IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Recently, the NTPC (National Thermal Power Corporation) has signed a non-binding MOU with Tecnimont (Italy) to explore production of green methanol.
About Green Methanol:
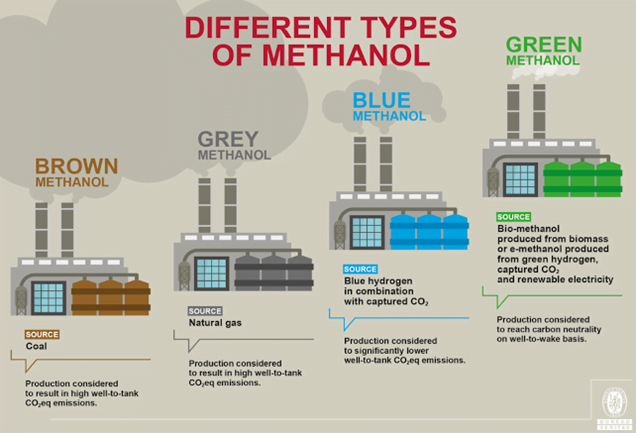
- Green methanol is a low-carbon fuel that can be made from either biomass gasification or renewable electricity and captured carbon dioxide (CO2).
Applications:
- The green methanol has a wide range of applications:
- Serving as a base material for the chemical industry
- Storing renewable electricity
- Transportation fuel.
- Maritime fuel: It is also considered as a substitute fuel for maritime fuel applications.
- Automotive industry: Methanol can be blended with gasoline in low-quantities and used in existing road vehicles, or it can be used in high-proportion blends such as M85 in flex-fuel vehicles or M100 in dedicated methanol-fuelled vehicles as a substitute for gasoline or diesel.
About National Thermal Power Corporation:
- NTPC is India’s largest power utility with an installed capacity of 68,961.68 MW plans to become a 130 GW company by 2032.
- NTPC comes under the ministry of power.
- Established in 1975, NTPC aims to be the world’s largest and best power major.
- NTPC has comprehensive Rehabilitation & Resettlement and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) policies well integrated with its core business of setting up power projects and generating electricity.
- The company is committed to generating reliable power at competitive prices in a sustainable manner by optimising the use of multiple energy sources with innovative eco-friendly technologies thereby NTPC is contributing to the economic development of the nation and upliftment of the society.
Source: Financial Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: South Korea reported its first case of infection from Naegleria fowleri or “brain-eating amoeba.
About Naegleria fowleri:
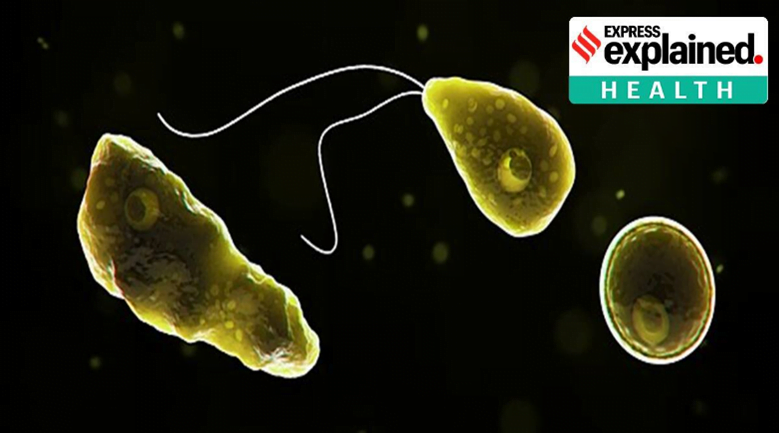
- Naegleria is a free-living amoeba (a single-celled living organism).
- It is so small that it can only be seen with a microscope.
- It is commonly found in warm fresh water (such as lakes, rivers, and hot springs) and soil.
- Only one species of Naegleria infects people: Naegleria fowleri.
- The organism best grows in high temperatures up to 46°C and sometimes can survive at even higher temperatures.
- In very rare instances, people have gotten Naegleria fowleri infections from recreational water that didn’t have enough chlorine in it, such as pools, splash pads, or surf parks.
- There is no evidence that Naegleria fowleri can spread through water vapor or aerosol droplets (such as shower mist or vapor from a humidifier).
- People cannot be infected with Naegleria fowleri by drinking contaminated water.
- Treatment: At present, doctors treat it with a combination of drugs, including amphotericin B, azithromycin, fluconazole, rifampin, miltefosine, and dexamethasone.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Consider the following:
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Virus
Which of the above can be cultured in an artificial/ synthetic medium? (2021)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Q.2) Which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
Viruses can infect
- bacteria
- fungi
- plants
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Two wars (Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and an economic war – a geopolitical confrontation between two superpowers – the US and China) are raging in 2022, which have undermined the assumption of “hyper-globalisation”.
About hyper globalisation:
- The term ‘Hyper-globalisation’ is used to describe the dramatic increase in international trade witnessed for about a decade and a half from the early 1990s.
- It led to an unprecedented movement of capital and of people.
- Capital and labour flowed across the world.
- In a hyper-globalised world, countries produce things in which they have comparative advantage and import those others can make at lower opportunity cost.
- For example, Indonesia and Malaysia produce palm oil; and Ukraine and Russia produce sunflower oil.
- They have comparative advantages in the palm oil and sunflower oil.
- Therefore, Indonesia alone is the largest exporter of palm oil.
- Three forces of hyper-globalization:
- Economic force in which extensive growth in global trade creates cross-border economic integration,
- Human communications force via the Internet in which instant and global communication of social media and the Internet are changing norms of human communication blurring social barriers, and
- Technological disruption force coming from new innovations in technology driven by Internet-of-Things (IoT), big data, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) bringing massive economic and rapid social changes leading to a world of Singularity.
- Palm oil example:
- Recently, Indonesia, the world’s largest producer and exporter of the palm oil has been experiencing domestic shortages of the same.
- This led to spike in the domestic palm oil prices in Indonesia and the world (including India).
- Therefore, Indonesia has announced to ban all exports.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Consider the following statements:
- Tight monetary policy of US Federal Reserve could lead to capital flight.
- Capital flight may increase the interest cost of firms with existing External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs).
- Devaluation of domestic currency decreases the currency risk associated with ECBS.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: The Union government has made digitally capturing MGNREGA attendance universal from January 1, 2023 through (NMMS). From May 16, 2022, capturing attendance via the app was made compulsory for all worksites with 20 or more workers.
About NMMS:
- The National Mobile Monitoring Software (NMMS) App was launched by the Ministry of Rural Development in 2021.
- It aimed at bringing more transparency and ensuring proper monitoring of the schemes.
- Significance:
- The NMMS App permits taking real time attendance of workers at Mahatma Gandhi NREGA worksites along with geo-tagged photographs.
- The app helps in increasing citizen oversight of the programme.
- Issues:
- Poor internet connectivity, little access to smartphones and glitches in the app have created a problem in the daily activities of the workers.
- The workers are forced to buy a smartphone which is pushing them to leave the job.
- Many workers have complained that the process is very difficult, and they are illiterate.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
In News: A new research clarifies how sepsis can lead to cell death.
Sepsis:
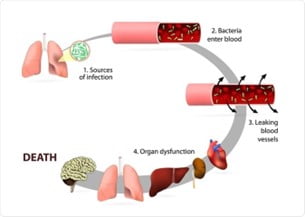
- Sepsis is a life-threatening condition arising from the body’s overreactive response against an infection, leading it to injure its own tissues and organs.
- The first known reference to “sepsis” dates back more than 2,700 years, when the Greek poet Homer used it as a derivative of the word “sepo,” meaning “I rot.
- Affects 750,000 people in the US and nearly 50 million people globally each year.
- Sepsis accounted for 11 million deaths worldwide in 2017, and is the most expensive medical condition in the US, costing over tens of billions of dollars annually.
How autoimmunity works
- The body’s response to infection starts when immune cells recognise components of the invading pathogen.
- These cells then release molecules like cytokines that help eliminate the infection.
- Cytokines are a broad group of small proteins that recruit other immune cells to the site of infection or injury.
- Excessive and uncontrolled cytokine production can lead to a dangerous cytokine storm that can cause sepsis.
- Cytokine storms occur in graft versus host disease, transplant complications, viral infections, including COVID-19.
- This uncontrolled immune response can lead to multi-organ failure and death.
Tumour necrosis factor(TNF):
- It is the most potent cytokines
- It induces tumour cells to die when the immune system is stimulated by a bacterial extract called Coley’s toxin (a lipopolysaccharide, or LPS – component of outer membrane of certain types of bacteria).
- LPS is the strongest known trigger of TNF, which, once on alert, aids in the recruitment of immune cells to the infection site to eliminate invading bacteria.
- In normal conditions, TNF promotes beneficial processes such as cell survival and tissue regeneration.
- Uncontrolled TNF production can lead to the development of rheumatoid arthritis and similar inflammatory conditions.
- Uncontrolled TNF during infections can lead to sepsis.
- Hence, TNF production must be tightly regulated to avoid sustained inflammation and continuous proliferation of immune cells and to prevent excessive tissue and organ damage from inflammation and an overactive immune response.
Treatment:
- Blocking TNF activity can effectively treat numerous autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Neutralizing TNF can prevent the death of the animal from bacterial LPS
- Blood cells made in the bone marrow, or myeloid cells, are known to be the major producers of TNF.
- TRIF and CD14 as potential treatment targets for sepsis, with the ability to both reduce cell death and inflammation.
- TNF blockers have been unsuccessful in preventing the cytokine storm that can arise from COVID-19 infections and sepsis.
Source: The hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body ? (2022
- They protect the body from environmental allergens.
- They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
- They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
- They protect the body from the diseases caused by pathogens.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
In News: Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Madras, Tel Aviv University and Columbia University are studying a rare genetic brain disease called “GNB1 Encephalopathy” and trying to develop a drug to treat it effectively.
GNB1 Encephalopathy
- It is a kind of brain disease or neurological disorder which affects individuals in the foetus stage.
- With less than 100 documented cases worldwide
- Children born with GNB1 mutation experience delayed physical and mental development, intellectual disabilities, epilepsy (abnormal brain activity), movement problems, muscle hypotonia or hypertonia.
- A potassium channel called G-protein gated Inwardly Rectifying K+ (GIRK) channel (present in brain, heart and endocrine glands) function is affected significantly.
- As I80T mutation is the most prevalent variant in GNB1 encephalopathy patients.
How it occurs:
- A single nucleotide mutation in the GNB1 gene that makes one of the G-proteins, the “Gβ1 protein,” causes Encephalopathy.
- Every cell in the human body has a wide variety of signalling molecules and pathways that help in communicating with other cells and within itself.
- The major signalling mechanism used by cells is ‘G-Protein Coupled Receptor’ (GPCR) signalling.
- GPCR is a receptor that receives a signal (e.g. a hormone, light, neurotransmitter) from the outside of the cell and transduces it to the inside of the cell.
- GPCR is present in the cell membrane and has a G-protein (αβγ) attached to it from inside the cell.
- G-proteins are the immediate downstream molecules that relay the signal received by the GPCR.
- These G-proteins are present in every cell, and any malfunction will cause disease.
Treatment:
- As the developmental issues start at the fetal stage, gene therapy is the most plausible option to alleviate the effects of the mutation.
- Whole genome sequencing, the elucidation of the full genetic analysis of the baby, can be very helpful in early diagnosis of the disease.
- Epilepsy can be treated using specific drugs to increase the patient’s quality of life.
- To treat epilepsy, specific targets have to be identified.
- Most epilepsies are caused due to altered ion channel function.
- Ion channels are proteins that underlie the electrical activity of neurons and heart cells.
Source: The hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) In the context of hereditary diseases, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Passing on mitochondrial diseases from parent to child can be prevented by mitochondrial replacement therapy either before or after in vitro fertilization of egg.
- A child inherits mitochondrial diseases entirely from mother and not from father.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
In News: Neem trees has been identified as twig blight and dieback disease in Telangana.
Neem:

- Neem is a member of the mahogany family, Meliaceae
- Neem trees are attractive broad-leaved evergreens that can grow up to 30 m tall and 2.5 m in girth.
- The roots penetrate the soil deeply
- When injured, they produce suckers – This suckering tends to be especially prolific in dry localities.
- It is grown from the southern tip of Kerala to the Himalayan hills, in tropical to subtropical regions, in semiarid to wet tropical regions, and from sea level to about 700 m elevation.
- Neem trees are strong can take considerable abuse.
- They can easily withstands pollarding (repeated lopping at heights above about 1.5 m)
- Neem shows antibacterial, antifungal, and other versatile properties
- But neem trees are sometimes hit by insect and fundal infestation
Dieback disease:
- The dieback disease affects leaves, twigs and the inflorescence of neem trees of all ages
- It causes almost 100% loss of fruit production in severely infected trees
- The dieback disease is mainly caused by the fungi Phomopsis azadirachtae.
- The dieback disease was first reported in the country during the 1990s near Dehradun in Uttarakhand, while it was first noticed in Telangana in 2019.
- The appearance of symptoms starts with the onset of the rainy season and becomes progressively severe in the later part of the rainy season and early winter.
Control measures:
- The twigs affected by the disease should be cut and a blend of fungicide and insecticide can be sprayed after their removal.
- Alternatively, a pit should be dug around an affected tree, and water mixed with fungicide and an insecticide should be poured into it.
- However, the efforts to treat the affected trees should be taken up as a cluster either in a village or in a residential locality in urban areas as the fungus is airborne.
- Even if treatment is carried out for one tree, the fungus spores from a nearby tree can affect the treated plant again.
- Spraying chemicals on big trees is a difficult task as it may hit insects like butterflies and also pollute water bodies nearby.
Source: The hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
In News: As part of India’s G20 presidency, the Minister for Electronics & Information Technology, Communications and Railways has launched the “Stay Safe Online” campaign and the “G20 Digital Innovation Alliance” (G20-DIA).
About Stay Safe Online Campaign
- The objective of the ‘Stay Safe Online Campaign’ is to raise awareness among citizens to stay safe in the online world due to the widespread use of social media platforms and the rapid adoption of digital payments.
- This campaign will make citizens of all age groups, especially children, students, women, senior citizens, specially-abled, teachers, faculty, officials of Central/State Governments, etc. aware of the cyber risk and ways to deal with it.
- The campaign will be carried out in English, Hindi and local languages to reach a wider audience.
- The campaign involves the dissemination of multilingual awareness content in the form of infographics, cartoon stories, puzzles, short videos, etc. and amplifying the same through extensive use of the MyGov website ( https://www.mygov.in/staysafeonline ) and prominent social media platforms.
- Besides this, various publicity, promotion and outreach activities would be carried out throughout the year through print, electronics & social media to reinforce the stay safe online message.
- In addition, collaboration and involvement of key stakeholders viz. Union Ministries / Departments, industry associations/partners, NGOs, civil society organizations, etc. would be sought for wider outreach of the campaign.
About G20 Digital Innovation Alliance (G20-DIA)
- The objective of the G20 Digital Innovation Alliance (G20-DIA) is to identify, recognize, and enable the adoption of innovative and impactful digital technologies developed by start-ups, from G20 nations as well as the invited non-member nations, which can address the needs of humanity in the critically important sectors of Agri-tech, Health-tech, Ed-tech, Fin-tech, Secured Digital Infrastructure, and Circular Economy.
- Start-up products in the aforementioned six themes enabled through Digital Public Goods Infrastructure can create a global population-scale impact and reduce the digital divide and enable sustainable, and inclusive techno-socio-economic development.
- The G20 Digital Innovation Alliance (G20–DIA) summit which will be held in Bangalore on the side-lines of the Digital Economy Working Group (DEWG) meeting will be a multi-day program where top nominated start-ups from each of the theme areas from all of the G20 countries and the non-member invited countries will showcase their solutions to the global community of investors, mentors, corporates, and other government stakeholders.
- The engagement of innovators, entrepreneurs, start-ups, corporations, investors, mentors, and other ecosystem stakeholders will lead to the speedy acceptance of the platform that India plans to offer through the G20 Digital Innovation Alliance (G20-DIA).
- The G20-DIA Summit will bring together the key players in the innovation ecosystem from both G20 member countries and the invited non-member countries
Source PIB
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 Economy, Science and Technology
Context:
- India has already emerged as a leader when it comes to creating digital public infrastructure and goods that provide development solutions at the population scale.
- For instance, Aadhaar has provided Indians with a foundational identity, the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has accelerated financial inclusion, and the CoWIN platform has helped drive India’s COVID inoculation programme.
- In April 2022, Aadhaar enrolment reached 1.33 billion, and the number of Aadhaar-based transactions crossed 73.5 billion.
Challenges of traditional lending:
- The lack of ‘expansionability’ of the traditional lenders has created a credit gap of around US $380 billion in the Indian MSME sector.
- Even the credit card industry has not sufficiently been able to penetrate the massive Indian market
- Only 3 percent of the population has a formal credit card today, and this number is largely limited to the country’s tier 1 cities
- Tedious process – Acquiring a loan currently requires lending service providers(LSPs) to shoulder a host of responsibilities.
- These include sourcing, identity verification, underwriting, disbursement, recollections and dispute management.
- Each of these is a process unto itself and their execution impacts the profits earned by an LSP.
Solutions – Open Credit Enablement Networks(OCEN):
- The Open Credit Enablement Network s(OCEN) is an emerging digital public good (DPG) that has the potential to democratise and transform India’s digital lending landscape.
- Designed as a framework of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), OCEN could be integrated with a wide range of digital platforms and apps
- It aims to empower individuals and micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) by directly delivering financial products to them, thereby eliminating their dependence on traditional lenders.
- OCEN is being developed by iSPIRT, an Indian software industry think tank, and could be instrumental in building a credit marketplace, or more broadly, a digital ecosystem of lenders and loan service providers (LSPs).
Significance of OECN:
- It automates screening processes to decide on loan-worthy customers and the onboarding of new borrowers.
- The OCEN API can be integrated with e-commerce websites, digital marketplaces, and other apps to help secure a loan while making a purchase.
- OCEN can also be used by non-bank small-scale lenders, thus expanding the scope of lending and borrowing.
- Integrating verification process with Aadhaar’s existing eKYC system.
- In September 2022, 25.25 crore eKYC transactions were done through the platform, raising the total number of transactions to 1,297.93 crore.
- Democratise credit systems by connecting loan providers with customers who are not part of any formalised credit system.
- An example on the iSPIRT website reflects the list of lenders available for a customer.
- Quality of services – A wider adoption of the technology in the marketplace will bring borrowers more diverse and personalised options.
- Overcome limitations of traditional lending: Borrowing money would not be limited to the assets and incomes owned by a person, one of the biggest hurdles that has limited the growth of traditional lending.
- Lending online would reduce the time and cost of loan disbursements and could reflect in more favourable interest rates charged by lenders.
OCEN’s challenges:
- Risk of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) – Since OCEN will involve credit and a likely increase in the number of borrowers, there may be a probable rise in the incidence of loan defaults.
- Transparency with respect to loan-related data could pose a challenge – With an increase in data, companies will come to possess a list of defaulters who might then be excluded from the lending process.
- Cybersecurity risks such as data breaches may occur.
- Recently, the data of around 110 million users of Mobiwik, a fintech start-up, was sold on the dark web.
- Lack of adequate regulatory frameworks associated with data privacy, confidentiality, and security.
- Lack of technical know-how could lead to online theft and financial fraud.
Suggestions for future:
- Political will to create the confidence necessary for more private players to enter the space and for the technology to be adopted on a wider scale.
- Targeted digital literacy programmes must accompany the rollout of new technologies and platforms.
- Creation of a task force, a system for online dispute resolution and A digital ombudsman.
Way forward
- Fintech is among the fastest growing sectors in India, with start-ups in the space receiving funding worth US$9.8 billion in 2021.
- Around 10 fintech companies have scaled up as unicorns in 2021, and the fintech market is expected to grow to US$ 84 billion by 2025.
- India’s other major instances of DPGs–the Aadhaar and UPI–have experienced massive scale and success and same can be expected for OCEN.
Source: ORF
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (History and Art and Culture) and GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The Janardana Temple in Kerala, the Haveli of Agah Khan in Agra and Gonpa complex in Ladakh are among the 14 ancient sites which have been declared protected by the Archaeological Survey of India over the last three years.
- The list of these monuments and sites has been declared protected under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958 was shared by Culture Minister in the Rajya Sabha.
- The other monuments and sites in the List Includes
- The temple complex of Navratnagarh in Jharkhand’s Gumla district.
- The group of monuments in Bolangir, Odisha.
- Vishnu Temple in Pithorgarh, Uttarakhand.
- Trilochannath Temple in Kathua, Jammu and Kashmir.
- Udhampur are the sites which have been declared protected.
- The Baori and surrounding archaeological remains in Neemrana Rajasthan.
- Archaeological remains in Baghpat, Uttar Pradesh.
- The archaeological sites and remains of Ashwamedh Yagna.
- Village Virbhadra in Dehradun
- Rangdum Monastery in Kargil, Ladakh.
- Hathi Khana’ in Agra.
- Also, the government has provided ₹15,622 lakhs over the last three years as grant to Zonal Cultural Committees to strengthen the micro-culture in the country.
- Out of which, ₹5,881.46 lakh has been allotted in the year 2021-22.
About Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act (AMASR), 1958:
- The Act was introduced in 1958 for safeguarding the cultural heritage of the country.
- The main objective of the act is to protect ancient and historical monuments and archaeological sites and remains of national importance.
- The act also regulates the archaeological excavations and the protection of sculptures, carvings and other like objects.
- The Act prohibits construction in ‘prohibited areas’, an area of 100 meters around protected monuments.
- The central government can extend the prohibited area beyond 100 meters.
- The Archaeological Survey of India functions under the provisions of the act.
About Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) and National Monuments Authority (NMA):
Archaeological Survey of India
- It is a premier organization under the Ministry of Culture, for the archaeological research and protection of the cultural heritage of the nation.
- It regulates all archaeological activities in the country as per the provisions of the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958.
- It also regulates the Antiquities and Art Treasure Act, 1972.
- It was founded in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham– the first Director-General of ASI.
- Alexander Cunningham is also known as the “Father of Indian Archaeology”.
National Monuments Authority
- National Monuments Authority (NMA) under the Ministry of Culture, Govt. of India has been setup as per provisions of The Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains AMASR (Amendment and Validation) Act, 2010 which was enacted in March, 2010.
- Several functions have been assigned to the NMA for the protection and preservation of monuments and sites through management of the prohibited and regulated area around the centrally protected monuments.
- The Act provides for NMA to be constituted with a Chairperson and up to 5 Whole Time and 5 Part Time Members each and a Member Secretary.
- DG ASI is an ex officio Member.
About Zonal Cultural Centres:
- The Zonal Cultural Centres (ZCCs) were set up in the mid-80s to develop the cultures of various regions and also to set up mechanisms for preservation and promotion of various elements of India’s rich cultural heritage as autonomous bodies.
- The ZCCs were required to concentrate on the folk arts, dance and music.
- The mandate behind setting up the ZCCs was to bind the nation culturally while retaining the individuality of the regions that comprise them.
- The Seven Zonal Cultural Centres are-
- North Zone Cultural Centre (NZCC), Patiala.
- Eastern Zonal Cultural Centre (EZCC), Kolkata.
- West Zone Cultural Centre (WZCC), Udaipur.
- North Central Zone Cultural Centre (NCZCC), Prayagraj.
- North East Zone Cultural Centre (NEZCC), Dimapur.
- South Central Zone Cultural Centre (SCZCC), Nagpur.
- South Zone Cultural Centre (SZCC), Thanjavur.
Significance of AMASR Act:
- When a monument is declared protected under the AMASR Act then the maintenance of the monument is taken over by the Archaeological Survey of India.
- Construction activities in and around the monument or site are regulated and no construction is permitted without prior permission of concerned authorities.
- The area extending to 200 meters around the monument in all directions is called a regulated area.
- As per the AMSAR (Amendment and Validation) Act, 2010 construction is prohibited within a 100-meter periphery of a protected area.
Issues associated with heritage conservation in India:
- Lack of a concrete policy on archaeological exploration and excavation: Recently a CAG report categorically noted that there was no national policy on archaeological exploration and excavation which seems to be true for antiquities as well.
- Lacks required resources and crunch of funds for ASI:
- The ASI has estimated about 58 lakh plus antiquities all over India, but there is no database or inventory in its possession.
- The budget of ASI, the primary institutional guardian of monuments is reduced by 200 crores in 2021-22 whose total budget stood at about ₹ 1200 crores.
- Also the budget for exploration and excavations is less than 1 per cent of total budget which was supposed to be 5% as informed to the Public Accounts Committee (PAC).
- Lack of synergy between the different conservation agencies
- The National Culture Fund, which allows individuals and corporate groups to fund conservation, has utilized only 14 percent of its funds because of the lack of coordination with the ASI.
- The National Monuments Authority who implements heritage by-laws and site plans for each monument has notified only 31 monuments and about 210 are in finalization state which is a fraction of the 3,693 monuments on the list of Centrally Protected Monuments.
- Faulty government policies: The Union government is pushing to amend the AMASAR act which will drastically reduce the prohibited and regulatory area around monuments.
- This will minimize the security net around monuments which would endanger them.
Suggestive measures and way forward:
- There is a need to create infrastructure such as databases or inventory of protected sites, CCTV cameras installation, proper lighting etc. to provide a fillip to heritage site conservation.
- The ASI needs an overhaul in its functioning in line with the modern heritage conservation techniques and it should come up with more stringent regulations, criteria etc.
- There should be a quick reboot to the conservation methodology of ASI.
Thus, Strengthening conservation institutions through enhancing their financial and human resources rather than amending the laws which will weaken the heritage conservation framework of the country is need of the hour.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Consider the following pairs:
Site of Ashoka’s major rock edicts Location in the State of
- Dhauli Odisha
- Erragudi Andhra Pradesh
- Jaugada Madhya Pradesh
- Kalsi Karnataka
How many pairs given above are correctly matched? (2022)
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Baba’s Explainer – Year End Review-2022: Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change
Syllabus
- GS-3: Environment & Conservation
- GS-3: Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Context: The year 2022 saw the launch of Mission LiFE by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi, a flagship programme to promote sustainable lifestyle across the globe.
- The central elements of Mission LiFE i.e., sustainable lifestyle and sustainable patterns of consumption to address climate change were mentioned in the cover decision of Sharm El Sheikh Implementation Plan of COP 27.
- Cheetah reintroduction in India by the Prime Minister was another important milestone in the global conservation efforts of the species.
Read Complete Details on Year End Review-2022: Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change
Practice MCQs
Q.1) With reference to “Neem trees”, consider the following statements:
- They are broad-leaved evergreen trees.
- They are found only in the north and north-western India
- They are fragile and must be protected against pests and diseases.
Which of the following statements are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to ‘cytokines’, frequently in the news, which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
- Cytokines are proteins-based cells.
- Cytokines do not have cell membrane.
- Their excess production may lead to sepsis.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.3) Consider the following pairs:
Archaeological site and state
- Rangdum Monastery Arunachal Pradesh
- Bolangir Odisha
- Navratnagarh Haryana
- Kathua Uttar Pradesh
How many pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- One pair only
- Two pairs only
- Three pairs only
- All four pairs
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 29th December 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 28th December – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – b












