IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography; International Relations
In News: The global attention on the war in Ukraine has remained nervously focused on Zaporizhzhia, an important town in the country’s southeast that houses the largest nuclear power plant in Europe.
- A team of officials from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) arrived in Ukraine to assess the condition of the plant,
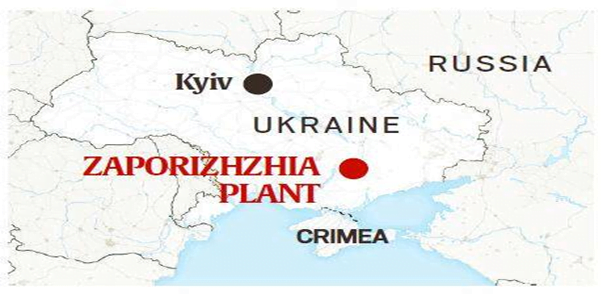
About: Zaporizhzhia power plant
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
- Widely known as the world’s “Atoms for Peace and Development” organization within the United Nations family, the IAEA is the international centre for cooperation in the nuclear field.
- The IAEA was created in 1957 in response to the deep fears and expectations generated by the discoveries and diverse uses of nuclear technology.
- Headquarter: Vienna, Austria.
Objectives and Functions
- The Agency works with its Member States and multiple partners worldwide to promote safe, secure and peaceful use of nuclear technologies.
- IAEA seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons.
- It reports annually to the United Nation General Assembly.
- When necessary, the IAEA also reports to the UN Security Council in regards to instances of members’ non-compliance with safeguards and security obligations.
- In 2005, it was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for their work for a safe and peaceful world.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) In the Indian context, what is the implication of ratifying the ‘Additional Protocol’ with the ‘International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)’? (2018)
- The civilian nuclear reactors come under IAEA safeguards.
- The military nuclear installations come under the inspection of IAEA.
- The country will have the privilege to buy uranium from the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG).
- The country automatically becomes a member of the NSG.
Q.2) In India, why are some nuclear reactors kept under “IAEA Safeguards” while others are not? (2020)
- Some use Uranium and others use thorium.
- Some use imported uranium and others use domestic supplies.
- Some are operated by foreign enterprises and others are operated by domestic enterprises.
- Some are State- owned and others are privately-owned.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science & Technology
In News: Sonali Phogat (Actor and a Politician) who was recently killed by giving the recreational drug methamphetamine on the eve of her death.
- She died after a heart attack caused by an overdose of methamphetamine.
The stimulant drug
- Methamphetamine — meth for short — is a powerful, highly addictive stimulant that affects the central nervous system, and is used to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy, a sleep disorder.
- Crystal methamphetamine or crystal meth is a form of the drug that looks like glass fragments or shiny, bluish-white rocks.

- It is chemically similar to amphetamine.
- Methamphetamine can be smoked, swallowed in the form of a pill or tablet, snorted, and injected after dissolving the powder in water or alcohol.
- Methamphetamine can lead to myocardial infarction (heart attack); it can cause stroke.
- The drug can affect the heart, the brain, and the kidneys. It can result in the blood pressure shooting up suddenly. So, it is a very dangerous drug if there is an overdose.
Effect on the brain
- Meth raises the amount of dopamine in the brain.
- Dopamine, a natural chemical, plays a role in body movement, motivation, and reinforcement of rewarding behaviours.
- The ability of the drug to rapidly release high levels of dopamine in reward areas of the brain strongly reinforces drug-taking behaviour, making the user want to repeat the experience.
Role in heart attack
- Methamphetamine on its own might not cause the heart attack but it can result in a cardiac arrest if consumed in an excess quantity.
- The recreational drug can lead to over sedation, which can affect the organs, including the heart.
- It affects the cardiovascular system by triggering blood vessel spasms and life-threatening spikes in blood pressure.
- It can also increase plaque in the arteries and rewire the heart’s electrical system.
- It leads to narrowing and spasms in the blood vessels, rapid heart rate (tachycardia), high blood pressure, and death of cardiac muscles.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Triclosan considered harmful when exposed to high levels for a long time, is most likely present in which of the following? (2021)
- Food preservatives
- Fruit-ripening substances
- Reused plastic containers
- Toiletries
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
Context: Prime Minister of India will unveil the new naval ensign (flag) for the Indian Navy

Details:
- The new naval ensign will replace the present ensign that carries the Saint George’s Cross with the Tricolour in the canton (top left corner of flag).
- This ensign is essentially a successor to the pre-Independence ensign of the Indian Navy which had the red George’s Cross on a white background with the Union Jack of the United Kingdom on the top left corner.
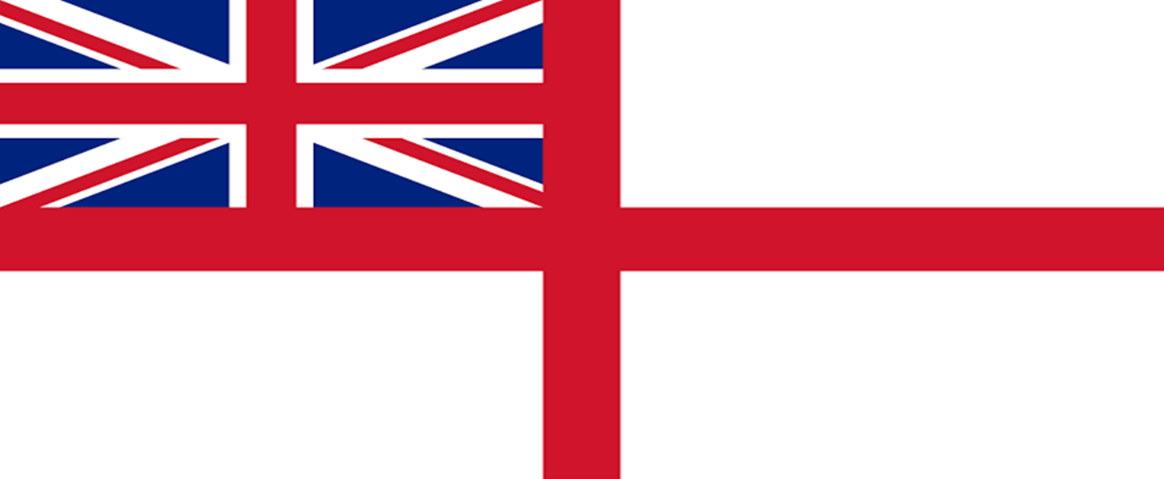

- After Independence, on August 15, 1947, the Indian defence forces continued with the British colonial flags and badges and it was only on Jan 26, 1950 that a changeover to Indianised pattern was made.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
In News: The Union Social Justice Ministry has so far received 402 online applications from across the country to avail benefits under SEED, a scheme meant for the upliftment of Denotified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Tribes (DNTs/NTs/SNTs).
Who are Denotified Nomadic Tribes (DNTs):
- DNTs are the tribes which were notified as criminal tribes under Criminal Tribes Act, 1871, by the British colonial government.
- Under this Act, millions of nomadic and semi-nomadic communities were declared criminals and put under continuous surveillance.
- After decades of facing horrors of this racial Act, they were denotified by the Government of independent India on August 31, 1952.
- While most DNTs are spread across the Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST) and Other Backward Classes (OBC) categories, some DNTs are not covered in any of the SC, ST or OBC categories.
- The DNTs are a heterogenous group engaged in various occupations such as transport, key-making, salt trading, entertaining — acrobats, dancers, snake charmers, jugglers — and pastoralists.
Difference between Nomadic, Semi-nomadic and DNTs:
- The nomadic tribes maintain constant geographical mobility while semi-nomads are those who are on the move but return to fixed habitations once a year, mainly for occupational reasons.
- All nomadic tribes are not DNTs, but all DNTs are nomadic tribes.
- There are nearly 1,500 nomadic and semi-nomadic tribes and 198 denotified tribes, comprising 15 crore Indians, according to the Renke Commission (2008).
What is the Scheme for Economic Empowerment of DNTs (SEED)?
- In February 2022, Scheme for Economic Empowerment of DNTs (SEED) was launched by the Union Ministry for Social Justice and Empowerment.
- The four components of the SEED scheme are –
- Educational Empowerment – Free coaching to students from these communities for Civil Services, entry to professional courses like medicine, engineering, MBA, etc.
- Health Insurance – Through Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana of National Health Authority
- Livelihoods – To support income generation,
- Housing – Through Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana
- Expenditure of Rs 200 crore to be spent over five years 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- One important feature of this scheme is the online portal which has been developed by the Department. This portal will ensure seamless registration and will also act as a repository of the data on these communities.
What may the reason behind the delay in implementation?
- Inconsistencies in terms of categorization of DNTs have been hindering the process of SEED applications.
- The categorisation of these communities by the Idate Commission left room for inaccuracies as outlined by the commission in its 2018 report.
- Idate Commission was formed by the Government of India in 2015 to study and prepare state-wise lists of different castes of DNTs.
- For instance, some communities such as the Banjara were under the SC list in Delhi, the ST list in Rajasthan and the OBC list in Uttar Pradesh.
- The categorisation of DNTs, NTs and SNTs is essential for the implementation of SEED.
Many commissions and committees constituted since Independence have referred to the problems of these communities.
- The Criminal Tribes Inquiry Committee, 1947 constituted in the United Provinces (now Uttar Pradesh).
- Ananthasayanam Ayyangar Committee in 1949 (it was based on the report of this committee the Criminal Tribes Act was repealed),
- Kaka Kalelkar Commission (also called first OBC Commission) constituted in 1953.
- The B P Mandal Commission constituted in 1980 also made some recommendations on the issue.
- The National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (NCRWC), 2002 held that DNTs have been wrongly stigmatised as crime prone and subjected to high handed treatment as well as exploitation by the representatives of law and order and general society.
- The NCRWC was established under the chairmanship of Justice M N Venkatachaliah.
- The National Idate Commission was constituted in 2015 under the chairmanship of Shri Bhiku Ramji Idate.
- Based on the recommendation of this commission, the Government of India set up the Development and Welfare Board for DNTs, SNTs &NTs (DWBDNCs) in 2019.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Consider the following statements about Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in India: (2019)
- PVTGs reside in 18 States and one Union Territory.
- A stagnant or declining population is one of the criteria for determining PVTG status
- There are 95 PVTGs officially notified in the country so far.
- Irular and Konda Reddi tribes are included in the list of PVTGs.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 2 and 4
- 1, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
- Mains – GS 1 (Geography)
In News: The La Nina conditions prevailing over the equatorial Pacific Ocean since September 2020 has entered the third year. There are only six instances of La Nina lasting for more than two years since 1950s.
What is La Nina and El Nino?
They are two natural climate phenomena occurring across the tropical Pacific Ocean and influence the weather conditions all over the world.
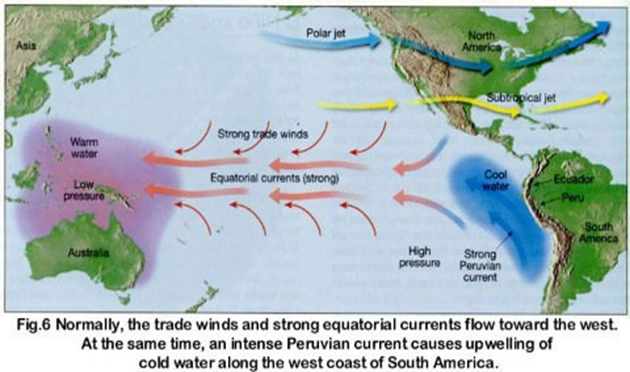
Normal Conditions:
- In a normal year, a surface low pressure develops in the region of northern Australia and Indonesia and a high-pressure system over the coast of Peru. As a result, the trade winds over the Pacific Ocean move strongly from east to west.
- The easterly flow of the trade winds carries warm surface waters westward, bringing convective storms (thunderstorms) to Indonesia and coastal Australia. Along the coast of Peru, cold bottom cold nutrient rich water wells up to the surface to replace the warm water that is pulled to the west.
EL Nino:
- The phrase “El Nino” refers to the Christ Child and was coined by fishermen along the coasts of Ecuador and Peru to describe the warming of the central and eastern pacific.
- El Nino is the name given to the occasional development of warm ocean surface waters along the coast of Ecuador and Peru. El Niño events occur irregularly at intervals of 2–7 years, although the average is about once every 3-4 years.
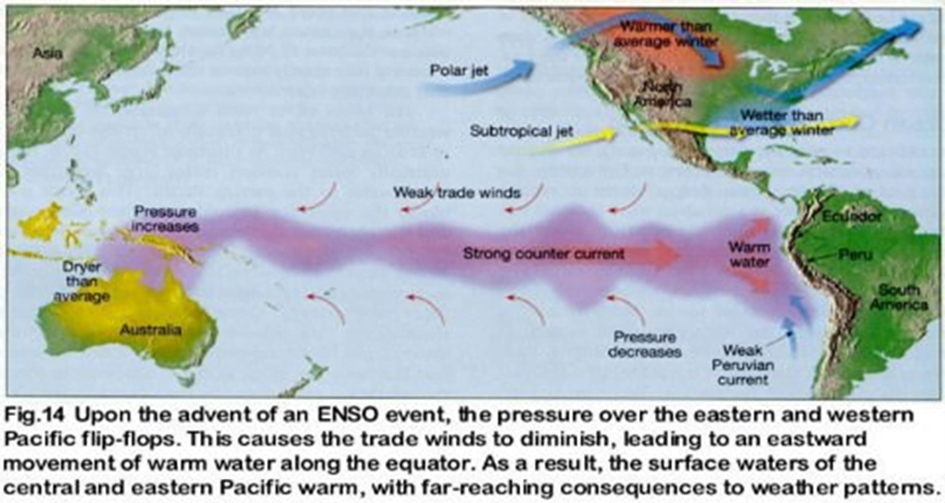
Impacts:
How El Nino impacts monsoon rainfall in across the globe:
- El Nino impacts ocean temperatures, the speed and strength of ocean currents, the health of coastal fisheries, and local weather from Australia to South America and beyond.
- Rainfall increases drastically in South America, contributing to coastal flooding and erosion.
How El Nino impacts monsoon rainfall in India:
- El Nino and Indian monsoons are inversely related.
- The most prominent droughts in India – six of them – since 1871 have been El Nino droughts, including the recent ones in 2002 and 2009
- However, not all El Nino years led to a drought in India. For instance, 1997/98 was a strong El Nino year but there was no drought (Because of IOD).
- On the other hand, a moderate El Nino in 2002 resulted in one of the worst droughts.
- El Nino directly impacts India’s agrarian economy as it tends to lower the production of summer crops such as rice, sugarcane, cotton, and oilseeds.
La Nina:
- After El Nino event weather conditions usually return back to normal.
- However, in some years the trade winds can become extremely strong and an abnormal accumulation of cold water can occur in the central and eastern Pacific. This event is called a La Niña.
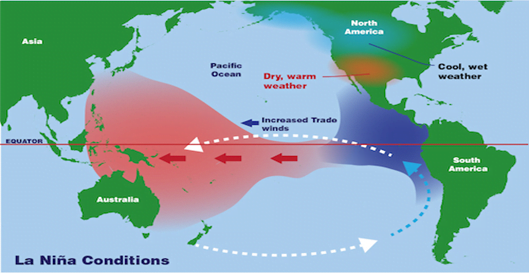
Impacts:
- La Nina tends to lead to milder winters in Northern Europe and colder winters in southern/western Europe leading to snow in the Mediterranean region.
- It is continental North America where most of these conditions are felt.
- La Nina causes drought in the South American countries of Peru and Ecuador.
- It usually has a positive impact on the fishing industry of western South America.
- In the western Pacific, La Nina increases the potential for landfall in those areas most vulnerable to their effects, and especially into continental Asia and China.
- It also leads to heavy floods in Australia and high temperatures in Western Pacific, Indian Ocean, off the Somalian coast and a comparatively better monsoon rains in India.
What will be the Impacts of Third Consecutive La Nina?
Impacts on India:
- The India Meteorological India (IMD) has predicted that some parts of India may witness heavy rains.
- The Western Ghats may receive average or below-average rain.
- Winter rainfall is less than normal in North India.
- Snowfall over Western Himalayas is less than normal.
- Winter temperatures in the plains are less than normal.
- Prolonged Winter Season over North India (extended winters).
- More rain during the second half of the Northeast Monsoon.
Negative Impact on Agriculture:
- Farmers will be at risk of losing their standing Kharif crops if it rains during this period.
- As the harvesting of the Kharif crops begins in September-end or early October and any rain just before that would prove detrimental to the standing crops.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct (2017)
- IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity
- Mains – GS 1 (Society)
In News: The Supreme Court dismissed a writ petition challenging provisions of the Special Marriage Act (SMA), 1954 requiring couples to give a notice declaring their intent to marry 30 days before their marriage.
What does the petition seek?
- The Supreme Court dismissed a writ petition challenging the Constitutional validity of certain provisions of the SMA under which couples seek refuge for inter-faith and inter-caste marriages.
- The writ petition has called these provisions violative of the right to privacy guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- The writ petition also said that the provisions contravene Article 14 on prohibition of discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste and sex as well as Article 15 on right to equality as these requirements are absent in personal laws.
Controversial Sections
- Section 5 of the SMA requires a person marrying under this law to give a notice of intended marriage.
- Section 6(2) says it should be affixed at a conspicuous place at the office of the marriage officer.
- Section 7(1) allows any person to object to the marriage within 30 days of the publication of the notice, failing which a marriage can be solemnised under Section 7(2).
Due to these provisions breaching personal liberties, several inter-faith couples approached the Court, challenging Sections 6 and 7 of the Act.
How do these provisions make couples vulnerable?
- These public notices have been used by anti-social elements to harass couples getting married.
- For instance, in Athira’s case, who got married in 2019 under SMA, her marriage notice containing her address was circulated on Social media calling on people to visit her parents and make them “aware” about her marriage.
- There have been instances, where marriage officers have gone over and beyond the law and sent such notices to the parents.
- The Haryana government has laid down 16 pre-requisites which ask couples to issue a notice in a newspaper and that such notices be sent to their parents.
- In certain States, couples have to seek a no-objection certificate from their parents.
- With as many as 11 States passing anti-conversion (or so called love-jihad) laws, parents and the State are now armed to punish and harass such couples.
The Special Marriage Act (SMA), 1954
- It is the legislation made to validate and register interreligious and inter-caste marriages in India.
- It allows two individuals to solemnise their marriage through a civil contract.
- No religious formalities are needed to be carried out under the Act.
- This Act includes Hindus, Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Jains, and Buddhists marriages.
- This Act applies not only to Indian citizens who belong to different castes and religions but also to Indian nationals who live abroad.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Data gathering by public agencies picks up even as law hangs fire.
Data gathering by Public Agencies
- The Customs department mandating airlines to share personal details of international flyers,
- The Civil Aviation Ministry’s facial recognition system DigiYatra,
- The MeitY’s proposal to share non-personal data collected by the government with start-ups and researchers,
- CERT-In’s mandate asking virtual private network (VPN) service providers to store data of their users.
These are among a rising number of moves made by the Central government and its agencies to collect and process citizens’ data — all in the absence of a data protection law.
Recently the Centre withdrew the Data Protection Bill, 2021, saying that it will soon come out with a “comprehensive legal framework” for the online ecosystem.
Concerns
- There is a fundamental issue in treating citizens’ data as a “wealth resource”.
- With this approach of trying to treat data as a ‘sovereign wealth resource’ which then creates incentives for attempts to accumulate, and subsequently monetise large volumes of data.
- The government’s primary concern should be service delivery and safeguarding the information it gathers from citizens towards this end. Its key objective should not be to monetise this data for profit.
- The 2018-2019 Economic Survey of India referred to data as a ‘public good’. By definition, that means it should be treated as ‘non-excludable and non-rivalrous public good’ and not traded as if it were a commodity.
Laws for Data Protection across the Globe:
- European Union: The primary aim of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is to give individuals control over their personal data.
- US: It has sectoral laws to deal with matters of digital privacy such as the US Privacy Act, 1974, Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act etc.
Need for Data Protection law in India:
- For efficient management of data in the age of digitisation, a data protection law is needed.
- To check unauthorised leaks, hacking, cyber crimes, and frauds. Economic cost of data loss/theft is high.
- Large amounts of personal data have been collected by state agencies and private companies and their flow across national boundaries has been a cause for concern.
- The state and private agencies that are using the personal data are not transparent on the purpose for which the data is being utilised.
- To uphold the landmark judgement of Supreme Court (SC) in Justice K.S Puttaswamy vs Union of India case, that maintained the right to privacy as an inherent part of the fundamental right under Article 21 of the constitution.
- To improve business process, and for securing digital transactions and addressing customer and privacy protection issues.
- India has the 2nd highest internet user base in the world. A strong data protection law is needed to protect their personal data.
- To curtail the perils of unregulated and arbitrary use of personal data. As most of the servers like Google, Facebook is outside India.
Way Forward
- In this digital age, data is a valuable resource that should not be left unregulated. In this context, the time is ripe for India to have a robust data protection regime.
- It is important to strike a right balance between digital economy and privacy protection. The law should encompass all the aspects- data collection, processing and sharing practices.
- Government should ensure that the law focuses on user rights with an emphasis on user privacy.
- The technological leaps made in the last two to three years also need to be addressed knowing that they have the capacity of turning the law redundant.
Source: Indian Express
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Scheme for Economic Empowerment of DNTs (SEED), is an initiative of?
- Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India Limited (TRIFED)
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
Q.2) Consider the following statements
- In a normal year, the trade winds over the Pacific Ocean move strongly from east to west.
- El Nino results the warming of the central and eastern pacific.
- El Nino years always led to a drought in India.
Choose the correct statements:
- 1 only
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.3) Consider the following statements
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) was created in 1945 afternath of atomic bomb incidents on Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
- IAEA reports annually to the United Nation General Assembly.
- In 2005, it was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for their work for a safe and peaceful world.
Choose the incorrect statements:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’31st August 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.
ANSWERS FOR 30th August 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – a











