IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
- Mains – GS 3 (Environment & Ecology)
In News: World’s first fishing cat census was conducted by Chilika Development Authority (CDA) in collaboration with The Fishing Cat Project (TFCP)
- This is the world’s first population estimation of the fishing cat, which has been conducted outside the protected area network.
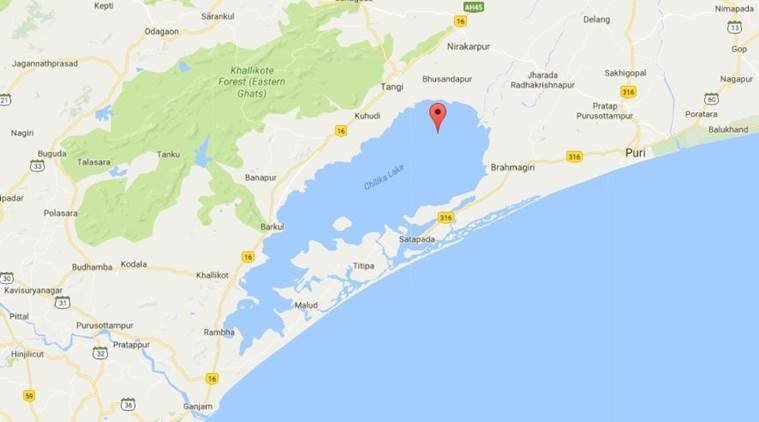
- The Chilika Lake, Asia’s largest brackish water lagoon, has 176 fishing cats
- A total of 150 camera traps were deployed in two phases with each fixed in the field for 30 days. Spatially Explicit Capture Recapture (SECR) method was used to analyse the data
Fishing Cat
- It is about twice the size of a typical house cat
- Scientific Name: Prionailurus viverrinus
- The fishing cat is an adept swimmer and enters water frequently to prey
- Habitat: Wetlands are the favorite habitats of the fishing cat. In India, fishing cats are mainly found in the mangrove forests of the Sundarbans, on the foothills of the Himalayas along the Ganga and Brahmaputra river valleys and in the Western Ghats.
- The fishing cat is nocturnal and apart from fish also preys on frogs, crustaceans, snakes, birds, and scavenges on carcasses of larger animals.
- It is capable of breeding all year round
- It is a state animal of West Bengal

Protection Status
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- CITES: Appendix II
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
Chilika Lake
- Chilika is Asia’s largest and world’s second largest lagoon.
- It is located in Odisha, India.
- In 1981, Chilika Lake was designated the first Indian wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention.
- Major attraction at Chilika is Irrawaddy dolphins which are often spotted off Satapada Island.
- The large Nalabana Island (Forest of Reeds) covering about 16 sq km in the lagoon area was declared a bird sanctuary in 1987.
- Chilika lake hosts birds migrating from thousands of miles away from the Caspian Sea, Lake Baikal, Aral Sea, remote parts of Russia, Kirghiz steppes of Mongolia etc.
Spatially explicit capture-recapture method
- SECR or SCR is used to estimate the density of an animal population from capture-recapture data collected using an array of ‘detectors’.
- Detectors may be live-capture traps, with animals uniquely marked; they also may be sticky traps or snags that passively sample hair, from which individuals are distinguished by their DNA microsatellites, microphones, or cameras that take photographs from which individuals are recognized by their natural marks
The Fishing Cat Project (TFCP)
- The Fishing Cat Project (TFCP) is the world’s longest-running research and conservation project on fishing cats and has been functional since 2010.
- It is currently functioning in two states of India – West Bengal and Odisha.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) With reference to Indian elephants, consider the following statements: (2020)
- The leader of an elephant group is a female.
- The maximum gestation period can be 22 months.
- An elephant can normally go on calving till the age of 40 years only.
- Among the States in India, the highest elephant population is in Kerala.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 3 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology)
In News: The Government of India is exploring the possibility of inviting manufacturers of Electric Vertical Takeoff and Landing (eVTOL) aircraft to set up base in India.
What is eVTOL?
- As the acronym suggests, an electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft is one that uses electric power to hover, take off, and land vertically.
- Most eVTOLs also use what is called as distributed electric propulsion technology which means integrating a complex propulsion system with the airframe.
- It has grown on account of successes in electric propulsion based on progress in motor, battery, fuel cell and electronic controller technologies
- Thus, eVTOL is one of the newer technologies and developments in the aerospace industry.
- eVTOL is being described as “a runway independent technological solution” for the globe’s transportation needs – it opens up new possibilities which aircraft with engines cannot carry out in areas such as manoeuvrability, efficiency and even from the environmental point of view.
- The global market for eVTOLs was put at $8.5 million in 2021 and is to grow to $30.8 million by 2030. The demand will be on account of green energy and noise-free aircraft, cargo carrying concepts and the need for new modes of transport.
Origin
- It all began in 2009-10 by NASA researcher Mark D. Moore who came up with the concept of a personal (one man) air vehicle “Puffin”
- In his paper, “NASA Puffin Electric Tailsitter VTOL Concept”, Moore described “electric propulsion as offering dramatic new vehicle mission capabilities, but the only penalising characteristic” being “the current energy storage technology level”.
What are the challenges?
- As the technology so far is a mix of unpiloted and piloted aircraft, the areas in focus include “crash prevention systems”.
- There are also issues such as ensuring safety in case of powerplant or rotor failure.
- Aircraft protection from cyberattacks is another area of focus.
- Operating in difficult terrain, unsafe operating environments and also bad weather are cause of concern.
Indian Scenario
The government of India has asked the market players to look into the Indian market.
Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) Taskforce for Urban Air Mobility has suggested regulatory authorities in India to look at:
- formulating regulations for pilotless vehicles, airworthiness certifications, and the need for a pilot’s licence;
- implementing efficient energy management systems, onboard sensors, collision detection systems and advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence;
- having in place infrastructural support such as take-off and landing zones, parking lots, charging stations and what are called vertiports;
- creating a robust air traffic management system that is integrated with other modes of transportation, and putting in place a database to ensure operational and mechanical safety.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) What is the purpose of ‘evolved Laser Interferometer Space Antenna’ (eLISA) project? (2017)
- To detect neutrinos
- To detect gravitational waves
- To detect the effectiveness of missile defence system
- To study the effect of solar flares on our communication systems
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment – CA
- Mains – GS 3 (Environment and Ecology)
Stats:
Heavy Toxic Metal Pollution
- Three out of every four river monitoring stations in India posted alarming levels of heavy toxic metals such as lead, iron, nickel, cadmium, arsenic, chromium and copper.
- Of the 33 monitoring stations in Ganga, 10 had high levels of contaminants.
- India has 764 river quality monitoring stations across 28 states.
- Of the 588 water quality stations monitored for pollution, total coliform and biochemical oxygen demand were high in 239 and 88 stations across 21 States – an indicator of poor wastewater treatment from industry, agriculture and domestic households.
- India dumps 72% of its sewage waste without treatment.
- Ten States do not treat their sewage at all, as per the Central Pollution Control Board.
Coastline erosion
- Over a third of India’s coastline that is spread across 6,907 km saw some degree of erosion between 1990 and 2018.
- West Bengal is the worst hit with over 60% of its shoreline under erosion.
- The reasons for coastal erosion include increase in frequency of cyclones and sea level rise and anthropogenic activities such as construction of harbours, beach mining and building of dams.
- While the global average of the Ocean Health Index, a measure that looks at how sustainably humans are exploiting ocean resources, has improved between 2012 and 2021, India’s score in the index has declined over the same period.
Forest Cover
- India’s total forest cover has registered a little over a 0.5% increase between 2017 and 2021 though most of the increase has taken place in the open forest category, which includes commercial plantations.
- This has happened at the cost of moderately dense forest, which is normally the area closest to human habitations.
- At the same time, very dense forests, which absorb maximum carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, occupy just 3% of total forest cover.
- India has a forest cover of 77.53 million hectares. But recorded forests—the area under the forest department— with forest cover are only 51.66 million. This gap of 25.87 million hectares —a size bigger than Uttar Pradesh— remains unaccounted
State of Environment Report 2022
- State of Environment Report 2022 is published by Centre for Science and Environment (CSE), an NGO
- The report is the annual publication of the CSE and Down To Earth (magazine).
- The report focuses on climate change, migration, health and food systems.
- CSE is a public interest research and advocacy organisation based in New Delhi.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science & Technology
Context: Ceramic implants can regenerate broken bones
- A bone replacement following a fracture, it is often based on a metal part.
- But metal parts are sometimes toxic over time, and will not help the original bone regrow.
- The Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) research found that, Calcium phosphate ceramics are in principle an ideal alternative to conventional metals because bone can eventually replace the ceramic and regrow.
- Calcium phosphate ceramics are substitutes for the bone mineral hydroxyapatite.
- TMDU and collaborators have studied the transformation of a ceramic into the bone mineral.
- However, applications of such ceramics in medical settings have been limited, because there is insufficient control over the rate of absorption and replacement by bone after implantation.
- The researchers have reported that most of the studied ceramics underwent chemical transformations into particulate or fibrous hydroxyapatite within a few days
- Now with specific chemical knowledge on how to tailor the rate of hydroxyapatite growth from calcium phosphate ceramics – the knowledge will be useful for bench researchers and medical practitioners to more effectively collaborate on tailoring bone reformation rates under medically relevant conditions.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) With reference to carbon nanotubes, consider the following statements: (2020)
- They can be used as carriers of drugs and antigens in the human body.
- They can be made into artificial blood capillaries for an injured part of the human body.
- They can be used in biochemical sensors.
- Carbon nanotubes are biodegradable.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 1,2,3 and 4
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Post Independence
- Mains – GS 1 (History)
Context: Recently, Telangana celebrated its 8th anniversary after becoming a separate state in 2014
Telangana rebellion
- The Telangana rebellion was started by a group of peasants in late 1945, against the prevalent jagirdari system where power to collect revenue and govern certain landholdings was installed in certain officers.
- Represented by the Comrades Association, who were affiliated with the Communist Party of India, the rebellion turned violent and clashed with the Razakars, a militia headed by Kasim Rizvi.
- In 1945 Nizam of Hyderabad put forward multiple conditions to join India — all of which were unacceptable to the Indian state
- In the meantime, Kasim Rizvi and his Razakars became increasingly dominating, difficult to ignore presence in Hyderabad.
- He influenced all major decisions the Nizam undertook and installed his chosen men in the government.
- In order to ensure that Hyderabad’s already deteriorating law and order condition did not worsen further, India signed the Standstill Agreement with Hyderabad, stating that all administrative agreements that were in place between the Nizam and the British Crown would continue between the Nizam and India.
‘Operation Polo’
- The signing of the Standstill Agreement, however, ensured peace for only about a year. Almost instantly, Hyderabad started violating the conditions, simultaneously the violent activities of the Razakars increased, creating an atmosphere of anarchy in the state.
- As a last resort, India launched ‘Operation Polo’ in September 1948 and defeated the rebel forces within five days to make Hyderabad an integral part of India.
Linguistic reorganisation
- In 1955, States Reorganization Committee recommended that Hyderabad be linguistically reorganised.
- Andhra had expressed the desire to integrate the Andhra State and Telangana in order to create Vishalandhra, however the SRC was against this.
- The Committee suggested the idea of maintaining Telangana as an separate state till 1961, where post general elections the state could voluntarily vote to integrate itself with the Andhra State.
- The government ignored this and on passing the States Reorganisation Act later that year, Andhra State and Telangana were merged into a single state called Andhra Pradesh, with Hyderabad becoming the capital.
The ‘Mulki Rules’ agitation
- Telangana region also had what were called the Mulki Rules, which were safeguards in place to ensure that Mulkis or native residents did not face difficulty in procuring government jobs.
- The rules had 4 conditions to be met in order to be classified as a Mulki. When in 1952, the Hyderabad government accepted a large number of non-Mulkis into government positions, protests broke out.
- January 1969 was a turning point as Andhra Pradesh witnessed widespread student protests over the violations of the safeguards that the Gentlemen’s Agreement signed between Telangana and Andhra State in February 1956 to allow the formation of Andhra Pradesh.
- While the government took measures to placate the population, the fire barely subsided.
Call for Telangana statehood
- In 1969, the Telangana Praja Samiti was formed to further the call for a separate Telangana state, and when protests for the same turned increasingly violent, the Andhra Pradesh High Court state declared the Mulki Rules null and void, only for the decision to be stopped by a divisional bench of the same court.
- In 1972, when the Supreme Court upheld the Mulki Rules, the Jai Andhra movement asking for a separate Andhra state picked up, causing the state to be put under President’s Rule in January 1973.
- Days prior to this in December 1972, Parliament also passed the Mulki Rules Act to limit the operation of Mulki Rules.
- In September of 1973, Indira Gandhi initiated the 32nd Amendment to the Constitution, which declared that Andhra Pradesh would be divided into 6 zones, with reservation for jobs being decided on the basis of zones. As a result of the same, the Mulki Rules Act was repealed.
The Telangana movement and KCR
- K Chandrashekhar Rao revived the movement in 2001 when he established his own political party — the Telangana Rashtra Samithi which had the singular aim of establishing a separate Telangana.
- While in 2009 the TRS’s performance at the polls was dismal, the party continued to push forward and in September that, post the death of Andhra Pradesh’s Chief Minister Y S Rajsekhara Reddy, an opportunity presented itself.
- KCR exploited the political turmoil, beginning a fast unto death and eventually the then Union Home Minister declared that Telangana would achieve statehood, separate from Andhra Pradesh.
- The state of Telangana was finally created on June 2, 2014 after years of political turmoil and repeated reassessment of state boundaries to emerge as a separate state
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology)
In News: Indian drug regulator Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) has given green signal Corbevax as a booster dose for all adults above 18 years who have received two doses of either Covishield or Covaxin as part of primary vaccination
- With the approval of Corbevax as a booster dose, India will have a heterologous shot
- India has been using the same vaccine for both primary vaccination and booster (homologous boosting).
- In clinical trials, a booster dose using a vaccine that is different from the one used for primary vaccination — technically called heterologous boosting — produced higher immune responses when compared with a same vaccine for primary and booster vaccination.
- Bio E’s phase-3 heterologous booster vaccine trial using Corbevax in people who have received two doses of either Covaxin or Covishield did produce significantly higher immune responses.
- But with the control group not receiving a homologous booster shot but only a placebo, the trial failed to bring out the enhanced immune responses by using Corbevax as a heterologous boost
- Any vaccine administered as a booster — immaterial of being homologous or heterologous — months after primary vaccination will, by default, increase the immune responses.
- The trial has thus only shown that Corbevax as a heterologous booster increases the immune responses but failed to show that heterologous boosting with this vaccine produces superior immune responses than homologous boosting with Covishield or Covaxin.
Drug Controller General of India (DCGI)
- Drugs Controller General of India is the head of department of the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization of the Government of India.
- Responsible for approval of licences of specified categories of drugs such as blood and blood products, IV fluids, vaccines, and sera in India
- DCGI also sets standards for manufacturing, sales, import, and distribution of drugs in India.
- Comes under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare
- DCGI lays down the standard and quality of manufacturing, selling, import and distribution of drugs in India.
- Acting as appellate authority in case of any dispute regarding the quality of drugs
- Preparation and maintenance of national reference standard
- To bring about the uniformity in the enforcement of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act
- Analysis of Cosmetics received as survey samples from CDSCO (central drug standard control organization)
- DCGI will also act as Central Licensing Authority (CLA) for the medical devices which fall under the purview of Medical Device Rules 2017
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
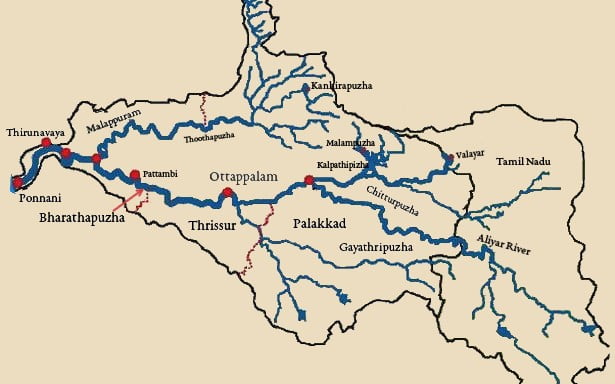
About
- Chulliyar Dam is one of the major irrigation project in palakkad
- Constructed in 1960, it is built across Chulliyar River, one of the tributaries of the river Gayathripuzha.
- Gayathripuzha is one of the main tributaries of the Bharathapuzha River, the second-longest river in Kerala, south India.
- The adjacent Nelliyampathy Mountains multiply the charm of this locality.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) Consider the following pairs (2022)
Reservoirs States
- Gataprabha Telangana
- Gandhi Sagar Madhya Pradesh
- Indira Sagar Andhra Pradesh
- Maithon Chhattisgarh
How many pairs given above are not correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations – CA
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Context: India needs to be cautious and have clarity on the U.S.-led Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity
- Recently in Quad Summit, United States announced the establishment of Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) with other partner countries
- Within days of its launch, IPEF expanded its membership to the Pacific Island states, with Fiji joining the initiative.
- At its launch, the IPEF was proposed as an elaborate framework of rules covering four pillars, namely, fair and resilient trade, supply chain resiliency, clean energy decarbonisation, and tax and anti-corruption.
Areas of Concern
On IPRs
- Under the “fair and resilient trade” pillar, the initiative aims to develop high-standard, worker-centered commitments covering labour rights, the environment and climate etc
- Notable exclusion from this list is intellectual property rights (IPRs) that have generally been at the heart of the U.S.’ economic engagements with its partner countries.
Import tariffs
- The primary objective of the IPEF is to ensure a high degree of regulatory coherence and to make market access contingent upon realisation of regulatory standards.
- The standards and regulations in most developed countries often create discriminatory barriers to trade and overcoming these barriers is usually beyond the capacities, both institutional and otherwise, of lesser developed countries.
Labour rights and the environment and climate change
- Labour rights and the environment and climate change are included in IPEF
- WTO members had arrived at a consensus that the internationally recognized core labour standards of the ILO should be used to deal with issues pertaining to labour rights.
- The UNFCCC had cautioned that measures taken to combat climate change, including unilateral ones, should not constitute a means of arbitrary or unjustifiable discrimination or a disguised restriction on international trade.
- The IPEF could threaten abrogation of these decisions at the WTO and the UNFCCC.
Data portability
- Control over data, the driver of the digital economy, will increasingly determine the dynamics of economies, and hence the issue of data portability assumes critical importance
For India to watch
- On this issue of data localisation, the Government of India has not yet taken a clear position.
- In 2019 in the Draft National e-Commerce Policy, wherein it had backed restrictions on cross-border data flows. The key challenge for India is to sustain this diametrically opposite view to an uncompromising position of the U.S. on data localisation.
- India should also be wary of emphasis that is being given to strengthening labour rights in the on-going discussions on the IPEF
Way Forward
- Establishing Common Standards: Such standards will cover labour rights, environmental standards, protection of intellectual property rights.
- Addressing Tech-related Issues: Clear framework on Data flow
- Balancing Self-Reliance and Globalisation: India has always expressed its desire to attract foreign investment and become part of global supply chains, it is time to utilize the opportunities provided under IPEF with carefully framed policies.
Source: The Hindu
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements
- In India fishing cats are found only in the states of West Bengal and Odisha
- Fishing cats are nocturnal in nature
- It is a state animal of Odisha
- It is listed as Critically Endangered in the IUCN Red list
Which of the above statements about the fishing cat is/are correct?
- 2 only
- 2 and 3
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1 and 4
Q.2) Consider the following statements
- Bone replacement by both the methods, i.e. using metal part and ceramic implants leads to regrowth of the original bone
- Calcium phosphate ceramics are substitutes for the bone mineral hydroxyapatite
Choose the correct statements:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements about Drug Controller General of India (DCGI)
- DCGI is the head of the department of the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization
- It works under the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers
- DCGI sets standards for manufacturing, sales, import, and distribution of drugs in India
Choose the correct statements:
- 1 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ‘6th JUNE 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.
ANSWERS FOR 4th JUNE 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – d













