IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science & Tech
In News:
- Ethereum has undergone a technical upgrade and this upgrade is called the ‘Merge’.
- Ethereum has changed its algorithm from the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus method of setting transactions to the Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
- Ethereum is introducing a new programming language that will help developers build more robust decentralised applications.
About:
- PoW algorithms are used in most blockchains. PoW is a system of distributed consensus that relies on computing power to prove that someone has put in the required amount of work to create a valid block proportional to their influence on the network. These algorithms create a trust less system e., trust the system and not one person or one organization.
- PoS is a type of consensus mechanism used to validate cryptocurrency transactions through randomly selected validators. With this system, owners of the cryptocurrency can stake their coins, which gives them the right to check new blocks of transactions and add them to the blockchain. This is known as concept of staking.
Significance of the upgrade:
- Increased scalability: Decreased size of blocks will reduce amount of data that nodes need to process making the network more scalable and easier to process more transactions per second while maintaining the same level of security.
- Easy to store: Make it easier for people running nodes to store the blockchain on less expensive hardware. That will make the network more resistant to spam attacks
- Reduce the amount of energy required to secure the network will make it more environmentally friendly and attract more users.
- Concept of staking: meaning locking up your tokens like depositing money in a savings account. The more tokens you stake, the more influence you have over the network.
- Faster transaction times due to less gap between blocks
- Low transaction latency
- No need for hardware mining infrastructure: due to trust less, distributed consensus algorithm that doesn’t require costly hardware.
About Ethereum:
- Launched in 2014 second-largest cryptocurrency in the world
- Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain. Ether is the native cryptocurrency of the platform.
- Ethereum was conceived in 2013 by programmer Vitalik Buterin.
- Ethereum today has the highest adoption among developers and it is the primary infrastructure layer of Web3.
Way forward
- The need of the hour is to work on an indigenous solution of the people, for the people, and by the people.
- A digital infrastructure based on blockchain technology will transform the digital ecosystem in India, and will enable the future of digital services, platforms, applications, content, and solutions.
- Considering the current situation worldwide, one can safely assume that we are at the beginning of the curve, but the days are not far.
MUST READ: India Blockchain Platform
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to Web 3.0, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Web 3.0 technology enables people to control their own data.
- In Web 3.0 world, there can be blockchain based social networks.
- Web 3.0 is operated by users collectively rather than a corporation
Which of the following given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q2) With reference to “Blockchain Technology”, consider the following statements: (2020)
- It is a public ledger that everyone can inspect, but which no single user controls.
- The structure and design of blockchain is such that all the data in it are about cryptocurrency only.
- Applications that depend on basic features of blockchain can be developed without anybody’s permission.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science & Tech
In News: Malaria booster vaccine shows up to 80 per cent efficacy: Lancet study
About the vaccine:
- R21/Matrix-M malaria vaccine is licensed to Serum Institute of India.
- In 2021, University of Oxford reported findings – the vaccine demonstrated efficacy of 77% over 12-months of follow-up.
- This vaccine is the first to meet the World Health Organization’s Malaria Vaccine Technology Roadmap goal of a vaccine with at least 75% efficacy
- Study involved 450 participants aged 5 to 17 months and recently reported an efficacy of over 80%.
About Malaria:
- Mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals
- Caused by single-celled microorganisms of the Plasmodium group and spread exclusively through bites of infected Anopheles mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito’s saliva into a person’s blood.
- Symptoms include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
- The disease is widespread in the tropical and subtropical regions that exist in a broad band around the equator.
- Distribution of malaria in India is as follows:
Way forward:
The results hold out hope that the vaccine can be an effective weapon in the fight against malaria, which is one of the biggest killers of children globally.
Source: Indian express
Syllabus
- Prelims: International Groupings
Context: On September 15, two years ago, Israel, the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain signed the United States-brokered Abraham Accords. It was a historic moment for our peoples and nations, fostering new hope for peace and prosperity in the Middle East.

Key points:
- It brought exciting opportunities for India and its thriving business community, which enjoys strong relations and engagement with our countries.
- New joint ventures among Bahrain, Israel, UAE, and India are being undertaken in critical sectors such as clean energy, health, innovation, technology, agriculture, water, trade, tourism, and sustainability.
- The Accords have paved the way for greater regional and multinational cooperation.
- Expanding economic opportunities continue to reach India.
- One concrete example of high-level economic cooperation between our governments is the formation of the I2U2 Group, established by Israel, India, the UAE, and the United States.
About I2U2 Group:
Background:
- I2U2 was initially formed in October, 2021 following the Abraham Accords between Israel and the UAE, to deal with issues concerning maritime security, infrastructure, and transport in the region.
- At that time, it was called the ‘International Forum for Economic Cooperation’.
- That was referred as the ‘West Asian Quad’.
About:
- I2U2 initiative is a new grouping of India, Israel, USA, and UAE.
- In the grouping’s name, ‘I2’ stands for India and Israel, whereas ‘U2’ stands for USA and the UAE.
What will be the Significance of I2U2 for India?
- Advantage from Abraham Accords:
- India will get advantage of the Abraham Accords to deepen engagement with Israel without risking its ties with the UAE and the other Arab states.
- Benefit Market:
- India is a massive consumer market. It’s a massive producer of high-tech and highly sought-after goods as well. India will benefit from this grouping.
- Alliances:
- It will help India in building alliances — political alliances, social alliances.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
- Argentina, Mexico, South Africa, and Turkey
- Australia, Canada, Malaysia, and New Zealand
- Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and Vietnam
- Indonesia, Japan, Singapore, and South Korea
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
In news: On September 16, a modified passenger B-747 Jumbo Jet will take off from Namibia for Jaipur to transport eight Namibian wild cheetahs, five females and three males, the founders of a new population in Kuno National Park, Madhya Pradesh.
Moving wild animals to new locations for conservation began only in the 1960s.
Unlike royal imports to be held in captivity, these animals require to settle down and survive in their new locations in the wild. That poses a host of different challenges.
About IUCN guidelines:
- Genetic diversity: Absence of the same can lead to inbreeding depression in the new population.
- Habitat and prey base: Physical security, enough space, and ample food so that colonies of reintroduced animals become large enough as quickly as possible to withstand fluctuations in both the environment and population size.
- Landscape viability: animals will remain susceptible to demographic and environmental events in a landscape
- Curbing the cats’ homing instincts: risks from losing the released animal from the target site and human-animal conflict
About Kuno National Park, Madhya Pradesh:
- Established in 1981 as a wildlife sanctuary in the Sheopur and Morena districts.
- In 2018, it was given the status of a national park. It is part of the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forests ecoregion.
- Area of 344.686 km2
- Fauna: Indian leopard, jungle cat, sloth bear, dhole, Indian wolf, golden jackal, striped hyena, and Bengal fox, chital, Sambar deer, nilgai, four-horned antelope, chinkara, blackbuck and wild boar
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following: (2012)
- Black-necked crane
- Cheetah
- Flying squirrel
- Snow leopard
Which of the above are naturally found in India?
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity and Constitution
- Mains – GS 2 (Polity and Constitution)
Context:
- The recently concluded monsoon session of Parliament (July-August), saw the Competition (Amendment) Bill, 2022 and the Electricity (Amendment) Bill, 2022 being sent to the Standing Committee of Parliament for detailed examination in the wake of constant criticism by the Opposition in previous sessions.
In this context let us understand the meaning and roles of parliamentary committees.
What are Parliamentary committees?
- The Parliamentary committees are established to study and deal with various matters that cannot be directly handled by the legislature due to their volume.
- They monitor the functioning of the executive branch and provide legislature with various policy input, playing an important role in Indian democracy.
- They act as ‘Mini-Parliament’: smaller units of MPs from both Houses, across political parties, that function throughout the year.
Types of Parliamentary committees—Standing Committees and Ad Hoc Committees.
- Standing Committees : Permanent (constituted every year or periodically) and work on a continuous basis. They can be categorized into following broad groups
- Financial Committees
- Departmental Standing Committees (24)
- Committees to Inquire
- Committees to Scrutinise and Control
- Committees Relating to the Day-to-Day Business of the House
- House-Keeping Committees or Service Committees
- Ad Hoc Committees: Temporary and cease to exist on completion of the task assigned.
- Ad hoc committees can be divided into two categories, that is, Inquiry Committee and Advisory Committee.
Departmental Standing Committees (DSCs) of Parliament in detail:
- Departmental Standing Committees are where a proposed law is discussed in detail.
- Parliament has 24 Department Related Parliamentary Standing Committees (DRSC), comprising members of the Parliament of both the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha in the ratio 2:1, which are duly constituted by the Speaker of the Lok Sabha and the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, jointly.
Role of Standing Committees :
- Main role of the department-related standing committees is to ensure the accountability of government to the Parliament through more detailed consideration of measures in these committees, its intention is not to weaken or criticize the administration or government but to strengthen it by investing in it more Parliamentary support.
- Hence the main role of departmental standing committees is to secure more accountability of the executives i.e., the Council of Ministers to the Parliament.
- These Departmental standing committees are working particularly while scrutinizing the Budget.
Standing Committees – Members:
- Each committee consists of 31 members, of which 21 are nominated by the Speaker of Lok Sabha from amongst its members and 10 are nominated by the Chairman of Rajya Sabha from amongst its members. The tenure of each of the members is for 1 year.
- A minister cannot hold the committee’s membership. If a member after assuming his membership becomes a minister, he ceases to be a member of the respective committee.
Relevant parliamentary data on the working of Parliament and its committees:
- The functioning of the monsoon session of Parliament this year bears testimony to this fact: the Lok Sabha’s productivity was 47% and the Rajya Sabha only 42%.
- The percentage of Bills having been referred to the DRSCs during the tenures of the 14th (2004-2009), 15th (2009-2014) and 16th Lok Sabha (2014-2019) has been 60%, 71% and 27%, respectively.
Difference between Committee versus Parliament
- It has been alleged that Bills which are not being referred to the parliamentary committees, are not examined properly.
- As proof of this, the case of the three Farm Bills is cited as they were passed without being referred to the DRSC and had to be withdrawn later.
- The examination of the Bills by the parliamentary committees is more to the benefit of the Government than the Opposition.
- The committee meetings are in camera and, therefore, the meetings are held in a comparatively congenial atmosphere of bonhomie and cordiality than they would be in Parliament.
Way forward:
It has been observed that the reluctance to refer the Bills to the committee arises more out of inaction and ignorance of the Ministry concerned, and rarely out of ideological or policy reasons. So, the following changes could be suggested to be made into procedures meant for consideration of Bills.
- The Speaker of the Lok Sabha and the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha have powers to refer Bills to a DRSC of Parliament. Make this a compulsory/ automatic requirement.
- All discussions in the Parliamentary Standing Committee should be frank and free.
- For this, it may be provided that during the discussions of the committee meetings, no whip of the party would apply to them. In any case, they have the liberty to vote in favour or against the Bill in Parliament.
- The Speaker/Chairman should have the right to fix a time limit, sometimes even stringent, if the government of the day asks for it and the demand is found to be reasonable by the Speaker/Chairman.
- But to deal with just political exigencies, it can be provided that in case the committee fails to give its recommendation within the approved/extended time, the Bill may be put up before the House concerned directly.
- To ensure quality work in the committees, experts in the field may be invited who could bring with them the necessary domain knowledge and also help introduce the latest developments and trends in that field from worldwide.
The sanctity and good work of ‘mini-Parliaments’ must be continued by both the government and the opposition, which will strengthen Parliamentary democracy.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
- Mains – GS 2 ( International Relations)
Context: Recently, India’s Defence Minister “conveyed concerns” to his American counterpart on the US decision to provide Pakistan with a $450 million package for what the Pentagon has called the “F-16 Case for sustainment and related equipment.”
About the package to Pakistan:
- US released it Defense Security Co-operation Agency press release which announced $450 million package, the proposed contractor for technical and logistics services for follow-on support of Pakistan’s F-16 fleet.
- Under this, there is participation in several technical coordination groups, aircraft and engine hardware and software modifications and support, equipment support, manuals, precision measurement, and a range of related elements of aircraft maintenance.
However, USA clarified that “The proposed sale does not include any new capabilities, weapons, or munitions,”
- It will support the foreign policy and national security objectives of the United States by allowing Pakistan to retain interoperability with US and partner forces in ongoing counter-terrorism efforts and in preparation for future contingency operations” .
Why this deal now?
- one revolves around the killing of Ayman al-Zawahiri in Kabul, Questions have swirled, including in Afghanistan and Pakistan, as to who provided the intelligence for the drone strike that killed the al-Qaeda chief in a posh house that belonged to Interior Minister Sirajuddin Haqqani. So, it is considered as reward for providing the information.
- Earlier, Pakistan Army chief Gen Qamar Javed Bajwa and ISI head Lt Gen Nadeem Anjum have been in active touch with their US interlocutors. Anjum visited the US in May, and Bajwa reportedly asked for help secure an IMF package for Pakistan, which has been granted.
- Another reason could be the geopolitical churn arising from the Russia-Ukraine war, the US is trying to break China’s hold on Pakistan with sweeteners of its own.
- The Pakistan Air Force now has more Chinese JF-17 Thunder fighter jets than F-16s — but it continues to rely on the ageing American aircraft, as the India-Pakistan 2019 skirmish demonstrated.
India, Pak, the aircraft
- According to Brig. Rahul Bhonsle (retd), the sustainment programme for Pakistan’s F-16 fleet would enhance conventional deterrence versus India.
- He says that the last aerial skirmish between Pakistan and India in February 2019 — during which the PAF brought down a MiG-21 flown by IAF pilot Abhinandan Varthaman — showed that the F-16 is the aircraft that Pakistan will use in any future encounter with India.
Conclusion:
- India-U.S. bilateral relations holds “global strategic partnership“, which is based on shared democratic values and increasing convergence of interests on bilateral, regional, and global issues.
- Both are member of Global platform which has strategical importance such as Quad and I2U2 Grouping (India, Israel, the United Arab Emirates, and the United States) And, such incident is not going to strain relation between two nations, even it is expected to strengthen technological and industrial collaboration and also explore co-operation in emerging and critical technologies between two nations in upcoming time.
- However, India needs to effectively enhance conventional combat capability of the IAF to continue to meet the challenge of a resurgent PAF.
About F-16 Fighting Falcon:
- The F-16 Fighting Falcon is a compact, single engine, 4th generation, multi-role fighter aircraft developed by General Dynamics Corporation, USA.
- It is highly manoeuvrable and has proven itself in air-to-air combat and air-to-surface attack. It provides a relatively low-cost, high-performance weapon system for the United States and allied nations.

Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) What is “Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD)”, sometimes seen in the news ? (2018)
- An Israeli radar system
- India’s indigenous anti-missile programme
- An American anti-missile system
- A defence collaboration between Japan and South Korea
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Federalism)
“Once is happenstance. Twice is coincidence. Three times is enemy action,” Ian Fleming famously wrote in the James Bond classic Goldfinger. Change the words “enemy action” to “trend” and it will explain what’s going on between Maharashtra and Gujarat.
Context: Maharashtra’s repeated loss of projects to Gujarat appears to indicate Centre’s preference, damage to federal structure including recently concluded Vedanta – Foxconn project.
- Earlier the projects such as International Financial Services Centre (IFSC), Nanar oil refinery, a joint venture between India’s state-owned PSUs and Saudi Arabia’s Aramco, and the National Academy of Coastal Policing are proposed to set up in Maharashtra but later moved to Gujrat.
This, as the legendary Fleming notes, is enough to underline a trend that seriously undermines our federal structure. It’s always heartening to see states vying for investments, but it’s equally damaging to see the powerful Centre favouring one state over the other.
It not only makes the battle unfair, but also threatens the federal fabric of the nation. However, Maharashtra politicians undoubtedly owe explanations for their consistent flip-flop over mega projects, beginning with Enron’s ambitious power project.
In this context let us understand Federal structure of India:
The Federal Structure of India:
- Nature of Indian Federalism: A Federal theorist K.C. Wheare has argued that the nature of Indian Constitution is quasi-federal in nature.
- The SC in Sat Pal v State of Punjab and Ors (1969), held that the Constitution of India is more Quasi-federal than federal or unitary.
- Constitutional Provisions for Ensuring Federalism: The respective legislative powers of states and Centre are traceable to Articles 245 to 254 of the Indian Constitution.
- The lists in the 7th Schedule of the Constitution — Union, State and Concurrent also exemplify equitable share of powers, wherein each level of government has its own sphere, enabling context-sensitive decision-making.
- Article 263 provided for the establishment of an Inter-State Council for smooth transition of business between the Union and states and resolution of disputes.
- Article 280 provided for the constitution of the Finance Commission to define the financial relationship and terms between the Union and states.
- Also, the institutions for local self-government were added through the 73rd and 74th amendments, to strengthen the grass roots democracy.
- Institutions for Federalism: The Planning Commission always had space for discussion on issues concerning the federal nature of the polity and was sensitive to the different developmental requirements of states.
- The inter-state tribunals, the National Development Council and other informal bodies have served as vehicles of consultations between the Union, states and UTs.
- These bodies have been instrumental in tackling difficult issues democratically through deliberations while upholding the cooperative spirit between the Union and states.
Challenges in Maintaining the Federal Spirit of India
Apart from above mentioned tussle between Gujrat and Maharashtra, the following are the major challenges to cooperative federalism in India.
- Ineffective Functioning of Several Bodies: The Planning Commission has been scrapped; the Inter-State Council has met only once in the last seven years while the National Development Council has not met at all.
- Issues in Tax Regime: The misconceived Goods & Services Tax (GST) has already taken away much of the autonomy available to states and has made the country’s indirect tax regime unitary in nature.
- During the pandemic, the Union government repeatedly violated the compensation guarantees to the States under the GST regime. Delay in paying the States their due worsened the impact of the economic slowdown.
- Encroachments Upon States’ Autonomy in State Subjects: Many important and politically sensitive decisions have been taken in the past few years, without reference to, and consultation with, the concerned states such as:
- Parliament legislated on “agriculture” in the state list, to enact the three contentious farm laws, overstepping its jurisdiction and imposing a law on the states.
- The New Education Policy 2020 has also been flagged as encroaching on the federal nature of the polity.
- Additionally, the BSF’s jurisdiction was extended in Assam, West Bengal, and Punjab without any consultation with the concerned states.
- Impact of Covid-19: The states were curtailed in aspects relating to Covid-19 management such as procurement of testing kits, vaccination, the use of the Disaster Management Act, 2005, and the unplanned national lockdown.
Way Forward:
- Recognition of Federalism: It should be underlined that Article 1 of the Constitution declares that “India that is Bharat is a union of states”, and that devolution of powers is necessary in such a setting.
- A conscious recognition of the federal character of India’s polity is essential to protect its national character.
- Strengthening Inter-State Relations: State governments shall consider deploying human resources to support them in preparing responses to the consultations initiated by the Union, especially with a focus on the federalism angle.
- Bringing Reforms while Balancing Federalism: A diverse country India requires a proper balance between the pillars of federalism (autonomy of states, centralisation, regionalisation etc).
- Extreme political centralisation or chaotic political decentralisation shall be avoided as both lead to the weakening of Indian federalism.
MUST READ: Uncooperative Federalism
MUST READ: Asymmetrical federalism
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains: GS 2 (International Relations)
In News: Russia hosted the seventh Eastern Economic Forum (EEF) Vladivostok from September 5 to 8. The four-day forum is a platform for entrepreneurs to expand their businesses into Russia’s Far East (RFE).
About RFE:
- The region encompasses one-third of Russia’s territory and is rich with natural resources such as fish, oil, natural gas, wood, diamonds, and other minerals.
- The region’s riches and resources contribute to five per cent of Russia’s GDP. But despite the abundance and availability of materials, procuring and supplying them is an issue due to the unavailability of personnel.
About EEF:
- The Eastern Economic Forum was established in 2015 to encourage foreign investments in Russia’s the Far East.
- As an annual gathering, EEF displays the economic potential, suitable business conditions and investment opportunities in the region.
- As of 2022, almost 2,729 investment projects are being planned in the region with a focus on infrastructure, transportation projects, mineral excavations, construction, industry, and agriculture.
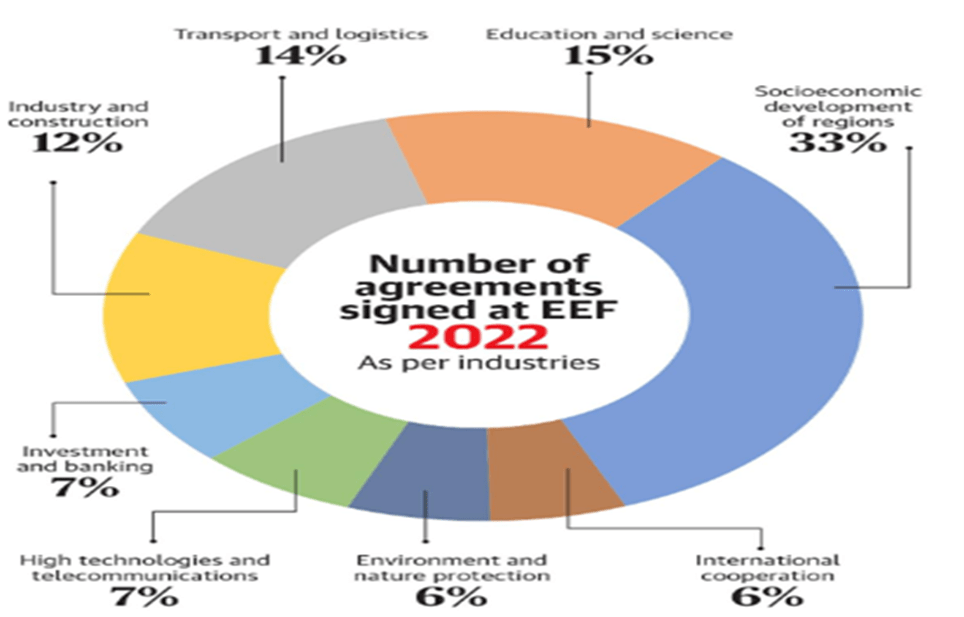
Trading partners:
- Russia and China: This year, the Forum aimed at connecting the Far East with the Asia Pacific region. The two countries share a 4000-kilometer-long border, which enables them to tap into each other’s resources with some infrastructural assistance. China is the biggest investor in the region (90% of total investments) in light of promoting the Chinese Belt and Road Initiative and the Polar Sea Route in the RFE. The Trans-Siberian Railway, supply of natural gas and a rail bridge has further helped Russia and China in advancing trade ties.
- Russia and South Korea: has invested in shipbuilding projects, manufacturing of electrical equipment, gas-liquefying plants, agricultural production, and fisheries including intention to inject $2 billion in the RFE in a span of three years.
- Russia and Japan: Japan depends on Russian oil and gas resources also sees a market for its agro-technologies. In 2017, Japanese investments through 21 projects amounted to $16 billion. Japan identified eight areas of economic cooperation and pushed private businesses to invest in the development of the RFE. Challenge of Kuril Islands dispute exists between both countries.
- Russia and India: Prime Minister expressed the country’s readiness in expanding trade, connectivity, cooperation, and investments in Russia especially in energy, pharmaceuticals, maritime connectivity, healthcare, tourism, the diamond industry, and the Arctic.
- In 2019, India also offered a $1 billion line of credit to develop infrastructure in the region. Through the EEF, India aims to establish a strong inter-state interaction with Russia. Business representatives of Gujarat and the Republic of Sakha have launched agreements in the diamond and pharmaceuticals industry.
What does the EEF aim for?
- The primary objective of the EEF is to increase the Foreign Direct Investments (FDI) in the RFE.
- The region encompasses one-third of Russia’s territory and is rich with natural resources such as fish, oil, natural gas, wood, diamonds, and other minerals.
- The sparse population living in the region is another factor for encouraging people to move and work in the Far East.
- The region’s riches and resources contribute to 5% of Russia’s GDP. But despite the abundance and availability of materials, procuring and supplying them is an issue due to the unavailability of personnel.
- The RFE is geographically placed at a strategic location; acting as a gateway into Asia. The Russian government has strategically developed the region with the aim of connecting Russia to the Asian trading routes.
- The Ukraine invasion is a worrying issue as it affects the economic growth of the country. However, Russia believes that it can survive the economic crisis and the sanctions with the help of China and other Asian powers.
- The coming together of countries like Myanmar, Armenia, Russia, and China seems like the forming of an anti-sanctions group in the international order.
Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF):
Will India be able to achieve a balance between the EEF and the IPEF?
- The U.S.-led Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) and the EEF are incomparable based on its geographic coverage and the partnership with the host-countries. India has vested interests in both the forums and has worked towards balancing its involvement.
- India has not shied away from investing in the Russia-initiated EEF despite the current international conditions.
- At the same time, India has given its confirmation and acceptance to three of the four pillars in the IPEF.
- IPEF also presents an ideal opportunity for India to act in the region, without being part of the China-led Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) or other regional grouping like the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP).
- The IPEF will also play a key role in building resilient supply chains. India’s participation in the forum will help in disengaging from supply chains that are dependent on China and will also make it a part of the global supply chain network.
- Additionally, the IPEF partners will act as new sources of raw material and other essential products, further reducing India’s reliance on China for raw materials.
- India, Japan, and Australia last year also launched the Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI), a trilateral initiative of countries in the Indo-Pacific (IP) region to create a virtuous cycle of enhancing supply chain resilience with a view to eventually attaining strong, sustainable, balanced, and inclusive growth in the region.
Way forward:
- India has vested interests in both the EEF and the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) and has worked towards balancing its involvement.
- India should also balance its membership of multiple regional and global fora like IPEF, EEF, SCRI, QUAD etc, encompassing economic and strategic interests, in pursuit of its new policy of ‘multi-alignment’.
Source: The Hindu
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) With reference to the ” Eastern Economic Forum “, consider the following statements:
- It is an initiative endorsed by the G20 together with Russia.
- It is an initiative to support Low Income Eastern Economies in the field of infrastructure.
- It primarily focuses on the Far Eastern region of Russia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- 3 only
Q.2) Which of the following nations parks are located in Madhya Pradesh?
- Kuno National Park
- Kanha National Park
- Pench National Park
- Tadoba-Andhari National Park
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.3) R21/Matrix-M vaccine, which is recently in news, is related to
- Dengue
- Malaria
- Tuberculosis
- Hepatitis B
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’16th September 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.
ANSWERS FOR 15th September – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – b











