IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
In News: Ministry of Education released National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) 2022.
About National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF)
- The NIRF was launched by the Ministry of Education in 2015.
- It is the first-ever effort by the government to rank Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) in the country.
Assessment on Five Parameters:
- Teaching, Learning and Resources (TLR)
- Research and Professional Practice (RP)
- Graduation Outcomes (GO)
- Outreach and Inclusivity (OI)
- Perception
- A total of 4,786 institutions were evaluated on five parameters.
- While participation in the NIRF was voluntary in the initial years, it was made compulsory for all government-run educational institutions in 2018.
Key Highlights
- Indian Institute of Technology Madras retains its 1st position in Overall Category for fourth consecutive year and in Engineering for seventh consecutive year.
- IIT Madras is followed by Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru, and IIT Bombay.
- Among Indian universities, IISc, Jawahar Lal Nehru University, Jamia Milia Islamia, Jadavpur University and Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham were among the top five.
- And among the top five colleges in the country are Miranda House, Hindu College, Presidency College, Loyola College and Lady Shri Ram College for Women.
- The top five medical institutes are All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, Christian Medical College, Vellore, National Institute of Mental Health & Neuro Sciences, Bangalore and Banaras Hindu University.
- The top five management institutes are Indian Institute of Management (IIM), Ahmedabad, IIM Bengaluru, IIM Kolkata, IIT Delhi and IIM Kozhikode.

Source: Pib.Gov
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which of the following brings out the ‘Consumer Price Index Number for Industrial Workers? (2015)
- The Reserve Bank of India
- The Department of Economic Affairs
- The Labour Bureau
- The Department of Personnel and Training
Syllabus
- Prelims – History
- Mains – GS 1 (History)
In News: The national memorial and museum dedicated to Mahatma Gandhi – Gandhi Smriti and Darshan Samiti’s (GSDS) has brought out a special edition of its monthly magazine dedicated to V D Savarkar.
Veer Savarkar
- Born on 28th May, 1883 in Bhagur, a village near Nashik in Maharashtra.
- He studied in Fergusson College, Pune.
- He was inspired by leaders like Bal Gangadhar Tilak, Lala Lajpat Rai and Bipin Chandra Pal. He was also influenced by the protests against the partition of Bengal and the Swadeshi movement.
- He was a staunch patriot and was attracted to radical views and movements.
Trial and Sentences:
- Arrested in 1909 on charges of plotting an armed revolt against the Morley-Minto reform (Indian Councils Act 1909)
- Arrested in 1910 for his connections with the revolutionary group India House
- One of the charges on Savarkar was abetment to murder of Nashik Collector Jackson and the second was waging a conspiracy under Indian Penal Code 121-A against the King emperor
- Following the two trials, Savarkar was convicted and sentenced to 50-years imprisonment also known as Kala Pani and transported in 1911 to the Cellular Jail in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Death: He died on 26th February 1966 due to fasting on his own wish of death.
Contribution and Works
- Founded a secret society called Abhinav Bharat Society
- Went to the United Kingdom and was involved with organizations such as India House and soon founded the Free India Society, based on the thoughts of the Italian nationalist Giuseppe Mazzini
- He was the president of Hindu Mahasabha from 1937 to 1943.
- Savarkar wrote a book titled ‘The History of the War of Indian Independence’ in which he wrote about the guerilla warfare tricks used in 1857 Sepoy Mutiny.
- He also wrote the book ‘Hindutva: who is hindu?’
Abhinav Bharat Society (Young India Society)
- It was a secret society founded by Vinayak Damodar Savarkar and his brother Ganesh Damodar Savarkar in 1904.
- Initially founded at Nasik as Mitra Mela, the society was associated with several revolutionaries and political activists with branches in various parts of India and London.
Hindu Mahasabha
- Akhil Bharat Hindu Mahasabha is one of the oldest organizations of India as it was formed in 1907.
- The Eminent personalities who founded this Organisation and who presided over the ALL INDIA Sessions held include Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya, Lal Lajpat Rai, Veer Vinayak Damodar Savarkar,
Gandhi Smriti and Darshan Samiti (GSDS)
- GSDS was formed in September 1984 by the merger of Gandhi Darshan at Rajghat and Gandhi Smriti at 5 Tees January Marg as an autonomous body.
- It functions under the constructive advice and financial support from the Ministry of Culture, Government of India.
- The Prime Minister of India is its chairperson and it has a nominated body of senior Gandhians and representatives of various government departments to guide it in its activities.
- The basic aim and objective of the Samiti are to propagate the life, mission and thought of Mahatma Gandhi through various socio-educational and cultural programmes.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Annie Besant was (2013)
- responsible for starting the Home Rule Movement.
- the founder of the Theosophical Society.
- once the President of the Indian National Congress.
Select the correct statement/statements using the codes given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science & Technology
In News: The US House of Representatives has passed by voice vote a legislative amendment that approves waiver to India against the punitive CAATSA sanctions for its purchase of the S-400 missile defence system from Russia.
- Authored and introduced by Indian-American Congressman Ro Khanna, the amendment urges the Biden administration to use its authority to provide India with a Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA) waiver to help deter aggressors like China.
- CAATSA is a tough US law that authorises the US administration to impose sanctions on countries that purchase major defence hardware from Russia in response to Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014 and its alleged meddling in the 2016 US presidential elections.
- In October 2018, India signed a USD 5 billion deal with Russia to buy five units of the S-400 air defence missile systems.
- The US has already imposed sanctions on Turkey under the CAATSA for the purchase of a batch of S-400 missile defence systems from Russia.
S-400 system
- It is an upgraded version of the S-300 surface-to-air missile system.
- The S-400 is known as Russia’s most advanced long-range surface-to-air missile defence system.
- Capable of handling multiple objects: It is capable of simultaneously tracking numerous incoming objects including aircraft, missiles and UAVs in a radius of a few hundred kilometres and launching appropriate missiles to neutralise them.
- It is capable of protecting its air defence bubble against rockets, missiles, cruise missiles and even aircraft.
- Radars: It has radars that can pick up an incoming object up to a distance of 1,000 kilometres, track several dozen incoming objects simultaneously, distribute the targets to missile systems and ensure a high success rate.

Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to the Agni-IV Missile, which of the following statement(s) is/are correct? (2014)
- It is a surface-to-surface missile.
- It is fuelled by liquid propellant only.
- It can deliver a one-tonne nuclear warhead about 7500 km away.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
In News: Defence Minister launched Y- 3023 Dunagiri, Project 17A frigate built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders Limited (GRSE) in Kolkata
- Christened after a mountain range in the state of Uttarakhand, ‘Dunagiri’ is the fourth ship of P17A Frigates.
- These are follow-on of the P17 Frigates (Shivalik Class) with improved stealth features, advanced weapons and sensors and platform management systems.
- The first two ships of P17A Project, were launched in 2019 and 2020 at MDL and GRSE respectively.
- The third ship (Udaygiri) was launched at MDL on 17 May 2022 earlier this year.
- Seven P17A Frigates are under various stages of construction at Mazagaon Dock Limited (MDL) and GRSE.

P17A Frigates
- The Nilgiri-class frigate or Project 17A is follow-on of the Project 17 Shivalik-class frigate for the Indian Navy.
- The frigates are built with extensive use of low-observability technologies, including new radar-absorbing coatings, composite materials and “faceted” shape superstructures.
- P17A ships have been designed in-house by Indian Navy’s Directorate of Naval Design (DND), which has successfully spear-headed design of numerous class of indigenous warships in the past.
Source: Pib.Gov
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which one of the following is the best description of ‘INS Astradharini’, that was in the news recently? (2016)
- Amphibious warfare ship
- Nuclear-powered submarine
- Torpedo launch and recovery vessel
- Nuclear-powered aircraft carrier
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography (Places in News)
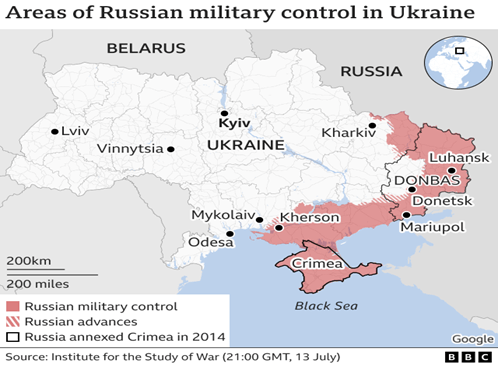
In News: Ukrainian rescue teams hunt for survivors in Vinnytsia
- Russia’s cruise missile strike recently on the Ukrainian city of Vinnytsia was directed at a building where top officials from Ukraine’s armed forces were meeting foreign arms suppliers.
- Ukraine has denied any military target was hit, saying the attack killed at least 23 people and struck a cultural centre used by retired veterans.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
In News: Assam, Arunachal CMs sign pact to resolve border dispute
- The two states signed an agreement (Namsai Declaration) to end border issues between the two states and decided to “restrict” the number of disputed villages to 86 instead of 123.
- Chief Ministers of the two North-eastern neighbours met at Namsai in Arunachal Pradesh and signed the agreement.
Background
- The two states share an 804.1 km-long border.
- The grievance of Arunachal Pradesh which was made a union territory in 1972 is that several forested tracts in the plains that had traditionally belonged to hill tribal chiefs and communities were unilaterally transferred to Assam.
- After Arunachal Pradesh achieved statehood in 1987, a tripartite committee was appointed which recommended that certain territories be transferred from Assam to Arunachal.
- Assam contested this and the matter is in the Supreme Court.
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
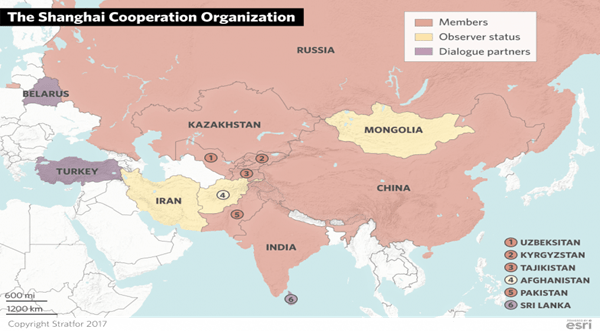
In News: Iran and Belarus are likely to be the two newest additions to the China and Russia-backed Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) grouping.
- The current SCO Secretary-General Zhang Ming, a Chinese diplomat, told the grouping hopes for an in-person summit in Samarkand, Uzbekistan.
- Expanding the group is among the issues that leaders of the grouping are likely to discuss at the SCO summit in Samarkand, Uzbekistan, in September.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
- The SCO is a permanent intergovernmental international organization.
- It’s a Eurasian political, economic and military organization aiming to maintain peace, security and stability in the region.
- It was created in 2001.
- The SCO Charter was signed in 2002, and entered into force in 2003.
- The SCO’s official languages are Russian and Chinese.
- Prior to the creation of SCO in 2001, Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and Tajikistan were members of the Shanghai Five.
- Shanghai Five (1996) emerged from a series of border demarcation and demilitarization talks which the four former Soviet republics held with China to ensure stability along the borders.
- Following the accession of Uzbekistan to the organization in 2001, the Shanghai Five was renamed the SCO.
- India and Pakistan became members in 2017.
- On 17th September, 2021, it was announced that Iran would become a full member of the SCO.
Objectives:
- Strengthening mutual trust and neighborliness among the member states
- Promoting effective cooperation in -politics, trade & economy, research & technology and culture.
- Enhancing ties in education, energy, transport, tourism, environmental protection, etc.
- Maintain and ensure peace, security and stability in the region.
- Establishment of a democratic, fair and rational new international political & economic order
Structure:
- Heads of State Council – The supreme SCO body which decides its internal functioning and its interaction with other States & international organisations, and considers international issues.
- Heads of Government Council – Approves the budget, considers and decides upon issues related to economic spheres of interaction within SCO.
- Council of Ministers of Foreign Affairs – Considers issues related to day-to-day activities.
- Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) – Established to combat terrorism, separatism and extremism.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2016)
- New Development Bank has been set up by APEC.
- The headquarters of New Development Bank is in Shanghai.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy – Growth & Development)
In News: Indian rupee recorded a historic low of 79.72 against the US dollar and it has declined nearly 6 per cent since January this year.
- Foreign exchange reserves fell by $8.06 billion to $580.02 billion during the week ended July 8 in the wake of the appreciation of the dollar and capital outflows from India, triggered by the rise in inflation and rate hikes by the US.
Why rupee is falling?
Demand and supply:
- If a country imports more than it exports, then the demand for the dollar will be higher than the supply and due to this, domestic currency will depreciate against the dollar.
Russia-Ukraine war:
- Global disruptions caused by the Russia-Ukraine war is making our imports costly, thus widening the current account deficit.
Rising inflation:
- Rising inflation depreciates domestic currency since inflation can be equated with a decrease in money’s buying power.
- As a result, countries experiencing high inflation tend to also see their currencies weaken relative to other currencies.
High crude oil prices:
- Increasing crude oil prices are further widening our trade deficit thus leading to decrease in the value of rupee.
Capital outflows from India:
- The US Federal Reserve recently increased the interest rates, and the return on dollar assets increased compared with those of emerging markets such as India.
- It has led to outflow of dollars from India to the US.
Impact
Increase cost of raw materials and imports
- Since, India imports many raw materials, the price of finished goods could go up thus impacting the consumers.
- India’s high import dependence for fuel means oil price trajectories affect most macro parameters, including inflation, growth, current account balances, fiscal management and the rupee.
- This leads to widening of the current account deficit (CAD).
Boosts exports:
- In an ideal scenario, devalued rupee could have led to increase in exports.
- However, in the current scenario of weak global demand and persistent volatility, exporters are not supportive of the currency fall.
Inflation:
- The falling rupee’s biggest impact is on inflation, given India imports over 80 per cent of its crude oil, which is the country’s biggest import.
- Travellers and students studying abroad will have to shell out more rupees to buy dollars from banks.
Stock market:
- Rupee depreciation may see foreign investors pulling out of Indian markets, resulting in a decline in stocks and equity mutual fund investments.
Floating exchange rate system
- Under the floating exchange rate regime, the market forces determine the value of domestic currency on the basis of the forces of demand and supply of the domestic currency.
Appreciation Vs Depreciation
Appreciation
- Currency Appreciation: It is an increase in the value of one currency in relation to another currency.
- Currencies appreciate against each other for a variety of reasons, including government policy, interest rates, trade balances and business cycles.
- Currency appreciation discourages a country’s export activity as its products and services become costlier to buy.
Depreciation Vs Devaluation:
- Currency depreciation is a fall in the value of a currency in a floating exchange rate system.
- Currency depreciation can occur due to factors such as economic fundamentals, interest rate differentials, political instability or risk aversion among investors.
- If the value of the Indian Rupee is weakened through administrative action, it is devaluation.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which one of the following is not the most likely measure the Government/RBI takes to stop the slide of Indian rupee? (2019)
- Curbing imports of non-essential goods and promoting exports
- Encouraging Indian borrowers to issue rupee denominated Masala Bonds
- Easing conditions relating to external commercial borrowing
- Following an expansionary monetary policy
Q.2) Consider the following statements:
The effect of devaluation of a currency is that it necessarily
- improves the competitiveness of the domestic exports in the foreign markets
- increases the foreign value of domestic currency
- improves the trade balance
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
- 2 and 3
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements about National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF)
- National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) is published by Ministry of Education
- Institutions are assessed based on the five parameters
- In NIRF 2022 by Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru secured 1st position in Overall Category
Choose the correct statements:
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 1 only
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Veer Savarkar
- He founded a secret society called Abhinav Bharat Society
- He was the president of Hindu Mahasabha from 1937 to 1943
- He wrote a book titled The History of the War of Indian Independence
Choose the incorrect statements:
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 2 only
- None
Q.3) Which of the following measures to be taken by RBI or Government of India to stop the depreciation of Indian rupee?
- Relaxing conditions relating to external commercial borrowing
- Steps to cut non-essential imports and increase exports
- Encouraging Indian borrowers to issue rupee denominated Masala Bonds
Choose the correct statements:
- 1 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2 only
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’16th JULY 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.
ANSWERS FOR 15th JULY 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – a











