IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Government Schemes & Policies
In News: WEST, a new I-STEM (Indian Science Technology and Engineering facilities Map) initiative called “Women in Engineering, Science, and Technology (WEST)” was launched by the GoI.
What is WEST initiative?
- The WEST programme will cater to women with a STEM background and empower them to contribute to the science, technology, and innovation ecosystem.
- Through the WEST initiative, I-STEM shall provide a separate platform to scientifically inclined women researchers, scientists, and technologists.
- Women may join the WEST program and explore opportunities to become stakeholders in various domains and pursue careers in R&D at various levels: technicians, technologists, scientists, and entrepreneurs.
- The Skill Development programmes under the WEST initiative will provide training for women with S&T backgrounds to brush up on their abilities and become engaged “in the field” as lab technicians and maintenance engineers, filling crucial gaps in the R&D infrastructure of the country.
- This initiative will also help bring women back into S&T domains after a career break.
- Under the WEST initiative, the current support being provided to S&T startups by women entrepreneurs by I-STEM will be enhanced.
- A dedicated team of women will ensure the successful implementation of the WEST initiative.
Indian Science, Technology and Engineering facilities Map (I-STEM)
- I-STEM is a National Web portal for sharing R&D (Research and Development) facilities.
- The portal facilitates researchers to access slots for the use of equipment, as well as to share the details of the outcomes, such as patents, publications and technologies.
Launch:
- Launched in January 2020.
- It is an initiative of the Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India under the aegis of Prime Minister Science, Technology and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC) mission.

- PM-STIAC: It is an overarching Council that facilitates the Principal Scientific Adviser’s Office to assess the status in specific science and technology domains, comprehend challenges in hand, formulate specific interventions, develop a futuristic roadmap and advise the Prime Minister accordingly.
Must Read: Number of women scientists goes up + Women in Science
Source: Pib.gov
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to ‘Stand Up India Scheme’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- Its purpose is to promote entrepreneurship among SC/ST and women entrepreneurs.
- It provides for refinance through SIDBI,
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography (Map)
Gogra-Hotsprings area
In News: India and China announced that their Armies have begun to disengage from Patrolling Point-15 in the Gogra-Hotsprings area of eastern Ladakh, marking a step forward towards ending the stand-off ongoing since May 2020.
Patrolling Point 15 and 17A:
- Along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) between India and China, Indian Army has been given certain locations that its troops have access to patrol the area under its control.
- These points are known as patrolling points, or PPs.
- Barring certain areas, like Depsang Plains, these patrolling points are on the LAC, and troops access these points to assert their control over the territory.
- It is an important exercise since the boundary between India and China is not yet officially demarcated.
- PP15 and PP17A are two of the 65 patrolling points in Ladakh along the LAC.
- Both these points are in an area where India and China largely agree on the alignment of the LAC.
- PP15 is located in an area known as the Hot Springs, while PP17A is near an area called the Gogra post.
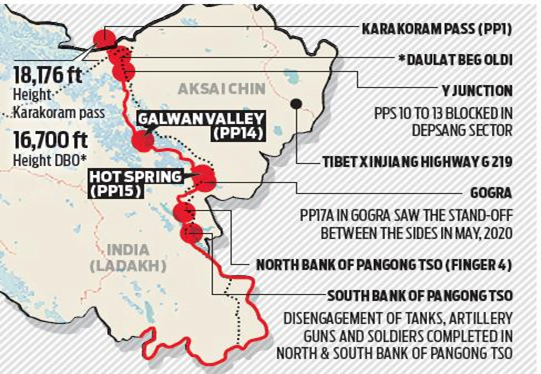
Location of Hot Springs and Gogra Post:
- Hot Springs is just north of the Chang Chenmo river and Gogra Post is east of the point where the river takes a hairpin bend coming southeast from Galwan Valley and turning southwest.
- The area is north of the Karakoram Range of mountains, which lies north of the Pangong Tso lake, and south east of Galwan Valley.
Importance
- The area lies close to Kongka Pass, one of the main passes, which, according to China marks the boundary between India and China.
- India’s claim of the international boundary lies significantly east, as it includes the entire Aksai Chin area as well.
- Hot Springs and Gogra Post are close to the boundary between two of the most historically disturbed provinces (Xinjiang and Tibet) of China.
Galwan Valley
- The valley refers to the land that sits between steep mountains that buffet the Galwan River.
- The river has its source in Aksai Chin, on China’s side of the LAC, and it flows from the east to Ladakh, where it meets the Shyok river on India’s side of the LAC.
- The valley is strategically located between Ladakh in the west and Aksai Chin in the east, which is currently controlled by China as part of its Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region.
Chang Chenmo River
- Chang Chenmo River or Changchenmo River is a tributary of the Shyok River, part of the Indus River system.
- It is at the southern edge of the disputed Aksai Chin region and north of the Pangong Lake basin.
- The source of Chang Chenmo is near the Lanak Pass.
Kongka Pass
- The Kongka Pass or Kongka La is a low mountain pass over a hill that intrudes into the Chang Chenmo Valley. It is in the disputed India-China border area in Ladakh.
Karakoram Range
- A mountain range in Kashmir spanning the borders of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwest extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan.
- Most of the Karakoram mountain range falls under the jurisdiction of Gilgit-Baltistan which is controlled by Pakistan.
- Highest peak (and world’s second highest), K2, is located in Gilgit-Baltistan.
- Begins in the Wakhan Corridor (Afghanistan) in the west, encompasses the majority of Gilgit-Baltistan, and extends into Ladakh (controlled by India) and Aksai Chin (controlled by China).
- One of the world’s most geologically active areas, at the plate boundary between the Indo-Australian plate and the Eurasian plate.
- Maximum development of glaciers occurs in the Karakoram range. This range accounts for about 16,000 sq km or about half of the snow bound area of the Himalayan region.
Location:
- Bounded on the east by the Aksai Chin plateau
- On the northeast by the edge of the Tibetan Plateau
- On the north by the river valleys of the Yarkand and Karakash rivers beyond which lie the Kunlun Mountains.
- At the northwest corner are the Pamir Mountains.
- The southern boundary of the Karakoram is formed, west to east, by the Gilgit, Indus and Shyok rivers, which separate the range from the northwestern end of the Himalaya range proper.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Siachen Glacier is situated to the (2020)
- East of Aksai Chin
- East of Leh
- North of Gilgit
- North of Nubra Valley
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science & Technology
In News: Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Indian Army have successfully completed six flight-tests of Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile (QRSAM) system.
- All the mission objectives were met establishing pin-point accuracy of the weapon system with state-of-the-art guidance and control algorithms including warhead chain.
Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile (QRSAM) system
- It is a short-range surface-to-air missile (SAM) system.
- Designed and developed by DRDO to provide a protective shield to moving armoured columns of the Army from enemy aerial attacks.
- QRSAM is a canister-based system – stored and operated from specially designed compartments.
- The system is capable of detecting and tracking targets on the move and engaging targets with short halts.

- Can operate on the move with search and track capability & fire on short halt
- The entire weapon system has been configured on mobile and is capable of providing air defence on the move.
- It has a range of 25 to 30 km.
- It also consists of two radars – Active Array Battery Surveillance Radar and Active Array Battery Multifunction Radar – with one launcher.
- Both radars have 360-degree coverage with “search on move” and “track on move” capabilities.
- The system uses a single-stage solid propelled missile and has a mid-course inertial navigation system with two-way data link and terminal active seeker developed indigenously by DRDO.
Source: PIB
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to the Agni-IV Missile, which of the following statement(s) is/are correct? (2014)
- It is a surface-to-surface missile.
- It is fuelled by liquid propellant only.
- It can deliver a one-tonne nuclear warhead about 7500 km away.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy – Current Affairs
In news: India’s rank on the Human Development Index has slipped from 130 in 2020 to 132 in 2021, in line with a global fall in HDI scores in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic, shows the Human Development Report 2021-22.
- A report on the 2021 Human Development Index (HDI) is part of the Human Development Report 2021-2022 released by the United Nations Development Programme.
- The HDI measures the average achievement of a country in three basic dimensions of human development — a long and healthy life, education, and a decent standard of living.
- It is calculated using four indicators — life expectancy at birth, mean years of schooling, expected years of schooling, and the Gross National Income (GNI) per capita.
Indian Scenario:
India ranked 132nd among 191 countries and territories on the 2021 Human Development Index (HDI). The decline in the country’s performance from its previous level was on account of a fall in life expectancy.
Key points:
- India’s latest HDI value of 0.633 places the country in the medium human development category, lower than its value of 0.645 in the 2020 report.
- The report attributes the drop in HDI from 0.645 in 2019 to 0.633 in 2021 to India’s falling life expectancy — from 69.7 years to 67.2 years during the survey period.
- India’s expected years of schooling stand at 9 years, down from 12.2 years in the 2020 report, although the mean years of schooling is up at 6.7 years from 6.5 years in the 2020 report.
- Although India retained its 132nd position in the Gender Development Index, the female life expectancy dropped from 71 years in the 2020 report to 68.8 years in the 2021 report.
- The mean years of schooling for females declined from 12.6 to 11.9 years in the corresponding period.
- India scored 0.123 in the Multi-Dimensional Poverty Index (MPI) with a headcount ratio of 27.9 per cent, with 8.8 per cent population reeling under severe multidimensional poverty.
- Over the last decade, India has lifted a staggering 271 million out of multidimensional poverty, the report noted.
Asian Countries:
- Among India’s neighbours, Sri Lanka (73rd), China (79th), Bangladesh (129th), and Bhutan (127th) are ranked above India, while Pakistan (161st ), Nepal (143rd ), and Myanmar (149th) are worse off.
- The report said around 90 per cent of countries registered a decline in their HDI value in 2020 or in 2021.
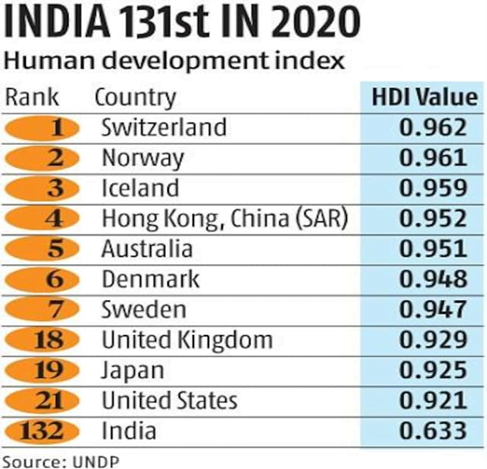
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which of the following gives the ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2022)
- World Economic Forum
- UN Human Rights Council
- UN Women
- World Health Organization
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
- Mains – GS 2 (Government Policies & Interventions)
Context: The Central government has made it simpler and cheaper for various entities to set up a range of infrastructure on Railway land on long-term lease.
- These including cargo-related enterprises, public utilities, renewable energy projects and even schools.
What Policy changes have been introduced?
- Under the new land policy, setting up of cargo terminals and cargo-related activities on Railway land will attract a rate of 1.5 per cent of current market value of land per annum with a 6 per cent annual increment accounting for inflation, for up to 35 years.
- Through the new land policy, the Central government envisages cargo-related activities to be taken up by any player, be it PSU, Railways, private players, existing and future players.
- Renewable energy plants, water recycling and treatment plants are to be for exclusive use of Railways while social infrastructure like schools and hospitals may be for Railway beneficiaries and the public at large.
- The changes introduced are in line with the one of the key concepts of the PM Gati Shakti programme which is to bring all infrastructure and utility projects in sync with each other.
Must Read: PM Gati Shakti
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
- Mains – GS 2 (Government Policies & Interventions)
Context: The Department of Consumer Affairs, Legal Metrology Division has notified a draft amendment to the Legal Metrology (Packaged Commodities) Rules 2011.
Legal Metrology (Packaged Commodities) Rules, 2011
- It is mandatory under the Legal Metrology (Packaged Commodities) Rules, 2011 to ensure a number of declarations, such as:
- the name and address of the manufacturer/packer/importer,
- the country of origin,
- the common or generic name of the commodity,
- the net quantity,
- the month and year of manufacture,
- the Maximum Retail Price (MRP)
- Consumer care information.
- All pre-packaged commodities should also be inspected.
- The rules says that the principal display panel means the total surface area of a package containing the information required in accordance with these rules
- the pre-printed information could be grouped together and given in one place and the online information in another place.
- The rules provide that the declaration on the package must be legible and prominent.
- The consumers’ ‘right to be informed’ is violated when important declarations are not prominently displayed on the package.
- If there is more than one major product the rules states that the name or number of each product shall be mentioned on the package.
- This sub-rule is not applicable to mechanical or electrical commodities.
The proposed amendments
- The proposed amendments suggest that at least two prime components should be declared on the package’s front side along with the brand name.
- Currently, manufacturers list the ingredients and nutritional information only on the back of the packaging.
- This declaration must also include the percentage/quantity of the USPs of the product in the same font size as the declaration of the USPs.
- Mechanical or electrical commodities are excluded from this.
- When this new provision is added, consumers will not be misled by the fake claims of manufacturers relating to the content in blended foods and cosmetics.
Earlier amendment:
- In July 2022, the Department of Consumer Affairs had notified the Legal Metrology (Packaged Commodities), (Second Amendment) Rules 2022.
- It allowed the electronic products to declare certain mandatory declarations through the QR Code for a period of one year, if not declared in the package itself.
- This amendment allows the industry to declare the elaborated information in the digital form through the QR Code.
Need for the amendments:
- It is common for consumers to assume that brands’ claims are accurate, but such claims are usually misleading.
- The front side of the package must contain the percentage of the composition of the unique selling proposition (USP).
- A USP also known as a unique selling point, is a marketing strategy designed to inform customers about the superiority of one’s own brand or product.
- Listing the USP of a product on the front of the package without disclosing its composition percentage violates consumer rights.
- Also, packages displaying key constituents must display a percentage of the content used to make the product.
- For example, if a brand sells aloe vera moisturiser or almond milk/biscuits, then the maximum percentage of the product should be aloe vera and almond, otherwise, the product name is misleading.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context:
- Several Indians have ended their lives owing to harassment by recovery agents of unregulated digital lending apps mostly linked to entities based in China.
- The apps offering quick loans without much documentation or collateral to unsuspecting borrowers mushroomed in the country during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- It became a popular option for borrowing money, especially for cash-strapped families and people facing joblessness.
- However, their high interest rates, short repayment windows, coercive recovery methods and misuse of personal information have prompted the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Central probe agencies to crack down on the entities that run these loan apps and the payment gateways and crypto exchanges used by them to transfer overseas the money extracted from borrowers.
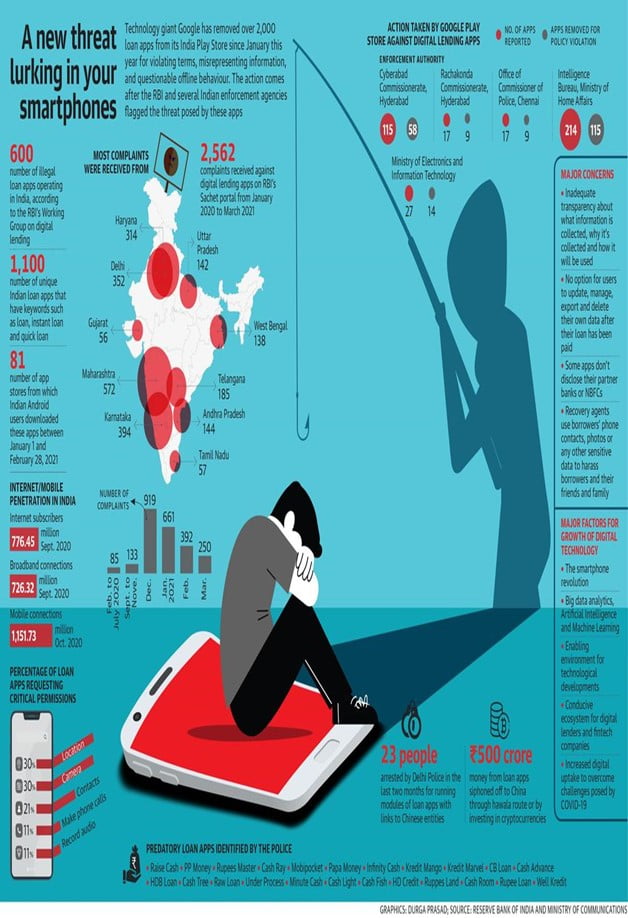
How it works
- The apps offer loans, ranging from ₹2,000 to ₹20,000, to thousands of customers with minimum KYC requirements and based only on online verification.
- According to the police, to provide a loan, the apps ask customers to upload their Aadhaar card, PAN card and a live photograph.
- Customers are also asked to share a One Time Password (OTP) that is generated.
- The borrowers give various permissions while activating the app, giving it complete access to their contact list, location, chats, photo gallery and camera.
- This information is then uploaded to servers hosted in China and other parts of the world.
- And the loan recovery agents operate from call centres situated in different parts of the country that have access to the data stored in these servers.
- The catch is that at the time of sanctioning the loan, 15%-25% of the amount is deducted as processing fee and the remaining sum carries an interest rate ranging from 182% to 365% per annum.
- A steep rate of penalty is added to the total repayable amount in case of default.
- The rate of recovery of loans is as high as 90%. The net profit is 25% or more.
Measures taken
- On August 10, the RBI issued its first set of guidelines to crack down on illegal activities in the digital lending industry.
- As per the new norms, all loan disbursals and repayments will be required to be executed only between the bank accounts of the borrower and the regulated entities — such as a bank or an NBFC — without any pass-through or pool account of the lending service providers or any third party.
- The norms are designed to end regulatory arbitrage and protect customers, and puts the onus on the regulated entities on behalf of whom the apps do the lending.
Going forward the passage of a law banning lending by unauthorised entities and the creation of a self-regulatory organisation for digital lenders will bring transparency to the industry.
Must Read: Digital lending – Comprehensively covered
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims: Current Affairs
- Mains: GS 1 (Society – Urbanization – case study); GS 3 (Environment – case study)
Context: Kuharianwali, a village in the Fazilka district of Punjab, has become a trendsetter in expanding forest cover. As of 2021, according to data from the Forest Research Institute, the district had just 1.34 per cent forest cover, one of the lowest in the state.
The district administration knew it had to do something to drastically change the picture. So, they launched a pilot project called “ MY VILLAGE, MY FOREST’ by applying ‘MIYAWAKI METHOD’ as a result the forest is now self-sustainable as plants have gained enough strength.
What is this Miyawaki method is all about?
- Miyawaki is a technique pioneered by Japanese botanist Akira Miyawaki, that helps build dense, native forests in a short time.
- It has revolutionised the concept of urban afforestation by turning backyards into mini-forests.
- This method includes planting trees (only native species) as close as possible in the same area which not only saves space, but the planted saplings also support each other in growth and block sunlight reaching the ground, thereby preventing the growth of weed.
- The saplings become maintenance-free (self-sustainable) after the first three years.
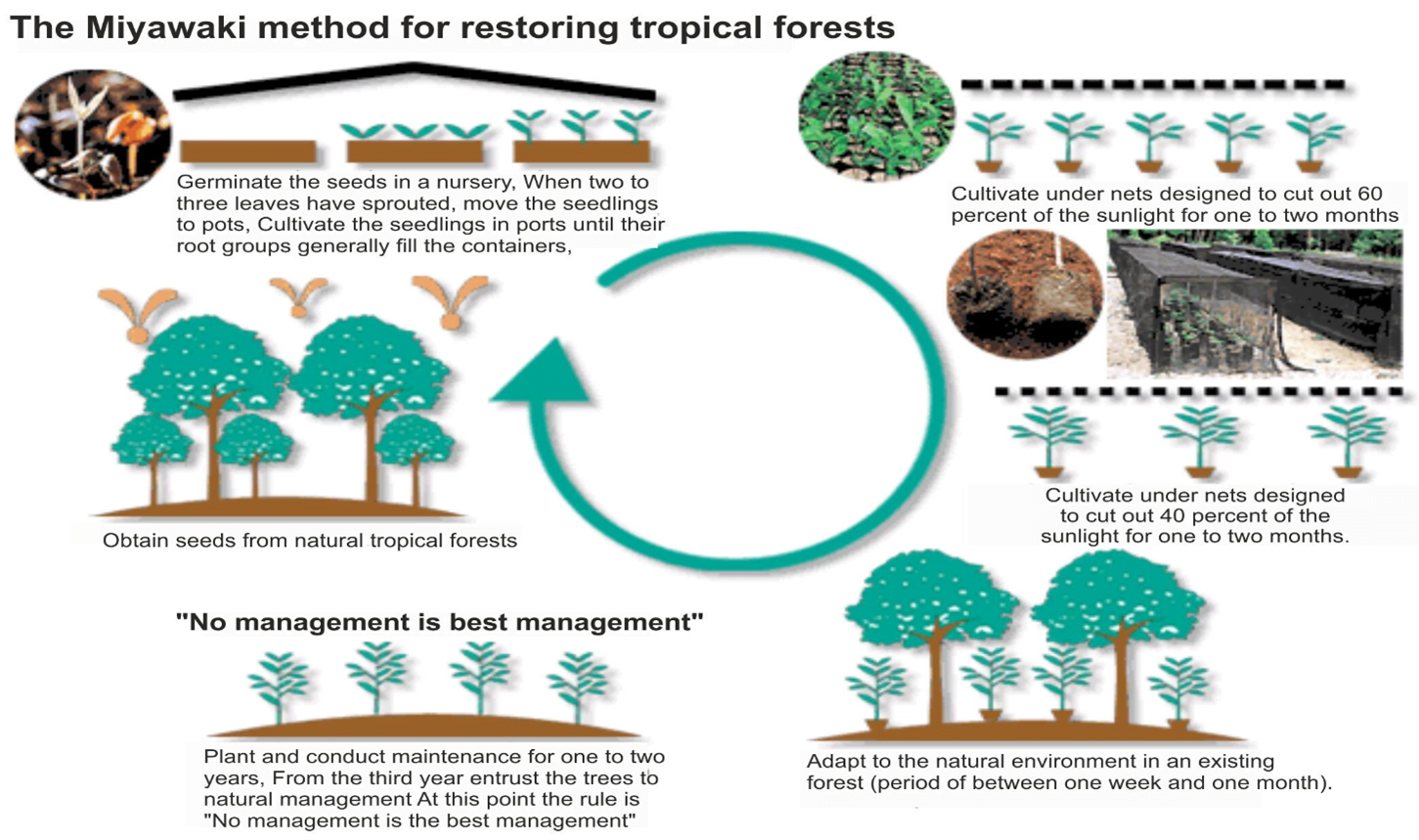
Miyawaki Process:
- The native trees of the region are identified and divided into four layers — shrub, sub-tree, tree, and canopy.
- The quality of soil is analysed and biomass which would help enhance the perforation capacity, water retention capacity, and nutrients in it, is mixed with it.
- A mound is built with the soil and the seeds are planted at a very high density — three to five sapling per square meter.
- The ground is covered with a thick layer of mulch.
Benefits of Miyawaki Method:
- Faster Process and Dense Forest: This method creates mini forests. They grow 10 times faster and become 30 times denser and 100 times more biodiverse than those planted through conventional methods.
- Faster Regeneration of Land: Miyawaki forests are designed to regenerate land in far less time. It takes over 70 years for a forest to recover on its own.
- Self-Sustainable: The saplings become self-sustainable after the first three years.
- Environmental Benefits: These mini forests help lower temperatures in concrete heat islands, reduce air and noise pollution, attract local birds and insects, and create carbon sinks.
- Miyawaki method helps to create a forest in just 20 to 30 years, while through conventional methods it takes anywhere between 200 to 300 years.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) The “Miyawaki method” is well known for the:
- Promotion of commercial farming in arid and semi-arid areas
- Harvesting wind energy on coastal areas and on sea surfaces
- Development of gardens genetically modified flora using
- Creation of mini forests in urban areas
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements
- WEST programme is an initiative of I-STEM that provides a separate platform to women researcher and scientists.
- I-STEM, national web portal for sharing Research and Development facilities is an initiative of Department of Science and Technology.
Choose the correct statements:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements
- Hot Springs is east of the Chang Chenmo river.
- Chang Chenmo River is a tributary of the Shyok River.
- Kongka Pass is a low mountain pass over a hill in Arunachal Pradesh – Myanmar boundary.
Choose the incorrect statements:
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- 1 and 2
Q.3) Which of the following gives the ‘Human Development Index’ ranking to the countries of the world?
- World Economic Forum
- United Nations Environmental Programme
- United Nations Development Programme
- World Bank
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’9th September 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.
ANSWERS FOR 8th September – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – d











