IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Global Youth Tobacco Survey
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- II – Health
In news Recently, the Health Minister released the Global Youth Tobacco Survey (GYTS-4).
What are the key findings of the Survey?
- More than 29% of students in India were exposed to second-hand smoke.
- There has been a 42% decline in tobacco use among 13-15-year-old schoolchildren in the past decade.
- Use of any form of tobacco was higher among boys
- States with highest use among school children: Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram
- States with lowest use among school children: Himachal Pradesh and Karnataka.
- 38% of cigarettes, 47% of bidi smokers and 52% of smokeless tobacco users initiated the use before their 10th birthday.
Suggestions to curb smoking amongst school children
- The role of teachers is most crucial in creating awareness among children and their parents regarding the harm of tobacco use.
- Harmful effects of tobacco use should be incorporated in school curricula at various levels starting right from the primary school level.
What are the measures taken by the government to control smoking?
| Measures | Features |
| WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) |
|
| Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products Act (COTPA), 2003 |
|
| National Tobacco Control Programme (NTCP), 2008 |
|
| Cigarettes and other Tobacco Products (Packaging and Labelling) Amendment Rules, 2020 |
|
| mCessation Programme |
|
| Prevention and Control of Pollution Act of 1981 |
|
| Cable Television Networks Amendment Act of 2000 |
|
News Source: TH
Census 2021: Put off due to COVID-19
Part of: Prelims and GS – II – Government policies and interventions
In news Owing to the outbreak of COVID-19 pandemic, Census 2021 and other Census-related field activities have been postponed until further orders.
- The forthcoming Census is to be the first digital Census and there is a provision for self-enumeration.
- Self-enumeration refers to completion of census survey questionnaires by the respondents themselves.
- A mobile application for data collection and a Census portal for managing and monitoring various Census related activities have been developed.
What is Census?
- In Census ( decennial census), data is collected on demographic and various socio-economic parameters like education, SC/ST, religion, language, marriage, fertility, disability, occupation and migration of the individuals.
- Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India under Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India is responsible for carrying out the census.
- It provides information on size, distribution and socio-economic, demographic and other characteristics of the country’s population.
- The first synchronous census in India was held in 1881. Since then, censuses have been undertaken uninterruptedly once every ten years.
- As per the official Gazette, the individual data collected in Census under the Census Act, 1948, are not made public as per the provisions contained in the Act.
- The individual data are not used for the preparation of any other database, including the National Register of Citizens.
- Only the aggregated Census data at various administrative levels are released.
What are the Benefits of Census?
- Evidence based Policy Making: Enumerating, describing and understanding the population of a society and what people have access to, and what they are excluded from, is important not only for social scientists but also for policy practitioners and the government.
- Ensures Equity in Governance: Since Independence, aggregated Census data on the SCs & STs on certain parameters such as education have been collected. This data will help the government to remedy inequalities present in the society.
- Delimitation Exercise: Delimitation Commission sets up boundaries of electoral constituencies based on the data obtained from decennial census
- Developmental Purposes: Businesses use census data to decide where to build factories, offices and stores, and this creates jobs. Developers use the census to build new homes and revitalize old neighbourhoods.
- Cooperative Federalism: Central government funds, grants and support to states and local governments consider population totals and breakdowns by sex, age, caste and other factors.
- Civic Participation in Governance: Commenting on the 1941 Census, Census Commissioner Yeatts observed that, “Thanks to the acute interest in community figures, practically all communities this time were census-conscious and took pains to see that their houses were in the list and that they themselves were counted.” Census thus ensures that Democracy is participative in nature.
News Source: The Hindu
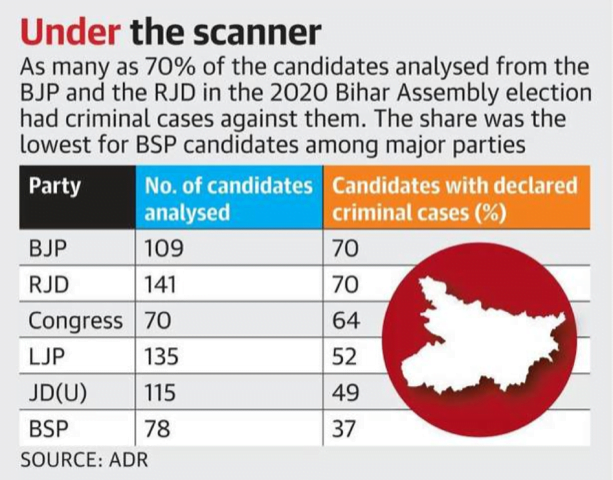
Parties get 48 hours to publish candidates’ criminal records
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- II- Elections
In news The Supreme Court recently warned Parliament that the nation is losing patience with the advent of criminals in politics.
- It also imposed fines on major political parties for covering up from voters the criminal past of the candidates they had fielded in the Bihar Assembly polls last year.
Key Points
- The court had directed political parties to publish the criminal history, if any, of their election candidates on the homepage of their party websites under the caption ‘candidates with criminal antecedents’ within 48 hours of their selection
- In Public Interest Foundation and Ors. v. Union of India, 2018 judgment, SC had also directed them to prominently publish the criminal antecedents of their candidates in newspapers and on social media accounts, including Twitter and Facebook. Political parties had flouted this judgement
- In a series of directions to make the right of information of a voter “more effective and meaningful”, the court further ordered the Election Commission of India to launch a dedicated mobile app for voters to get details of the criminal history of the candidates at the touch of a button.
- The Commission should also form a separate cell to monitor political parties on their compliance with the court’s judgment.
News Source: TH
India Internet Governance Forum (IGF) -2021
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Governance
In news India will host the first Internet Governance Forum in the country.
About IIG forum-
- The CEO of National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI), Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY) announced the launch of India IIGF -2021.
- IIGF- 2021 will be planned for three days, starting from 20th October, 2021.
- Theme: Inclusive Internet for Digital India.
- The forum is an Internet Governance policy discussion platform to bring representatives together from various groups, considering all at par to discuss public policy issues related to the Internet.
- This Multi Stakeholder concept is adopted by IGF under United Nations and by Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN).
- Significance: As India is the second-largest broadband subscription country in the world and also has the highest data consumption per user per month, with IIGF, the aspirations of the Indians would be reflected in International policy formation and stakeholder discussion.
About the Internet Governance Forum (IGF) under United Nations
- IGF is a multistakeholder governance group for policy dialogue on issues of Internet governance.
- The convening of the IGF was announced by the Secretary-General of UN in 2006 and has held an annual meeting since then.
- Various stakeholder groups come together to exchange information and share good policies and practices relating to the Internet and technologies.
- It facilitates common understandings and knowledge exchange of how to maximize Internet opportunities and address risks and challenges.
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN)
- To reach another person on the Internet you have to type an address into your computer – a name or a number. That address has to be unique so computers know where to find each other. ICANN coordinates these unique identifiers across the world. Without that coordination we wouldn’t have one global Internet.
- ICANN is an internationally organized, non-profit corporation, HQ in Los Angeles, California, that has responsibility for Internet Protocol (IP) address space allocation, protocol identifier assignment, generic and country code Top-Level Domain Name System (such as .com, .info, etc.) management, and root server system management functions.
- ICANN doesn’t control content on the Internet. It cannot stop spam and it doesn’t deal with access to the Internet. But through its coordination role of the Internet’s naming system, it does have an important impact on the expansion and evolution of the Internet.
- As a private-public partnership of people from all over the world , ICANN is dedicated
- To preserving the operational stability of the Internet
- To promoting competition;
- To achieving broad representation of global Internet communities;
- To developing policy appropriate to its mission through bottom-up, consensus-based processes
Related Articles
- Web 3.0
- Internet rights: Internet shutdown in India
- A quest for order amid cyber insecurity
- India & evolving digital market
Government e-Marketplace
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Policies and Interventions
In news The Government e-Marketplace (GeM) system has resulted in a 10% savings in public procurement costs in five years, but has still tapped only 5% of India’s total government purchases of about Rs 20 lakh crore a year.
- 56% of the order value processed through the GeM portal has been delivered by Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), with seven lakh small firms on board.
About Government e-Marketplace (GeM)
- GeM is a one-stop National Public Procurement Portal to facilitate online procurement of common use Goods & Services required by various Central and State Government Departments/Organizations/Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs).
- The procurement of goods and services by Ministries and the Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) is mandatory for goods and services available on GeM.
- It also provides the tools of e-bidding and reverse e-auction to facilitate the government users achieve the best value for their money.
- At present, GeM has more than 30 lakh products, over Rs. 10 lakh crore worth of transactions have happened so far at the portal.
- It was launched in 2016 to bring transparency and efficiency in the government buying process.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
News Source: TH
Hong Kong set to adopt China’s anti-sanctions law
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – International relations
In news China’s anti-sanctions law will be implemented in some form in Hong Kong.
- The law includes denying visas, deportation, or seizing assets of those who formulate or comply with sanctions against Chinese businesses or officials.
- Foreign companies can be sued in Chinese courts for applying sanctions and the law can also be wielded against family members.
- It will add fresh regulatory pressure on international companies located in Hong Kong.
Do you know about China’s One Country- Two system model?
- This policy was originally proposed by Deng Xiaoping shortly after he took the reins of the country in the late 1970s.
- Deng’s plan was to unify China and Taiwan under the One Country Two Systems policy which provided autonomy to Taiwan.
- Under this system, Taiwan could follow its capitalist economic system, run a separate administration and keep its own army but under Chinese sovereignty. Taiwan, however, rejected the Communist Party’s offer.
- The idea of two systems in one country is replicated again in Hong Kong and Macau when Britain and Portugal, who were running these territories under lease (since colonial times) returned it to China in 1997 & 1999 respectively.
- These territories were also given autonomy in its functioning in return for recognition of China’s Sovereignty over these areas.
News Source: TH
(News from PIB)
National Commission for Homoeopathy
Part of: GS Prelims
In news: Action Plan for effective and efficient inclusion of Homeopathy in Integrative care
- The Homoeopathy Education and Practice is regulated by the National Commission for Homoeopathy (NCH) Act, 2020.
About the National Commission for Homoeopathy (NCH) Act, 2020
- The NCH, Act, 2020 come in to force w.e.f. 5th July 2021 after repealing the Homoeopathy Central Council Act, 1973 and applies to whole of India.
- The 2020 Act replaced the Council with a National Commission of Homoeopathy for regulating homoeopathic education and practice.
- The Act is having the provision for having interface between Homoeopathy, Indian system of Medicine and Modern system of Medicine to promote medical pluralism.
- It also provides provision for the State Government to take necessary measures to address various issues related to health including promotion of public health through Homoeopathy.
About National Commission of Homoeopathy
- The Commission shall consist of the following persons, namely: –(a) a chairperson; (b) seven ex officio Members; and (c) nineteen part-time Members.
- Functions of the National Commission for Homoeopathy:
- Framing policies for regulating medical institutions and homoeopathic medical professionals.
- Assessing the requirements of healthcare related human resources and infrastructure.
Source: PIB
National Dairy Plan
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-III- Economy
In news: National Dairy Plan Phase I (NDP-I) a Central Sector Scheme (CSS) with an outlay of Rs. 2242 Crore was implemented during March 2012 to Nov 2019 across 18 major dairying states including Gujarat which together account for over 90% of the country’s milk production.
- Funding was through a line of credit from the International Development Association (IDA), which along with the share of the Government of India flew from Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying & Fisheries (DADF) to National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) and in turn to eligible End Implementing Agencies (EIAs).
Objectives:
- Increase productivity of milch animals and thereby increase milk production to meet the rapidly growing demand for milk.
- Provide rural milk producers with greater access to the organized milk processing sector.
NDP I had the following major components:
- Productivity Enhancement: aiming at increasing bovine productivity following a scientific approach in animal breeding and nutrition.
- Village based milk procurement systems for weighing, testing quality of milk received and making payment to milk producers: aiming at increasing the number of milk producers organised into milk producer institutions.
- Project Management and Learning: aiming at effective coordination of project activities among various EIAs and a comprehensive and functional Management Information System (MIS) for the Project.
Some of the key achievement of the NDP I:
- NDP I was able to make available more than 2,456 High Genetic Merit Bulls to A & B graded semen stations across the country which propelled the production of quality disease-free semen.
- The project also contributed towards lowering the cost of feeding per kg of milk resulting in increase of net daily income of milk producers by Rs 25.52.
- Market access was provided to more than 16.8 lakh additionally enrolled milk producers of which 7.65 lakh are women members.
- The project covered around 59 lakh beneficiaries across 97,000 villages.
Source: PIB
Fit India Freedom Run 2.0
Part of: GS Prelims
In News: Minister of Youth Affairs & Sports will launch the Nationwide programme of Fit India Freedom Run 2.0 on 13th August 2021, as part of celebration of Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav
- Through this initiative, more than 7.50 Crore youth and citizen will be reached to take part in the run.
About the Fit India Freedom Run 1.0
- The aim of ‘Fit India Freedom Run’ is to encourage people to take up fitness activities such as running and sports in their daily lives and get freedom from obesity, laziness, stress, anxiety, diseases etc.
- It was conceived in 2020 in the wake of COVID-19 Pandemic when social distancing became new normal lifestyle, so as to keep the imperative need of fitness active even while following the social distancing norms.
- Fit India Freedom Run was launched on the concept of virtual run i.e., ‘it can be run anywhere, anytime! You run a route of your choice, at a time that suits you. Basically, you run your own race and time your own pace’.
Fit India Freedom Run 2.0
- The key activities of Fit India Freedom Run 2.0 include pledge, rendering of National Anthem, Freedom Run, cultural functions at venues, awareness among Youth Volunteers to participate and also organize similar Freedom Runs in their villages.
- People can register and upload their run on Fit India portal https://fitindia.gov.in and promote freedom run on their social media channels with #Run4India and #AzadikaAmritMahotsav.
- Through this campaign, citizens will be given call to make a resolve to include physical activity of at least 30 minutes daily in their lives “FITNESS KI DOSE AADHA GHANTA ROZ”.
Source: PIB
Porous Carbon Nano-Particles from waste onion peels
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-III- Science & Tech
In news: Using porous carbon nanoparticles from waste onion peels, a team of scientists have developed soft robotic actuators with enhanced photomechanical capacity.
- It can act as efficient traps for the illuminating low-power near-infrared (NIR) light and can convert a control signal into mechanical motion
- This it finds bioengineering applications such as drug delivery, wearable and assistive devices, prostheses, and even artificial organs.
What are soft robots or actuators?
- Actuators or soft robots consists of rubber-like polymer with embedded nanomaterials which converts a source of energy (like light energy) to mechanical motion.
- Generation of predesigned motion facilitated by their flexibility, affordability, and easy customization are the main reasons for increasing interest of these nano-robots with targeted applications in areas including bio-medical, military, and remote space operations.
- The high thermal conductivity of these nanoforms results in rapid distribution of the heat generated locally by thermal and photo-thermal stimuli.
Using porous carbon nanoparticles
- To take these actuators to the next level of development, heat traps can be created to capture and contain the generated heat for slightly longer durations such that the achieved photomechanical actuation can be enhanced.
- Team of Bangalore scientist has realized such a possibility by utilizing porous carbon nanoparticles (PCNs) from waste onion peels.
Source: PIB
Operation Greens Scheme
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-II- Government Schemes
In news: Ministry of Food Processing Industries launched Operation Greens scheme in November, 2018 for integrated development of Tomato, Onion and Potato (TOP) value chain.
Operation Greens scheme
- The scheme provides for
- short term intervention by way of providing transportation and storage subsidy @ 50% and
- long-term intervention through value addition projects in identified production clusters with Grant-in-aid @ 35% to 70% of eligible project cost subject to maximum of Rs. 50 crore per project.
- The crop-wise/state-wise specific funds are not earmarked under the scheme as the scheme is demand driven and projects are sanctioned in the identified production clusters on the basis of the applications received from investors against Expression of Interest (EOI) issued from time to time.
- The scheme aims to promote Farmer Producers Organizations (FPOs), Agri-logistics, processing facilities and value addition etc. in identified production clusters.
- 6 projects worth project cost of ₹363.30 Crore, with grant-in-aid of ₹136.82 Cr, targeting 31 FPOs in 6 production clusters are approved so far one each for tomato, onion and potato in Gujarat (3), two for onion in Maharashtra (2) and one for tomato in Andhra Pradesh.
- Objectives Of Operation Greens Scheme
- To enhance value realization of top farmers;
- Reduction in post-harvest losses;
- Price stabilization for producer and consumers and
- Increase in food processing capacities and value addition etc.
- As per budget Announcement 2021-22, expanded operation greens scheme covers 22 perishables including shrimp.
Source: PIB
PM Atmanirbhar Swasth Bharat Yojana
Part of: GS Prelims
In news: In the Budget speech of FY 21-22, ‘Prime Minister Atmanirbhar Swasth Bharat Yojana’ (PMASBY) scheme has been announced on 1st February, 2021, for an outlay of about Rs. 64,180 Cr over six years (till FY 25-26).
- This will be in addition to the National Health Mission.
The main interventions under the scheme, to be achieved by FY 2025-26, are:
- Support for 17,788 rural Health and Wellness Centres in in 10 High Focus States
- Establishing 11,024 urban Health and Wellness Centres in all the States.
- Setting up of Integrated Public Health Labs in all districts and 3382 Block Public Health Units in 11 High Focus states;
- Establishing Critical Care Hospital Blocks in 602 districts and 12 Central Institutions;
- Strengthening of the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC), its 5 regional branches and 20 metropolitan health surveillance units;
- Expansion of the Integrated Health Information Portal to all States/UTs to connect all public health labs;
- Operationalisation of 17 new Public Health Units and strengthening of 33 existing Public Health Units at Points of Entry, that is at 32 Airports, 11 Seaports and 7 land crossings;
- Setting up of 15 Health Emergency Operation Centres and 2 mobile hospitals; and
- Setting up of a National Institution for One Health, a Regional Research Platform for WHO South East Asia Region, 9 Bio-Safety Level III laboratories and 4 regional National Institutes for Virology.
Source: PIB
(Mains Focus)
GOVERNANCE
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
A call for improving civil registration systems
Context: The Hindu Newspaper has come out with estimates of excess deaths based on Civil Registration System (CRS) data for many States which showed that the death toll was several times higher than the official death toll.
- A working paper for the Center for Global Development, co-authored by former Chief Economic Adviser Arvind Subramanian, also states that excess deaths during the pandemic period could be as high as 49 lakh in India as against the 4.14 lakh reported in government data.
- ‘Excess deaths’ are defined as the difference between the observed number of deaths in specific time periods and the expected number of deaths in the same time periods.
Organisational structure of the administrative machinery that is responsible for recording deaths and bring out reports
- While the Registrar General, India, is the head of the national organisation tasked with the registration of births and deaths, the actual work is carried out by the State and Union Territory (UT) administrations.
- The heads of the State organisations are called Chief Registrars.
- These officers come from the Health Department in 21 States/UTs and the Department of Planning, Economics and Statistics in 13 States/UTs. In two States/ UTs, they are from the Panchayat/Local Administration Departments.
- We also have Secretaries to the State government functioning as Chief Registrars in a few States.
- The multiplicity of agencies responsible for the registration of births and deaths is replicated at the district and lower levels with municipalities and panchayats playing a major role in registration.
- Coordination of Multiple stakeholders are involved – Hospitals, Police & individuals – in registration process.
Issues
- Technology enables the States to release data on the number of deaths registered on a monthly, weekly or daily basis. However, it is shameful that governments don’t leverage the advancements in technology in pro-actively publishing data.
- Multiplicity of agencies responsible for the registration of births and deaths impedes effective oversight.
- The traditional bureaucratic practice to function within departmental silos leads to poor coordination that brings down efficiency of registration process.
- The State governments have not given adequate attention to the CRS. This has resulted in an inadequate budget for carrying out its regular activities including processing of the data.
- Apart from the problem that reports are overdue, they do not contain all the tables that are prescribed even under our own Rules.
- Data include deaths that took place in previous years but are registered in the years that the report is published. This distorts the accuracy of the report.
Way Ahead
- For every country, it’s important to capture excess mortality which is the only way to prepare the health system for future shocks & to prevent further deaths.
- There is a need to invest in strong civil registration and vital statistics, so policies can be adjusted based on real data.
- Central and State governments must announce a time-bound commitment to achieve 100% registration of deaths in the country.
- There is a need for data that fully meets quality standards.
Connecting the dots:
(RSTV Debate)
RSTV 28 July, 2021: The Big Picture – Talks with US: Blinken’s visit
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NdH08GPMnBY
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
- GS-2: India Foreign Policy
- GS-2: Bilateral & Multilateral relationships.
India- US Relationship: US Secretary of State visit to India
- The US Secretary of State Antony Blinken met PM Modi, External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar and NSA Ajit Doval for the discussions.
- During the talks, Blinken attached great importance to the relationship between India and the US and assured that it will continue to be stronger under the Biden administration.
- The US Secretary of State also focused on Afghanistan, Quad Vaccine, and the determination to end the COVID-19 pandemic.
Significance of the timing of the visit
- Antony Blinken’s maiden visit to India assumes significance in the backdrop of the security crisis in Afghanistan and China’s aggressive stance in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Blinken and Jaishankar talked on a range of issues, including the security crisis in Afghanistan in the aftermath of the US troop pullout, China’s assertiveness in the Indo-Pacific region and coordinated Covid-19 response.
Significant strategic areas that were discussed
- US Secretary of State, during his visit to India, expressed Biden administration’s intent of growing stronger bilateral relations with India and also stressed the importance of cooperation on various issues such as COVID-19 and Climate Change. The issues include:
Human rights issues:
- It was widely expected that the Biden, unlike his predecessor, would not hold back to call out New Delhi for issues related to human rights.
- Regarding the Indian Government’s stand on human rights matters, Blinken said that every democracy is a work in progress and that the challenges it faces, renews, and strengthens the democracies.
- The reason for the downgrade is that the US will side step being too harsh or critical against India as it does not want to disturb many aspects of the growing bilateral relationship.
Quad engagement
- The United States had announced support for waiving intellectual property protection for Covid-19 vaccines, saying extraordinary circumstances call for extraordinary measures.
- Both the countries are determined to end the deadly pandemic together with the Quad vaccine partnership. The two will be the world leaders to bring this pandemic to an end and the focus is on expanding the vaccine production to make it globally accessible and affordable.
- About the strategic dialogue between India, the US, Japan, and Australia, the four like-minded countries are coming together to work on some significant issues that are going to impact the lives of the people.
- It is not a military alliance rather its purpose is to advance the cooperation on the regional challenges while also reinforcing the international rules and values that underpin prosperity, peace, and stability in the region.
- Main challenge for quad is to deliver on the so many ideas and commitments that it claim in the statement and if it can deliver it then it will give a boast to its own credibility.
Massive Violence in Afghanistan:
- Afghanistan region peace and stability is very crucial and most pressing security challenge with significant long-term implications for India at the moment.
- The US sudden withdrawal instead of planned and slow-paced sequential withdrawal has led to the emanation of so many problems.
- This has created a level of uncertainty in the region because the regional interests are very divergent at the moment.
- India has invested heavily in Afghanistan, including granting $3 billion in development assistance since 2001, and has enjoyed close ties with all post-Taliban governments. But India now worries Pakistan and China, its two main rivals, will fill the vacuum left by the United States and deepen their influence.
- Despite the withdrawal of US troops from Afghanistan, the US will remain engaged in the country.
- Keeping in mind the ongoing violence in Afghanistan, as the Taliban invades the cities leading to the deteriorating conditions in the country, the US not only has a strong embassy there but also has significant programmes that support the country economically through security assistance and development.
Indo-Pacific region:
- Both India and the US will exchange assessments about the Indo-Pacific region, with a focus on the economic slowdown, COVID assistance, and the security scenario.
- U.S view Indian democracy as a force for good in defence of a free and open Indo-Pacific, indeed a free and open world.
Climate Change:
- It remains an important area of conversation between India and the US, particularly the potential for green collaborations as well as climate finance and the transfer of clean technologies to developing nations.
- The United States and India both recognize the unique role they have to play in reducing the world’s emissions, as well as their complementary strengths when it comes to tackling the climate crisis. The two have launched the US-India Climate and Clean Energy Agenda 2030 partnership in April this year.
- The partnership will reinforce US and India’s collective efforts to achieve both the goals of the Paris Agreement and their own ambitious 2030 targets for climate action and clean energy, are an excellent example of how the United States and India can bring their strengths to bear on some of the world’s most challenging issues.
Can you attempt this question now?
US Secretary of State, during his visit to India, expressed intent of growing stronger bilateral relations with India and also stressed the importance of cooperation on various issues such as COVID-19 and Climate Change. Illustrate.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding Cigarettes and other Tobacco Products (Packaging and Labelling) Amendment Rules, 2020:
- It was mandated that the specified health warning shall cover at least 85% of the principal display area of the package.
- Of this, 25% shall cover pictorial health warning and 60% shall cover textual health warning.
- This shall be positioned on the top edge of the package.
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
Q.2 Which of the following is responsible for carrying out the Census in India?
- Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation
- Ministry of Home affairs
- NITI Aayog
- National Population Commission
Q.3 IGF is a multistakeholder governance group for policy dialogue on issues of Internet governance announced by which of the following?
- NITI Aayog
- Internet Architecture Board
- United Nations
- Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers
ANSWERS FOR 10th August 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | D |
Must Read
On Global Trade in post-COVID era:
On Collegium System:
On Climate Crisis:












