IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
CBI and ED
Part of: Prelims and GS II – Polity
Context: Chief Justice of India (CJI) recently said there was an immediate need for the creation of an independent umbrella institution, so as to bring various central agencies like the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI), Enforcement Directorate (ED) and the Serious Fraud Investigation Office (SFIO) under one roof.
- He said the organisation should be headed by an independent and impartial authority.
- He also highlighted that with the passage of time, like every other institution of repute, the CBI had also come under deep public scrutiny. Its actions and inactions had raised questions regarding its credibility, in some cases.
About Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)
- The CBI is the premier investigating agency of India.
- Ministry: Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions.
- Role: It was originally set up to investigate bribery and governmental corruption. In 1965, it received expanded jurisdiction to investigate breaches of central laws enforceable by the Government of India, multi-state organised crime, multi-agency or international cases.
- CBI is exempted from the provisions of the Right to Information Act.
- CBI is India’s officially designated single point of contact for liaison with the Interpol.
- The CBI headquarter: New Delhi.
About Enforcement Directorate (ED)
- It is a law enforcement agency and economic intelligence agency responsible for enforcing economic laws and fighting economic crime in India.
- Ministry: Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance
- The prime objective is the enforcement of two key Acts:
- The Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999 (FEMA)
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act 2002 (PMLA)
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Five regional offices: Mumbai, Chennai, Chandigarh, Kolkata and Delhi headed by Special Directors of Enforcement.
News Source: TH
Thalli Bidda Express
Part of: Prelims and GS II – Welfare schemes
Context: Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister recently flagged off YSR ‘Talli-Bidda’ Express, a dedicated transportation facility for new mothers who deliver at government hospitals in the state.
- 500 vehicles that were flagged off would be sent to various parts of the State to cater to the needs of mothers and newborn children.
- The ‘Talli-Bidda’ vehicles would provide free transport to pregnant women, mothers and infants.
- The service is coordinated by 102 /108 call centre which operates 24X7.
News Source: TH
Olive Ridley turtles
Part of: Prelims and GS III – Environment
Context: As a record number of 4.92 lakh Olive Ridley turtles have crawled to the Rushikulya coast in Odisha, scientists have tagged more than 6,000 turtles to gather more information about their breeding behaviour and migration.
- This is the highest nesting which has broken all records for the coast.
- Before the tagging of the turtles, it was assumed that it was a migratory species.
- Now the tagging has revealed that the Olive Ridley turtles can travel up to Sri Lanka.
- Also, the migratory turtle is present in the entire Bay of Bengal and even on the coast of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
Olive Ridley
- The Olive Ridley sea turtle is the most abundant of all sea turtles found in the world.
- It is found in warm and tropical waters, primarily in the Pacific and Indian Oceans.
- It is best known for their unique mass nesting called arribada, where thousands of females come together on the same beach to lay eggs.
- IUCN status: Vulnerable.
Marine Turtles
- Five species of sea turtles are known to inhabit Indian coastal waters and islands.
- Olive Ridley turtle
- Green turtle
- Hawksbill turtle
- Loggerhead turtle
- Leatherback turtle
- Except the Loggerhead, the remaining four species nest along the Indian coast.
News Source: TH
(Mains Focus)
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
- GS-2: Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
BIMSTEC after the Colombo summit
Context: The fifth summit of the regional grouping, the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) was held virtually in Colombo on March 30.
About BIMSTEC
- It is a regional organisation comprising seven Member States: five deriving from South Asia, including Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka and two from Southeast Asia, including Myanmar and Thailand.
- This sub-regional organisation came into being on 6 June 1997 through the Bangkok Declaration (25th Anniversary in 2022)
- It member countries consists of 21.7% of the world’s population with combined Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of USD 3.8 trillion (only 4% of the global GDP)
What were the key Highlights of the Summit?
- BIMSTEC Charter was the main outcome of the summit. It presents BIMSTEC as “an inter-governmental organization” with “legal personality.”
- It has an emblem, it has a flag.
- It has a formally listed purpose and principles that it is going to adhere to.
- The grouping re-constituted and reduced the number of sectors of cooperation from the unwieldy 14 to a more manageable seven. Each member-state will serve as a lead for a sector
- Trade, investment and development (Bangladesh);
- Environment and climate change (Bhutan);
- Security, including energy (India);
- Agriculture and food security (Myanmar);
- People-to-people contacts (Nepal); s
- Science, technology and innovation (Sri Lanka)
- connectivity (Thailand).
- The summit participants adopted the Master Plan for Transport Connectivity applicable for 2018-2028. It lists 264 projects entailing a total investment of $126 billion. Projects worth $55 billion are under implementation.
- Three new agreements signed by member states, relating to mutual legal assistance in criminal matters, cooperation between diplomatic academies, and the establishment of a technology transfer facility.
- India will provide the (BIMSTEC) secretariat USD 1 million US dollars to increase its operational budget.
- The organisation decided to host a summit every two years
Challenges
- Despite signing a framework agreement for a comprehensive Free Trade Agreement (FTA) in 2004, BIMSTEC stands far away from this goal. Of the seven constituent agreements needed for the FTA, only two are in place as of now.
- The need for expansion of connectivity was stressed by one and all, but when it comes to finalising legal instruments for coastal shipping, road transport and intra-regional energy grid connection, much work remains unfinished.
- As security and economic development are interrelated, it is essential to ensure an equitable balance between the two pillars.
- Thailand and India will need to be astute in managing Myanmar’s engagement until the political situation there becomes normal.
Way Ahead
- BIMSTEC should focus more in the future on new areas such as the blue economy, the digital economy, and promotion of exchanges and links among start-ups and MSMEs.
- Personal engagement of the political leadership should be stepped up.
- In the medium term, an annual summit should be the goal, with an informal retreat built into its programme.
- BIMSTEC needs greater visibility. India’s turn to host the G20 leaders’ summit in 2023 presents an opportunity. Perhaps all its members should be invited to the G20 summit as the chair’s special guests.
Connecting the dots:
FEDERALISM/ SECURITY
- GS-2: Federalism and Challenges
- GS-3: Internal Security
Withdrawal of AFSPA from major parts of North East
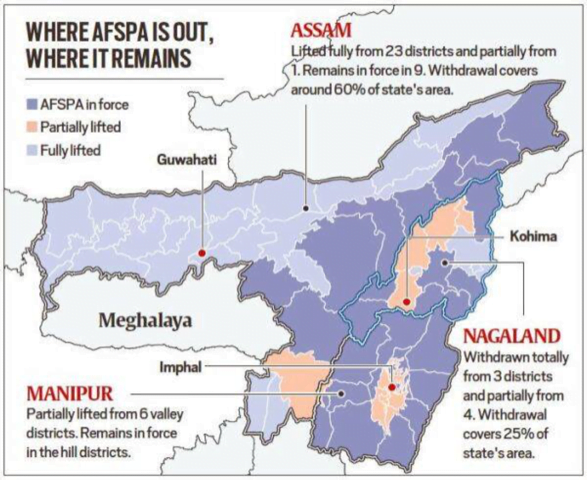
Context: Recently, Union government significantly reduced the footprint of the Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA), 1958 in the Northeast.
- It is withdrawn entirely from 23 districts in Assam.
- It is partially withdrawn from seven districts in Nagaland, six districts in Manipur, and one district in Assam
What is AFSPA?
- Colonial Legacy continued: The Act in its original form was promulgated by the British in response to the Quit India movement in 1942. After Independence, government decided to retain the Act, which was first brought in as an ordnance and then notified as an Act in 1958.
- Power of imposition: AFSPA can be imposed by the Centre or the Governor of a state, on the state or parts of it, after it is declared “disturbed’’ under Section 3. The Act defines these as areas that are “disturbed or dangerous condition that the use of armed forces in aid of the civil power is necessary’’.
- Special Power to Armed Forces: The Act, which has been called draconian, gives sweeping powers to the armed forces. It allows them to open fire’, even causing death, against any person in contravention to the law or carrying arms and ammunition. It gives them powers to arrest individuals without warrants, on the basis of “reasonable suspicion”, and also search premises without warrants.
- Immunity to Armed Personnel: The Act further provides blanket impunity to security personnel involved in such operations: There can be no prosecution or legal proceedings against them without the prior approval of the Centre.
Why is the recent decision significant?
- The Northeast has lived under the shadow of AFSPA for nearly 60 years, creating a feeling of alienation from the rest of the country.
- Once the decision is notified in the gazette, AFSPA remains in force in parts of these three states as well as in parts of Arunachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir.
- The move is expected to help demilitarise the region
- It will lift restrictions of movements through check points and frisking of residents.
- It will also help the Centre calm the anger over the Mon killings in Nagaland and help aid the Naga peace process.
After being in force for many years, why has AFSPA been withdrawn now?
- The decision has come as the result of a combination of circumstances.
- Over the last two decades, various parts of the Northeast have seen a reduction in insurgencies
- A number of major groups were already in talks with the Indian government, and these talks received traction in past few years.
- In Nagaland, all major groups — the NSCN(I-M) and Naga National Political Groups (NNPGs) — are at advanced stages of concluding agreements with the government.
- In Manipur, insurgency as well as heavy militarisation have been on the decline since 2012.
Connecting the dots:
- Criticisms of AFSPA
- Asymmetrical Federalism
- Naga Peace Process
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Q.1 Enforcement Directorate (ED) comes under which of the following Ministry of India?
- Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions
- Ministry of Finance
- Ministry of Commerce
- Ministry of Urban affairs
Q.2 ‘Talli-Bidda’ Express, recently flagged off by Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister is associated with which of the following?
- Pregnant women
- Postnatal mothers
- Infants
- All of the above
Q.3 What is the IUCN status of Olive Ridley turtle?
- Nearly endangered
- Extinct
- Threatened
- Vulnerable
ANSWERS FOR 2nd April 2022 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | D |
Must Read
On Sri Lanka Economic Crisis:
On Tamil Nadu’s Vanniyar quota:
On building faith in investigative agencies:












