IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
- Mains – GS 2 (Bilateral, Regional and Global Groupings and Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests)
Why in News: India and 12 countries led by the US launched the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF)
- The framework aims to strengthen economic partnership among participating countries to enhance resilience, sustainability, inclusiveness, economic growth, fairness, and competitiveness in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Indian Prime Minister said “The Indo-Pacific Economic Framework is a declaration of our collective will to make the region an engine of global economic growth.”
- Leaders and officials joined in virtually from Australia, Brunei, Indonesia, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- A joint statement said that the countries share a commitment to a free, open, fair, inclusive, interconnected, resilient, secure, and prosperous Indo-Pacific region that has the potential to achieve sustainable and inclusive economic growth.
- The joint statement said that they are launching collective discussions toward future negotiations, and identified four pillars under the IPEF.
- Trade: To build high-standard, inclusive, free, and fair trade commitments and develop new and creative approaches in trade and technology policy that advance a broad set of objectives that fuels economic activity and investment, promotes sustainable and inclusive economic growth, and benefits workers and consumers
- Supply Chains: Committed to improving transparency, diversity, security, and sustainability in supply chains to make them more resilient and well-integrated.
- Clean Energy, Decarbonization, and Infrastructure: In line with Paris Agreement goals and efforts to support the livelihood of peoples and workers, the framework plan to accelerate the development and deployment of clean energy technologies to decarbonize economies and build resilience to climate impacts.
- Tax and Anti-Corruption: Committed to promoting fair competition by enacting and enforcing effective and robust tax, anti-money laundering, and anti-bribery regimes in line with existing multilateral obligations, standards, and agreements to curb tax evasion and corruption in the Indo-Pacific region.
Indo Pacific
- The Indo-Pacific is a geopolitical construct that has emerged as a substitute to the long-prevalent “Asia-Pacific”, which represented the eastwards shift of global developments from Euro-Atlantic dimension
- It is an integrated theatre that combines the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean, and the land masses that surround them.
- One of the reasons behind the popularity of this term is an understanding that the Indian Ocean and the Pacific are a linked strategic theater.
- Also, the centre of gravity has shifted to Asia. The reason being maritime routes, the Indian Ocean and the Pacific provide the sea lanes.
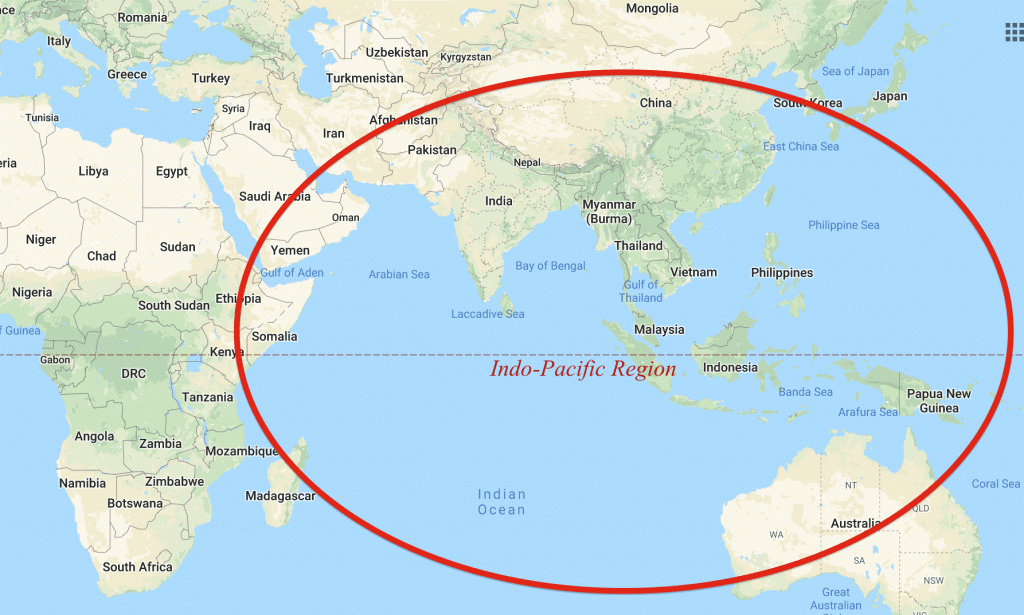
The term ‘Indo-Pacific’ is interpreted differently by different stakeholders.
- India considers the region as an inclusive, open, integrated and balanced space. India continuously emphasizes on strategic inter-connections, common challenges and opportunities between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific.
- The S. considers it to be a free and open Indo-Pacific, highlighting the importance of rules or norms of conduct in the region, thus trying to contain the role of China in the region.
- The ASEAN countries look at Indo-Pacific as a consociational model, thus bringing in China not only for the sake of giving it some stakeholdership but looking for ways to cooperate with it in the region.
Factors driving the global shift towards the Indo-pacific
- Important Sea Lines of Communication – presence of key choke points, from the Mozambique Channel and Bab-el-Mandeb in the west to Lombok Strait in the east
- Flourishing Trade and Economy – The Indo-Pacific Region shares 44% of the world surface area; includes 65% of the world population; accounts for 62% of the world GDP
- Natural resources: The expanse of Indian and Pacific Ocean combined has vast reserves of marine resources including- Offshore Hydrocarbons, Methane hydrates, Sea Bed minerals, Rare earth metals, fisheries etc
- China factor – China’s aggressive foreign policy, rapid economic expansion, military modernization and power projection has raised several red flags among regional and extra-regional countries
- Increasing Militarization of Indian Ocean Region (IOR) – China has established commercial ports across the Indo Pacific, such as Gwadar port (Pakistan), port in Hambantota (Sri Lanka) etc., in addition to its overseas naval base in Djibouti.
India’s interest in the region
- Peace and security in the Indian Ocean: Nearly 50% of India’s trade is centered in the Indo-Pacific Region and the Indian Ocean carries 90% of India’s trade and its energy sources. India wants to assure freedom of navigation, secure choke points, resolve conflicts peacefully and address non-traditional security threats in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Geo-political aspirations: To expand its own presence in the region
- Countering China: Ensuring that China does not gain a significant strategic foothold in the region
- Enhancing Trade and Investment Cooperation: by encouraging greater flow of goods, services, investment and technology between India and other countries in the region.
- Promoting sustainable development in the region, combating marine pollution, Regulating illegal fishing etc
Challenges faced by India in the region
- Limited Naval Capacity and Lack of military bases
- Poor infrastructure connectivity
- Countering China – China has established commercial ports across the Indo Pacific, such as Gwadar port (Pakistan), port in Hambantota (Sri Lanka) etc – India lacks resources for such major projects
Way forward
- It is important to establish connectivity in the region based on respect for sovereignty and territorial integrity, consultation, good governance, transparency, viability and sustainability.
- The countries in the region should have equal access as a right under international law to the use of common spaces on sea and in the air that would require freedom of navigation, unimpeded commerce and peaceful settlement of disputes in accordance with international law.
- Strong naval capabilities, multilateral diplomacy, economic integration in the region is the need of the hour
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)’,
Consider the following statements: (2015)
- It was established very recently in response to incidents of piracy and accidents of oil spills.
- It is an alliance meant for maritime security only
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)’
- Argentina, Mexico, South Africa, and Turkey
- Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
- Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
- Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Source: Indian Express & PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity
- Mains – GS2 (Functions and Responsibilities of the Union and the States, Issues and Challenges Pertaining to the Federal Structure, Devolution of Powers and Finances up to Local Levels and Challenges Therein)
In News: Vinai Kumar Saxena is appointed as Delhi’s new Lieutenant Governor by President of India
The Lieutenant Governor and the NCT Delhi:
Constitutional provisions:
- Under Article 239 of the Constitution of India, the administration of UT’s is handled by an administrator appointed by the President of India.
- However, the Constitution (Sixty-ninth Amendment) Act, 1991 introduced Article 239AA which created an elected Legislative Assembly and a Council of Ministers including a Chief Minister for NCT Delhi.
- This Assembly has the power to make laws for NCT Delhi with respect to any of the matters under the State or Concurrent Lists (except public order, police and land matters).
- The Lieutenant Governor (LG) of Delhi was designated the Administrator of the NCT Delhi.
Powers of Lieutenant Governor:
- He/She acts on the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers, except when he/she is compelled to act in his/her discretion.
- If the LG and the Ministers disagree on any issue, the LG shall refer it to the President for decision and act accordingly.
- When such a decision is pending with the President, it shall be competent for the LG to take prompt action in any scenario where the matter (in his opinion) is urgent.
- Under Article 239AB, the President may, on receipt of a report from the LG or otherwise, suspend the operation of any provision of Article 239AA by order when a situation arises in which the administration of the NCT cannot be carried out in accordance with the provisions of Article 239AA.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
- Mains – GS 3 (Conservation, Environmental Pollution and Degradation)
In News: India is moving faster than any other country towards a green transition, Petroleum Minister says at Davos
- Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas stated that India will emerge as the leader of green hydrogen
Hydrogen
- Hydrogen is one of the most abundant elements on earth for a cleaner alternative fuel option.
Type of hydrogen depends up on the process of its formation:
- Green Hydrogen
- Green hydrogen is produced by electrolysis of water using renewable energy (like Solar, Wind) and has a lower carbon footprint.
- Electricity splits water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- By Products: Water, Water Vapor.
- Brown hydrogen is produced using coal where the emissions are released to the air.
- Grey hydrogen is produced from natural gas where the associated emissions are released to the air.
- Blue hydrogen is produced from natural gas, where the emissions are captured using carbon capture and storage.
Uses:
- Hydrogen is an energy carrier, not an energy source and can deliver or store a tremendous amount of energy.
- It can be used in fuel cells to generate electricity, or power and heat
- Due to their high efficiency and zero-or near zero-emissions operation, hydrogen and fuel cells have the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emission in many applications.
Green Hydrogen Policy (GHP)
- Recently, the Ministry of Power (MoP) announced a Green Hydrogen Policy (GHP).
- The policy has set a target of 5 million tonnes per annum (MTPA) of green hydrogen production by 2030, more than 80% of the current hydrogen demand in the country.
- Under the policy, the government is offering to set up manufacturing zones for production, connectivity to the ISTS (Inter-State Transmission System) on priority basis, and free transmission for 25 years if the production facility is commissioned before June 2025.
- Producers will be allowed to set up bunkers near ports for storage of green ammonia for export by shipping.
- Manufacturers of Green hydrogen and ammonia are allowed to purchase renewable power from the power exchange or set up Renewable Energy (RE) capacity themselves or through any other developer, anywhere.
Significance of the Policy
- India’s largest oil refiner, Indian Oil Corp (IOC) estimates that GHP measures will reduce the cost of green hydrogen production by 40-50%.
- Fuels like Green Hydrogen and Green Ammonia are vital for any nation’s environmentally sustainable energy security.
- India has already committed to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2070, and green hydrogen will play a significant role as a disruptive feedstock in India’s transition from oil and coal.
- The GHP lays a solid foundation for developing a competitive green hydrogen sector in India.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) Which of the following best describes/describe the aim of ‘Green India Mission’ of the Government of India? (2016)
- Incorporating environmental benefits and costs into the Union and State Budgets thereby implementing the ‘green accounting’
- Launching the second green revolution to enhance agricultural output so as to ensure food security to one and all in the future
- Restoring and enhancing forest cover and responding to climate change by a combination of adaptation and mitigation measures
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Important Schemes
- Mains – GS 2 (Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources)
In News: The World Health Organisation (WHO) has recognized the contribution of India’s 1 million Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- It is acknowledged that ASHAs facilitate linking households to health facilities, and play pivotal roles in house-to-house surveys, vaccination, public health and Reproductive and Child Health measures.
Genesis & evolution of the ASHA programme
- The ASHA programme was based on Chhattisgarh’s successful Mitanin programme, in which a Community Worker looks after 50 households.
- The National Health Mission was launched to provide effective health care to the entire rural population in the country – The core strategy of the mission is to provide well trained female health activist (Accredited Social Health Activist- ASHA) in each village (1/1000 population) to fill the gap of unequal distribution of health services in rural area.
- Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA) is a trained female community health activist.
- Selected from the community itself and accountable to it, the ASHA will be trained to work as an interface between the community and the public health system.
- At present there are over 9 Lakh ASHAs.
Roles and responsibilities
- The role of an ASHA is that of a community level care provider.
- This includes a mix of tasks: facilitating access to health care services, building awareness about health care entitlements especially amongst the poor and marginalized, promoting healthy behaviours and mobilizing for collective action for better health outcomes and meeting curative care needs as appropriate to the organization of service delivery in that area and compatible with her training and skills.
Success of the programme
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) has recognized the contribution of India’s 1 million Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- ASHAs facilitate linking households to health facilities, and play pivotal roles in house-to-house surveys, vaccination, public health and Reproductive and Child Health measures thus help in keeping track and monitoring of diseases, outbreak, MMR and IMR etc
- In many states, ASHAs are involved in national health programmes
- With newly acquired skills in health care and the ability to connect households to health facilities, ASHAs were able to secure benefits for households.
- In a way, it became a programme that allowed a local woman to develop into a skilled health worker.
Issues
- They get performance-based payments, not a fixed salary like government servants. There have been agitations demanding employee status for ASHA workers.
- In many states, the payout is low, and often delayed.
- The original idea was never to deny the ASHA a compensation that could be even better than a salary — it was only to prevent “governmentalisation”, and promote “communitisation” by making her accountable to the people she served.
- There is a strong argument to grant permanence to some of these positions with a reasonable compensation as sustaining motivation.
Way forward
- It is important to ensure that compensation for performance is timely and adequate.
- Provide opportunities for moving up the skill ladder in the formal primary health care system as an ANM/ GNM or a Public Health Nurse
- Upgrading skill sets and providing easy access to credit and finance will ensure a sustainable opportunity to earn a respectable living while serving the community.
- Strengthening access to health insurance, credit for consumption and livelihood needs at reasonable rates, and coverage under pro-poor public welfare programmes will contribute to ASHAs emerging as even stronger agents of change.
National Health Mission
- National Health Mission (NHM) was launched by the government of India in 2013 subsuming the National Rural Health Mission and the National Urban Health Mission.
- The main programmatic components include Health System Strengthening in rural and urban areas for – Reproductive-Maternal- Neonatal-Child and Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A), and Communicable and Non-Communicable Diseases.
- The NHM envisages the achievement of universal access to equitable, affordable & quality health care services that are accountable and responsive to people’s needs.
The National Health Mission seeks to ensure the achievement of the following indicators:
- Reduce Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) to 1/1000 live births
- Reduce Infant Mortality rate (IMR) to 25/1000 live births
- Reduce Total Fertility Rate (TFR) to 2.1
- Prevention and reduction of anemia in women aged 15–49 years
- Prevent and reduce mortality & morbidity from communicable, non-communicable; injuries and emerging diseases
- Reduce household out-of-pocket expenditure on total health care expenditure
- Reduce annual incidence and mortality from Tuberculosis by half
- Reduce the prevalence of Leprosy to <1/10000 population and incidence to zero in all districts
- Annual Malaria Incidence to be <1/1000
- Less than 1 percent microfilaria prevalence in all districts
- Kala-azar Elimination by 2015, <1 case per 10000 population in all blocks.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity
- Mains – GS 2 (Federalism)
In News: The Centre has reconstituted the Inter-State Council
- Headed by the PM, the Council will comprise six Union ministers, besides the Chief Ministers of the 28 states and UTs with a legislature, and administrators of UTs without a legislature.
- It will also have 10 Union ministers as permanent invitees.
- The government has also reconstituted the standing committee of the Council, with Union Home Minister as it chairman
Constitutional Provisions
- According to Article 263 of the Indian Constitution, an Inter-State Council (ISC) may be constituted “if it seems to the President at any time that the public interests would be served by the creation of a Council.”
- It was set up in 1990 through a presidential ordinance for the first time as per the recommendations of the Sarkaria Commission under the Ministry of Home affairs.
- The interstate council is proposed to meet thrice a year. But in 26 years, it has met only 11 times. The latest meeting was held after a gap of 10 years in Delhi in July 2016.
Inter-State Council Composition
- Prime Minister acts as the chairman of the council.
- Union Ministers of Cabinet rank in the Union
- Council of Ministers nominated by the Prime Minister.
- Chief Ministers of all states
- Chief Ministers of Union Territories having a Legislative Assembly
- Administrators of UTs not having a Legislative Assembly
- Governors of the states being administered under President’s rule
Functions of Inter-State Council
- Inter-State Council is a recommendatory body with duties to investigate and discuss the subjects of common interest between the Union and State(s) or among the States, making recommendations particularly for better coordination of policy and action on these subjects and deliberating upon such other matters of general interest to the States which may be referred to it by its Chairman
- Making suggestions on any such subject, for the better coordination of policy and action with respect to that subject.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) Who among the following constitute the National Development Council? (2013)
- The Prime Minister
- The Chairman, Finance Commission
- Ministers of the Union Cabinet
- Chief Ministers of the States
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Source: The Hindu & Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs – Important Reports
In News: World of work – the ninth edition of the International Labour Organisation (ILO) Monitor was published
Key findings
- The report says that after significant gains during the last quarter of 2021, the number of hours worked globally dropped in the first quarter of 2022, to 3.8% below the employment situation before the pandemic.
- About 11.2 crore jobs might have lost between this period, according to the report.
- The report added that a “great and growing divergence between richer and poorer economies” continues to characterise the recovery.
- While high-income countries experienced a recovery in hours worked, low- and lower-middle-income economies suffered setbacks in the first quarter of the year with a 3.6 and 5.7 per cent gap respectively when compared to the pre-crisis benchmark
- The fresh lockdowns in China, the conflict between Ukraine and Russia, and the global rise in the prices of food and fuel are cited as the main reasons for the findings.
- The ILO urged its member countries to take a humane approach to address the situation.
Findings related to India
- The report said both India and lower-middle-income experienced a deterioration of the gender gap in work hours in the second quarter of 2020
- It report said that for every 100 women at work prior to the pandemic, 12.3 women would have lost their job as an average through the entire period considered by the report.
- In contrast, for every 100 men, the equivalent figure would have been 7.5.
- Hence, the pandemic seems to have exacerbated the already substantial gender imbalances in employment participation in the country.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) The Global Competitiveness Report is published by the (2019)
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
- World Economic Forum
- World Bank
Source: The Hindu
Baba’s Explainer – QUAD
Syllabus
- GS-2: Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
- GS-2: Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Why in News: Since the introduction of the National Education Policy, 2020 (NEP), Kerala has viewed the policy document with serious disagreements.
- However, two years down the line, the State has begun to warm up to some of the provisions, but with considerable hesitance. The government has hinted that the reforms might be introduced only during the 2023-24 academic year.
- The last NEP was that of 1986 and modified in 1992.
- NEP 2020 is based on the report filed by the committee headed by eminent space scientist Kasturirangan.
Read Complete Details on QUAD – CLICK HERE
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements
- Hydrogen is not a source of energy but an energy carrier
- Grey hydrogen is produced using coal where the emissions are released to the air
- Under the Green Hydrogen Policy (GHP), GOI has set a target of 5 million tonnes per annum (MTPA) of blue hydrogen production by 2030
Choose the correct statements:
- 3 only
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 only
Q.2) Consider the following statements
- Article 262 of the Indian Constitution provides for the establishment of an Inter-State Council (ISC)
- Inter-State Council is headed by Union Home Minister
- The recommendations of ISC are binding on Union and States governments.
Choose the incorrect statements
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
Q.3) Arrange the following seas from north to south
- Sea of Japan
- East China Sea
- Banda Sea
- Coral Sea
Choose the correct code:
- 1-2-4-3
- 2-1-3-4
- 2-1-4-3
- 1-2-3-4
ANSWERS FOR 24th MAY 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d Q.2) – c Q.3) – d











