IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Bhalia Wheat
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Intellectual Property Rights
In news: In a major boost to wheat exports, the first shipment of Geographical Indication (GI) certified Bhalia variety of wheat was exported to Kenya and Sri Lanka from Gujarat.
About Bhalia Wheat
- The wheat has high protein content
- It is sweet in taste.
- The crop is grown mostly across Bhal region of Gujarat which includes Ahmadabad, Anand, Kheda, Bhavanagar, Surendranagar, Bharuch districts.
What is Geographical Indication (GI)?
- It is a sign on products having a unique geographical origin and evolution over centuries with regard to its special quality or reputed attributes.
- It is a mark of authenticity and ensures that registered authorized users or at least those residing inside the geographic territory are allowed to use the popular product names.
- GI tag in India is governed by Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration & Protection) Act, 1999.
- It is issued by the Geographical Indications Registry (Chennai).
What are the Benefits of GI Tag?
- It provides legal protection to Indian Geographical Indications thus preventing unauthorized use of the registered GIs by others.
- It promotes economic prosperity of producers of goods produced in a geographical territory.
- It leads to recognition of the product in other countries thus boosting exports.
INS Tabar Exercises
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – International relations
In news: INS Tabar Exercises were held recently with Italian navy off Naples, Italy as part of an ongoing deployment to the Mediterranean
- The exercise covered a wide range of naval operations including air defence procedures, communication drills etc.
- The exercise was mutually beneficial in enhancing interoperability and towards consolidating combined operations against maritime threats.
Major Indian Maritime Exercises
| Name of the Exercise | Name of the Country |
| SLINEX | Sri Lanka |
| Bongosagar and IN-BN CORPAT | Bangladesh |
| JIMEX | Japan |
| Naseem-Al-Bahr | Oman |
| Indra | Russia |
| Za’ir-Al-Bahr | Qatar |
| Samudra Shakti | Indonesia |
| Indo-Thai CORPAT | Thailand |
| IMCOR | Malaysia |
| SIMBEX | Singapore |
| AUSINDEX | Australia |
| Malabar Exercise | Japan, and the USA |
Solar Energy
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Solar Energy
In news
- A new Concentrated Solar Thermal (CST) based test rig facility was established at Hyderabad recently.
- It can help test the capability and performance of solar thermal components like solar receiver tubes, heat transfer fluids, and concentrating mirrors.
- The facility is set up by the International Advanced Research Centre for Powder Metallurgy and New Materials (ARCI), an autonomous institute of the Department of Science & Technology (DST).
About Solar energy
- Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of ever-evolving technologies such as solar heating, photovoltaics, solar thermal energy, solar architecture, molten salt power plants and artificial photosynthesis
- Some of its advantages include: Pollution free, virtually inexhaustible supply and global distribution.
- Due to global warming and climate change, world is now compelled to move from fossil based energy towards clean and green energy.
What is the Technology used to harness solar energy?
- Solar Photovoltaic: Solar photovoltaic (SPV) cells convert solar radiation (sunlight) into electricity. A solar cell is a semi-conducting device made of silicon and/or other materials, which, when exposed to sunlight, generates electricity.
- Solar thermal: Solar Thermal Power systems, also known as Concentrating Solar Power systems, use concentrated solar radiation as a high temperature energy source to produce electricity using thermal route (water converted into steam to turn turbines).
Solar Energy in India
- India’s Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDC’s) commitment includes 100 GW of solar power out of 175 GW of renewable energy by 2022.
- India’s current installed solar power capacity: 26025.97 MW which is 34% of total renewable energy sources i.e, 75055.92 MW till February 2019.
- Ministry of new and renewable energy is the nodal agency to tackle India’s renewable energy issues.
- Recently, India achieved 5th global position in solar power deployment by surpassing Italy.
- National Solar Mission aims to establish India as a global leader in solar energy by creating the policy conditions for its deployment across the country.
- Rooftop Solar Scheme: To generate solar power by installing solar panels on the roof of the houses
- Production-linked Incentive (PLI) scheme to promote manufacturing of high efficiency solar PV modules in India.
- International Solar Alliance (ISA): Launched by the Indian Prime Minister and the French President in 2015 with a vision to enable One World, One Sun, One Grid (OSOWOG).
- One Sun, One World, One Grid (OSOWOG): A framework for facilitating global cooperation, building a global ecosystem of interconnected renewable energy resources (mainly solar energy) that can be smoothly shared.
Bone Tissue Regeneration
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Biotechnology; Science and tech
In news: A nano biomaterial with a stable link between two molecules was recently synthesized at Savitribai Phule Pune University, India. The development may soon help in tissue regeneration.
What is a Biomaterial?
- It is a biological or synthetic substance which can be introduced into body tissue as part of an implanted medical device or used to replace an organ, bodily function, etc.
About Bone tissue regeneration
- Critical size bone defects due to trauma or disease. These are very difficult to repair via the natural growth of host tissue.
- Therefore, there exists a need to fill these defects with a bridging (usually porous) material (termed scaffold), which should also, in combination with relevant cells and signaling molecules, promote the regeneration of new bone tissue.
- The biomaterials of choice for the development such scaffolds should exhibit bioactive properties i.e. react with physiological fluids and form tenacious bonds for bone formation.
Additional Info
- Biomimicry: A novel method of repairing bone structure using coral and marine sponges as scaffolds
- COVID-19 pandemic has revived the interlinkage between Synthetic Biology & National Security of Nation
Navegaon-Nagzira Tiger Reserve
Part of: GS Prelims and and GS III – Conservation
In news: Recently, a rare Melanistic Leopard (commonly known as Black Panther) has been recorded in Navegaon-Nagzira Tiger Reserve (NNTR) of Maharashtra.
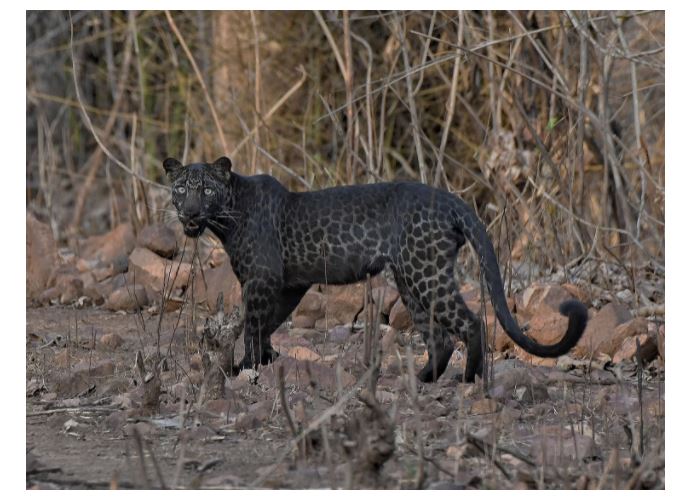

About Melanistic Leopard/Black Panther
- The melanistic leopards are either all-black or very dark in coloration.
- It is a color variant of spotted Indian leopards, reported from densely forested areas of south India.
- Black coat coloration is attributed to the expression of recessive gene in leopards and dominant gene in jaguars.
- In each species, a certain combination of gene stimulates the production of large amounts of the dark skin pigment melanin in the animal’s fur and skin.
- It is as shy as a normal leopard and very difficult to detect.
- Habitat:
- They are mainly found in Southwestern China, Burma, Nepal, Southern India, Indonesia, and the southern part of Malaysia.
- In India they can be spotted in the states of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Maharashtra etc.
- Threats: Habitat loss, Collision with vehicles, Diseases, Human encroachment, Poaching.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable.
- CITES: Appendix I.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I.
About Navegaon-Nagzira Tiger Reserve
- NNTR was notified as 46th tiger reserve of India on 12thDecember, 2013.
- Navegaon-Nagzira Tiger Reserve has connectivity with the major tiger reserves in Central India like,
- Kanha and Pench tiger reserve in Madhya Pradesh,
- Tadoba-Andhari Tiger reserve in Maharashtra,
- Indravati Tiger Reserve in Chhattisgarh,
- It is also connected to important tiger bearing areas like Umred-Karhandla sanctuary and Brahampuri Division (Maharashtra).
- It is one of the six Tiger reserve of Maharashtra
- Melghat Tiger reserve (1974)
- Tadoba Tiger Reserve (1993)
- Pench Tiger Reserve (1999)
- Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (2007)
- Bor Tiger Reserve (2014)
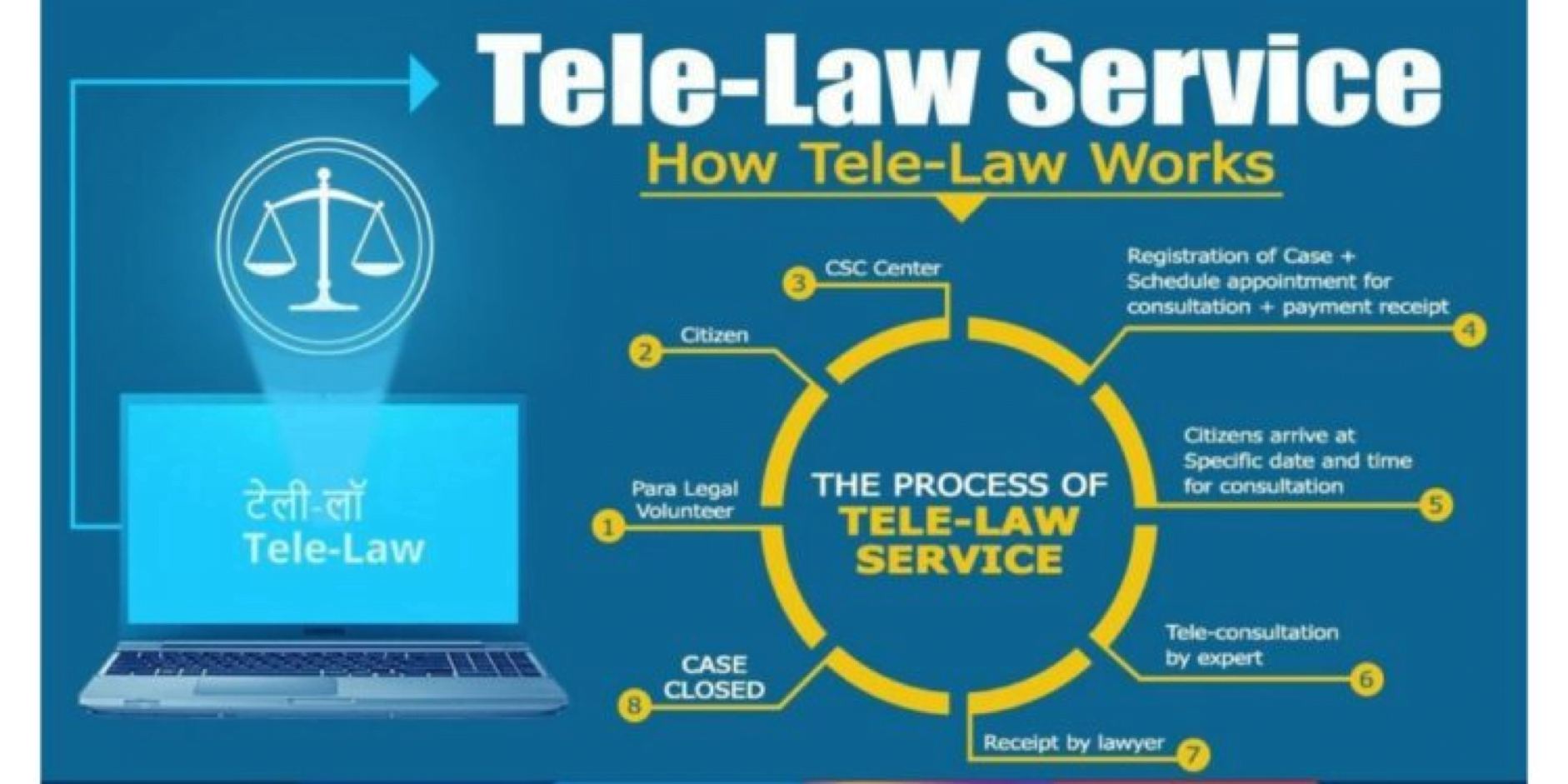
Tele-Law
Part of: GS Prelims and GS II – Welfare schemes; E-Governance
In news: Recently, the Justice Department commemorated the milestone of crossing 9 lakh beneficiaries under its Tele-Law programme through Common Service Centres.
- Common Services Centre (CSC) programme is an initiative of the Ministry of Electronics & IT (MeitY), that serves as the access points for delivery of various electronic services to villages in India
About Tele-Law
- It was launched by the Ministry of Law and Justice in collaboration with the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) in 2017 to address cases at the pre–litigation stage.
- It is presently operating in 633 districts (including 115 Aspirational Districts) across 34 States/UTs through a network of 50,000 CSCs.
- Under this programme, smart technology of video conferencing, telephone/instant calling facilities available at the vast network of CSC.
- It enables anyone to seek legal advice without wasting precious time and money.
- The service is free for those who are eligible for free legal Aid as mentioned under Section 12 of the Legal Services Authority Act, 1987. For all others a nominal fee is charged
- This is useful for weaker & vulnerable sections of society to gain access to justice.
- Even though the Tele-law programme is technology driven, its success is dependent on the working of field functionaries comprising Village Level Entrepreneurs (VLEs), Para Legal Volunteers (PLVs), State Coordinators and Panel Lawyers.
Malaria Free China
Part of: GS Prelims and GS II – health
In news: The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared China as “malaria-free”.
- It is a result of a seven decade-long, multi-pronged health strategy that was able to entirely eliminate indigenous cases for four straight years.
- 40 countries and territories have been granted a malaria-free certification from WHO – including, most recently, El Salvador (2021), Algeria (2019), Argentina (2019), Paraguay (2018) and Uzbekistan (2018) [India is not yet Malaria free]
About Malaria
- Malaria is a life threatening mosquito borne blood disease caused by plasmodium parasites.
- It is predominantly found in the tropical and subtropical areas of Africa, South America as well as Asia.
- The parasites spread through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- Symptoms: Fever and flu-like illness, including shaking chills, headache, muscle aches, and tiredness.
- It is preventable as well as curable.
- According to the World Malaria Report, 2020, the number of malaria cases worldwide in 2019 was around 229 million, with 4,09,000 lives lost to the mosquito-borne disease.
China’s Malaria Strategy
- The efforts began in the early 1950s starting with a multi-pronged approach of providing anti-malarial medicines while targeting mosquito breeding grounds and using insecticide spraying.
- The 523 Project: It led to the discovery of artemisinin in the 1970s. Artemisinin is the core compound of antimalarial drugs available today.
- Insecticide-treated Nets: In the 1980s, China began using insecticide-treated nets widely, distributing 2.4 million nets by 1988.
- 1-3-7 Strategy: The strategy refers to:
- A one-day deadline to report a malaria diagnosis,
- Confirming a case and determining the spread by the third day, and
- Measures taken to stop the spread by the seventh day, along with continued surveillance in high-risk areas.
- Leveraging Global Fund: With assistance from the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria starting in 2003, China “stepped up training, staffing, laboratory equipment, medicines and mosquito control.”
(Mains Focus)
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
Topic:
- GS-2: India and its neighborhood- relations.
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
The Surge (Rise of Taliban)
Context: The rapid territorial gains made by the Taliban over the last two months.
How is the ground situation changing in Afghanistan?
- US had announced that it is going to exit completely from Afghanistan by Sep 11, 2021 after a prolonged two decade war (started in the aftermath of 9/11 attacks) in Afghanistan against Taliban & other terror groups.
- Offensive Strategy: The Taliban started their latest offensive on May 1 as it was certain that US troops won’t be supporting Afghan National forces any more.
- Expansion of Taliban Control: With 90% of U.S. withdrawal complete, the Taliban have taken control of 195 of Afghanistan’s 407 districts, and are contesting 129 others
- Recent Gains in Northern areas: Most of their recent victories are in the northern provinces which had resisted Taliban rule in the 1990s. In several northern districts, Afghan troops have either surrendered or retreated
- Possibility of collapse of government at Kabul: If the north, home to Afghanistan’s elite power brokers and leaders, is lost, the risk of a total collapse of the government in Kabul would increase.
What can we expect in next couple of months?
- Afghanistan government still controls most of the provincial capitals and cities but are practically surrounded by the Taliban.
- Given the pace of the Taliban’s advancement in the countryside, it is possible they could launch an offensive to take the population centres once the foreign troops are out
Will Taliban engage in negotiations for peaceful transition of country post US Exit?
- The Taliban’s strategy is still not clear.
- Their political office in Doha, which started peace talks with Afghan government representatives in September 2020, continues to say they are committed to the dialogue.
- But on the battlefield in Afghanistan, they continue a relentless campaign aimed at capturing more territories.
Why is there criticism about US plan of pulling out its troops?
- Irresponsible behaviour of US: The country faces an imminent civil war, chaos & takeover by conservative Taliban primarily due to total abdication of leadership and responsibility by the U.S., which invaded Afghanistan 20 years ago.
- US wanted exit not peace in country: When direct talks between the U.S. and the Taliban began, the U.S.’s focus was not on finding a peaceful settlement to the crisis that it partly created, but on exiting the war.
- US ignored concern of Afghan Govt.: Therefore, instead of putting pressure on the Taliban to extract concessions, the U.S. struck a deal with them, completely ignoring the concerns of Kabul.
- Now, the Taliban are much more powerful on the ground and even if the peace process is revived after American pullout, they would negotiate from a position of strength.
Can other powers steer the situation from going out of control?
- US insensitive action should not stop Kabul and regional powers China, Russia, Iran, Pakistan and India from seeking a political settlement.
- A violent takeover of the country by the Taliban, like in 1996, would not serve anybody’s interests.
- The Taliban would also not find international legitimacy if they capture Kabul through bloodshed.
- Hence, efforts should be made for a peaceful negotiated settlement so as to ensure the stability of the broader region.
Conclusion
- Now that the invading troops are exiting Afghanistan, the warring parties’ focus should shift towards settlement and building lasting structures of power. Else, Afghanistan would fall into another cycle of violence.
Connecting the dots:
- March 2020: Donald Trump’s Doha Agreement
- March 2021: Joe Biden’s initial Peace Plan
- April 2021: Final Biden’s Plan of US Exit from Afghanistan
HEALTH/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- GS-2: Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States
Vaccination Hesitancy & Mandatory Vaccination
Context: In the wake of Vaccine Hesitancy, three high courts in the country have set off a much needed legal debate around the feasibility of State-mandated persuasive measures to boost inoculation rate.
What is Vaccine Hesitancy?
In 2015, the World Health Organization (WHO) defined vaccine hesitancy as a “delay in acceptance or refusal of vaccination despite the availability of vaccination services”.
Chief reasons for Vaccine Hesitancy
- Misinformation
- Lack of trust in safety and efficacy of the vaccine
- Fear of side-effects
- Socio-political notions
- Inconvenience of getting vaccinated
- Absence of incentives
There are no direct judgments of the Supreme Court (SC) on the aspect of mandatory vaccination. However, three High Courts in the country have dealt with the issue and its conflict with fundamental rights & authority of government.
Meghalaya high court disapproves coercion
- Meghalaya government had made it mandatory for shopkeepers, vendors, local taxi drivers and others to get themselves vaccinated before they can resume their businesses. This was challenged before the high court.
- Meghalaya high court has declared that mandatory vaccination affects an individual’s right, choice and liberty significantly more than affecting the general public, and impinges upon the autonomous decision of an individual human being of choosing not to be vaccinated.
- It encouraged the state government to sensitise people in order to facilitate informed decision making particularly in a situation where the beneficiaries are skeptical, susceptible and belonging to vulnerable/marginalised section of the society.
Gauhati high court underlines fundamental rights
- The Gauhati high court held that restrictions imposed by the Mizoram government on movement and work of persons who are yet to get vaccinated for Covid-19 are unconstitutional and arbitrary.
- Such restrictions are violation of right to earn livelihood and right to equality (both unvaccinated & vaccinated with first dose can be infected by virus)
Madras high court bats for public health
- The Madras high court has set about to examine whether a person can refuse to get vaccinated as a matter of right when he or she can prove to be a threat to public health.
- The court left the matter for a detailed examination at an appropriate stage while it implored the state government to try and persuade persons with awareness campaigns
What are the arguments for making Vaccination Mandatory?
- Public Health: In the larger public interest, vaccination can be made compulsory since those not vaccinated are threats to others’ rights to life.
- Right to Life supersedes Right to Freedom: Right to self-determination or bodily autonomy are aspects of right to privacy which is inferior to the right of life of other people.
- Within Domain of Government: It is within the authority of the Centre and states to make vaccination compulsory since the Constitution arms them with the status of parens patriae (parents of the nation).
- No need of incentive: There cannot be a bigger incentive than the government giving vaccines free to citizens where their lives can be saved
Conclusion
Government should begin with “mild sanctions” along with sensitisation to persuade people so as to overcome the Vaccine Hesitancy.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 “The 523 Project”, “1-3-7 strategy” recently seen in news are related to?
- Covid-19 Treatment strategy of the USA
- Tuberculosis elimination strategy by India
- Covid 19 control, tracking, treatment strategy of Brazil
- Malaria eradication strategy by China
Q.2 consider the following statements regarding GI tag:
- GI tag in India is governed by Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration & Protection) Act, 1999.
- It is issued by the Geographical Indications Registry (Chennai).
Select the correct statements
- 1 Only
- 2 Only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Common Services Centre (CSC) programme is an initiative of which Union Ministry?
- Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY)
- Union Home Ministry
- Ministry of Rural Development
- None of the above
ANSWERS FOR 7th July 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | D |
Must Read
On India’s Demography:
On CBSE’s new assessment scheme:
On COVID-19 impact on India’s economy:











