IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: The Association of Man-made Fibre Industry of India (AMFII) has appealed to the Union Finance Ministry to accept the recommendations of the Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR) on levy of anti-dumping duty (ADD) on imports of Viscose Staple Fibre from Indonesia.
About The Association of Man-made Fibre Industry of India (AMFII)
- The AMFII was set up in 1951 as “The Rayon Manufacturers’ Association”.
- In 1959, its name was changed to “Association of Man-Made Fibre Industry of India” to include all the modern Man-Made Fibres of 20th Century origin thereby expanding its scope and membership.
- Thus, the Membership of the AMFII varied from time to time and included both Synthetic and Cellulosic Man-Made Fibres and Filament Yarn Manufacturers.
- On 29th April 1987, the AMFII was registered as a Private Limited Company under section 25 A of the Companies Act 1956.
- It was also registered under section 12 of the Income Tax Act as an organization for charitable purpose for “advancement of an object of general public utility”.
- The main object of the Association is to help the man-made fibre industry in India to formulate general policy on production and development of the industry.
- The Association also acts as a liaison body on behalf of the industry and communicates with the Chambers of Commerce and other public bodies within and outside India, with a view to promote and protect the man-made fibre industry and trade.
- The Association has its Registered Office in Mumbai.
- It has a Branch Office in New Delhi.
About Viscose Staple Fibre:

- Viscose Staple Fiber (VSF), is a natural and biodegradable fiber which has characteristics that are similar to cotton.
- Due to its versatility, VSF is widely used for manufacturing
- Apparels
- Home textiles
- Dress materials
- Knitted wear and
- Non-woven applications.
About Anti-Dumping Duty:
- Anti-dumping is a protectionist tariff, imposed by a domestic government on foreign imports that are at a price lower than the price it normally charges in its own home market.
- Anti-dumping duty is imposed as a remedy to the distortive trade which arises due to the dumping of goods.
- The use of anti-dumping measures as an instrument of fair competition is permitted by the World Trade Organisation.
- Where dumping occurs, the WTO allows the government of the affected country to take legal action against the dumping country as long as there is evidence of genuine material injury to industries in the domestic market.
- The Government must show that dumping took place, the extent of the dumping in terms of costs, and the injury or threat to cause injury to the domestic market.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to foreign-owned e-commerce firms operating in India, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2022)
- They can sell their own goods in addition to offering their platforms as market-places.
- The degree to which they can own big sellers on their platforms is limited.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Which one of the following situations best reflects “Indirect Transfers” often talked about in media recently with reference to India? (2022)
- An Indian company investing in a foreign enterprise and paying taxes to the foreign country on the profits arising out of its investment
- A foreign company investing in India and paying taxes to the country of its base on the profits arising out of its investment
- An Indian company purchases tangible assets in a foreign country and sells such assets after their value increases and transfers the proceeds to India
- A foreign company transfers shares and such shares derive their substantial value from assets located in India
Q3.) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements are correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends for the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps the Public Sector Banks in developing strategies and capital raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – History and Art and Culture
Context: Recently, the Prime Minister of India has paid tributes to Rajmata Jijau on her Jayanti.
About Jijabai Bhonsle (12 January 1598 – 17 June 1674):

- Jijabai was born to Mahalasabai Jadhav and Lakhuji Jadhav of Deulgaon, near Sindkhed, in present-day Maharashtra.
- Jijabai was married at an early age to Shahaji Bhosle.
- She was the mother of Shivaji, founder of the Maratha Empire.
- She died at Pachad village near Raigad Fort.
Role and Contributions of Jijabai Bhonsle:
- She managed her husband’s Jagir in Pune and developed it.
- Mentored a great person like Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- She taught Shivaji about swarajya and raised him to be a warrior.
- She also renovated Kevareshwar Temple and Tambadi Jogeshwari Temple.
Source: PIB
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following pairs:
King Dynasty
- Nannuka Chandela
- Jayashakti Paramara
- Nagabhata II Gurjara-Pratihara
- Bhoja Rashtrakuta
How many pairs given above are correctly matched? (2022)
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Q.2) Consider the following statements:
- It was during the reign of Iltutmish that Chengiz Khan reached the Indus in pursuit of the fugitive Khwarezm prince.
- It was during the reign of Muhammad bin Tughluq that Taimoor occupied Multan and crossed the Indus.
- It was during the reign of Deva Raya II of Vijayanagara Empire that Vasco da Gama reached the coast of Kerala.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2021)
- 1 only
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
- 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: Weeding out the invasive tropical American shrub, Lantana camara, appears to alter the composition of bird species in a forest, according to a new study conducted in Central India.
About Lantana Camera:

- Lantana camara (common lantana) is a species of flowering plant within the verbena family (Verbenaceae), native to the American tropics.
- Lantanas arrived in India as a decorative shrub during British colonial period but quickly took over several ecosystems as an invasive plant.
- The shrub can spread on the forest ground, climb over trees a creeper and entangle with other native plants with ease.
- It is a very adaptable species, which can inhabit a wide variety of ecosystems.
- Once it has been introduced into a habitat it spreads rapidly between 45ºN and 45ºS and more than 1,400 metres (4,600 feet) in altitude.

MUST READ: Invasive Species
Source: DownToEarth
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Among the following crops, which one is the most important anthropogenic source of both methane and nitrous oxide ? (2022)
- Cotton
- Rice
- Sugarcane
- Wheat
Q.2) If a particular plant species is placed under Schedule VI of The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, what is the implication? (2020)
- A licence is required to cultivate that plant
- Such a plant cannot be cultivated under any circumstances
- It is a Genetically Modified crop plant
- Such a plant is invasive and harmful to the ecosystem
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Recently, The World Report 2023 of Human Rights Watch (HRW) said that Indian authorities had intensified and broadened their crackdown on activist groups and the media through 2022.
Highlights of the report:
- According to the Hindu nationalist Bharatiya Janata Party-led government used abusive and discriminatory policies to repress Muslims and other minorities.
- The HRW said authorities across India arrested activists, journalists, and other critics of the government on what it called “politically motivated” criminal charges, including that of terrorism.
- It added that they also misused laws forbidding forced religious conversions to target Christians, especially from Dalit and Adivasi communities.
- On Jammu and Kashmir, the HRW said that even after three years of dilution of Article 370, the government continued to restrict free expression, peaceful assembly, and other basic rights there.
- It added that rights groups were harassed by Indian authorities throughout the country through tax raids, the use of the Foreign Contributions Regulation Act, and other allegations of financial irregularities.
About Human Rights Watch:
- Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization headquartered in New York City.
- It conducts research and advocacy on human rights.
- The group pressures governments, policymakers, companies, and individual human rights abusers to denounce abuse and respect human rights.
- It often works on behalf of refugees, children, migrants, and political prisoners.
- In 1997, Human Rights Watch shared the Nobel Peace Prize as a founding member of the International Campaign to Ban Landmines.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to India, consider the following statements:
- Government law officers and legal firms are recognized as advocates, but corporate lawyers and patent attorneys are excluded from recognition as advocates.
- Bar Councils have the power to lay down the rules relating to legal education and recognition of law colleges.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2022)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Uganda recently declared the end of the Ebola disease outbreak caused by Sudan ebolavirus.
About Ebola Disease:
- Ebola spreads through EBOV (Ebola virus) which is a virus belonging to the Filoviridae family of viruses.
- It is mainly found in animals.
- Ebola is a virus that causes severe inflammation and tissue damage throughout the body.
- It is known as a haemorrhagic fever virus, because it can cause problems with the clotting system of the body and lead to internal bleeding, as blood leaks from small blood vessels.
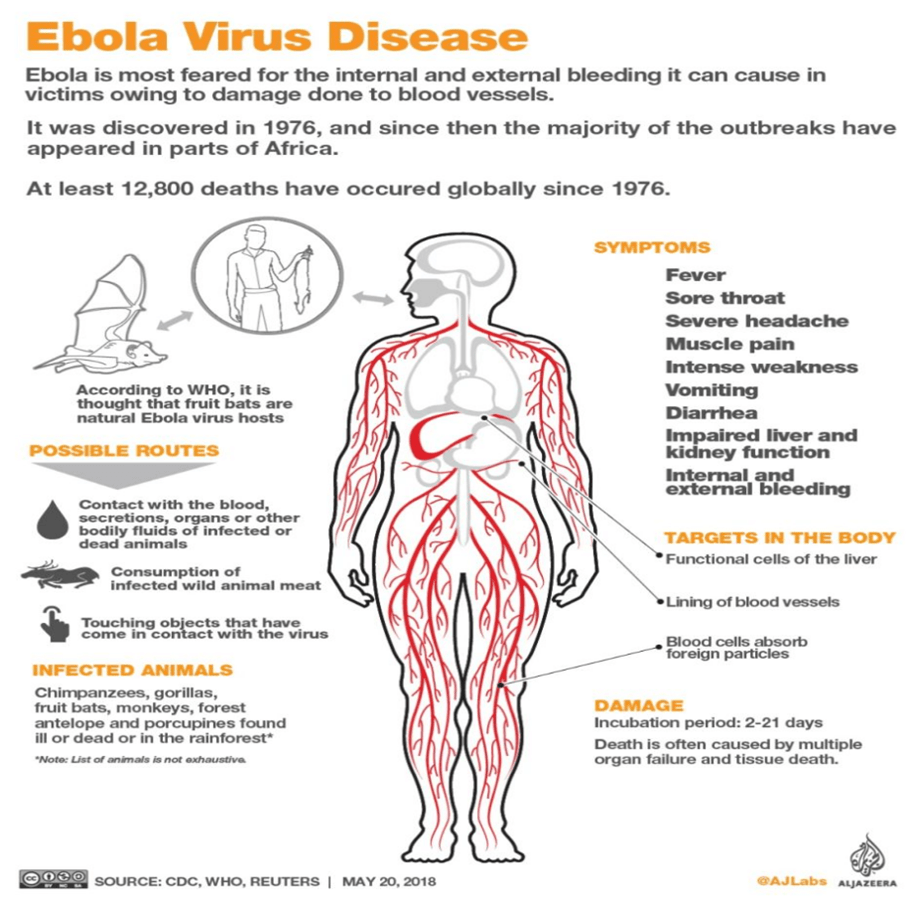
- Six different species of the virus have been found, but only four are known to cause disease in humans.
- Ebola is spread through direct contact with body fluids ― blood, saliva, sweat, tears, mucus, vomit, faeces, breast milk, urine and semen of people infected with it.
- It is also spread by touching things that have been contaminated with these fluids.
- The virus is named after the Ebola river (Republic of Congo ) — as a village situated on its bank witnessed the first instance of the viral outbreak in 1976.
Treatment:
- A vaccine for Ebola was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2019.
- It is a one-dose shot that protects against the variant of the Ebola virus that has caused the most serious outbreak so far.
- This vaccine is not likely to be effective against the Ebola Sudan strain that caused a 2022 outbreak in Uganda.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q,1) Consider the following statements in respect of probiotics :
- Probiotics are made of both bacteria and yeast.
- The organisms in probiotics are found in foods we ingest but they do not naturally occur in our gut.
- Probiotics help in the digestion of milk sugars.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2022)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
Q.2) In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent COVID-19 pandemic, consider the following statements:
- The Serum Institute of India produced COVID-19 vaccine named Covishield using mRNA platform.
- Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using vector based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims: Culture
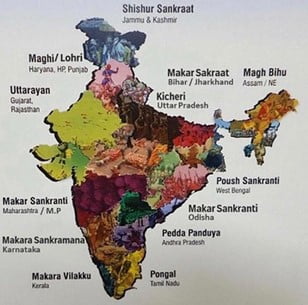
About: Lohri is celebrated on the last day of Paush month (12-13 January) In Punjab. Generally, after Lohri farmers start cutting their winter crops.
About Makar Sankrant
- Makar Sankranti is a festival day in the Hindu calendar, in reference to the deity Surya (sun).
- Makar Sankranti is observed according to solar cycles.
- It is held normally on the 14th of January, or a day before or after.
- In certain regions celebrations can go on for even four days and vary a lot in the rituals.
- It marks the – first day of sun’s transit into the Makara (Capricorn), marking the end of the month with the winter solstice and the start of longer days.
- It is also celebrated as a harvest Festival.
Different names of the same festival
- Makar Sankranti – Odisha, Maharashtra-Goa, Andhra-Telengana, Kerala and most of north India
- Paush Parbon – Bengal
- Pongal – Tamil Nadu
- Pongal is celebrated with the distribution of new crop “Shankarai Pongal” which is basically rice cooked in milk and jiggery distributed as a Prasadam.
- Bhogali Bihu – Assam
- The farmers of Assam celebrate and cherish the efforts of cultivation. It marks the beginning of Assamese New Year. Assamese celebrate Bihu thrice a year, which signify the distinct cycles of farming – Bhogali/Magh Bihu (January), Bohag/Rongali Bihu (April), and Kongali Bihu (October).
- Lohri – Punjab and Jammu
- Maghi – Haryana and Himachal
- Khichdi Parwa – parts of Bihar, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh
News Source: News on AIR
Syllabus
- Prelims: Governance
In News: Under the PM SVANidhi scheme loans worth around 4,606 crore rupees have been disbursed to over 45 lakh beneficiaries.
- Has provided a platform for financial inclusion by facilitating the street vendors to carry out digital transactions.
- Has enabled the onboarding of 9,326 street vendors on food delivery platforms.
About the Scheme
- Ministry of Housing & Urban Affairs launched a scheme PM Street Vendor’s Atma Nirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) to empower Street Vendors by not only extending loans to them, but also for their holistic development and economic upliftment.
- The scheme intends to facilitate collateral free working capital loans of up to INR10,000/- of one-year tenure, to approximately 50 lakh street vendors, to help resume their businesses in the urban areas, including surrounding peri-urban/rural areas.
The PM SVANidhi scheme offers incentives in the form of:
- Interest subsidy @ 7% per annum on regular repayment of loan
- Cashback upto INR1200/- per annum on undertaking prescribed digital transactions
- Eligibility for enhanced next tranche of loans
- Close to 2 million applications have been received under this scheme, of which 752191 have been sanctioned, and 218751 loans have already been disbursed.
Eligibility Criteria: The PM SVANidhi scheme is available to all street vendors who are engaged in vending in urban areas as on or before March 24, 2020. The eligible vendors are identified as per following criteria:
- Street vendors in possession of Certificate of Vending/Identity Card issued by Urban Local Bodies (ULBs).
- The vendors, who have been identified in the survey but have not been issued Certificate of Vending/Identity Card; Provisional Certificate of Vending would be generated for such vendors through an IT based Platform.
- ULBs are encouraged to issue such vendors the permanent Certificate of Vending and Identification Card immediately and positively within a period of one month
- Street Vendors, left out of the ULB led identification survey or who have started vending after completion of the survey and have been issued Letter of Recommendation (LoR) to that effect by the ULB/Town Vending Committee (TVC).
- The vendors of surrounding development/peri-urban/rural areas vending in the geographical limits of the ULBs and have been issued Letter of Recommendation (LoR) to that effect by the ULB/TVC.
About New Extension:
- Extension of lending period till December 2024;
- Introduction of 3rd loan of upto ₹50,000 in addition to 1st & 2nd loans of ₹10,000 and ₹20,000 respectively.
- To extend ‘SVANidhi Se Samriddhi’ component for all beneficiaries of PM SVANidhi scheme across the country.
News Source: News on AIR
Syllabus
- Prelims: Governance
In News: Telecom Regulatory Authority of India has released a Consultation Paper on Telecommunication Infrastructure Sharing, Spectrum Sharing and Spectrum Leasing.
Objective: To promote optimum resource utilization among the licensees – it is proposed to allow sharing of all kinds of telecom infrastructure and network elements among all categories of service providers.
Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI)
- It is a statutory body, established in 1997 by the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India Act, 1997
- It is headed by a chairman and not more than two full-time members and not more than two part-time members.
- TRAI is administered through a secretariat headed by a secretary.
- It comes under Ministry of Communications and Broadcasting.
- The TRAI Act was amended by an ordinance, effective from 24 January 2000, establishing a Telecommunications Dispute Settlement and Appellate Tribunal (TDSAT) to take over the adjudicatory and disputes functions from TRAI.
- TDSAT was set up to adjudicate any dispute between a licensor and a licensee, between two or more service providers, between a service provider and a group of consumers, and to hear and dispose of appeals against any direction, decision or order of TRAI.
- TRAI has brought out the Mycall app, MySpeed app and Do not disturb (DND 2.0) apps to ensure that there is transparency between what consumers are paying for and what telecom operators are promising to provide at a certain rate.
- Ensures welfare of citizens:
- to create and nurture conditions for growth of telecommunications in India to enable the country to have a leading role in the emerging global information society.
- to provide a fair and transparent environment that promotes a level playing field and facilitates fair competition in the market.
- issue orders and directions on various subjects such as tariffs, interconnections, quality of service, Direct To Home (DTH) services and mobile number portability.
- to regulate telecommunication services, adjudicate disputes, dispose appeals and protect the interest of the service providers as well as consumers.
- To establish standards for Quality of Services (QoS) and supervise how service providers share revenue
- To conduct periodical surveys to ensure that telecom service providers are acting in the best interest of consumers and are opening in compliance with universal service obligations.
- Recommend government or the license providers on Efficient management of available spectrum, the introduction of new service provider, Revocation of license for non-compliance, Technological improvements in the services and so on.
Connecting the dots:
Syllabus
- Prelims: Infrastructure
In News: PM Modi unveils inland waterways projects worth over Rs 1000 crore to increase transport, trade & tourism in eastern India.
- He flagged off World’s Longest River Cruise-MV Ganga Vilas at Varanasi.
- Declared that this is the decade of transformation of infrastructure in the country.
Potential of Waterways in India
India has great potential in waterways transport. In 2014 there were only five waterways in the country now this number is 111 and around two dozen are functional and transportation of cargo has increased triple times.
The inland water transport is a cheap, fuel-efficient, environment-friendly mode with a higher employment generation potential and is suitable for heavy and bulky goods. But, the share of inland water transport in total transport in India is only around 3.5 per cent.
Status of inland water transport:
- The Government of India is working to develop inland waterways as an alternative mode of transport in the country, which is cleaner and cheaper than both road and rail transport.
- There are 111 National Waterways in the country today, after 106 waterways were declared as National Waterways, adding to the list of 5 existing NW, in 2016. Some of the National Waterways in the country are already operational/navigable and are being used for transportation. Some of these include Ganga system, Brahmaputra system, etc.
- The Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) is working on developing the new National Waterways and enhancing their navigational potential. As per the feasibility reports completed so far, 36 NWs have been found to be technically viable. Out of these 36 NWs, developmental activities have been initiated on the following 8 NWs in 2017-18.
Exploring the untapped potential:
- RIS (River Information system) has been implemented in some places where RIS is a combination of tracking and meteorological equipment with specialized software designed to optimize traffic and transport processes in inland navigation.
- Moving a step ahead towards ensuring optimum use of National Waterways, the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) also launched a portal LADIS – Least Available Depth Information System.
- The Jal Marg Vikas Project (JMVP), for capacity augmentation of navigation on National Waterway-1 (NW-1), has also been approved.
- New integrated systems are being developed wherein the waterway will form part of a larger multi-modal transport network having linkage with the Eastern Dedicated Rail Freight Corridor and also with the area’s existing network of highways.
Economic benefits due to expansion of waterways:
- A well-coordinated inland waterways network could bring a fundamental alteration in the logistics scenario of the country. It represents a ready-built infrastructure network, which can be utilised without any further capital investment.
- Waterways do not involve challenges associated with land acquisition, which has always been a sensitive issue, causing time and cost overruns of numerous projects. The significant investment which India needs to build its roads/highways infrastructure network can be conserved through increased utilisation of the waterways.
- Waterways are a cheaper mode of transportation vis-à-vis the available alternatives, significantly reducing the point-to-point cost of goods transportation. As per a recent study of the Integrated National Waterways Transportation Grid, one litre of fuel will move 24 tons through one kilometre on road, 95 on rail and 215 kilometres on inland water transport.
- Movement of goods and passengers through inland waterways would necessitate setting up large number of landing and loading/unloading points. This has the potential to open up large and accessible hinterland for supply of goods which can be transported at a lower cost.
Implementation of the national waterways network is, however, fraught with challenges like –
- There is seasonal fall in water levels particularly rain-fed rivers of peninsular India which are almost dry during summer.
- Less flow of water due to diversion of water for irrigation. Hard for even steamboats to sail. Example: Ganga.
- Reduced navigability due to siltation, waterfalls and cataracts in rivers and salinity in coastal rivers.
- Dredging carried out to maintain a minimum depth of water may negatively affect the aquatic ecosystem, and entry of saline water into creeks in coastal areas.
- Lack of Public Funds: The financing requirement for NWs is huge and open-ended. Heavy investment will be needed to procure equipment, including dredgers, shipping vessels, and barges of different sizes.
- Disinterest by Private Players: Even after liberalisation and economic reforms, there has been very less active participation from private players in this sector.
- The channel draft of the national waterways is not uniform at 2 meters throughout the year, as is required. Some of these rivers are seasonal and do not offer navigability through the year.
- Around 20 out of the 111 identified national waterways have reportedly been found unviable.
- Further, all the identified waterways require intensive capital and maintenance dredging, which could be resisted by the local community on environmental grounds, including displacement fears, thereby posing implementation challenges.
Way Forward
- As every riverine system is unique and presents diverse challenges, separate studies based on a detailed micro-level review to assess viability need to be done for each, before taking up implementation.
- An effective waterways network would necessitate drawing up a well-coordinated strategy on lines of complementarity between the national network and other waterways, not declared as such, as well as between waterways and roadways/railways.
- The said strategy should closely look into the various undercurrents, including competing uses/needs, possible local resistance and also work closely and in coordination with local governments for quick and successful implementation of this important national project.
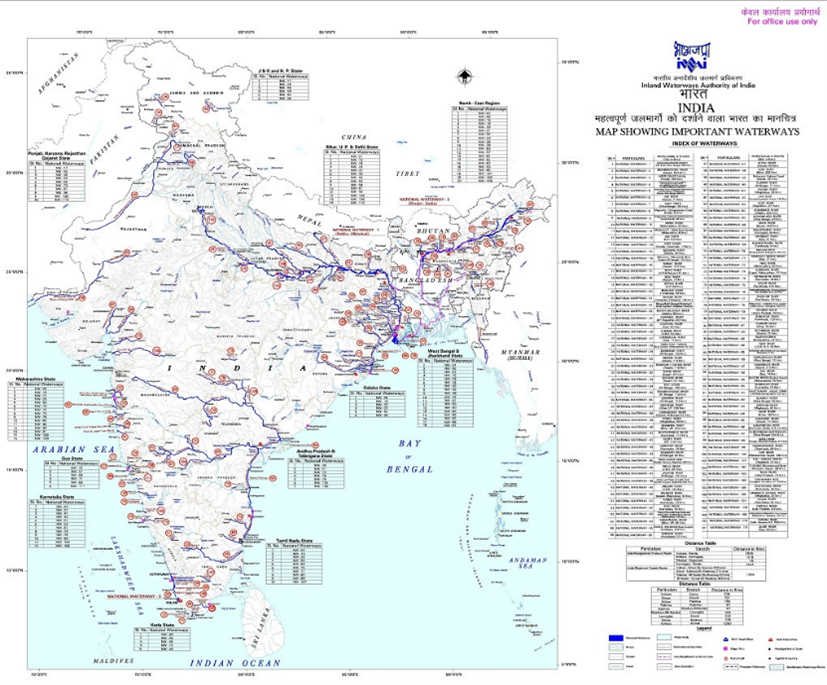
Map of important inland waterways [Source: Inland Waterways Authority of India]
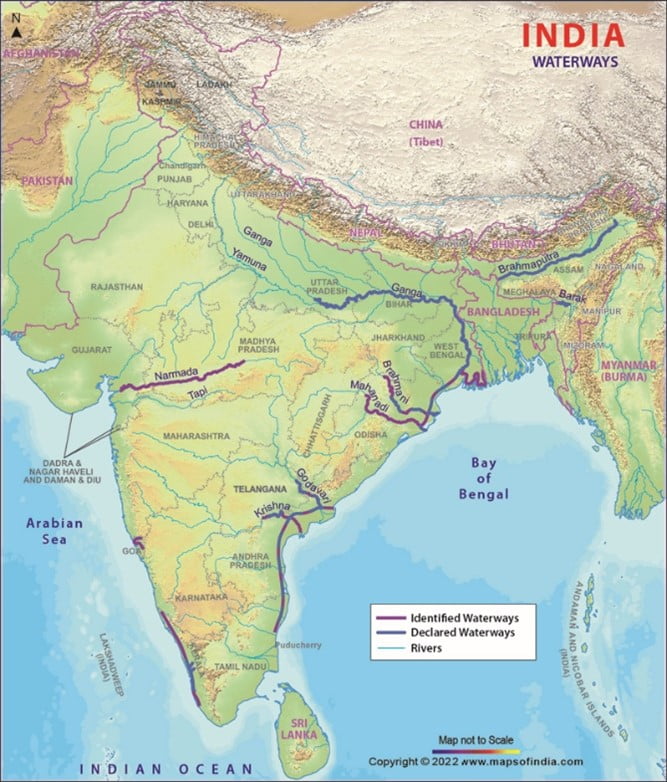
Image source: Maps of India
Source:
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently, the 5th Global Mental Health Summit, cosponsored by more than a half-dozen mental health organizations, was held in Chennai in December 2022 to discuss mental health in the context of human rights, ethics, and justice.
- It emphasized the importance of mental health and issued a call to action against society’s general neglect and, in particular, the governments at the federal and state levels.
About Mental Health:

- It is a state of mental well-being that enables people to cope with the stresses of life, realize their abilities, learn well and work well, and contribute to their community.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) defines health as ” a state of physical, mental, social and spiritual well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity”.
- WHO defines mental health as mental well-being in which an individual realizes his or her own abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and is able to contribute to his or her community.
- In this sense, mental health is the foundation for individual well-being and the efficient operation of a community.
- It is a basic human right. And it is crucial to personal, community, and socio-economic development.
Types of Mental Disorders:

Causes of Mental Illness:
- Individual psychological and biological factors such as emotional skills, substance use and genetics can make people more vulnerable to mental health problems.
- associated with them have had a detrimental effect on mental well-being
- Early adverse life experiences, such as trauma or a history of abuse (for example, child abuse, sexual assault, witnessing violence, etc.)
- Exposure to unfavourable social, economic, geopolitical and environmental circumstances – including poverty, violence, inequality and environmental deprivation – also increases people’s risk of experiencing mental health conditions.
- Over the past two years, the pandemic-led lockdowns and the uncertainties lead mental illness
- Use of alcohol or drugs
- Having feelings of loneliness or isolation.
Issues and Concerns associated with mental illness:
- Mental health problems have been growing rapidly over the last few decades.
- In 2015, the GOI carried out a National Mental Health Survey — 2015-16 to assess the prevalence of mental health in the country.
- The report showed mental disorders at 10.6 per cent among above 18-year-olds, 16 per cent among the productive age group of 30-49-year-olds — and lifetime morbidity affecting 150 million people with one per cent reporting high suicidal risk.
- The human resources and treatment facilities are woefully low.
- For policymakers, mental health is a low priority.
- Such poor policy attention is often ascribed to indifference among bureaucrats and politicians.
- Designing a policy is the most challenging piece of policy-making.
National Mental Health Survey
- The Government of India conducted a National Mental Health Survey — 2015-16 in 2015 to assess the prevalence of mental health in the country.
- According to the report, mental disorders affect 10.6 percent of people over the age of 18, 16 % of people in the productive age group of 30-49 years old, and 150 million people have lifetime morbidity, with one percent reporting a high suicidal risk. Even so, human resources and treatment facilities are woefully inadequate.
- Madhya Pradesh 0.05 psychiatrists per lakh people, and the treatment gap in India is approximately 80%.
- In 2019, the Union government allocated Rs 600 crore to tertiary institutions such as NIMHANS and medical college psychiatry departments, leaving only Rs 40 crore for the District Mental Health Programme and other community-based initiatives, despite an estimated need of over Rs 93,000 crore investment to address this massive morbidity.
- Only Rs 2.91 crore of the pitiable sum of Rs 40 crore was spent.
Need of Mental Health Policy
- Without the active participation of community leaders, implementation among the poorest and most marginalized, particularly criminalized groups, would have been impossible.
- Despite the fact that the central government fully funded the central sector program, each intervention was developed with active participation and dialogue among the states and, more importantly, the affected constituencies.
- A similar approach is required when developing a good, implementable mental health strategy.
- It is so intertwined with the type of society we live in — the pressures and stress caused by poverty and growing inequalities of opportunity, the frustrations of joblessness, the judgmental and discriminatory environment due to social barriers of caste, gender, religion, and so on are powerful triggers — that if completely unaddressed, the ailment can recur despite medication.
- The limitations of the biomedical approach and confining patients in hospitals are now recognized and supported by evidence.
- Mental health is even more complicated than HIV/AIDS because mental disorders are not a one-time ailment that can be cured with certain medications.
Government of India Initiatives:
- The Government has developed comprehensive Training Modules for Healthcare Providers to deal with Post COVID Mental Health Issues to equip Doctors, Nurses, paramedical healthcare workers, community health workers and other frontline workers with knowledge and skills to provide psychosocial support to those affected by post COVID mental health issues.
- the Government has announced a “National Tele Mental Health Programme” in the Budget of 2022-23, to further improve access to quality mental health counselling and care services in the country.
- As mandated by the Mental Healthcare Act, of 2017, mental healthcare services have been integrated into general healthcare services like National Health Mission, PMSSY, Rashtriya Kishore Swasthya Karyakram, AYUSHMAN Bharat, PMJAY, etc.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding The Association of Man-made Fibre Industry of India (AMFII):
- AMFII was registered as a Private Limited Company under section 25 A of the Companies Act 1956
- The Association also acts as a liaison body on behalf of the industry and communicates with the Chambers of Commerce
- The Association has its Registered Office in Delhi
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Q.2) The term “ Lantana Camara ” often mentioned in news, is related to
- Native plant species
- Malware
- Invasive plant species
- A bug
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding Ebola Disease:
- It is a fungal disease
- It is mainly found in animals
- It is spread through direct contact with body fluids ― blood, saliva, sweat, tears, mucus, vomit, faeces, breast milk, urine and semen of people infected with it.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 14th January 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 13th January – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – b











