IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Deepor Beel Wildlife Sanctuary
Part of: Prelims and GS – III – Conservation
In news Recently, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change notified the eco-sensitive zone of Deepor Beel Wildlife Sanctuary
What is Deepor Beel?
- Deepor Beel is located to the south-west of Guwahati city, in Kamrup district of Assam, India.
- It is a permanent freshwater lake, in a former channel of the Brahmaputra River, to the south of the main river.
- It is a wetland under the Ramsar Convention which has been listed since November 2002.
- Considered as one of the largest beels in the Brahmaputra valley of Lower Assam, it is categorised as a representative of the wetland type under the Burma monsoon forest biogeographic region.
- It is also an important bird sanctuary inhabiting many migrant species.
What are the concerns?
- A garbage dump and encroachment for human habitation and commercial units.
- A railway track which is set to be doubled and electrified, on its southern rim.
- Deepar Beel’s water has become toxic and lost many of its aquatic plants that elephants would feed on.
Do You Know?
- Traditionally viewed as a wasteland or breeding ground of disease, wetlands actually provide fresh water and food and serve as nature’s shock absorber.
- Wetlands, critical for biodiversity, are disappearing rapidly, with recent estimates showing that 64% or more of the world’s wetlands have vanished since 1900.
- Major changes in land use for agriculture and grazing, water diversion for dams and canals and infrastructure development are considered to be some of the main causes of loss and degradation of wetlands.
News Source: TH
Tamil Nadu moves SC over Mekedatu
Part of: Prelims and GS – II – State Relations
In news The Tamil Nadu government has urgently moved the Supreme Court seeking judicial orders to restrain Karnataka from proceedings with “any activity” in regard to the proposed construction of a reservoir at Mekedatu across the inter-State Cauvery river.
What is the Background?
- On July 6, Karnataka Chief Minister said in Bengaluru that his government would go ahead with the long-pending Mekedatu dam project.
- The Mekedatu multi-purpose project involves building a balancing reservoir across the Cauvery River near Kanakapura in Ramanagaram district of Karnataka.
- It envisages supplying drinking water to Bengaluru and Ramanagaram districts, besides generation of power.
Why is Tamil Nadu opposed to it?
- Tamil Nadu feels that Karnataka, as the upper riparian State has adequate infrastructure even now to address the water needs of Bengaluru, there is no need for the Mekedatu project.
- The Mekedatu project also does not find mention in the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal’s final order or the Supreme Court judgment.
- Besides, given the unpleasant experiences that it has had with Karnataka in securing its share of the Cauvery water over the years, Tamil Nadu is wary of the assurances of the other side.
News Source: TH
Children’s Climate Risk Index: UNICEF
Part of: Prelims and GS – II – Issues related to children and GS – III -Environmental Impact assessment
In news Recently, the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) in collaboration with Fridays for Future launched a report named ‘The Climate Crisis Is a Child Rights Crisis: Introducing the Children’s Climate Risk Index’.
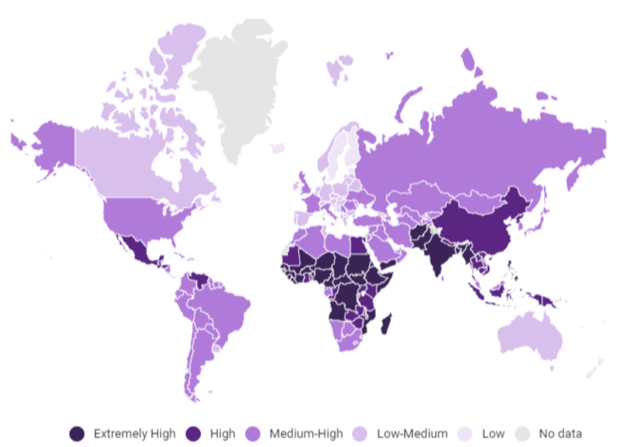
What is Children’s Climate Risk Index?
- It is the first comprehensive analysis of climate risk from a child’s perspective.
- It ranks countries based on children’s exposure to climate and environmental shocks, such as Cyclones and Heatwaves, as well as their vulnerability to those shocks, based on their access to essential services.
- Pakistan (14th), Bangladesh (15th), Afghanistan (25th) and India (26th) are among four South Asian countries where children are at extremely high risk of the impacts of the climate crisis.
Indian Scenario:
- India is among four South Asian countries where children are most at risk of the impacts of climate change threatening their health, education, and protection.
- It is estimated that more than 600 million Indians will face ‘acute water shortages’ in the coming years, while at the same time Flash Flooding is to increase significantly in the majority of India’s urban areas once the global temperature increase rises above 2 Celsius.
- Twenty-one of the world’s 30 cities with the most polluted air in 2020 were in India.
Global Scenario:
- Young people living in the Central African Republic, Chad, Nigeria, Guinea, and Guinea-Bissau are the most at risk of the impacts of climate change.
- These children face a deadly combination of exposure to multiple climate and environmental shocks with a high vulnerability due to inadequate essential services, such as water and sanitation, healthcare and education.
What are the Recommendations?
- Increase Investment
- Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Countries must cut their emissions by at least 45% (compared to 2010 levels) by 2030 to keep warming to no more than 1.5 degrees Celsius.
- Provide Climate Education
- Include Young People in Decisions
- Ensure Pandemic Recovery is Inclusive
News source: DTE
Chikungunya Vaccine
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health and GS- III – SCI and Tech
In news International Vaccine Institute (IVI) has announced that Bharat Biotech’s Chikungunya vaccine candidate (BBV87) has entered into Phase II and III clinical trials. Currently, there is no commercial chikungunya vaccine.
About the Vaccine:
- BBV87 is an inactivated virus vaccine, similar to Covaxin.
- Inactivated vaccines contain viruses whose genetic material has been destroyed by heat, chemicals or radiation so they cannot infect cells and replicate, but can still trigger an immune response.
- Bharat Biotech’s Chikungunya vaccine candidate was developed in partnership with the International Vaccine Institute (IVI).
- Development of Chikungunya Vaccine is an initiative of the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), as part of the Global Chikungunya Vaccine Clinical Development Program (GCCDP).
- It was funded by the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) with support from the Ind-CEPI mission of the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India.
What is Chikungunya?
- Chikungunya is a mosquito-borne viral disease first described during an outbreak in southern Tanzania in 1952.
- The name is derived from the local Kimakonde language and means “to become contorted”, evoking the stooped appearance of patients suffering acute joint pain.
- Transmission: It is transmitted to people through the bite of an infected mosquito.
- It is most often spread to people by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. These are the same mosquitoes that transmit dengue virus.
- Mosquitoes acquire the infection by biting infected humans or animals.
- Weather conditions also affect their breeding and survival.
- Symptoms: Include severe joint pain, muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue and rashes.
- Treatment: Currently, there are no vaccines or antiviral drugs available to cure Chikungunya, and the treatment is only focused on relieving the symptoms associated with the infection.
- Reasons Behind the Spurt in Cases: There has been an increasing incidence of vector borne diseases in urban, peri-urban and rural areas because of:
- Haphazard urbanisation.
- Deficient water and solid waste management leading to proliferation of mosquito breeding sites.
- Absence of specific antiviral drug or vaccine.
Government Initiatives to Control Chikungunya:
- National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP) is a comprehensive programme for prevention and control of vector borne diseases namely Malaria, Filaria, Kala-azar, Japanese Encephalitis (JE), Dengue and Chikungunya.
- It works under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
News source: IE
Tokenization by RBI
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Economy
In news Recently, the Reserve Bank of India has decided to extend the scope of tokenisation to include consumer devices such as laptops, desktops, wearables like wristwatches and bands, as well as Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
What is RBI Tokenization?
- Tokenization refers to the replacement of actual card details with a unique alternate code called the ‘token‘, which is unique for a combination of card, token requestor (i.e. the entity which accepts request from the customer for tokenization of a card and passes it on to the card network to issue a corresponding token) and identified device.
- Normally, in a tokenized card transaction, parties / stakeholders involved are merchant, the merchant’s acquirer, card payment network, token requestor, issuer and customer.
- However, an entity, other than those indicated, may also participate in the transaction.
About tokenization-
- It aims at improving the safety and security of the payment system.
- The Reserve Bank had earlier permitted ‘tokenization’ services, under which a unique alternate code is generated for transaction purposes, on mobile phones and tablets of cardholders.
- RBI had issued guidelines on “Tokenization – Card transactions” in 2019, permitting authorised card networks to offer card tokenization services to any token requestor, subject to conditions.
- Prior to the latest circular, the facility was available only for mobile phones and tablets of interested cardholders.
- A tokenized card transaction is considered safer as the actual card details are not shared with the merchant during transaction processing.
Safety and Security of card details-
- Actual card data, token and other relevant details are stored in a secure mode by the authorised card networks.
- Token requestor cannot store Primary Account Number (PAN), i.e., card number, or any other card detail.
- Card networks are also mandated to get the token requestor certified for safety and security that conform to international best practices / globally accepted standards.
News source: BL
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine
Part of: Prelims and GS – II – Health
In news: Recently, the Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh has launched Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) immunisation drive for infants.
- Earlier in December 2020, India’s first fully indigenously developed pneumococcal conjugate vaccine “Pneumosil” was launched.
About the vaccine
- It prevents pneumococcal disease. It can protect both children and adults from pneumococcal disease.
- The vaccine is a mix of several bacteria of the pneumococci family, which are known to cause pneumonia—hence ‘conjugate’ is included in the name of the vaccine.
- Conjugate vaccines are made using a combination of two different components.
What is Pneumococcal disease?
- Pneumococcal disease is a name for any infection caused by bacteria called Streptococcus pneumoniae or pneumococcus.
- Most people carry pneumococcus in their nose and throat, where the bacteria do not cause any symptoms.However, sometimes the bacteria grow and spread to other parts of the body and that’s when people become sick.
- Besides pneumonia, pneumococcal bacteria can also cause:
- Ear infections.
- Sinus infections.
- Meningitis (infection of the tissue covering the brain and spinal cord).
- Bacteremia (infection of the blood).
What is Universal Immunization Programme?
- It was launched in 1985 to prevent mortality and morbidity in children and pregnant women against 12 vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Under UIP, free of cost vaccination is provided against twelve vaccine-preventable diseases i.e. Tuberculosis, Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus, Polio, Hepatitis B, Pneumonia and Meningitis due to Haemophilus Influenzae type b (Hib), Measles, Rubella, Japanese Encephalitis (JE) and Rotavirus diarrhoea.
- The programme is one of the largest health programmes in the world. Despite being operational for many years, UIP has been able to fully immunize only 65% of children under 1 year of age.
News source: TH
Havana Syndrome
Part of: Prelims and GS – II – Health
In news Nearly four years ago a mysterious neurological illness, referred to as “Havana syndrome”, started to afflict American diplomats and intelligence operatives in Cuba, China, and other countries.
- Now, a report by the National Academies of Sciences (NAS) has found “directed” microwave radiation to be its “plausible” cause.
What is the ‘Havana syndrome’?
- In late 2016, US diplomats and other employees stationed in Havana reported feeling ill after hearing strange sounds and experiencing odd physical sensations in their hotel rooms or homes.
- The symptoms included nausea, severe headaches, fatigue, dizziness, sleep problems, and hearing loss, which have since come to be known as “Havana Syndrome”.
What causes the ‘Havana syndrome’?
- Directed pulsed RF energy appears to be the most plausible mechanism in explaining these cases among those that the committee considered.
- The immediate symptoms that patients reported including sensations of pain and buzzing sound apparently emanated from a particular direction, or occurred in a specific spot in a room.
News source: TH
(News from PIB)
QSim Toolkit
Part of: Prelims and GS – III- Science & Tech
In news: Quantum Computer Simulator (QSim) Toolkit was launched by the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY).
About
- QSim is a first-of-its-kind indigenously developed toolkit that helps in learning and understanding the practical aspects of programming using Quantum Computers.
- QSim provides a platform to acquire the skills of ‘programming’ (Quantum Code) as well as ‘designing’real Quantum Hardware.
- It enables the researchers and students to carryout research in Quantum computing in a cost effective manner.
- Developed collaboratively by IISc Bangalore, IIT Roorkee and C-DAC with the support of MeitY under the ‘Design and Development of Quantum Computer Toolkit (Simulator, Workbench) & Capacity Building’ project.
- Features – QSim offers a QC Simulator integrated with a Graphic User Interface (GUI) based Workbench allowing people to create Quantum programs.
- QSim helps simulate Quantum circuits with and without noise and test how well various algorithms work with imperfect quantum components.
- It has pre-loaded Quantum programs and algorithms providing a head start to the users.
- QSim – Offering Model
- PARAM SHAVAK QSim – Standalone system with Quantum Simulator in a box
- PARAM QSim Cloud – Available on cloud using HPC infrastructure PARAM SIDDHI AI (developed under NSM program).
Source: PIB
BH-Series
Part of: Prelims and GS – III- Economy
In news: Ministry of Road Transport & Highways has introduced a new registration mark for new vehicles i.e. Bharat series (BH-series).
- This series will help in the vehicle re-registration process while moving from one state to another state.
Key Takeaways
- Need for new registration – Under section 47 of the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988, a person is allowed to keep the vehicle for not more than 12 months in any state other than the state where the vehicle is registered.
- But a new registration with the new state- registering authority has to be made within the stipulated time of 12 months.
- A passenger vehicle user takes the following steps to re-register a vehicle
- No Objection Certificate from the Parent State for assignment of a new registration mark in another state.
- Assignment of new registration mark after the road tax on prorata basis is paid in the new State
- Application for refund of road tax in parent State on pro rata basis.
- Registration Mark Format in BH-series that will facilitate seamless transfer of vehicles is YY BH #### XX.
- YY is the code for Year of 1st registration, BH is the code for Bharat Series, #### for 0000 to 9999, XX for Alphabets (AA to ZZ).
- A vehicle bearing this BH-series registration mark shall not require assignment of a new registration mark when the owner of the vehicle shifts from one State to another.
- This vehicle registration facility under “BH-series” will be available on voluntary basis to
- Defense personnel,
- Employees of Central & State Governments/ Central & State PSUs,
- Employees of private sector companies/organizations, which have their offices in 4 or more States/UTs.
Source: PIB
(Mains Focus)
POLITY/ GOVERNANCE
- GS-2: Polity & Judiciary
Judicial Hierarchy
Context: India has integrated Judiciary compared to Federal Judicial system in USA. There is also the presence of hierarchy in Indian Judicial System.
Issues:
- The Constitution contemplates a hierarchy of jurisdictions, but no judge, acting within her jurisdiction, is “inferior” or “subordinate”.
- As constitutional beings, judges are limited in jurisdiction but also supreme within their own jurisdiction.
- However, Article 235 speaks of “control over subordinate courts”. This Article adds insult to injury by describing these entities and agents as persons “holding a post inferior to the post of a district judge”.
- While the Constitution allows “supervision”, it does not sanction judicial despotism.
- Arbitrary practices in writing confidential reports of district justices seem to continue that perpetuates the inferior status associated with such “subordinate” judges.
Model Judgement to be replicated across India
- The August 11 order of the Himachal Pradesh High Court resolves that “hereinafter, all the courts in the state other than the high court shall be referred to as district judiciary”.
- Furthermore, “these courts shall not be referred to as subordinate court” but as trial courts.
- The colonial idea of “subordination” stands replaced by the constitutional idea of independence of the judiciary.
Way Ahead:
Senior-most district judges and judges of the high courts constituting the collegiate system to facilitate judicial administration, infrastructure, access, monitoring of disposal rates, minimisation of undue delays in administration of justice, alongside matters concerning transfers, and leave.
Connecting the dots :
WOMEN/ GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY
- GS-1: Society & issues related to women.
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to it
India’s gendered digital divide:
Context: As COVID-19 coursed through countries, governments responded with lockdowns that drove people towards digital marketplaces. Globally, digital adoption escalated by five years in merely two months in 2020.
- India has set a target of reaching a US $1 trillion digital economy by 2025, a five fold growth from the US $200 million in 2017–18.
Progress of digitalization in the wake of COVID-19 Pandemic
- 500 percent increase in tele-health consultations
- A structural shift towards online shopping with e-retail reaching 95 percent of Indian districts
- Digital payments touching the 100 million transactions per day mark.
COVID-19 amplified another trend: The gendered digital divide.
- Indian women are 15 percent less likely to own a mobile phone, and 33 percent less likely to use mobile internet services than men.
- In 2020, 25 percent of the total adult female population owned a smartphone versus 41 percent of adult men.
- Within Asia-pacific, India had the widest gender gap in internet usage in recent years, a gender gap of 40.4 percent with only 15 percent of women accessing the internet versus 25 percent of men.
This gendered digital divide is often born out of a triple disadvantage for women in India.
- First, there is a rural-urban digital divide, such that rural broadband penetration is only 29 percent against a national average of 51 percent. Across states, women in rural areas are less likely to own mobile phones.
- Second, there is an income-based digital divide between households. Given the average price for data is $0.68/GB in India, estimates show that each GB of data costs low-income households (earning less than $2/day) 3% of their monthly income versus 0.2% for middle-income households (earning US $10–$20 per day).
- Finally, intra-household discrimination prevents women from equitably accessing digital devices within the domestic sphere, which in turn widens the gender-based digital divide.
Social Factors that excludes women from accessing digital economy
- Even when they are permitted to own or use household-level mobile devices, women’s online activity is often governed by male relatives.
- While mobile phones are viewed as a risk to women’s reputation pre-marriage; post-marriage, phone-use is viewed as an interruption to caregiving responsibilities.
- Women generally refrain from speaking on their phones in public places, preferring to conduct their conversation within the home, owing to prevailing social norms and fear of judgement.
- Digital illiteracy and unfamiliarity with digital platforms deterred women entrepreneurs from moving to online marketplaces post COVID-19.
Way Forward
It is imperative to not only increase women’s smartphone ownership as it assists in internet adoption, but also to accelerate digital literacy programmes and work towards ending digital discrimination based on gender norms.
Connecting the dots:
- Invisible women in India’s labour market
- Women Issues
- Women Employment
- Women Friendly Cities
- Women with disabilities
(AIR Spotlight)
Spotlight 19 (Aug): Prashant Kumar Singh, CEO, GOVERNMENT E- MARKET PLACE (GEM) ON REFORMS IN PUBLIC PROCUREMENT
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P2s-OA-xQ4A
GOVERNANCE
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Government e-Marketplace (GeM)
On the occasion of World Environment Day, a new product category of Green Room Air Conditioners was launched on the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) under the Sustainable Public Procurement (SPP) program.
Government e-Marketplace (GeM) and its significance:
- Launched in 2016 to bring transparency, speed and efficiency in the government buying process, the GeM is a one-stop National Public Procurement Portal to facilitate online procurement of common use Goods & Services required by various Government Departments / Organizations / PSUs.
- It is a completely paperless, cashless and system driven e-marketplace that enables procurement of common use goods and services with minimal human interface that provides the tools of e-bidding, reverse e-auction and demand aggregation to facilitate the government users to achieve the best value for their money.
- It has been developed by Directorate General of Supplies and Disposals (Ministry of Commerce and Industry) with technical support of National e-governance Division (MEITy).
- Being an open platform, GeM offers no entry barriers to bonafide suppliers who wish to do business with the Government and also eliminates human interface in vendor registration, order placement and payment processing, to a great extent.
- It facilitates a Single window system for aggregating demands and ordering thus enhancing transparency and ease of buying.
- User friendly dash board for buying and monitoring supplies and payments and is useful for low value buying and also for bulk buying at competitive price using Reverse Auction/ e-bidding.
GeM SAHAY project and its significance:
- Presently out of the 20 lakh sellers on GeM, there are around 7 lakhs MSE sellers and repair suppliers onboard contributing over 56 % of the full order value on GeM, which is a testimony to GeM’s success in not solely onboarding but additionally participating with the MSEs to assist them take part in public procurement.
- In a bid to address the credit access challenges faced by MSMEs, the Government e Marketplace (GeM) implemented the SAHAY project in collaboration with the Indian Software Product Industry Round Table (iSPIRT), a non-profit tech thinks tank’s volunteer team which is a mobile application for proprietorships which will enable them to avail financing opportunities on the GeM.
- The GeM-SAHAY portal can be used to provide frictionless financing for MSMEs on the Government e marketplace, allowing them to obtain a loan at the point of order acceptance on the GeM platform.
- Using the portal, the loan payment will be instant, rather than the traditional principle of approving the loan, which usually does not end with the actual payment.
- The GeM SAHAY platform is ‘lender agnostic,’ allowing any lender that is duly regulated by the Reserve Bank of India to participate and provide capital and smart collection accounts to GeM sellers.
- Sellers who apply for the loan facility will have a seamless end-to-end digital experience via a mobile application.
Can you answer this question now?
Discuss the significance of the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) under the Sustainable Public Procurement (SPP) program.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 Which of the following is not a Ramsar Convention site in India?
- Suraj Tal, Ladakh
- Lonar Lake, Maharashtra
- Sur Sarovar, Uttar Pradesh
- Deepor Beel, Assam
Q.2 Consider the following statements Children’s Climate Risk Index:
- It ranks countries based on children’s exposure to climate and environmental shocks, such as Cyclones and Heatwaves, as well as their vulnerability to those shocks, based on their access to essential services.
- Pakistan, Bangladesh, Afghanistan and India are among four South Asian countries where children are at extremely high risk of the impacts of the climate crisis.
Select the correct statements:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding Chikungunya:
- It is most often spread to people by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes.
- There are several vaccines available to prevent Chikungunya.
Select the correct statements:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 27th August 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
On Asset Monetisation:
On Agrarian Reforms:
On Indo-Russia Ties and China:











