storage”
(Topic: Economy)
Aim: To achieve a manufacturing capacity of 50 GigaWatt Hour of ACC and five Giga Watt Hour of Niche ACC with an outlay of 18,100 crore.
- ACCs are the new generation of advanced storage technologies that can store electric energy either as electrochemical or as chemical energy and convert it back to electric energy as and when required.
- It will also give a big push to electric mobility, benefiting three-wheelers, four-wheelers and heavy vehicles.
- India is currently importing Battery Storage Equipment
- The scheme will be helpful in making the country self-reliant (Atmanirbhar).
Biodegradable yoga mat developed by 6 young girls from Assam may save lakes from water hyacinth menace
(Topic: Environment)
The girls belong to the fishing community living in the fringe of the Deepor Beel, a permanent freshwater lake in south west of Guwahati city, recognised as a Ramsar Site (a wetland of international importance) and a bird wildlife sanctuary. The lake has been a source of livelihood for 9 villages of the fishing community who shared this biome for centuries, but over the years suffered from excessive growth and accumulation of water hyacinth.
The innovation by the girls, whose families are directly dependent on the wetland for survival, could contribute significantly towards the environmental conservation and sustainability of Deepor Beel and also ensure local livelihood. The mat called ‘Moorhen Yoga Mat’ will soon be introduced to the world market as a unique product; named after Kam Sorai (Purple moorhen, a resident bird of Deepor Beel Wildlife sanctuary).
The intervention was triggered through an initiative by North East Centre for Technology Application and Reach (NECTAR), an autonomous body under Department of Science & Technology (DST), Govt. of India to involve the entire women community associated with a collective called ‘Simang’ meaning dream, led by the 6 girls to create wealth from water hyacinth plants.
Considering all aspects of water hyacinth’s properties and the functional requirements of a product like a mat, a hand-woven 100% biodegradable and 100 % compostable mat to be used for doing Yoga was ideated as a means to provide multiple ecological and social benefits.
- The mat developed through fiber processing and technological interventions could improve the aquatic ecosystem of the wetland through removal of water hyacinth, help sustainable production of utility products with community engagement and generate of livelihood for indigenous communities to become completely ‘Atamanirbhar’.
- As the collection, drying and preparation of the water hyacinth before using it for weaving is the most important process, small interventions of technology were introduced like using ‘solar dryer’ which reduced the drying time to about 3 days. It could also compensate for the loss in time due to heavy rains that take place very frequently in this part of the country over a six month long rainy season (May-October).
- The women wove water hyacinth using traditional Assamese loom with the help of different combinations of techniques, materials and tools to develop a high quality, comfortable and thoroughly biodegradable and compostable Yoga Mat. It has resulted in engagement of 38 women from 3 fringe villages (Keotpara, Notun Basti and Borbori). Technology intervention could also increase the production rate.
Prelims-oriented News
Statehood Day of Gujarat and Maharashtra: 1st May
Assam CM: Shri Himanta Biswa Sarma
National Technology Day: 11th May
India’s first Olympic-bound Fencer: Bhavani Devi
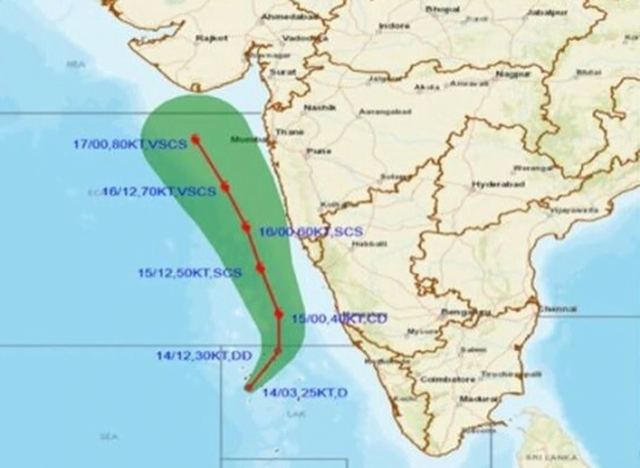
Cyclone Tauktae: Cyclone ‘Tauktae’, which lay as a deep depression over the Arabian Sea close to Lakshadweep, was likely to intensify into a ‘very severe cyclonic storm’ bringing heavy to very heavy rain to many parts of the western coast
Sovereign Gold Bond Scheme 2021-22: The Central Government in consultation with the RBI, has decided to issue Sovereign Gold Bonds.
- The Sovereign Gold Bonds will be issued in six tranches from 17th May to September 2021.
- The Bonds will be sold through Scheduled Commercial banks (except Small Finance Banks and Payment Banks), Stock Holding Corporation of India Limited (SHCIL),designated post offices, and National Stock Exchange of India Limited and Bombay Stock Exchange Limited.
- The minimum permissible investment will be one gram of gold.
- Investors will be compensated at a fixed rate of 2.50% per annum payable semi-annually on the nominal value.
- The Bonds will be restricted for sale to resident individuals, Hindu Undivided Families, Trusts, Universities and Charitable Institutions.
- The tenor of the Bond will be for a period of 8 years with exit option after 5th year to be exercised on the next interest payment dates.
Section 142 of the Social Security Code – 2020 Notified: Section 142 of the Social Security Code, 2020 has been notified by Ministry of Labour & Employment covering applicability of Aaadhar. The notification of section will enable Ministry of Labour and Employment to collect Aaadhar details for the database of beneficiaries under various social security schemes.
National Data Base for unorganised workers (NDUW) is at an advanced stage of development by National Informatics Centre. The portal is aimed at collection of data for unorganised workers including migrant workers for the purpose of giving benefits of the various schemes of the Government. An inter-state migrant worker can register himself on the portal on the basis of submission of Aaadhar alone.
Release of the new framework for implementation of SVAMITVA Scheme: The SVAMITVA Framework developed by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj provides a detailed roadmap and guidelines for the various States in terms of the Scheme objectives, coverage, various components involved, year-wise funding pattern, survey approach and methodology, stakeholders involved and their roles and responsibility, monitoring and evaluation, and deliverables.
- Property cards have been distributed in more than 7400 villages and more than 7,00,000 beneficiaries have been benefited from the Scheme across the country. The scheme will benefit rural residents by providing them with property cards that can be used for taking loans and the creation of accurate land records for rural planning.
- SVAMITVA Scheme aims to provide property rights to the residents of rural inhabited areas in India by using Drone survey and CORS Networks which provides mapping accuracy of 5 cms. It was launched by the Prime Minister on the occasion of National Panchayati Raj Day on 24th April 2021 after successful completion of the pilot phase of the Scheme in 9 States.
- The Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR) is the Nodal Ministry for implementation of the SVAMITVA scheme. In the States, the Revenue Department/Land Records Department will be the Nodal Department and shall carry out the scheme with the support of State Panchayati Raj Departments.
Government of India and European Investment Bank sign finance contract for second tranche of Euro 150 million for Pune Metro Rail project: The project aims to provide efficient, safe, economic and pollution-free Mass Rapid Transit System in densely populated area in the city of Pune served with heterogeneous traffic options. The financing from EIB will help to fund construction and operation of Corridor 1 (North-South) – Pimpri Chinchwad Municipal Corporation (PCMC) to Swargate and Corridor 2 (West-East) –Vanaz (Kothrud) to Ramvadi, totaling about 31.25 kilometers (km) and related purchase of a related fleet of metro cars. Further, the project will serve large population which consisting working class in providing urban mobility for their livelihood.
Boost to India’s rice exports potential: First consignment of non-basmati rice exports from Paradip port, Odisha flagged off to Vietnam;
- This is the first time in the history of Paradip Port, non-basmati rice will be exported.
- The rice exports through PICT would hugely boost India’s exports of non-basmati rice to south-east countries while boosting income of at least two lakh farmers from Odisha and adjoining states
India begins exports of organic millets grown in Himalayas to Denmark: In a major boost to organic products exports from the country, first consignment of millets grown in Himalayas from snow-melt water of Ganges in Dev Bhoomi (Land of the God), Uttarakhand would be exported to Denmark.
- The exports of millets to Denmark would expand exports opportunities in European countries.
- The exports would also support thousands of farmers that are getting into organic farming.
- Millets are gaining a lot of popularity globally because of high nutritive values and being gluten free also.
About Millet:
- Millets are considered as ‘superfood’ and ‘eat smart’ strategies.
- High protein content, short growing season, climate change resilience and low water requirement make millets an ideal crop for the State.
- Millets can grow in poor soil conditions with less water, fertiliser and pesticides. They can withstand higher temperatures, making them the perfect choice as ‘climate-smart’ cereals.
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) scheme
- Under this programme, vulnerable landholding farmer families, having cultivable land, will be provided direct income support at the rate of Rs. 6,000 per year.
- This income support will be transferred directly into the bank accounts of beneficiary farmers, in three equal installments of Rs. 2,000 each.
Objectives of PM KISAN scheme:
- To supplement the financial needs of small and marginal farmers for procuring various inputs related to agriculture and allied activities.
- To give a boost to rural consumption.
- To augment government efforts in aim of doubling farmers income by 2022.
Features of PM KISAN Scheme:
- PM KISAN is a Central Sector scheme with 100% funding from Government of India
- Under the scheme income support of Rs.6000/- per year in three equal instalments will be provided to small and marginal farmer families
- Definition of the family for the scheme is husband, wife and minor children.
- State Government and UT Administration will identify the farmer families which are eligible for support as per scheme guidelines.
- The fund will be directly transferred to the bank accounts of the beneficiaries.
Significance of PM KISAN Scheme
- It provides support to small and marginal farmers who are largely involved in subsistence farming and struggles to invest in agriculture inputs or technology,
- It will boost the rural consumption and positive for agriculture and allied sectors.
- Poverty reduction: Cash transfer programmes are an important tool of social protection and poverty reduction. They have an immediate impact on reducing hunger and rural poverty.
- Better use: This can increase productive investment, increase access to markets and stimulate local economies. Income support can be used to make a repayment or at least activate a bank account which can then receive a loan.
- Rural development: It can serve as an important complement to a broader rural development agenda, including a pro-poor growth strategy focusing on agriculture.
Asiatic Lions housed in Hyderabad zoo infected with SARS-COV2 recovering well: Further analyses of the samples have revealed that the infection was not caused by any variant of concern. The eight lions have been isolated and due care and necessary treatment has been provided. All the eight lions have responded well to the treatment and recovering. They are behaving normally and eating well.
- Preventive measures are already in place for all zoo staff and the zoo has been closed to visitors to avoid minimal external contact.
- Based on experience with zoo animals elsewhere in the world that have experienced SARS-COV2 positive last year, there is no factual evidence that animals can transmit the disease to humans any further.
Asiatic Lion
- It is a Panthera leo leo population in India.
- Its current range is restricted to the Gir National Park and environs in the Indian state of Gujarat.
- It is one of five pantherine cats inhabiting India. Others are:
- Bengal tiger
- Indian leopard
- Snow leopard
- Clouded leopard
- It is also known as the “Indian lion” and the “Persian lion”.
- Status:
- Listed in Schedule I of Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972
- Appendix I of CITES
- Endangered on IUCN Red List.
- It is slightly smaller than African lions.
- The most striking morphological character is a longitudinal fold of skin running along belly of Asiatic Lions.
Van Dhan Yojana
- It is an initiative of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and TRIFED, launched in 2018, to improve tribal incomes through the value addition of tribal products.
- It is a Market Linked Tribal Entrepreneurship Development Program for forming clusters of tribal Self-Help-Groups (SHGs) and strengthening them into Tribal Producer Companies
- It aims to set-up tribal community owned Minor Forest Produce (MFP)-centric multi-purpose Van Dhan Vikas Kendras.
- The Kendras would act as common facility centres for procurement cum value addition to locally available MFPs.
- One typical Van Dhan Vikas Kendra comprises of 15 Self Help Groups, each consisting of 20 Tribal gatherers.
- These SHGs will get training on sustainable harvesting/collection, primary processing & value addition and also provided with working capital to conduct their business.
SUTRA model: Scientists working for charting the trajectory of COVID-19 using a mathematical model
Nitrogen generating plants to be converted to generate oxygen: Considering the requirement of medical oxygen amidst the COVID-19 pandemic situation, the Government of India explored the feasibility of conversion of existing nitrogen plants to produce oxygen.
- The process of converting the existing Pressure Swing Absorption (PSA) nitrogen plants for production of oxygen was discussed. In the nitrogen plants Carbon Molecular Sieve (CMS) is used whereas Zeolite Molecular Sieve (ZMS) is required for producing oxygen. Therefore, by replacing CMS with ZMS and carrying out few other changes such as oxygen analyzer, control panel system, flow valves etc. existing nitrogen plants can be modified to produce oxygen.
- On deliberation with the industries, so far 14 industries have been identified where conversion of plants is under progress. Further 37 Nitrogen plants have been also identified with the help of industry associations.
- A nitrogen plant modified for the production of oxygen can be either shifted to a nearby hospital or, in case it is not feasible to shift the plant, it can be used for on-site production of oxygen, which can be be transported to hospital through specialized vessels/cylinders.
IIT develops portable tech-traditional eco-friendly mobile cremation system: Indian Institute of Technology, Ropar has developed a prototype of a moveable electric cremation system which claims to be using first of its kind technology that involves smokeless cremation despite using wood.
- It uses half of the wood otherwise required for the cremation and still is eco-friendly because of the technology that uses combustion air system.
- It is based on wick-stove technology in which the wick when lighted glows yellow. This is converted into smokeless blue flame with the help of combustion air system installed over the wicks.
- The cart-shaped incinerator has wheels and can be transported anywhere without much efforts. The cart is equipped with combustion air for primary and secondary hot air system. The disposal of the body is completed within 12 hrs including cooling time as against 48 hours required in the normal wood-based cremation.
Personality in News
Guru Tegh Bahadur (1621–1675) – 400th Birth Anniversary (Prakash Purab)
The period of history in India in the last four centuries cannot be imagined without the influence of Guru Tegh Bahadur, the ninth Sikh Guru.
- Guru Tegh Bahadur was the ninth of ten Gurus of the Sikh religion. Born at Amritsar in 1621, was the youngest son of Guru Hargobind.
- One hundred and fifteen of his hymns are in Guru Granth Sahib.
- There are several accounts explaining the motive behind the assassination of Guru Tegh Bahadur on Aurangzeb’s orders. He stood up for the rights of Kashmiri Pandits who approached him against religious persecution by Aurangzeb.
- He was publicly killed in 1675 on the orders of Mughal emperor Aurangzeb in Delhi for himself refusing Mughal rulers and defying them.
- Gurudwara Sis Ganj Sahib and Gurdwara Rakab Ganj Sahib in Delhi mark the places of execution and cremation of his body.
Impact of his martyrdom: The execution hardened the resolve of Sikhs against religious oppression and persecution. His martyrdom helped all Sikh Panths consolidate to make the protection of human rights central to its Sikh identity. Inspired by him, his nine-year-old son, Guru Gobind Singh Ji, eventually organized the Sikh group into a distinct, formal, symbol-patterned community came to be known as Khalsa (Martial) identity.
Gurudev Rabindranath Tagore
- Also known by his pen name Bhanu Singha Thakur (Bhonita), and also known by his sobriquets Gurudev, Kabiguru, and Biswakabi, was a polymath, poet, musician, artist and ayurveda-researcher from the Indian subcontinent
- He is sometimes referred to as “the Bard of Bengal”
- Author of the “profoundly sensitive, fresh and beautiful verse” of Gitanjali, he became in 1913 the first non-European to win the Nobel Prize in Literature
- As a humanist, universalist, internationalist, and ardent anti-nationalist, he denounced the British Raj and advocated independence from Britain. As an exponent of the Bengal Renaissance, he advanced a vast canon that comprised paintings, sketches and doodles, hundreds of texts, and some two thousand songs; his legacy also endures in the institution he founded, Visva-Bharati University.
- Gitanjali (Song Offerings), Gora (Fair-Faced) and Ghare-Baire (The Home and the World) are his best-known works, and his verse, short stories, and novels were acclaimed—or panned—for their lyricism, colloquialism, naturalism, and unnatural contemplation.
- His compositions were chosen by two nations as national anthems: India’s Jana Gana Mana and Bangladesh’s Amar Shonar Bangla. The Sri Lankan national anthem was inspired by his work.
- Tagore’s Nobel Prize was stolen from the safety vault of the Visva-Bharati University, along with several other of his belongings on March 25, 2004. However, on December 7, 2004, the Swedish Academy decided to present two replicas of Tagore’s Nobel Prize, one made of gold and the other made of bronze, to the Visva-Bharati University. It inspired the fictional film Nobel Chor.
- In the year 2011, to mark and honour Gurudev’s 150th birth anniversary, the Government of India had issued five rupee coins.
- It was Tagore who conferred the title of ‘Mahatma’ on MK Gandhi in 1915. Although Tagore is said to have admired Gandhi, he differed with him on certain issues.
- Rabindranath Tagore and Albert Einstein met four times between 1930 and 1931 and mutually revered each other for each other’s contributions.
Gopal Krishna Gokhale (1866-1915)
A protégé of Ranade and influenced by the British philosopher-parliamentarian Edmund Burke, Gokhale worked towards realising constitutional ideals in India for three decades and abjured the use of reactionary or revolutionary ways.
Gokhale first arrived on the national scene after cross-examining British colonial expenditure at the Welby Commission of 1897 in England. Gokhale’s work earned him praise in India as he laid bare British military financing policies that heavily burdened Indian taxpayers much to the chagrin of then Viceroy Lord Curzon — regarded among the most vituperative of racists to occupy that post.
In 1899, Gokhale joined the Indian National Congress, emerging as one of the main leaders of its ‘moderate’ wing, and gave up teaching three years later to work as a lawmaker for the remainder of his life.
At Bombay, Gokhale opposed the British government’s onerous land revenue policies, advocated free and compulsory primary education, and asked for the creation of equal opportunities to fight against untouchability. At the Imperial legislature, Gokhale played a key role in framing the Morley-Minto reforms of 1909 and advocated for the expansion of legislative councils at both the Centre and the provinces. A critic of British imperial bureaucracy, Gokhale favoured decentralisation and the promotion of panchayat and taluka bodies.
He also spoke for the Indian diaspora living in other parts of the British Empire and opposed tooth and nail the indentured labour system, raising their problems in the Imperial legislature as well as at Congress sessions.
Gokhale became Congress president at its Banaras session in 1905. This was also the time when bitter differences had arisen between his group of ‘Moderates’ and the ‘Extremists’ led by Lala Lajpat Rai and Bal Gangadhar Tilak among others. Matters came to a head when the two factions split at the Surat session of 1907. Historians note that despite ideological differences, Gokhale maintained cordial relations with his opponents. In 1907, he fervently campaigned for the release of Lala Lajpat Rai, who was imprisoned that year by the British at Mandalay in present-day Myanmar.
After Mahatma Gandhi’s return to India, he joined Gokhale’s group before going on to lead the independence movement. Gandhi regarded Gokhale as his political mentor, and wrote a book in Gujarati dedicated to the leader titled ‘Dharmatma Gokhale’.
Maharana Pratap
The 13th king of Mewar, a region in north-western India in the present-day state of Rajasthan
Rana Pratap’s defiance of the mighty Mughal empire, almost alone and unaided by the other Rajput states, constitute a glorious saga of Rajput valour and the spirit of self-sacrifice for cherished principles.
Battle of Haldighati was fought between Akbar and Maharana Pratap Singh.
Note: Maharana Pratap Sagar, also known as Pong Reservoir or Pong Dam Lake was created in 1975, by building the highest earthfill dam in India on the Beas River in the wetland zone of the Siwalik Hills of the Kangra district of the state of Himachal Pradesh. Named in the honour of Maharana Pratap (1540–1597), the reservoir or the lake is a well-known wildlife sanctuary and one of the 26 international wetland sites declared in India by the Ramsar Convention











