IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Global Economic Prospects Report by World Bank
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Economy
In news
- Recently, the World Bank has released its June 2021 Global Economic Prospects
- It has forecast India’s GDP growth to be 8.3% for the year 2021-22.
- India’s economy is expected to grow at 7.5% for 2022-23 and 6.5% for 2023-24.
Key findings of the report
- The world economy is expected to expand at 5.6%, the fastest post-recession growth rate in eighty years.
- However, global output will still be 2% below pre-pandemic projections by year-end.
- India’s recovery is being hampered by the largest outbreak of any country since the beginning of the pandemic.
- The forecast for FY22 (8.3%) takes into account expected economic damage from an enormous second Covid-19 wave and localised mobility restrictions since March 2021.
- For 2022-23, growth is expected to slow to 7.5% as a result of the pandemic’s effects on the financial position of households, companies and banks.
Suggestions by the report
- Globally coordinated efforts are essential to accelerate vaccine distribution and debt relief, particularly for low-income countries.
- Policymakers need to address the pandemic’s lasting effects.
- They need to take steps to stimulate green, resilient, and inclusive growth.
Major Reports by the World Bank
- Human Capital Index.
- World Development Report.
- Migration and Development Brief.
- Global Economic Prospects.
Indian Railways Gets 5 MHz Spectrum
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Infrastructure
In news
- Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the allotment of 5 MHz spectrum in the 700 MHz frequency band to the Indian Railways for improving its communication and signalling systems.
- Railways has also approved a indigenously developed Train Collision Avoidance System (TCAS).
- The target of the project is to complete in five years
- It is estimated to cost over Rs. 25,000 crore.
- The spectrum charges will be levied based on formula as prescribed by Department of Telecommunications for Royalty Charges and License Fee for captive use as recommended by the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI).
- With this spectrum, the railways will introduce Long-Term Evolution (LTE)-based Mobile Train Radio Communication (MTRC) on its routes.
- LTE is a fourth-generation (4G) wireless standard that provides increased network capacity and speed for cellphones and other cellular devices compared with third-generation (3G) technology.
Benefits of the allotment
- Provide Modern signalling and train protection systems
- Secure and reliable voice, video and data communication
- Help prevent train accidents and reduce delays
- Enable the railways to undertake Internet of Things (IoT) based remote asset monitoring
- IoT is a computing concept that describes the idea of everyday physical objects being connected to the internet and being able to identify themselves to other devices.
Train Collision Avoidance System (TCAS)
- It is a microprocessor based control system, which continuously monitors the speed, direction of travel, and alertness of the motorman.
- It will help in improving the safety and increasing the line capacity to accommodate more trains using the existing infrastructure.
- The modern rail network will result in reduced transportation cost and higher efficiency.
Important value additions
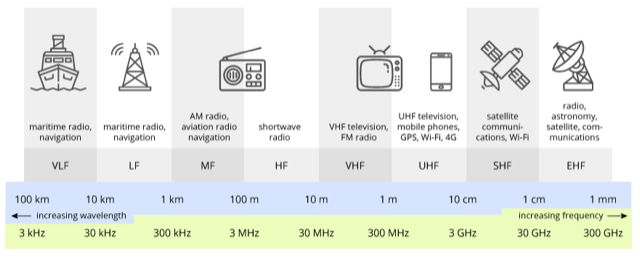
Radio Spectrum
- The radio spectrum (also known as Radio Frequency or RF) is a part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Electromagnetic waves in this frequency range are called radio frequency bands or simply ‘radio waves’.
- Radio waves have the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum.
- These were discovered by Heinrich Hertz in the late 1880s.
- RF bands spread in the range between 30 kHz and 300 GHz
- The generation and transmission of radio frequency bands is strictly regulated by national laws, coordinated by an international body, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Pic Courtesy: Terasense
Fast Tracking Freight in India: NITI Aayog
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Infrastructure
In news
- NITI Aayog, Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI) and RMI India’s new report, “Fast Tracking Freight in India: A Roadmap for Clean and Cost-Effective Goods Transport”, present key opportunities for India to reduce its logistics costs.
- The report outlines solutions for freight sector related to policy, Technology, Business models and infrastructure development
- Freight transportation is the process of transporting commodities, goods and cargo balance by land, sea or air
- Logistics sector represents 5% of India’s GDP and employs 2.2 crore people.
- Due to the rising demand for goods and services, freight transport demand is expected to grow rapidly in the future.
According to the report, India has the potential to
- Reduce its logistics cost by 4% of GDP
- Achieve 10 gigatonnes of cumulative CO2 emissions savings between 2020 and 2050
- Reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) emissions by 35% and 28%, respectively, until 2050
Issues
- High logistics costs
- Contributes to rising CO2 emissions and air pollution in cities.
Recommendations
- Increasing the rail network’s capacity
- Promoting intermodal transport
- Improving warehousing and trucking practices
- Policy measures
- Pilot projects for clean technology adoption
- Stricter fuel economy standards.
Recent Initiatives for freight transportation:
- Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC): Railway corridor that is exclusively meant for the transportation of freight,
- E-Way Bill Integration with FASTag, RFID
- FAME Scheme: adoption of electric vehicles (EV), with a goal of reaching 30% EV penetration by 2030.
- Bharat Stage VI norms
- Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE) Regulations: aim to increase fuel efficiency of vehicles on the road by 35% by 2030.
UNDP Report on Hindu Kush Himalayan Mountains
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Climate change; Conservation
In news
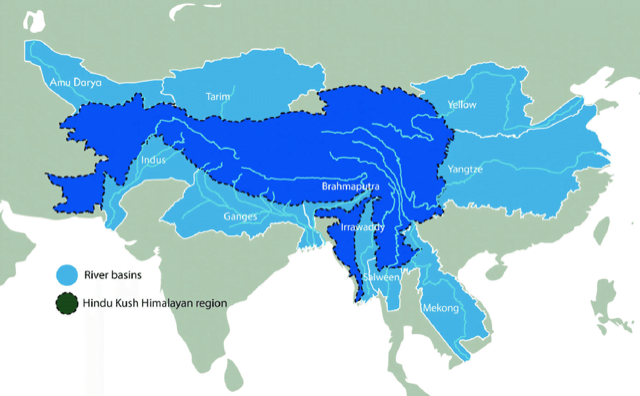
- According to UNDP (United Nations Development Programme) report, ‘Melting glaciers; Threatened livelihoods; Confronting climate change to save the Third pole’, the Hindu Kush Himalayan (HKH) mountain ranges could lose up to two-third of its ice by 2100.
- About 2 billion people may face food, water shortages by 2100.
- Glacier melting in HKH region is caused by:
- larger anthropogenic modifications of the atmosphere
- disruption in weather patterns and precipitation due to global warming
- changes in Glacier volume
- Unplanned urbanization
Impact
- Threatens climate as well as monsoon patterns
- It impacts 10 major river systems which help in agricultural activities, provide drinking water and hydro electricity production in the region
- socio-economic disruption and human displacement
Recommendation
- Shifting away from fossil fuel use in energy transport and other sectors
- Changing diets and agricultural practices to move to net zero emissions of greenhouse gases
- Improve data and information capacity building and early warning systems
Important value additions
- HKH extends over 8 countries – Afghanistan, Bhutan, Bangladesh, China, India Myanmar, Nepal and Pakistan
- It contains the world’s third largest storage of frozen water after Antarctica and Arctica
- It is also referred as the third pole of the world.
Pic courtesy: Researchgate
Dihing Patkai is Assam’s 7th National Park
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – National Parks
In news
- Dihing Patkai as a National Park was recently notified as Assam’s national Park.
- Raimona National Park in western Assam’s Kokrajhar district was also notified recently.
Key takeaways
- Assam now has the third most National Parks after the 12 in Madhya Pradesh and nine in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- The five older National Parks in the State: Kaziranga, Manas, Nameri, Orang and Dibru-Saikhowa.
- Kaziranga and Manas are UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
- They are also tiger reserves along with Nameri and Orang.
- Dihing Patkai is a major elephant habitat
- Short stretches of the Dirak and Buri Dihing rivers have been included in the park,
- Raimona adjoins the Buxa Tiger Reserve in West Bengal to its west, Phipsoo Wildlife Sanctuary in Bhutan to its north and the first addition to Manas National Park to the east.
- Raimona is home to the golden langur, elephant, tiger, clouded leopard and Indian gaur
Miscellaneous
Operation Pangea XIV: Interpol
-
Recently, the International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol) through its Operation Pangea XIV targeted the sale of fake medicines and products online.
- Operation Pangea, is a well-established international effort of Interpol to disrupt the online sale of counterfeit and illicit health products.
- Pangea works to raise awareness of the risks associated with buying medicines from unregulated websites.
- The first Operation Pangea was conducted in 2008.
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Indian Economic challenges
Context: According to NSO’s provisional estimates for 2020-21, the annual contraction in real GDP turned out to be 7.3 per cent, an improvement over the earlier estimate of 8 per cent.
Economic Projections
- A real GDP growth of 7.8 per cent would be required in 2021-22 to reach back to 2019-20 real GDP levels.
- It is estimated that with suitable policy interventions, a 9 per cent real GDP growth may still be feasible if the lockdowns wind-up by end July.
- The Controller General of Accounts’ data for the Centre’s fiscal aggregates indicate a gross tax revenues (GTR) of Rs 20.2 lakh crore and net tax revenue of Rs 14.2 lakh crore for 2020-21.
- The projected gross and net tax revenues for 2021-22 would mean Rs 22.7 lakh crore and Rs 15.8 lakh crore respectively.
- Taking into account RBI’s recently announced dividend of Rs 0.99 lakh crore to the Centre, the main shortfall may be in non-debt capital receipts. Together, the overall shortfall in total non-debt receipts may be limited to about Rs 0.9 lakh crore or 0.4 per cent of estimated nominal GDP.
What expenditure should be prioritised?
Given the economic challenges in the wake of the second wave, three expenditure heads need to be prioritised.
- First, an increase in the provision for income support measures for the vulnerable rural and urban population. This would require an amount of Rs 1 lakh crore which may be partly provided through expenditure restructuring.
- Second, in light of the recent decision, the budgeted expenditure on vaccination of Rs 0.35 lakh crore ought to be augmented, at the very least, doubled.
- Third, additional capital expenditure for select sectors, particularly healthcare, should also be provided for. This may be another Rs 1 lakh crore.
Together these additional expenditures would amount to Rs 1.7 lakh crore, about 0.8 per cent of the estimated nominal GDP.
What will the impact of all these on fiscal deficit?
- Thus, we need to plan for a fiscal deficit of about 7.9 per cent of GDP consisting of
- (a) a budgeted fiscal deficit of 6.7 per cent
- (b) 0.4 per cent to make up for the shortfall in total non-debt receipts and
- (c) 0.8 per cent for the additional stimulus measures.
- Given the higher fiscal deficit, it would need to add to its borrowing programme another Rs 2.6 lakh crore, taking the total borrowing, including GST compensation, to about Rs 16.3 lakh crore, from Rs 12.05 lakh crore now.
Way Ahead
- The success of the borrowing programme of the Centre depends on the support provided by the RBI.
- The support need not be direct. It can be indirect as is currently happening with RBI injecting liquidity into the system in a big way.
- The injection of liquidity has its limits. Even as we emphasise the expansion in government spending, it is necessary to keep in mind the implications that liquidity expansion will have for inflation.
Connecting the dots:
INTERNATIONAL/ ECONOMY
Topic:
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
- GS-2: Regional groupings involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
G-7 and India
Context: At the invitation of UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson, Prime Minister Narendra Modi will participate in the Outreach Sessions of the G7 Summit on June 12 and June 13, in virtual format.
The UK currently holds the presidency of the G7 and has invited India, along with Australia, Republic of Korea and South Africa, as guest countries for the Summit.
About G-7
- The G7 comprises the US, UK, France, Germany, Italy, Canada and Japan.
- It is an intergovernmental organisation that was formed in 1975.
- The bloc meets annually to discuss issues of common interest like global economic governance, international security and energy policy.
- The G-7 does not have a formal constitution or a fixed headquarters. The decisions taken by leaders during annual summits are non-binding.
- The G7 was known as the ‘G8’ for several years after the original seven were joined by Russia in 1997. The Group returned to being called G7 after Russia was expelled as a member in 2014 following the latter’s annexation of the Crimea region of Ukraine
What is on the agenda of G-7 this year?
The theme for the summit is ‘Build Back Better’ and the UK has outlined four priority areas for its presidency. These are
- Leading the global recovery from coronavirus while strengthening resilience against future pandemics;
- Promoting future prosperity by championing free and fair trade;
- Tackling climate change and preserving the planet’s biodiversity;
- Championing shared values and open societies.
Is India attending it for the first time?
- Since 2014, this is the second time PM Modi will be participating in a G7 meeting.
- India had been invited by the G7 French Presidency in 2019 to the Biarritz Summit as a “Goodwill Partner” and the Prime Minister participated in the Sessions on ‘Climate, Biodiversity and Oceans’ and ‘Digital Transformation’.
- During Prime Minister Manmohan Singh’s UPA rule, India attended the G8 five times.
- In 2020, US under President Donald Trump had extended an invitation to India.
- Calling the G7 a “very outdated group” Trump had suggested that the Group of 7 be called “G10 or G11” by including India, Australia, South Korea and Russia. That, however, did not happen owing to the pandemic and the US elections’ outcome.
What to watch out for at this G-7 summit?
- Break from Trump’s America First Policy: This will be US President Joe Biden’s first visit to Europe, where he will signal his key message “America is back”. This will be a shift from Trump’s American First Policy where US withdrew from Global leadership roles.
- US realignment with Russia: After meeting allies at the G7 summit US President Biden continue on to a NATO conclave in Brussels on June 14, before his conversation with Russian President Vladimir Putin in Geneva later.
- Strategic Rival in China: The key element that is making Washington take the important step of engaging with Moscow to contain the damage in their bilateral ties is that the US wants to focus on its strategic rival, China.
- Reviving Multilateralism: This ties in well with the US President’s initial foray into multilateralism — he held the first summit of leaders of “the Quad” — Australia, India, Japan and the US. This is considered as contrast to Trump’s style of dealing bilaterally.
- Post COVID Economic Recovery: The Group of Seven might make a further joint declaration on “a comprehensive plan to help end this pandemic as rapidly as possible”.
- Global Vaccination: Biden will announce a major new initiative to vaccinate the world against Covid-19 ahead of the G7 summit. According to US media reports, the Biden administration is set to buy 500 million doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine for international distribution. Doses will be aimed at developing countries.
What’s in it for India?
- Tackling China: With an assertive China looming, the US is calling all like-minded countries to partner in dealing with Beijing. If US and UK want to take the leap forward and constitute a global democratic alliance of 10-11 countries, it will be an important signal.
- Vaccine Shortage: As India faces a massive shortage of vaccines, Delhi will be watching the allocation announced by the US President very carefully. Recently, the US had said that it will distribute vaccines to India as part of it’s “strategy for global vaccine sharing”
- Russia: On Washington’s rapprochement with Moscow, New Delhi will be extremely relieved as the US can then focus on China. This will relieve some tension that are built into India-Russia relationship due to US rivalry with Russia.
Connecting the dots:
- India and G-11 – Critical Analysis
- G-20
- OECD
- FATF
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Hindu Kush Himalayan region does not extend over which of the following countries?
- China
- India
- Vietnam
- Bangladesh
Q.2 Operation Pangea, is a well-established international effort of Interpol to disrupt which of the following?
- Child trafficking
- Online sale of counterfeit and illicit health products
- Cyberbullying
- Terrorist activities
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding Train Collision Avoidance System (TCAS)
- It is indigenously developed in India.
- It will help in improving the safety and increasing the line capacity to accommodate more trains using the existing infrastructure.
Which of the above is or are correct
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 10th June 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | A |
Must Read
On growing Islamist violence in Africa:
About India’s nutritional challenge:











