IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
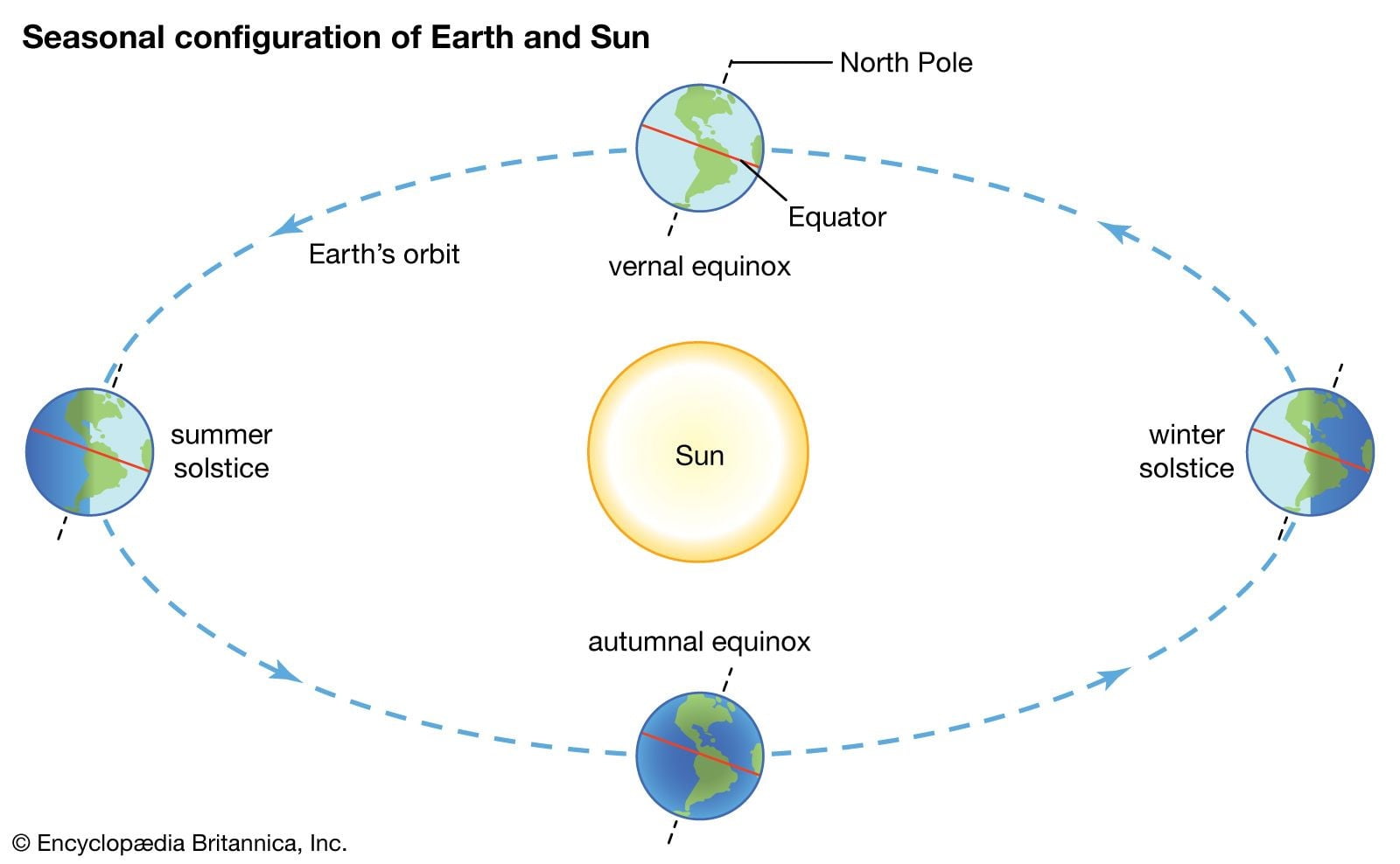
In News: June 21 is the day of Summer Solstice in 2022.
- The summer solstice marks the beginning of the astronomical summer and occurs when the earth has its maximum tilt towards the sun.
- For temperate regions, the summer solstice is when the sun reaches its highest point in the sky.
- The Earth orbits the sun at an angle.
- So for half the year, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun and therefore, it is summer for the Northern hemisphere and winter for the Southern Hemisphere.
- During the other half of the year, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted away from the sun, thus creating winter in the Northern Hemisphere and summer in the south.
- Solstices happen twice per year: one for the winter and one for the summer and this is interchanged depending on which Hemisphere you live in.
- The longest day of the year happens on the day of the summer solstice since the earth receives the longest period of daylight during the day.
- The solstice has been seen as a significant time of the year in many cultures and has been marked by festivals and rituals across the globe.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) In the northern hemisphere, the longest day of the year normally occurs in the: (2022)
- First half of the month of June
- Second half of the month of June
- First half of the month of July
- Second half of the month of July
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science
Context: The study published in The Lancet Microbe points to the reduced effectiveness of antibiotics for typhoid fever is threatened because of the emergence of resistant strains
- Typhoid fever causes 11 million infections and more than 100,000 deaths per year. South Asia accounts for 70% of the global disease burden.
- Since 2000, multi-drug-resistant (MDR) S Typhi has declined steadily in Bangladesh and India, remained low in Nepal, and increased slightly in Pakistan.
- However, these are being replaced by strains resistant to other antibiotics
- The genome analysis also reveals that resistant strains – almost all originating in South Asia – have spread to other countries 197 times since 1990.
Typhoid
- Typhoid fever is caused by the highly contagious Salmonella Typhi bacteria.
- The bacteria spread through contaminated food or water.
- Symptoms are prolonged fever, headache, nausea, loss of appetite, and constipation or sometimes diarrhoea.
- Clinical severity varies and severe cases may lead to serious complications or even death
- According to WHO children under the age of two years account for a large proportion of severe typhoid fever cases.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which one of the following statements is not correct? (2019)
- Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV.
- Hepatitis B unlike Hepatitis C does not have a vaccine.
- Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses arc several times more than those infected with HIV.
- Some of those infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
In News: The Monthly Economic Review highlights two key areas of concern for the Indian economy: the fiscal deficit and the current account deficit (or CAD)
Fiscal deficit
- As government revenues take a hit following cuts in excise duties on diesel and petrol, an upside risk to the budgeted level of gross fiscal deficit has emerged
- The fiscal deficit is essentially the amount of money that the government has to borrow in any year to fill the gap between its expenditures and revenues.
- Higher levels of fiscal deficit typically imply more borrowing by the government in the market which leads to crowding out effect.
- At a time when the government is trying its best to kick-start and sustain a private sector investment cycle, borrowing more than what it budgeted will be counter-productive.
Current account deficit
The current account essentially refers to two specific sub-parts:
- Import and Export of goods — this is the “trade account”.
- Import and export of services — this is called the “invisibles account”.
- The net effect of a trade account and the invisibles account is a deficit, then it is called a current account deficit or CAD.
- A widening CAD tends to weaken the domestic currency because a CAD implies more dollars (or foreign currencies) are being demanded than rupees.
- Costlier imports such as crude oil and other commodities will not only widen the CAD but also put downward pressure on the rupee. A weaker rupee will, in turn, make future imports costlier.
- The report underscores the need to trim revenue expenditure.
- Rationalizing non-capex expenditure has thus become critical, not only for protecting growth supportive capex but also for avoiding fiscal slippages
- Capex or capital expenditure essentially refers to money spent towards creating productive assets such as roads, buildings, ports etc.
- Capex has a much bigger multiplier effect on the overall GDP growth than revenue expenditure.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to the expenditure made by an organisation or a company, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2022)
- Acquiring new technology is capital expenditure.
- Debt financing is considered capital expenditure, while equity financing is considered revenue expenditure.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography (Places in News)
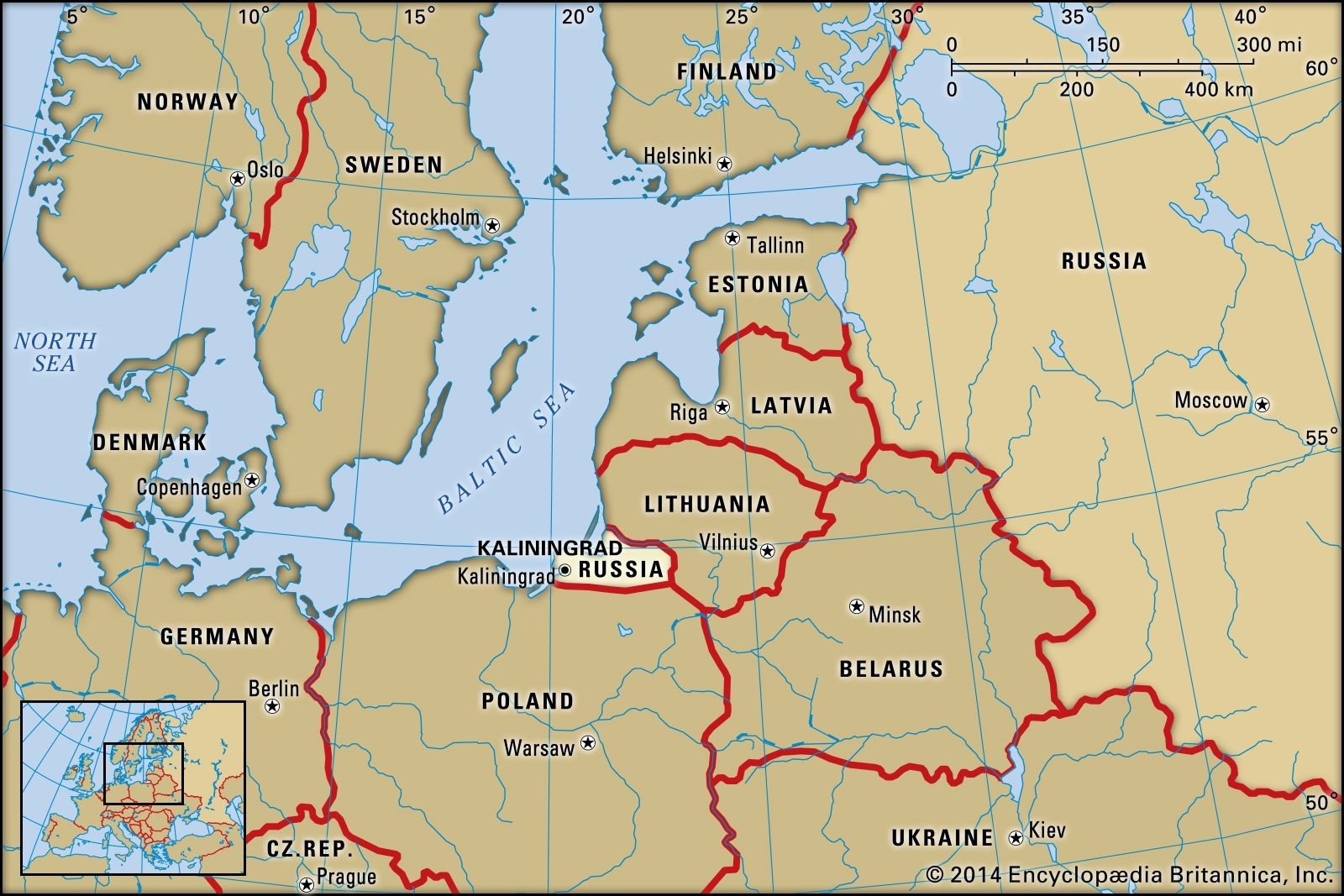
Kaliningrad
In News: Moscow warned Lithuania of serious consequences over its restriction of rail traffic to Russia’s Kaliningrad exclave
- Lithuania says it is simply adhering to EU-wide sanctions on Moscow
Kaliningrad
- Kaliningrad is a Russian exclave sandwiched between Poland and Lithuania.
- It was captured by Soviet troops from Nazi Germany in April 1945 and then became part of Soviet territory as a result of the Potsdam Agreement.
- It was renamed from the German Konigsberg in 1946
Importance of Kaliningrad
- Kaliningrad is the only Russian port on the Baltic Sea that is ice-free year round and is an important launch point for the nation’s naval fleet.
- Its strategic location prevents ships from having to circumnavigate Scandinavia by way of a northern passage, traveling through the Arctic Ocean.
Source: The Hindu
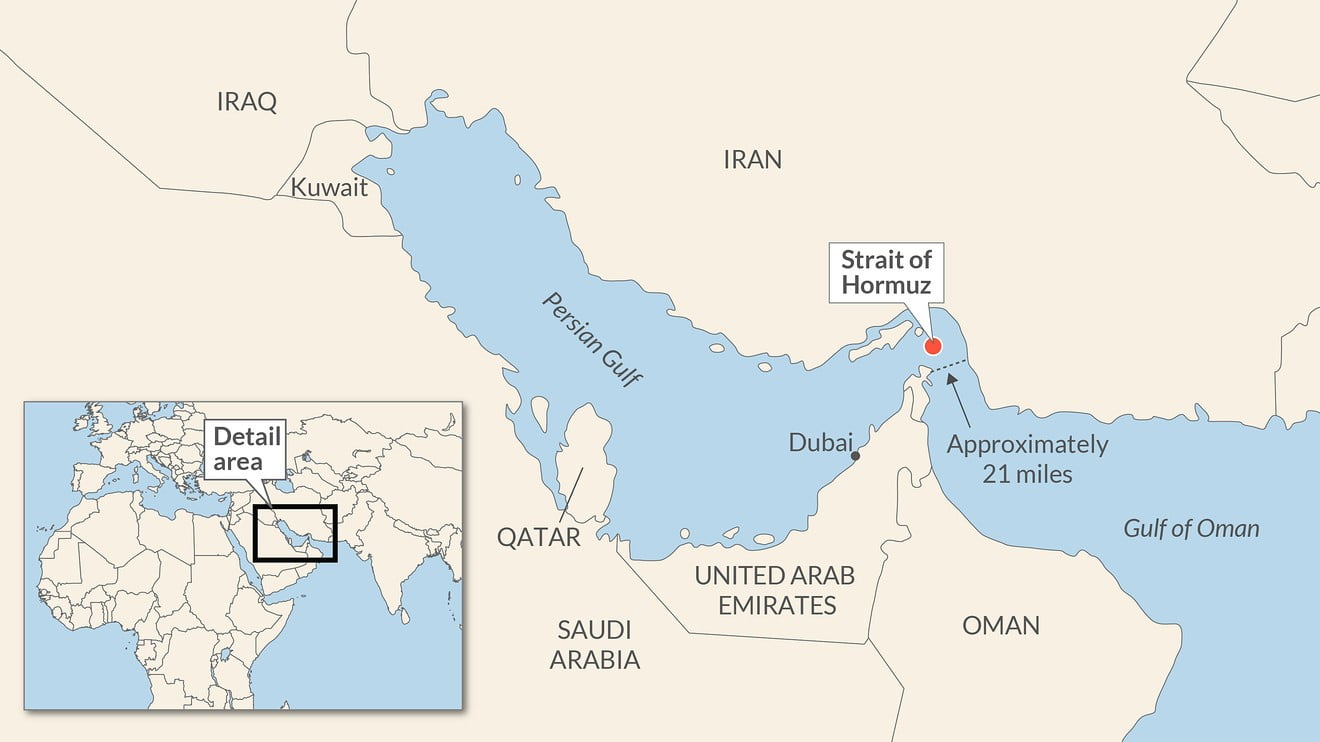
In News: A U.S. Navy warship fired a warning flare to wave off an Iranian Revolutionary Guard speedboat coming straight at it during a tense encounter in the strategic Strait of Hormuz
Strait of Hormuz
- The waterway separates Iran and Oman, linking the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea.
- The Strait is 33 km wide at its narrowest point, but the shipping lane is just three km wide in either direction.
- Most crude exported from Saudi Arabia, Iran, the UAE, Kuwait and Iraq – all members of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) – is shipped through this waterway.
- It is also the route used for nearly all the liquefied natural gas (LNG) produced by the world’s biggest LNG exporter, Qatar.
Background
- Iran and world powers agreed in 2015 to the nuclear deal, which saw Tehran drastically limit its enrichment of uranium in exchange for the lifting of economic sanctions.
- In 2018, then-President Donald Trump unilaterally withdrew America from the accord, raising tensions across the wider Middle East and sparking a series of attacks and incidents.
- Talks in Vienna about reviving the deal have been on a pause since March.
- Since the deal’s collapse, Iran has been running advanced centrifuges and rapidly growing stockpile of enriched uranium.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2022)
Regions in News Country
- Anatolia – Turkey
- Amhara – Ethiopia
- Cabo Delgado – Spain
- Catalonia – Italy
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Q.2) Consider the following pairs: (2018)
Regions sometimes mentioned in news Country
- Catalonia — Spain
- Crimea — Hungary
- Mindanao — Philippines
- Oromia — Nigeria
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 3 and 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Judiciary)
Context: Problems in India’s Higher Judiciary
Problems
Retirement age of judges
- Disparity between the retirement ages of High Court and Supreme Court judges; High Court judges now retire at 62 and Supreme Court judges at 65.
- Doing away with this disparity and increasing the age of retirement for both High Court and Supreme Court judges will reduce the burden of pending cases in higher judiciary
Lack of a culture of service
- Most of Supreme Court judges after their tenure focus on arbitrations and amass considerable fortunes with high fees and multiple sittings.
- A minority of judges devote themselves to public service
- Another lot are appointed to various constitutional posts and tribunals and commissions.
- It would be worthwhile reform to create a cadre of public service for retired judges and from this pool make appointments to the constitutional and statutory posts and special assignments.
Selection of Chief Justice of India
- It is generally assumed that the senior most judge of the Supreme Court should be the Chief Justice of India is not mentioned in the constitution
- Article 124 merely states that the President will appoint every judge of the Supreme Court, and this includes the Chief Justice
- Public purpose is better served by ensuring that the judges of the Supreme Court during their entire tenure are not swayed by their expectations or aspirations to the higher office of CJI
So who should be the CJI?
- CJI should be the best reputed Chief Justice of a High Court who has proved himself worthy both in judicial office as well as administrative leadership and has those qualities of heart and head which mark a good leader.
- The appointee should have a clear three year term — not the truncated weeks and months that some CJIs now get.
- He/she should work in a strict manner especially in regard to the roster of allotment of cases, especially the sensitive ones, and appointments to the Supreme Court and High Courts and other important matters of judicial and administrative importance.
The above mentioned reforms will increase the productivity of the higher judiciary and make it accountable to the people of India
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 4 (Ethics)
Context: UNESCO’s global agreement on the ethics of AI can guide governments and companies alike
- Artificial intelligence (AI) is more present in our lives than ever.
Issues in AI
- The data used to feed into AI often aren’t representative of the diversity of our societies, producing outcomes that can be said to be biased or discriminatory.
- For instance, while India and China together constitute approximately a third of the world’s population, Google Brain estimated that they form just 3% of images used in ImageNet, a widely used dataset.
- There are problems emerging in facial recognition technologies, which are used to access our phones, bank accounts and apartments, and are increasingly employed by law-enforcement authorities, in identifying women and darker-skinned people.
- For three such programs released by major technology companies, the error rate was 1% for light-skinned men, but 19% for dark-skinned men, and up to 35% for dark-skinned women.
- These issues are of particular importance to India, which is one of the world’s largest markets for AI-related technologies, valued at over $7.8 billion in 2021.
- To ensure that the full potential of these technologies is reached, the right incentives for ethical AI governance need to be established in national and sub-national policy.
A common rulebook
- Until recently, there was no common global strategy to take forward this importance agenda.
- This changed when 193 countries reached a groundbreaking agreement at UNESCO on how AI should be designed and used by governments and tech companies.
- It aims to fundamentally shift the balance of power between people, and the businesses and governments developing AI
- Countries which are members of UNESCO have agreed to implement this recommendation by enacting actions to regulate the entire AI system life cycle, ranging from research, design and development to deployment and use
Recommendations
- It underscores the importance of the proper management of data, privacy and access to information.
- It also calls on member states to ensure that appropriate safeguards schemes are devised for the processing of sensitive data and effective accountability, and redress mechanisms are provided in the event of harm.
- Recommendation taking a strong stance that
- AI systems should not be used for social scoring or mass surveillance purposes;
- that particular attention must be paid to the psychological and cognitive impact that these systems can have on children and young people;
- and that member states should invest in and promote not only digital, media and information literacy skills, but also socio-emotional and AI ethics skills to strengthen critical thinking and competencies in the digital era.
Significance
- The new agreement is broad and ambitious.
- It is a recognition that AI-related technologies cannot continue to operate without a common rulebook.
- Governments will themselves use the recommendation as a framework to establish and update legislation, regulatory frameworks, and policy to embed humanistic principles in enforceable accountability mechanisms.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Infrastructure)
Context: It is time India plans a hub airport flight path
- Transforming one of India’s metro gateway airports into a hub airport deserves consideration as the aviation market puts the novel coronavirus pandemic behind it and passenger demand surges.
- India is the third largest domestic aviation market in the world, next only to the United States and China
- In view of the surge in passenger demand, India’s airport operators have planned investments upwards of ₹90,000 crore to enhance capacity over the next four years or so.
- To boot, the conditions are just right for building a hub airport.
What is a hub airport?
- A hub airport is one served by a multitude of airlines, connecting several airports through non-stop flights.
- There are three basic requirements for becoming a major airport hub, whether domestic or international, i.e.
- sufficient local consumer demand;
- good geographic location, and
- necessary infrastructure to support high-volume traffic.
- A typical hub airport operates on the concept of waves.
- A wave of incoming flights arrives and connects with another wave of outgoing flights that departs an hour or two later.
- Hubbing allows for the maximum combination of flight pairs and a wider choice of destinations and frequencies for connecting passengers.
- Some global examples are (Hub airport/Home airline): London/British Airways; Frankfurt/Lufthansa
Significance
- It is a win-win for all.
- A hub creates economies of scale for the airport and airlines alike.
- The airport benefits from increased direct connectivity with other airports and more revenue opportunities due to increased passenger footfalls.
- Improved passenger throughput has a knock-on effect on the wider airport ecosystem, such as aero and non-aero service providers at the airport, including cargo and ground handling, etc.
- Airlines, on their part, get to serve city pairs that are otherwise economically unviable for non-stop flights.
- Frequent fliers get greater choice and flexibility with flights, destinations, and service frequencies, as well as lower ancillary costs, such as avoiding the time and cost of an overnight stay.
- It is well established that the creation of one job in the aviation sector affects the creation of up to six jobs in allied sectors, such as tourism and hospitality.
- All this propels the economic and social development of the city and its inhabitants, too.
An India perspective
- In India the first two requirements are largely addressed and the focus is rightly on addressing the third requirement i.e. infrastructure
Factors in favour
- India has the largest diaspora, or transnational community, at 18 million people across all six continents and regions being third largest domestic aviation market in the world it can go for airport hub
- India is located on busy international air corridors that connect Europe, Africa, and the Middle East with Asia, making it ideal for a transit hub and alternative/diversion/fuel stop/technical stop; being the fifth-largest economy
- Given these favourable factors India can support development of more than one hub airport
Impediments
- There are capacity constraints at major airports because of a lack of landing slots, especially during peak hours
- The Airports Authority of India Act (AAI), 1994 constrains the AAI/airport operators from commercially exploiting available land for non-aeronautical activities
- A high cost-low fare operating environment and increased competition hurts airline balance sheets and financials, which hurts the growth of airports
There is a need to develop inter-modal connectivity (rail/road – air) and logistics support infrastructure as a part of the future master plans to fully exploit potential with cargo and freight. With the carefully framed policy, India can bring down its logistic cost, increase people to people contact and raise the contribution of hospitality sector to the economy.
Source: The Hindu
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements
- Kaliningrad is a Russian exclave sandwiched between Lithuania and Belarus
- Kaliningrad is the only Russian port on the North Sea that is ice-free year round
- Its strategic location prevents ships from having to circumnavigate Scandinavia by way of a northern passage
Choose the incorrect statements:
- 1 and 2
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 only
- 2 only
Q.2) Strait of Hormuz connects?
- Mediterranean Sea and Red Sea
- Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman
- Black Sea and Aegean Sea
- Black Sea and Mediterranean Sea
Q.3) Consider the following statements about a Geneva package, recently signed by member countries of WTO
- A multilateral agreement was passed to curb harmful subsidies on illegal fishing
- Package includes temporary waiver of intellectual property patents on Covid-19 vaccines without the consent of the patent holder for 5 years
- Moratorium on custom duties on e-commerce transmissions has been extended
Choose the correct statements:
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
ANSWERS FOR 21st JUNE 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – b











