IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
Context: Recently, Central Mine Planning and Design Institute Limited (CMPDIL) invented method for Controlling Generation and Movement of Fugitive Dust.
About New Dust Control Technology:
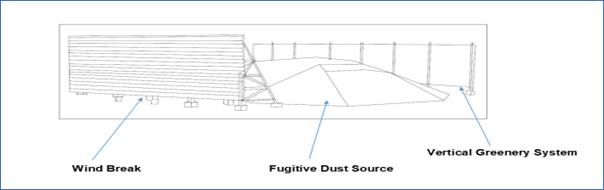
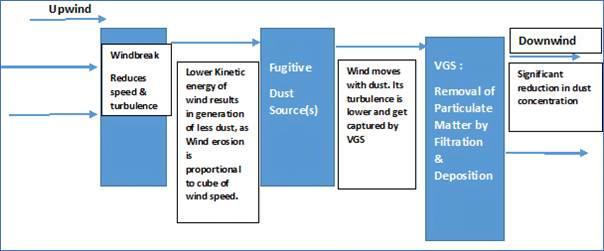
- It aims to minimize and control the fugitive dust in mining areas.
- Useful in Coal Mines, Thermal Power Plants, Railway Sidings and Ports
- It will help in reducing the dust generation from open sources.
- it will provide noise attenuation.
- Fugitive dust is a type of particulate matter that causes air pollution because it is produced by many sources but is released into the atmosphere without passing through a confined flow stream.
About Central Mine Planning and Design Institute Limited (CMPDIL):
- CMPDIL is a Government of India enterprise having its corporate headquarters at Ranchi in India.
- It is a fully owned subsidiary of Coal India Limited (CIL) and a Schedule-B company.
- It is a Mini Ratna (Category I) company since June 2019 and ISO 9001 certified since March 1998.
- In January 1974, CMPDI started functioning as a division of the then recently constituted Coal Mines Authority Limited (CMAL), and the planning wing of erstwhile National Coal Development Corporation (NCDC) forming its nucleus.
- In November 1975, CMAL was merged to form Coal India Limited, and CMPDI attained the status of a public limited company under CIL with declared scope of its business under its Memorandum of Association broadly in line with its original proposal.
Source: PIB
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Magnetite particles, suspected to cause neurodegenerative problems are generated as environmental pollutants from which of the following? (2022)
- Brakes of motor vehicles
- Engines of motor vehicles
- Microwave stoves within homes
- Power plants
- Telephone lines
Select the correct answer using the code given below
- 1, 2, 3 and 5only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 3, 4 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) “R2 Code of Practices” constitute a tool available for promoting the adoption of (2022)
- Environmentally responsible practices in the electronics recycling industry
- Ecological management of ‘’Wetlands of International Importance” under the Ramsar Convention
- Sustainable practices in the cultivation of agricultural crops in degraded lands
- ‘’Environmental Impact Assessment’’ in the exploitation of natural resources
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
Context: Four years since the Centre launched the National Clean Air Campaign (NCAP), analysts found that progress has been slow and pollution only incrementally reduced in most cities.
About National Clean Air Campaign:
- It was launched by the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change in January 2019.
- It is the first-ever effort in the country to frame a national framework for air quality management with a time-bound reduction target.
- It seeks to cut the concentration of coarse (particulate matter of diameter 10 micrometre or less, or PM10) and fine particles (particulate matter of diameter 2.5 micrometre or less, or PM2.5) by at least 20% in the next five years, with 2017 as the base year for comparison.
- The plan includes 103 non-attainment cities, across 23 states and Union territories, which were identified by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) on the basis of their ambient air quality data between 2011 and 2015.
- Non-attainment cities: These are those that have fallen short of the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for over five years.
About National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS):
- National Ambient Air Quality Standards are the standards for ambient air quality set by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
- The CPCB has been conferred this power by the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
- Ambient Air Quality Standards contains 12 pollutants.
- The pollutants that are covered under the NAAQS include: Sulphur dioxide (SO2), Nitrogen dioxide (NO2), PM10, PM2.5, Ozone, Lead, Carbon monoxide (CO), Arsenic, Nickel, Benzene, Ammonia, and Benzopyrene.
About Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB):
- The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), statutory organisation, was constituted under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974.
- Further, CPCB was entrusted with the powers and functions under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
- It serves as a field formation and also provides technical services to the Ministry of Environment and Forests of the provisions of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- Principal Functions of the CPCB, as spelt out in the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974, and the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981,
- to promote cleanliness of streams and wells in different areas of the States by prevention, control and abatement of water pollution, and
- to improve the quality of air and to prevent, control or abate air pollution in the country.
- The National Air Monitoring Programme (NAMP) has been established with objectives to determine the present air quality status and trends and to control and regulate pollution from industries and other source to meet the air quality standards. It also provides background air quality data needed for industrial siting and towns planning.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) In the Guidelines, statements: context of WHO consider the Air Quality following
- The 24-hour mean of PM2.5 should not exceed 15 ug/m³ and annual mean of PM 2.5 should not exceed 5 µg/m³.
- In a year, the highest levels of ozone pollution occur during the periods of inclement weather.
- PM10 can penetrate the lung barrier and enter the bloodstream.
- Excessive ozone in the air can trigger asthma.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1 and 4 only
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1 and 2 only
Q.2) Which one of the following has been constituted under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986? (2022)
- Central Water Commission
- Central Ground Water Board
- Central Ground Water Authority
- National Water Development Agency
Q.3) Which one of the following best describes the term “greenwashing”? (2022)
- Conveying a false impression that a company’s products are eco-friendly and environmentally sound
- Non-inclusion of ecological/ environmental costs in the Annual Financial Statements of a country
- Ignoring the consequences disastrous ecological while infrastructure development undertaking
- Making mandatory provisions for environmental costs in a government project/programme
Syllabus
- Prelims – History
Context: Recently the former in-charge of the Gandhi Smarak Bhawan in Punjab was arrested and remanded him in three days of police custody.
About Gandhi Smarak Bhavan:
- Gandhi Smarak Nidhi (GSN) was established by the Indian National Congress after the martyrdom of Mahatma Gandhi in 1948.
- It was inaugurated by Dr. Zakir Hussain then Vice-President of India.
- It is being run by GANDHI SMARAK NIDHI PUNJAB, HARYANA and HIMACHAL PRADESH and since its inception is contributing its share in spreading Gandhian thought and Ideology through Seminar, Meetings, Discussions and personal contacts.
- The ad hoc committee constituted as per the decision taken in February 1948 included great national leaders – Dr. Rajendra Prasad, Pt. Jawahar Lal Nehru, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, Chakravarty Rajagopalachari, Maulana Abdul Kalam Azad and Shri Jagjivan Ram amongst many others.
- In December 1948 the GSN was constituted as a public charitable Trust having a 24 member Board of Trustees including the above national leaders along with other equally eminent national leaders.
- The main purposes of the fund was to further the manifold constrictive activities in which Gandhiji was interested, and to preserve and propagate his teachings.
- When in 1966 the Punjab State divided into three states then Trust renamed as Gandhi Smarak Nidhi Punjab, Haryana and Himachal Pradesh.
- The Nidhi’s headquarter is situated in Swadhyay Ashram, Village Pattikalyana, Tehsil Samalkha, District Panipat, Haryana (India).
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Who among the following is associated with ‘Songs from Prison’, a translation of ancient Indian religious lyrics in English? (2021)
- Bal Gangadhar Tilak
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi
- Sarojini Naidu
Q.2) With reference to the British colonial rule in India, consider the following statements:
- Mahatma Gandhi was instrumental in the abolition of the system of ‘indentured labour’
- In Lord Chelmsford’s ‘War Conference’, Mahatma Gandhi did not support the resolution on recruiting Indians for World War.
- Consequent upon the breaking of Salt Law by Indian people, the Indian National Congress was declared illegal by the colonial rulers.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2019)
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Google has said that the order passed by India’s competition regulator — the Competition Commission of India (CCI) — against Android’s operating system policies will result in devices getting expensive in India and lead to proliferation of unchecked apps that will pose threats for individual and national security.
About Competition Commission of India:
- The Competition Commission of India has been established to enforce the competition law under the Competition Act, 2002.
- It comes under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- It should be noted that on the recommendations of Raghavan committee, the Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Act, 1969 (MRTP Act) was repealed and replaced by the Competition Act, 2002.
- The Commission consists of a Chairperson and not more than 6 Members appointed by the Central Government.
- It is the statutory duty of the Commission to eliminate practices having an adverse effect on competition, promote and sustain competition, protect the interests of consumers and ensure freedom of trade carried on by other participants, in markets in India as provided in the Preamble as well as Section 18 of the Act.
- The Commission is also mandated to give its opinion on competition issues to government or statutory authority and to undertake competition advocacy for creating awareness of competition law.
- Advocacy is at the core of effective competition regulation.
- Competition Commission of India (CCI), which has been entrusted with implementation of law, has always believed in complementing robust enforcement with facilitative advocacy.
- It is a quasi-judicial body.
- CCI also approves combination under the act so that two merging entities do not overtake the market.
The Competition Act
- The Competition Act, 2002, as amended by the Competition (Amendment) Act, 2007, follows the philosophy of modern competition laws.
- The Act prohibits anti-competitive agreements, abuse of dominant position by enterprises and regulates combinations (acquisition, acquiring of control and M&A), which causes or likely to cause an appreciable adverse effect on competition within India.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to foreign-owned e-commerce firms operating in India, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- They can sell their own goods in addition to offering their platforms as market-places.
- The degree to which they can own big sellers on their platforms is limited.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements are correct?
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends for the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps the Public Sector Banks in developing strategies and capital raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
In News: A sharp 61.2% sequential rise in capital spending by the Central and State governments lifted fresh investment plans announced in the third quarter (Q3) of 2022-23 to ₹7.1 lakh crore, even though private sector investments dropped 41% from ₹6.31 lakh crore in Q2 to ₹3.71 lakh crore between October and December 2022.
- Rising input costs, hardening interest rates and the slowdown expected in developed economies are the headwinds making mid-size Indian companies go slow on their investment plans
- However, all other major sectors posted positive growth in terms of fresh investments during the first nine months of 2022-23.
Capital Expenditure:
- Capital expenditure is the money spent by the government on the development of long term assets such as machinery, equipment, building, health facilities, education, etc.
- It also includes the expenditure incurred on acquiring fixed assets like land and investment by the government that gives profits or dividend in future.
- Capital spending is associated with investment or development spending, where expenditure has benefits extending years into the future.
- It includes – Acquiring fixed and intangible assets, Upgrading an existing asset, Repairing an existing asset, Repayment of loan
Significance of capital expenditure:
- It allows the economy to generate revenue for many years by adding or improving production facilities and boosting operational efficiency.
- It also increases labour participation, takes stock of the economy and raises its capacity to produce more in future.
- Repayment of loan is also capital expenditure, as it reduces liability.
Revenue expenditure:
- Unlike capital expenditure, which creates assets for the future, revenue expenditure is one that neither creates assets nor reduces any liability of the government.
- Salaries of employees, interest payment on past debt, subsidies, pension, etc, fall under the category of revenue expenditure. It is recurring in nature.
Source: The hindu
Previous Year Question
Q1) If the interest rate is decreased in an economy, it will (2014)
- decrease the consumption expenditure in the economy
- increase the tax collection of the Government
- increase the investment expenditure in the economy
- increase the total savings in the economy
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
In News: The Securities and exchange board of India has allowed alternative investment funds) to participate in credit default swaps (CDS) as protection for both buyers and sellers.
- Category I and Category II AIFs may buy CDS on underlying investment in debt securities, only for the purpose of hedging.
- Category III AIFs may buy CDS for hedging or otherwise, within permissible leverage
- Credit default swap market is very illiquid at present.
Alternate Investment Fund(AIFs):
- In India, AIFs are defined in Regulation 2(1) (b) of Securities and Exchange Board of India (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012.
- Meaning – It refers to any privately pooled investment fund, (whether from Indian or foreign sources), in the form of a trust or a company or a body corporate or a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP).
- They include angel funds, commodities, real estate, venture capital, private equity, etc.
- Categories of AIFs
- Category I: Mainly invests in start- ups, SME’s or any other sector which Govt. considers economically and socially viable
- Category II: private equity funds or debt funds for which no specific incentives or concessions are given by the government or any other Regulator
- Category III : hedge funds or funds which trade with a view to make short term returns or such other funds which are open ended and for which no specific incentives or concessions are given by the government
Benefits of AIF:
- Security against volatility – These schemes do not put their funds in investment options that trade publicly. Hence, they are not related to the broader markets and do not fluctuate with their ups and downs.
- Excellent portfolio diversification to a wide array of assets
- Profitable returns – as these funds have numerous investment options, They are a better source of passive income. Further, returns are less prone to fluctuations as these schemes are not linked to the stock market.
Credit Default Swap (CDS)
- They are a type of insurance, introduced by JP Morgan
- It is used for hedging counter-party concentration risk and credit risks
- It is a contract between two parties, called protection buyer and protection seller against default risk by a particular company.
- The company is called the reference entity and the default is called credit event.
- Under the contract, the protection buyer is compensated for any loss emanating from a credit event in a reference instrument. In return, the protection buyer makes periodic payments to the protection seller.
- In the credit event, the buyer receives the face value of the bond or loan from the protection seller.
- From the seller’s perspective, CDS provides a source of easy money if there is no credit event.
- If the credit event does not occur before the maturity of the loan, the protection seller does not make any payment to the buyer.
- The settlement of the CDS takes place either through cash settlement or physical settlement.
- There are different varieties of CDS, like binary CDS, basket CDS, contingent CDS and dynamic CDS.
- There are different types of credit events such as bankruptcy, failure to pay, and restructuring.
- Asset-backed securities (ABS) is the most common type of CDS.
- CDS can be structured either for the event of shortfall in principal or shortfall in interest. There are three options for calculating the size of payment by the seller to the buyer.
- Fixed cap: The maximum amount paid by the protection seller is the fixed rate.
- Variable cap: The protection seller compensates the buyer for any interest shortfall and the limit set is Libor plus fixed pay.
- No cap: In this case, the protection seller has to compensate for shortfall in interest without any limit.
Calculation:
- The modelling of the CDS price is based on modelling the probability of default and recovery rate in the event of a credit event.
- The value of CDS for the protection buyer = Expected present value of the contingent leg – Expected present value of fixed leg
- In the real world, modelling of the CDS price is difficult because of the problem in computing default probabilities and default correlation.
Uses:
- Although used for hedging credit risks, credit default swap (CDS) has been held culpable for vitiating financial stability of an economy.
- This is particularly attributable to the capital inadequacy of the protection sellers.
- When big protection sellers are inadequately capitalised, the over-the-counter (OTC) CDS market raises its ugly head.
Sources: Financialexpress
Previous Year Question
Q.1) What does venture capital mean? (2014)
- A short-term capital provided to industries
- A long-term start-up capital provided to new entrepreneurs
- Funds provided to industries at times of incurring losses
- Funds provided for replacement and renovation of industries
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
In News: Union Minister of State Science & Technology; Minister of State Earth Sciences; MoS PMO, Personnel, Public Grievances, Pensions, Atomic Energy and Space said, Entire Country will be covered by Doppler Weather Radar Network by 2025
- According to the Annual Statement on Climate of India 2022 issued by the India Meteorological Department (IMD), 2,227 extreme weather-related deaths in India.
Doppler Weather Radar Network:
- Aim – to predict extreme weather events more accurately.
- Doppler radar is a specialized tracking system that uses the Doppler effect to track weather conditions and calculate information about the location and velocity of a storm or other forms of extreme weather events.
- Forecasting with the help of doppler radar is more timely and accurate which can be critical during safe evacuations in the likelihood of extreme weather events.
- IMD has augmented Doppler Weather Radar network in HP, Uttarakhand, Ladakh and J&K which will help further to predict extreme weather events more accurately.
- Accuracy has increased by about 20-40% for different severe weather events forecast during last five years by making best use of Space based observation of INSAT-3D and 3DR, OceanSat satellites for prediction
Benefits:
- Warning and advisory services are helping farmers and fishermen to improve their economy as found from a latest survey by National Centre for Applied Economic Research. For example, the investment in monsoon mission programme has resulted in return of 50 rupees for investment of each one rupee.
- Farmers below the poverty line specially have benefited immensely as Agromet Advisories at District and Block Levels are used effectively by crores of farmers during various stages of farming and the service is being expanded.
- Climate Services are very important for short and long term planning and strategy development
- Soon a National Framework will be created on priority to provide climate products and information for Sectoral applications.
Other initiatives:
- Flash Flood Guidance in 2021 has been augmented further by increasing the number of watersheds from 30,000 to 1,00,000 of the country in 2022.
- It is being provided every 6 hours to Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka apart from our national use.
- The web GIS services launched by IMD in 2021 have been augmented further with addition of hazard and vulnerability element in collaboration with other state and central agencies is helping the public, disaster managers and stakeholders to initiate timely response action to mitigate the disasters further
Doppler effect
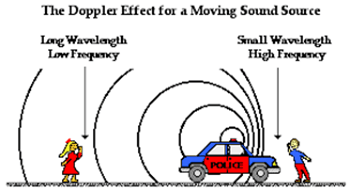
- Doppler Effect refers to the change in Wave Frequency during the relative motion between a wave source and its observer.
- It was discovered by Christian Johann Doppler who described it as the process of increase or decrease of starlight that depends on the relative movement of the star.
- Doppler Effect works on both light and sound objects.
- For instance, when a sound object moves towards you, the frequency of the sound waves increases, leading to a higher pitch.
- Conversely, if it moves away from you, the frequency of the sound waves decreases and the pitch comes down.
- The drop in pitch of ambulance sirens as they pass by and the shift in red light are common examples of the Doppler Effect.
- Edwin Hubble made the discovery that the universe expands as a consequence of the Doppler Effect. It has important applications in the fields of astronomy and space technology.
- The use of Doppler Effect in astronomy in relation to light waves depends on the fact that the spectra of stars are not constant.
- Different stars exhibit different absorption lines at defined frequencies, but Doppler Effect is identifiable only when these absorption lines are away from these defined frequencies.
- There are various applications of Doppler Effect. It is used in:
- Sirens
- Astronomy
- Radar
- Medical imaging and blood flow managemen
- Flow management
- Velocity profile management
- Satellite communication
- Audio
- Vibration measurement
Source: PIB
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2018)
- Light is affected by gravity.
- The Universe is constantly expanding.
- Matter warps its surrounding space-time.
Which of the above is/are the prediction/predictions of Albert Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity, often discussed in media?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
In News: The Annual Meeting of World Economic Forum (WEF) will begin at Davos in Switzerland.
- The theme for this year’s WEF meeting is, ‘Cooperation in a Fragmented World’.
World Economic Forum (WEF)
- It is a Swiss nonprofit foundation established in 1971, based in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It is recognised by the Swiss authorities as an international institution for public-private cooperation.
- The Founder and Executive Chairman of WEF is Klaus Schwab
Mission
- WEF is committed to improving the situation of the world by engaging business, political, academic, and other leaders of society to shape global, regional, and industry agendas.
Major reports by WEF
- Energy Transition Index
- Global Competitiveness Report
- Global IT Report (WEF along with INSEAD, and Cornell University publishes this report),
- Global Gender Gap Report
- Global Risk Report
- Global Travel and Tourism Report
Source: NewsOnAIR
Previous Year Question
Q.1) The Global Competitiveness Report is published by the (2019)
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
- World Economic Forum
- World Bank
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently, the Supreme Court reprimanded the government for its failure to stop hate speech and hate crimes in the country.
About Hate Speech:
- Hate speech is defined as any speech, gesture, conduct, writing, or display that may incite violence or prejudicial action against or by any individual or group, or because it disparages or intimidates a particular individual or group.
Significance of Curbing Hate Speech:
- It is used to provoke individuals or society to commit acts of terrorism, genocides, ethnic cleansing etc.
- It undermines social equality as it reaffirms historical marginalization, oppression & discrimination.
- It is enacted to cause psychological and physical harm to its victims as it incites violence.
- It is a tool to create panic through rumour mongering against targeted people. For example, the Northeast exodus.
Laws and regulations on hate speech in India: In India, hate speech is regulated by several laws and acts, including the Indian Penal Code (IPC), the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC), and the Indian Information Technology (IT) Act.
- Indian Penal Code (IPC): It contains provisions that prohibit hate speech, such as :
- Section 153A: It deals with actions promoting enmity between different groups on grounds of religion, race, place of birth, residence, language, etc., and doing acts prejudicial to maintenance of harmony.
- Section 295A: It deals with deliberate and malicious acts, intended to outrage religious feelings of any class by insulting its religion or religious beliefs.
- Section 505: It pertains to statements creating or promoting enmity, hatred or ill-will between classes)
- Indian Information Technology (IT) Act: It regulates online speech, including hate speech. Under the act, intermediaries such as social media platforms are required to remove content that is in violation of the law within 36 hours of being notified.
- Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC): It provides for the arrest of individuals who have committed a cognizable offense, such as hate speech.
- Representation of People’s Act(1951):
- Section 8: It prevents a person convicted of the illegal use of the freedom of speech from contesting an election.
- Sections 123(3A) and 125 of the RPA: It bars the promotion of animosity on the grounds of race, religion, community, caste, or language in reference to elections and includes it under corrupt electoral practices.
- Court Judgements: In the past, The Supreme court of India has issued several judgments on hate speech.
- Shreya Singhal v. Union of India (2015): The court struck down Section 66A of the IT Act, which had criminalized online speech, stating that it violated the right to freedom of speech and expression.
- Sukumar v. State of Tamil Nadu (2019): The court held that hate speech on social media platforms is not protected by the right to freedom of speech and expression.
- Freedom of speech: The right to freedom of speech is protected under Article 19 of the Constitution but it is not absolute and can be limited in certain circumstances, such as when it incites violence or discrimination.
- Online Hate speech: The internet has made it easier for hate speech to spread, and many social media platforms have policies in place to address hate speech on their platforms.
- However, the effectiveness of these policies can be limited, and more needs to be done to combat online hate speech.
- Prevention: It begins with education, raising awareness about the harmful effects of hate speech and promoting tolerance and inclusivity.
- In this regard, the government, civil society organizations and communities at large can play a role in preventing hate speech.
Challenges before curbing Hate speech:
- Defining hate speech: There is no universally accepted definition of hate speech, and different countries and cultures have different norms and expectations in this area.
- This makes it difficult to establish clear guidelines for what constitutes hate speech and what does not.
- Addressing hate speech by public figures and politicians: Expression of hate is not limited to anonymous internet users, public figures and politicians also contribute to spreading hate speech.
- However, due to their public platform, it may be challenging to hold them accountable for their statements.
- Identifying and removing hate speech online: The vast majority of hate speech takes place online, and it can be difficult to identify and remove this content.
- Platforms like Facebook and Twitter have struggled to effectively moderate hate speech, and there is no consensus on how to approach this problem.
- Balancing free speech and hate speech: Hate speech laws are often viewed as a restriction on free speech. This can lead to legal challenges and pushback from civil liberties groups.
- Addressing hate speech in non-English languages: Hate speech is not limited to English-speaking countries, and it can be difficult to identify and remove hate speech in other languages. Additionally, cultural and linguistic nuances may not be well understood by those trying to moderate content.
- Lack of resources and legal framework: Many countries lack the resources and legal framework to effectively address hate speech.
- This can make it difficult to enforce laws and regulations, and it can also create a sense of impunity for those who engage in hate speech.
Way Forward:
India has a diverse population with different languages, religions, and cultures, thus there is a need to curb incidents of hate speech and crimes that can have a detrimental impact on individuals and communities. It is a complex and multifaceted issue that poses significant challenges for regulators and policymakers which will require a multifaceted approach that includes education, technology, and legal enforcement.
Thus, it becomes important for governments, civil society organizations, and individuals to work together to combat hate speech and promote a more inclusive and tolerant society.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 Science and Technology
Context:
- In William Golding’s famous novel, Lord of the Flies, Jack emphasises the importance of following rules and establishing a system of governance among the boys.
- Self-regulation or no regulation can be disastrous at times.
- This lesson is particularly relevant in the context of Artificial Intelligence (AI) regulations and deepfakes in India.
Deep synthesis:
- It is defined as the use of technologies, including deep learning and augmented reality, to generate text, images, audio and video to create virtual scenes.
- One of the most notorious applications of the technology is deepfakes, where synthetic media is used to swap the face or voice of one person for another.
Deepfakes
- It leverages powerful techniques from machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) to manipulate or generate visual and audio content with a high potential to deceive.

Methodology:
- A neural network needs to be trained with lots of video footage of the person – including a wide range of facial expressions, under all kinds of different lighting, and from every conceivable angle – so that the artificial intelligence gets an in-depth ‘understanding’ of the essence of the person in question.
- The trained network will then be combined with techniques like advanced computer graphics in order to superimpose a fabricated version of this person onto the one in the video.
- The very latest technology, however, such as Samsung AI technology that has been created in a Russian AI lab, makes it possible to create deepfake videos using only a handful of images, or even just one.
Application examples:
- Deepfake technology will enable us to experience things that have never existed, or to envision a myriad of future possibilities.
- Researchers at Samsung’s AI lab in Moscow, for instance, recently managed to transform Da Vinci’s Mona Lisa into video.
- Editing video footage without the need for doing reshoots, or recreating artists that are no longer with us to perform their magic, live.
- Produce speech from text and edit it just like you would images in Photoshop
- For example, Adobe’s VoCo software
- Deep generative models offer new possibilities in healthcare
- help researchers develop new ways of treating diseases without being dependent on actual patient data
Issues:
- Lack of proper regulations creates avenues for individuals, firms and even non-state actors to misuse AI.
- Legal ambiguity, coupled with a lack of accountability and oversight, is a potent mix for a disaster.
- Policy vacuums on deepfakes are a perfect archetype of this situation.
- Since they are compelling, deepfake videos can be used to spread misinformation and propaganda.
- They seriously compromise the public’s ability to distinguish between fact and fiction.
- There has been a history of using deepfakes to depict someone in a compromising and embarrassing situation. For instance, there is no dearth of deepfake pornographic material of celebrities.
- Such photos and videos do not only amount to an invasion of privacy of the people reportedly in those videos, but also to harassment.
- Deepfakes have been used for financial fraud.
- Recently, scammers used AI-powered software to trick the CEO of a U.K. energy company over the phone into believing he was speaking with the head of the German parent company. As a result, the CEO transferred a large sum of money — €2,20,000 — to what he thought was a supplier.
- The audio of the deepfake effectively mimicked the voice of the CEO’s boss, including his German accent.
Creating tensions in the neighbourhood:

- There are three areas where deepfakes end up being a lethal tool in the hands of India’s non-friendly neighbours and non-state actors to create tensions in the country.
- Influence elections
- Recently, Taiwan’s cabinet approved amendments to election laws to punish the sharing of deepfake videos or images due to becoming increasingly concerned that China is spreading false information to influence public opinion and manipulate election outcomes
- Espionage activities
- Doctored videos can be used to blackmail government and defence officials into divulging state secrets.
- In 2019, the Associated Press identified a LinkedIn profile under the name Katie Jones as a likely front for AI-enabled espionage.
- In March 2022, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky revealed that a video posted on social media in which he appeared to be instructing Ukrainian soldiers to surrender to Russian forces was actually a deepfake.
- These deepfakes could be used to radicalise populations, recruit terrorists, or incite violence.
- Deny the authenticity of genuine content, particularly if it shows them engaging in inappropriate or criminal behaviour, by claiming that it is a deepfake.
- This could lead to the ‘Liar’s Dividend,’ – This refers to the idea that individuals can exploit the increasing awareness and prevalence of deepfake technology to their advantage by denying the authenticity of certain content.
Legislation and challenges:
- Currently, very few provisions under the Indian Penal Code (IPC) and the Information Technology Act, 2000 can be potentially invoked to deal with the malicious use of deepfakes.
- Section 500 of the IPC provides punishment for defamation.
- Sections 67 and 67A of the Information Technology Act punish sexually explicit material in explicit form.
- The Representation of the People Act, 1951, includes provisions prohibiting the creation or distribution of false or misleading information about candidates or political parties during an election period.
- The Election Commission of India has set rules that require registered political parties and candidates to get pre-approval for all political advertisements on electronic media, including TV and social media sites, to help ensure their accuracy and fairness.
- However, these rules do not address the potential dangers posed by deepfake content.
- There is often a lag between new technologies and the enactment of laws to address the issues and challenges they create.
- In India, the legal framework related to AI is insufficient to adequately address the various issues that have arisen due to AI algorithms.
Suggestions:
- The Union government should introduce separate legislation regulating the nefarious use of deepfakes and the broader subject of AI.
- Legislation should not hamper innovation in AI, but it should recognise that deepfake technology may be used in the commission of criminal acts and should provide provisions to address the use of deepfakes in these cases.
- Antivirus for deepfakes – Sensity, an Amsterdam-based company that develops deep learning technologies for monitoring and detecting deepfakes, has developed a visual threat intelligence platform that uses the same deep learning processes used to create deepfakes, combining deepfake detection with advanced video forensics and monitoring capabilities.
- Social media deepfake policies – For instance, Instagram’s and Facebook’s policy is to remove ‘manipulated media’ – with the exception of parodies.
Best practices from the world:
- The European Union’s Code of Practice 2018
- It brought together for the first time worldwide industry players to commit to counter disinformation.
- Signed by online platforms Facebook, Google, Twitter and Mozilla, as well as by advertisers and other players in the advertising industry including Microsoft and TikTok.
- If found non-compliant, these companies can face fines as much as 6% of their annual global turnover.
- U.S’s bipartisan Deepfake Task Force Act 2021
- To assist the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) to counter deepfake technology.
- The measure directs the DHS to conduct an annual study of deepfakes — assess the technology used, track its uses by foreign and domestic entities, and come up with available countermeasures to tackle the same.
- China’s new policy to curb deepfakes
- The policy requires deep synthesis service providers and users to ensure that any doctored content using the technology is explicitly labelled and can be traced back to its source.
- Further, it requires to take the consent of the person in question
Way forward:
- We can’t always rely on the policy of self-regulation hence regulations are much needed in the field of AI such as the proposed Digital India Bill
- In order to minimise deception and curb the undermining of trust, technical experts, journalists, and policymakers will play a critical role in speaking out and educating the public about the capabilities and dangers of synthetic media.
- With increased public awareness, we could learn to limit the negative impact of deepfakes, find ways to co-exist with them, and even benefit from them in the future.
Source The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q.1) With reference to ‘Alternate Investment Fund’, consider the following statements
- It is directly affected by volatility in securities market.
- It is regulated by The Reserve Bank of India.
Which of the following statements are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Energy Transition Index is published by the
- International Energy Agency
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
- International Atomic Energy Agency
- World Economic Forum
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding Central Mine Planning and Design Institute Limited (CMPDIL):
- It is a fully owned subsidiary of Coal India Limited (CIL).
- It is a Government of India enterprise having its corporate headquarters at Ranchi in India
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 16th January 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 14th January – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – d











