IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity
In news: The Supreme Court, in the Media One ban case, reiterated its intention to examine the legality of governments filing incriminating material in sealed covers without sharing the information with the accused/other party.
- Sealed cover jurisprudence has been frequently employed by courts in the recent past for example Rafale Fighter Jet Deal 2018, 2014, BCCI Reforms Case, Bhima Koregaon case 2018 etc.
What is Sealed Cover Jurisprudence?
- It is a practice used by the Supreme Court and sometimes lower courts, of asking for or accepting information from government agencies in sealed envelopes that can only be accessed by judges.
- While a specific law does not define the doctrine of sealed cover, the Supreme Court derives its power to use it from Rule 7 of order XIII of the Supreme Court Rules and Section 123 of the Indian Evidence Act of 1872.
Rule 7 of order XIII of the Supreme Court Rules:
- According to the rule, if the Chief Justice or court directs certain information to be kept under sealed cover or considers it of confidential nature, no party would be allowed access to the contents of such information, except if the Chief Justice himself orders that the opposite party be allowed to access it.
- It also mentions that information can be kept confidential if its publication is not considered to be in the interest of the public.
Section 123 of the Indian Evidence Act of 1872:
- Under this act, official unpublished documents relating to state affairs are protected and a public officer cannot be compelled to disclose such documents.
- Other instances where information may be sought in secrecy or confidence are when its publication impedes an ongoing investigation, such as details which are part of a police case diary.
Issues with the Sealed Cover Jurisprudence
- Against the Principles of Transparency and Accountability
- Obstruction to Fair Trial and Adjudication
- Sealed covers are dependent on individual judges thus making it Arbitrary in Nature
Thus the court expressed its intention to examine the larger issue of “sealed cover jurisprudence”.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) In India, Judicial Review implies (2017)
- the power of the Judiciary to pronounce upon the constitutionality of laws and executive orders.
- the power of the Judiciary to question the wisdom of the laws enacted by the Legislatures.
- the power of the Judiciary to review all the legislative enactments before they are assented to by the President.
- the power of the Judiciary to review its own judgements given earlier in similar or different cases.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
In News: RBI raised key policy rates to fight inflation
- RBI raised the repo rate by 40 basis points and CRR by 50 basis points
What is inflation?
- Inflation refers to the rise in the prices of most goods and services of daily or common use, such as food, clothing, housing, recreation, transport, consumer staples, etc.
Types of Inflation
1) Demand-Pull Inflation
- This type of inflation is caused due to an increase in aggregate demand in the economy.
Causes of Demand-Pull Inflation:
- A growing economy or increase in the supply of money – When consumers feel confident, they spend more and take on more debt.
- Deficit financing by the government, Increased borrowing etc causes demand pull inflation
2) Cost-Push Inflation
- This type of inflation is caused due to various reasons such as:
- Increase in price of inputs, hoarding and Speculation of commodities, defective Supply chain, increase in indirect taxes, depreciation of Currency, crude oil price fluctuation, defective food supply chain, interest rates increased by RBI etc
- Cost pull inflation is considered bad among the two types of inflation. Because the National Income is reduced along with the reduction in supply in the Cost-push type of inflation
- Indices used to measure inflation are Wholesale Price Index (WPI) and Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- RBI is mandated by the Government of India under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1924 to maintain the inflation target of 4%, with a tolerance band of +/- 2 percentage points
- Thus RBI Monetary Policy tools to control inflation
Monetary Policy Measures
- Monetary policy refers to the policy of the central Bank with regard to use of monetary instruments under its control to manage money supply and interest rates.
- In 2016, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Act, 1934 was amended to provide a statutory basis for the implementation of the flexible inflation targeting framework.
- Under amended RBI Act, 1934, the central government is empowered to constitute a six-member Monetary Policy Committee (MPC).
- Composition: the MPC shall consist of 6 members:
- RBI Governor as its ex officio chairperson,
- Deputy Governor in charge of monetary policy,
- An officer of the Bank to be nominated by the Central Board,
- Three persons to be appointed by the central government
| Tools | Features |
| Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) | The average daily balance that a bank is required to maintain with the Reserve Bank as a share of such per cent of its Net demand and time liabilities (NDTL) that the Reserve Bank may notify from time to time. |
| Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) | The share of NDTL that a bank is required to maintain in safe and liquid assets, such as, government securities, cash and gold. |
| Repo Rate | The interest rate at which the Reserve Bank provides overnight liquidity to banks against the collateral of government and other approved securities under the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF). |
| Reverse Repo Rate | The interest rate at which the Reserve Bank absorbs liquidity, on an overnight basis, from banks against the collateral of eligible government securities under the LAF. |
| Marginal Standing facility (MSF) | It is the rate at which Banks can borrow short term funds from RBI. Under MSF, banks can borrow funds from the RBI by pledging government securities within the limits of the SLR. |
| Open Market Operations (OMOs) | These include both, outright purchase and sale of government securities, for injection and absorption of durable liquidity, respectively. |
| Market Stabilisation Scheme (MSS) | It is a monetary policy intervention by the RBI to withdraw excess liquidity (or money supply) by selling government securities in the economy, the mobilised cash is held in a separate government account with the Reserve Bank. |
Note: The Policy Corridor in monetary policy of the RBI refers to the area between the reverse repo rate and the MSF rate
- MSF is upper band of the Policy Corridor (lower band being the Reverse Repo rate). Thus value of MSF is tied with the value of Repo Rate. Usually RBI changes Repo rate and MSF changes automatically.
- With this Quantitative Tools RBI also uses Qualitative Tools like fixing margin requirement, moral Suasion and selective credit control to fight inflation
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) With reference to the Indian economy, demand-pull inflation can be caused/increased by which of the following? (2021)
- Expansionary policies
- Fiscal stimulus
- Inflation-indexing wages
- Higher purchasing power
- Rising interest rates
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 3, 4 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)? (2017)
- It decides the RBI’s benchmark interest rates.
- It is a 12-member body including the Governor of RBI and is reconstituted every year.
- It functions under the chairmanship of the Union Finance Minister.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science & Tech – Health
In news: Food poisoning reported in Kasaragod district of Kerala
What is shigella infection?
- It is a contagious intestinal infection caused by a genus of bacteria known as shigella.
- The bacteria is one of the prime pathogens responsible for causing diarrhea, fluctuating between moderate and severe symptoms, especially in children in African and South Asian regions.
- As per reports, an estimated annual mortality of 35,000–40,000 is noted globally in both under-five and older-than-five age groups.
Symptoms: most people with Shigella infection have diarrhea (sometimes bloody), fever, and stomach cramps
How it spreads?
- Shigella is generally transmitted through contaminated food or water, or through person-to-person contact.
- Shigellosis is primarily a disease of poor and crowded communities that do not have adequate sanitation or safe water.
- The bacteria, after entering the body through ingestion, attack the epithelial lining of the colon resulting in inflammation of the cells and subsequently the destruction of the cells in severe cases.
- Handwashing is said to reduce shigella transmission by 70%.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) Consider the following diseases (2014)
- Diphtheria
- Chickenpox
- Smallpox
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- None of the above
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS – 2 (Bilateral, Regional and Global Groupings and Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests)
In News: Prime Minister of India participated in the 2nd India-Nordic Summit on May 04, 2022
- The summit is being hosted by Denmark
- Prime Ministers of Denmark, Iceland, Finland, Sweden and Norway have also participated in the summit.
Background
- The 1st India-Nordic Summit took place in 2018 in Stockholm
- The 2018 India-Nordic Summit reiterated the six countries’ commitment to global security, economic growth, innovation and climate change.
Key Discussions
- It primarily focused on post-pandemic economic recovery, climate change, renewable energy and the evolving global security scenario.
- The issue of Indo-Pacific too was discussed at the meeting
- The Prime Minister also held separate bilateral meetings with his counterparts of nordic countries
- With Finland the discussion focused on to expand cooperation in the fields of new and emerging technologies like AI, quantum computing, future mobile technologies, clean technologies and smart grids
- With Norway the discussion was to deepen engagement in areas like blue economy, renewable energy, and green hydrogen, solar and wind projects, green shipping, fisheries, water management, rainwater harvesting, space cooperation, long-term infrastructure investment, health and culture.
- Both Indian and Sweden PMs expressed satisfaction at the progress made by the Lead IT initiative.
- This was a India-Sweden joint global initiative to set up a Leadership Group on Industry Transition (LeadIT) in September 2019 at the UN Climate Action Summit to help guide the world’s heaviest greenhouse gas (GHG) emitting industries towards the low-carbon economy. Its membership has now grown to 35 with 16 countries and 19 companies
- With Iceland leaders discussed ways to further strengthen economic cooperation, especially in the sectors of geothermal energy, blue economy, Arctic, renewable energy, fisheries, food processing, education including digital universities, and culture
About Nordic Countries
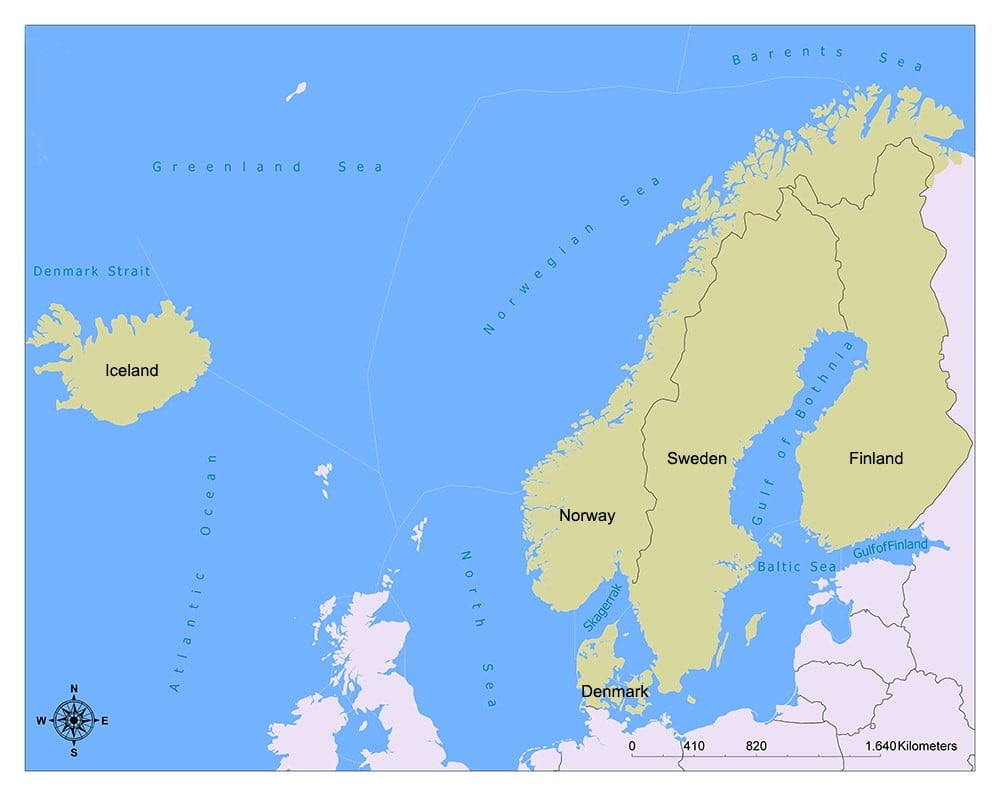
- The Nordic Countries are a group of countries in northern Europe.
- There are 5 Nordic countries, Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Finland, and Iceland.
- Denmark, Sweden, and Norway are constitutional monarchies and parliamentary democracies. Finland and Iceland are democratic republics.
Importance of Nordic Countries to India
- Nordic countries collectively represent an economy of more than $1.6 trillion.
- Total bilateral trade in goods and services between India and the Nordic countries is $13 billion.
- All these countries figure among the top achievers in several areas of human endeavour, particularly innovation, clean energy, green technologies, and education.
Importance of India to Nordic Countries
- India is the third-largest global economy at $9 trillion in purchasing power parity terms.
- It is also the fastest-growing major economy with annual GDP growth of 7.4% in 2022-23.
- India presents an ideal opportunity to these countries because of its large market as also its youth dividend.
- Maintaining peace, ensuring security and promoting sustainable economic development of the Arctic Region is another area which presents immense possibilities to strengthen the bilateral partnership.
Significance of Nordic Summit for India
- The significance of the event for India can be accessed from the fact that the US is the only other country with which the Nordic states have an engagement at the summit level.
- India Nordic Summit helps in expanding India’s multifaceted cooperation with the Nordic region.
Nordic countries are important partners for India in sustainability, renewable energy, digitisation and innovation. These present enormous opportunities for India to plug into the strengths of these countries to mutual benefit.
Source: The Hindu
Baba’s Explainer – Delhi-Centre Power Tussle
Syllabus
- GS-2: Structure, organization and functioning of the Executive; Issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure
Why in News: The Supreme Court has started hearing the dispute between the Delhi government and the Centre over the control of administrative services in the national capital.
- The case concerned an important question of law dealing with governance and administration of the capital.
- The reference to a larger Bench dates back to February 14, 2019, when a Division Bench of Justices A.K. Sikri and Ashok Bhushan (both retired) gave a split opinion on the question of ‘services’.
Read Complete Details on Delhi-Centre Power Tussle – CLICK HERE
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements
- Supreme Court of India derives its powers to use Sealed Cover Jurisprudence under the Supreme Court Rules
- In any case the court cannot allow access to the contents of such information to any party including the opposite party
Choose the correct statements:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Which of the following leads to cost-push inflation?
- Hoarding and Speculation of commodities
- Deficit financing by the government
- Interest rates increased by RBI
Choose the correct code:
- 1 only
- 1 and 2
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
Q.3) Consider the following statements
- Among Nordic countries Norway and Finland share borders with Russia
- The North Sea is completely bound by nordic countries
- India and Sweden jointly started a global initiative LeadIT to help the world’s heaviest greenhouse gas emitting industries towards the low-carbon economy
Choose the correct statements:
- 1 and 2
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
ANSWERS FOR 5th MAY 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
| 1 | a |
| 2 | d |
| 3 | c |














