IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Draft Rules for Live-Streaming Court Proceedings
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – JUdiciary; Governance
In news
- Recently, the Supreme Court has released the Draft Model Rules for Live-Streaming and Recording of Court Proceedings.
- The Rules are part of the National Policy and Action Plan for implementation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in the judiciary.
- The Supreme Court in Swapnil Tripathi v Supreme Court of India (2018) had ruled in favour of opening up the apex court through live-streaming.
- It held that the live streaming proceedings are part of the right to access justice under Article 21
Key features of the Draft Rules
- All proceedings in high courts can be telecast except for cases relating to matrimonial disputes, gender-based violence, those involving minors.
- The final decision to allow the Live-streaming of the Proceedings or any portion thereof will be of the Bench.
- Court proceedings can be archived for six months.
- The rules also prohibit recording or sharing the telecast on media platforms, including social media and messaging platforms, unless authorised by the court.
Benefits
- Justice delivery system will become affordable, transparent, speedy and accountable by limiting the paper filings.
- It can be time saving
Concerns:
- Lack of technical manpower in courts and awareness
- Cyber security threat.
- Issues of privacy may arise.
- Infrastructure, especially the internet connectivity is also a big challenge
BRICS issues Joint Statement on Multilateralism
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – International Relations & GS-III – Economy
In news
- The BRICS Foreign Ministers put out a joint statement on multilateralism recently.
- The idea is to form a common understanding among the BRICS countries.
- Multilateralism is the process of organizing relations between groups of three or more states.
Six Principles laid out by BRICS
- It should make global governance more inclusive, representative and participatory.
- It should be based on inclusive consultation and collaboration.
- It should make multilateral organisations more action-oriented and solution-oriented.
- It should use innovative solutions, including digital and technological tools.
- It should strengthen the capacities of individual States and international organizations.
- It should promote people-centered international cooperation at the core.
Important value additions
BRICS
- BRICS is an acronym for the grouping of the countries – Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
- India has assumed the BRICS Presidency from January 2021.
- It does not exist in the form of organization.
- The Chairmanship of the forum is rotated annually among the members, in accordance with the acronym B-R-I-C-S.
Surakshit Hum Surakshit Tum Abhiyan: Aspirational Districts
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Policies and interventions; Health
In news
- Recently, NITI Aayog and Piramal Foundation launched ‘Surakshit Hum Surakshit Tum Abhiyan’ in 112 aspirational districts.
- Objective: To assist the administration in providing home care support to Covid-19 patients, who are either asymptomatic or have mild symptoms.
- Most of these districts are in Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Maharashtra.
- The campaign is a part of a special initiative – Aspirational Districts Collaborative.
- Local leaders, civil societies and volunteers work with the district administrations to address emerging issues of the Aspirational Districts Programme.
Important value additions
‘Transformation of Aspirational Districts’ Programme (TADP)
-
- It was launched in January 2018.
- Aspirational Districts are those 112 districts in India that are affected by poor socio-economic indicators.
- It is carried out by the state governments
- Objective: To monitor the real-time progress of aspirational districts.
- Core Principles:
-
- Convergence (of Central & State Schemes) which brings together the horizontal and vertical tiers of the government.
- Collaboration (of Central, State level ‘Prabhari’ Officers & District Collectors) which enables impactful partnerships between government, market and civil society.
- Competition among districts driven by a spirit of the mass movement fosters accountability on district governments.
India elected to UN Economic and Social Council for 2022-24 term
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – International Relations
In news
- India has been elected to the United Nations Economic and Social Council, ECOSOC for the term 2022-24.
Important value additions
United Nations Economic and Social Council, (ECOSOC)
- The UN Charter established ECOSOC in 1945.
- It is one of the six main organs of the United Nations.
- Members:
- The Council consists of 54 Member States, elected yearly by the General Assembly for overlapping three-year terms.
- Seats on the Council are allotted based on geographical representation
- Mandate: It is the central platform for:
- fostering debate and innovative thinking
- forming consensus on ways forward
- coordinating efforts to achieve internationally agreed goals.
- It is also responsible for the follow-up to major UN conferences and summits
Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP) Program
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- The World Bank has approved a USD 500 million program to help boost India’s MSME sector.
- The program is the Raising and Accelerating Micro, Small and Medium Enterprise (MSME) Performance (RAMP) Program.
- It is the World Bank’s second intervention in this sector.
- The first intervention was the USD 750 million MSME Emergency Response Program.
Features of the RAMP
- The programme targets improvements in the performance of 5.5 lakh MSMEs.
- It is expected to mobilise financing of USD 15.5 billion, as part of the government’s USD 3.4 billion MSME Competitiveness – A Post-COVID Resilience and Recovery Programme (MCRRP).
- It will provide better access to finance and working capital for MSMEs by strengthening the financing markets.
- It will also scale up online dispute resolution mechanisms to address the problem of delayed payments.
Other Initiatives by India for MSME sector
- Prime Minister Employment Generation Programme and Other Credit Support Schemes
- Financial Support to MSMEs in ZED Certification Scheme
- A Scheme for Promoting Innovation, Rural Industry & Entrepreneurship (ASPIRE)
- National Manufacturing Competitiveness Programme (NMCP)
- Entrepreneurship Skill Development Programme (ESDP)
Miscellaneous
Quacquarell Symonds (QS) World University Rankings
- IIT-Bombay, IIT-Delhi and Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru Bada only Indian institutions that made it to the top 200 globally
- Globally Massachusetts Institute of Technology was ranked number one followed by University of Oxford.
- Stanford University and the University of Cambridge shared the third spot.
- QS uses 6 indicators to compile the ranking: Academic reputation, Employer reputation, citations per faculty, faculty/student ratio, International faculty ratio and international student ratio.
(Mains Focus)
INTERNATIONAL/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: India and its neighbourhood
- GS-2: Issues related to Health and Governance
South Asia’s healthcare burden
Context: On May 18 this year, India recorded 4,529 deaths from COVID-19, the highest daily death toll recorded in the world after the United States in January saw 4,468 deaths.
Several things are to blame for such high deaths
- super spreader events
- Fragile health infrastructure neglected for decades
- Citizens not following health protocols
- Logistical mismanagement
As India combats the pandemic, its neighbours are experiencing spillover from the menacing second wave.
- Sri Lanka added as many as 78,218 cases in May.
- Pakistan crossed over 200 daily deaths in April, its highest since the pandemic started.
- Bangladesh’s situation is precarious, given the recent detection of the highly contagious Delta variant.
- Bhutan is the only exception, with only one death and 1,724 cases so far. The country’s success stems from a well-funded and prepared public health system with stringent measures, responsible citizenship, and an accountable government
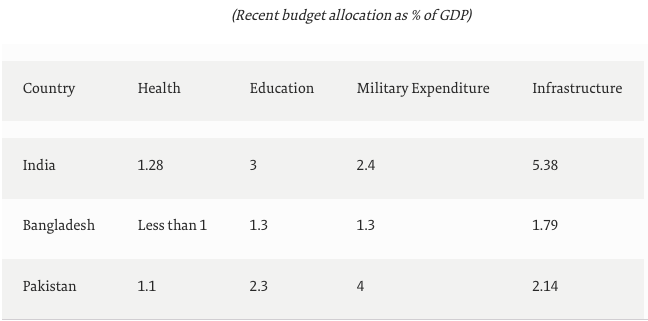
Health issues in South Asia
- India’s health expenditure is little over 1% of India’s GDP. Public healthcare sector has been operating at a pitiful 0.08 doctors per 1,000 people (WHO Standard is 1 per 1,000)
- India has only half a bed available for every 1,000 people. Bangladesh and Pakistan fare no better, with a bed to patient ratio of 0.8 and 0.6, respectively.
- While ideally, out-of-pocket expenditure should not surpass 15% to 20% of the total health expenditure, for India, Bangladesh and Pakistan, this figure stands at an appalling 62.67%, 73.87% and 56.24%, respectively.
- While India has the world’s third-largest military expenditure, its health budget is the fourth-lowest.
- In Pakistan, even amidst the pandemic, the defence budget was increased by 12% in the fiscal year 2020-21, to $7.85 billion, while the spending on health remained around $151 million.
- Major public sector investments by the ‘big three’ of South Asia, i.e., India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, are towards infrastructure and defence, with health taking a backseat.
Way Ahead
- South Asia can take lessons in pragmatic healthcare policy from Southeast Asia, which has prioritised investments in healthcare systems while broadening equitable access through universal health coverage schemes.
- Given the high chances of another wave or even the impending crisis of climate change, stopgap measures ought to be replaced by a well-thought-out vision and political commitment for long-term healing.
Connecting the dots :
INTERNATIONAL/ SCIENCE & TECH
Topic:
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
- GS-3: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life
Bitcoin: Legalised by El Salvador
Context: El Salvador, a small coastal country in Central America became the first in the world to make Bitcoin, a digital currency, legal. The El Salvador Parliament approved the move by a supermajority of 62 out of 84.
- The President added that the use of Bitcoin, whose use will be optional, would not bring risks to users.
- “The government will guarantee the convertibility to the exact value in dollars at the moment of each transaction,” El Salvador President said.
What were the reasons for EL Salvador taking such decision?
- No impact on Monetary policy: El Salvador has no monetary policy of its own and hence, no local currency to protect. The country was officially ‘dollarized’ in 2001 and runs on the monetary policy of the US Federal Reserve. Thus, it was easier for El Salvador to legalise Bitcoin for it doesn’t impact its monetary policy as much as it would have in case of other countries like India, US, Germany etc.
- To mitigate dependence on US Dollar: The move in El Salvador is in part motivated by loose and expansionary Federal Reserve policy. While banks in the US received liquidity with the stimulus, El Salvador did not but lost purchasing power instead. Thus, EL Salvador wanted a digital currency that cannot be altered by Central Bank (of USA)
- Co-existence with Dollar: President of El Salvador clarified that this does not constitutes “de-dollarization” of the economy. He believes the dollar will continue to remain the dominant currency in the country and Bitcoin would exist side by side.
- Attracting Investments: The overall use of Bitcoin appears less motivated by its use as a currency and much more by the image and investment boost this could give El Salvador towards innovation. This move is being used to portray innovator friendly environment for luring “technology, talent and new ideas” into the country.
- Potential shift in remittances: Remittances make up close to 20% of El Salavador’s GDP with flows approximating $6 billion annually. President Nayib Bukele has said that this move of legalising iotcoin will help people cut down on middleman payments during remittances.
Challenges
- Talk with IMF: Experts have said the move to Bitcoin could complicate talks with the IMF, where El Salvador is seeking a more than $1bn programme.
- Impact on Tax collection: The move makes it difficult for the government in raising of tax revenues. Cryptocurrencies are overall a very easy way to avoid taxation and a very easy way to simply avoid the authorities because it’s a completely decentralised system, one can do money laundering and one can do tax avoidance
- Implication on money laundering: With large scale cryptocurrency inflows and outflows, it would be expected that El Salvador would comply with the 2019 FATF guidance on Virtual Currencies which mandates multiple KYC requirements on cryptocurrency activity. It is unclear if these are in place in El Salvador or would be put in place.
Implication on India
- The impact Bitcoin has on these remittance inflows would be worth monitoring for India, which is home to the largest remittance market in the world.
- Although there might not be many lessons from a monetary policy perspective but efficiency, anti money-laundering and other aspects could be closely monitored.
- The overall takeaway for India from the El Salvador case is not in the monetary sense at all but as an example of how far countries are willing to go to attract innovators and entrepreneurs working on this emerging sector
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding United Nations Economic and Social Council, (ECOSOC):
- It is one of the main six organs of the UN.
- The Members are elected yearly by the General Assembly for three-year terms.
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Surakshit Hum Surakshit Tum Abhiyan’ in 112 aspirational districts was launched by which of the following?
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Health
- Ministry of Social JusticE and Empowerment
- National Commission for Backward Classes
ANSWERS FOR 9th June 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
Must Read
On global minimum tax:
On digital justice delivery:
About police reforms:











