IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Modern Indian History
Context: Recently, after objections, ICHR stopped singing the daily national anthem, and removed the images of Bharat Mata and Deen Dayal Upadhyaya.
About THE INDIAN COUNCIL OF HISTORICAL RESEARCH (ICHR) :
- The Indian Council of Historical Research (ICHR) is an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Education, Government of India.
- It was established by the Ministry of Education & Social Welfare, Govt. of India (now, Ministry of Education) in 1972.
- ICHR was registered under the Societies Registration Act (Act xxi of 1860), an Act for the registration of Literary, Scientific and Charitable Societies in India.
- The primary aim and objective of the Indian Council of Historical Research are to promote and give directions to historical research and to encourage and foster objective and scientific writing of history.
- Some of the objectives of the Council:
- To foster objective and scientific writing of history such as to inculcate an informed appreciation of the country’s national and cultural heritage;
- To review the progress of historical research from time to time.
- To advise the Government of India on all such matters pertaining to historical research and training in history methodology as may be referred to it from time to time.
- To sponsor historical research programmes.
- To provide technical assistance for the formulation of historical research programmes by individuals or institutions.
- To promote publications of historical research of a high standard
- Generally, take all such measures as may be found necessary from time to time to promote historical research and its utilization in the country.
Functions:
- To provide fellowships and financial assistance to young teachers in colleges, universities and registered research organizations,
- To publish a biannual Journal – the Indian Historical Review, and another journal Itihas in Hindi.
- To maintain a large and expanding Library-cum-Documentation Centre with facilities of DELNET and J-STOR.
- To maintain two regional centres namely ICHR North-East Regional Centre (Guwahati) and ICHR Southern Regional Centre (Bangalore)
MUST READ : About Pandit Deen Dayal Upadhyay
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following freedom fighters: (2022)
- Barindra Kumar Ghosh
- Jogesh Chandra Chatterjee
- Rash Behari Bose
Who of the above was/were actively associated with the Ghadar Party?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Q.2) Who among the following is associated with ‘Songs from Prison’, a translation of ancient Indian religious lyrics in English? (2021)
- Bal Gangadhar Tilak
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi
- Sarojini Naidu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has sought a “factual report” on the rhino population enumeration conducted in the Kaziranga National Park in March 2022.
About Kaziranga National Park:
- Kaziranga National Park is a prestigious national park of India situated in the northeastern part of the country in the district of Golaghat and Nagoan in the state of Assam.
- It was created in the year of 1904.
- It was declared a National Park in 1974.
- It was declared a tiger reserve in 2007.
- Kaziranga was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO for its unique natural environment in the year of 1985.
- The park has been identified as an Important Bird Area by the Birdlife International Society as it is home to various species of migrating and inhabitant birds.
- It is situated on the banks of the river Brahmaputra.
- It is majorly known for the ‘big four’ species— Rhino, Elephant, Royal Bengal tiger, and Asiatic water buffalo.
- The National Highway 37 passes through it.
- The Diphlu River runs through it.
- The landscape is marked by: Tropical moist mixed deciduous forests and tropical semi-evergreen forests, tall grasses, open jungle, and short grasses .
About the One -horned Rhino:
- The greater one-horned rhino (or “Indian rhino”) is the largest of the rhino species.
- It is found in Nepal, Bhutan, Pakistan and India.
- It is Vulnerable in the IUCN Red List and lies in Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act.
- It is in Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES):
- India is home to over 85 % population. It is found in UP, West Bengal and Assam.
- According to WWF data from 2012, Assam has 91 % of the total Rhino in India which is mainly concentrated in Kaziranga National Park, and Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary. Others include Manas Tiger Reserve, Orang Tiger Reserve and Laokhowa Reserved Forests
- There are five rhino species:
-
- Great One horned rhino- Vulnerable in the IUCN Red List.
- White rhinos – near threatened in the IUCN Red List.
- Black rhinos in Africa – critically endangered in the IUCN Red List.
- Javan rhino- Critically endangered in IUCN Red List.
- Sumatran rhinos- extinct.
- There are three species of rhino in Asia—Greater one-horned (Rhinoceros unicornis), Javan and Sumatran.
- Only the Great One-Horned Rhino is found in India.
- Also known as Indian rhino, it is the largest of the rhino species.
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following animals (2021)
- Hedeghog
- Marmot
- Pangolin
To reduce the chances of being captured by predators , which of the above organisms roll up /rolls up /protects its/their vulnerable parts ?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3
Q.2) With reference to Indian elephants, consider the following statements: (2020)
- The leader of an elephant group is a female
- The maximum gestation period can be 22 months
- An elephant can normally go on calving till the age of 40 years only
- Among the States in India, the highest elephant population is in Kerala
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 3 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: Recently, the Chief Justice of India (CJI) D Y Chandrachud announced that the Supreme Court will adopt a “neutral citation system” for its judgments.
About the Neutral citation system :
- A case citation is an identification tag for a judgment that would contain a reference number, the year of the judgment, the name of the court that delivered that judgment, and a shorthand for the journal publishing the judgment.
- A neutral citation means that the court would assign its own citation — distinct from those given by traditional Law Reporters.
- For example: in the All-India Reporter (AIR), the citation is AIR 1973 SC 1461
Significance of a Neutral citation :
- With artificial intelligence (AI) enabling the translation of judgments and transcribing of court proceedings, a uniform citation is necessary.
- To ease the adjudicatory process.
- To avoid confusion arising out of one case being cited by different people in a number of different ways.
- Several High Courts including Delhi High Court have started a neutral citation format.
Implementation :
- All 30,000 judgments are going to have neutral citations.
- The first tranche will be till January 1, 2023, then the other tranche will be till judgments from 2014 and then finally it will go back to 1950.
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Government law officers and legal firms are recognized as advocates, but corporate lawyers and patent attorneys are excluded from recognition as advocates.
- Bar Councils have the power to lay down the rules relating to legal education and recognition of law colleges.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to Indian Judiciary, consider the following statements. (2021)
- Any retired judge of the Supreme Court of India can be called back to sit by the Chief Justice of India with the prior permission of the President of India.
- A High court in India has the power to review its own judgment as the Supreme Court does.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Recently, the Agricultural and Process Food Export Development Authority (APEDA) participated in the 28th edition of Gulfood 2023 held in UAE.
About the Agricultural and Process Food Export Development Authority (APEDA):
- It is a statutory body established by the Government of India under the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority Act passed by the Parliament in 1985.
- The Authority replaced the Processed Food Export Promotion Council (PFEPC).
- Head Office: New Delhi
- It functions under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- APEDA also functions as the Secretariat to the National Accreditation Board (NAB) for the implementation of accreditation of the Certification Bodies under the National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP) for organic exports.
- Chairman – appointed by the Central Government.
Functions :
- Development of industries relating to the scheduled products for export by way of providing financial assistance.
- Registration of persons as exporters of the scheduled products on payment of such fees as may be prescribed.
- Fixing standards and specifications for the scheduled products for the purpose of exports;
- Carrying out inspection of meat and meat products in slaughterhouses, processing plants, storage premises, conveyances, or other places
- Improving packaging of the Scheduled products;
- Improving marketing of the Scheduled products outside India.
- Promotion of export-oriented production and development of the Scheduled products.
APEDA is mandated with the responsibility of export promotion and development of the following scheduled products:
- Fruits, Vegetables and their Products.
- Meat and Meat Products.
- Poultry and Poultry Products.
- Dairy Products.
- Confectionery, Biscuits, and Bakery Products.
- Honey, Jaggery, and Sugar Products.
- Cocoa and its products, chocolates of all kinds.
- Alcoholic and Non-Alcoholic Beverages.
- Cereal and Cereal Products.
- Groundnuts, Peanuts, and Walnuts.
- Pickles, Papads, and Chutneys.
- Guar Gum.
- Floriculture and Floriculture Products.
- Herbal and Medicinal Plants.
- De–oiled rice bran.
- Green pepper in brine.
- Cashew Nuts and Its Products.
- Basmati Rice has been included in the Second Schedule of the APEDA Act.
- APEDA has been entrusted with the responsibility of monitoring the import of sugar as well.
About Gulfood 2023:
- The 28th edition of Gulfood 2023 which was held in the UAE.
- GULFOOD which is a platform that connects food and beverage sectors around the globe.
- The Indian pavilion at Gulfood 2023 is one of the largest pavilions at the show to cater food product exports to more than 125 countries participating in the event.
- More than 50 Indian exporters from different categories like women entrepreneurs, Start-ups, merchants, and manufacturers showcasing agricultural, dairy, pulses, and meat-based produce with a focus on Millet and its products through the APEDA pavilion, are being showcased.
- Over the years APEDA has participated in Gulfood and brought a strong contingent of suppliers from the Indian diaspora.
Source: PIB
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which of the following factors/policies were affecting the price of rice in India in the recent past? (2020)
- Minimum Support Price
- Government’s trading
- Government’s stockpiling
- Consumer subsidies
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, and 4 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) In India, which of the following can be considered as public investment in agriculture? (2020)
- Fixing Minimum Support Price for agricultural produce of all crops
- Computerization of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies
- Social Capital Development
- Free electricity supply to farmers
- Waiver of agricultural loans by the banking system
- Setting up of cold storage facilities by the governments.
In India, which of the following can be considered as public investment in agriculture?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, and 5 only
- 1, 3, 4, and 5 only
- 2, 3, and 6 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, researchers, for the first time, have used the body’s own chemistry to develop electrodes in the tissues of zebrafish (a small freshwater fish).
About Zebrafish :
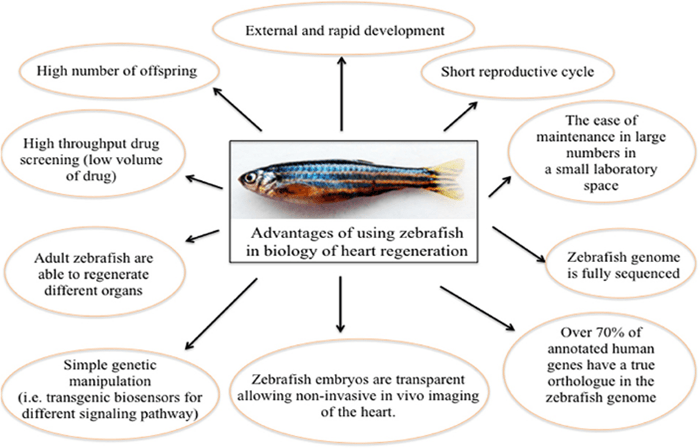
- It is a tropical freshwater fish belonging to the minnow family (Cyprinidae) of the order Cypriniformes.
- Habitat: Native to rivers and streams of South Asia.
- It is a freshwater fish found in tropical and subtropical regions.
- The fish is native to South Asia’s Indo-Gangetic plains, where they are mostly found in the paddy fields and even in stagnant water and streams.
- Features:
- It is a popular aquarium fish.
- It is about 4 cm long and has dark-blue and silvery longitudinal stripes.
- IUCN Red List Status: Least concerned.
Significance of Zebrafish:
- Zebrafish have the ability to heal their heart after injury through a regenerative process.
- If part of their heart is removed, they can grow it back in a matter of weeks.
- Humans cannot regenerate their hearts upon myocardial damage and a person who suffered a heart attack cannot functionally heal the damaged heart muscle, resulting in reduced pumping efficiency.
- Till now, there is no treatment available to restore the damaged heart function in humans.
- Hence scientists have sought to decode the heart regeneration processes using this model animal.
- In May 2021, it was announced by researchers at the Queen’s University in Belfast, UK that the hibernation form known as induced torpor found in zebrafish will give radio-protective effects, that may be useful for interplanetary voyages
- Replicating hibernation may therefore protect astronauts against the harsh conditions of space flight
- Zebrafish have also been found to regenerate photoreceptor cells and retinal neurons following injury.
Source: DOWN TO EARTH
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2020)
- Genetic changes can be introduced in the cells that produce eggs or sperm of a prospective parent.
- A person’s genome can be edited before birth at the early embryonic stage.
- Human-induced pluripotent stem cells can be injected into the embryo of a pig.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which of the following are detritivores? (2021)
- Earthworms
- Jellyfish
- Seahorse
- Woodlice
Select the correct answer using the code given below
- 1, 2, and 4 only
- 2, 3, 4, and 4 only
- 1, 3, and 5 only
- 1,2,3,4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework adopted recently, respects the rights of indigenous people regarding biodiversity.
About Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework:
- The “Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework” (GBF) was adopted by the 15th Conference of Parties (COP15) to the UN Convention on Biological Diversity.
- It includes four goals and 23 targets to be achieved by 2030.
- COP 15 took place in Montreal, Canada.
- Through Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF), countries agreed to protect 30 percent of the planet by 2030.
- The countries pledged to achieve 23 targets to reverse ecosystem degradation under four overarching goals for the survival of the natural world.
- Under the Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF), countries also agreed to reduce harmful government subsidies worth 500 billion dollars annually, while vowing to identify subsidies that are harmful to biodiversity by 2025.
- Its other targets include reducing the use of pesticides by half and raising annual international financial flows from developed to developing countries to at least 20 billion dollars by 2025, and to at least 30 billion dollars by 2030.
Impact on India:
- The Global Biodiversity Plan gives India legroom on farm subsidies.
- The GBF gives elbow space to India both in terms of continuing farm subsidies and pesticide use.
About Nagoya Protocol:
- This protocol was established at the Convention on Biological Diversity.
- The Nagoya Protocol is an international agreement that aims to fairly and equitably distribute the advantages that result from the use of genetic resources.
- The procedure was approved in Nagoya, Japan, in 2010 and came into effect in 2014.
- The Nagoya Protocol has been ratified by 137 parties as of April 2022, including the European Union and 136 UN member states.
- India signed the Nagoya Protocol in 2011 and ratified it in October 2012.
- The ratification by India was done at the 11th Conference of Parties (COP) to the CBD, which was conducted in Hyderabad.
- Members are required under the protocol to implement procedures pertaining to compliance, benefit sharing, and access to genetic resources.
Source: DOWN TO EARTH
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) “Climate Action Tracker” which monitors the emission reduction pledges of different countries is a : (2022)
- Database created by a coalition of research organizations
- Wing of “International Panel of Climate Change”
- Committee under “United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change”
- Agency promoted and financed by United Nations Environment Programme and World Bank
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Climate Group is an international non-profit organization that drives climate action by building large networks and running them.
- The International Energy Agency in partnership with the Climate Group launched a global initiative “EP100”.
- EP100 brings together leading companies committed to driving innovation in energy efficiency and increasing competitiveness while delivering on emission reduction goals.
- Some Indian companies are members of EP100.
- The International Energy Agency is the Secretariat of the “Under2 Coalition”.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1,2, 4 and 5
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 2,3 and 5 only
- 1,2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.3) With reference to the ‘’New York Declaration on Forests’’, which of the following statements is correct? (2021)
- It was first endorsed at the United Nations Climate Summit in 2014
- It endorses a global timeline to end the loss of forests
- It is a legally binding international declaration
- It is endorsed by governments, big companies, and indigenous communities.
- India was one of the signatories at its inception
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 5 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 5 only
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Polity and Governance)
Context: The 17th Lok Sabha has completed three years and seven months of its term; however, the House has not elected a Deputy Speaker.
Presiding officers of Lok Sabha:
- Speaker and Deputy Speaker: There are two presiding officers for the Lok Sabha, namely the Speaker and the Deputy Speaker, who are elected by the members of the House.
- Constitutional provisions: Under Article 93 of the Constitution, as soon as the House meets after the election these two presiding officers are elected one after the other.
- Article 178 contains the corresponding position for Speaker and Deputy Speaker of the Legislative Assembly of a state.
- Officers of Parliament: The Speaker and the Deputy Speaker are described in the Constitution as officers of Parliament, which signifies their importance in the parliamentary system.
About Deputy Speaker:
Article 93 of Constitution of India:
- The House of the People shall, as soon as may be, choose two members of the House to be respective Speaker and Deputy Speaker thereof and, so often as the office of Speaker or Deputy Speaker becomes vacant, the House shall choose another member to be Speaker or Deputy Speaker, as the case may be.
Election: In the Lok Sabha, the lower House of the Indian Parliament, both Presiding Officers – the Speaker and the Deputy Speaker are elected from among its members by a simple majority of members present and voting in the House.
Independent from Speaker: The Deputy Speaker is independent of the Speaker, not subordinate to him, as both are elected from among the members of the House.
- When he presides over a sitting, he has all the powers of a Speaker.
Gaining importance: In addition to presiding over the House in the absence of the Speaker, the Deputy Speaker chaired committees both inside and outside of Parliament.
Ensures continuity of Speaker’s office:
- The Deputy Speaker ensures the continuity of the Speakers office by acting as the Speaker when the office becomes vacant:
- Illness, or
- by death, or
- because of resignation or
- any other reason.
- When the Speaker’s post falls vacant, it is the Deputy Speaker who assumes all the powers of the Speaker and exercises both legislative powers and administrative powers.
Presiding officer in specific cases: When a resolution for removal of the Speaker is up for discussion, the Constitution specifies that the Deputy Speaker presides over the proceedings of the House.
- A Deputy Speaker is also the ex-officio chairman of some committees by virtue of his position.
From ruling party or opposition:
- In the case of the Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha, the position has varied over the years.
- Until the fourth Lok Sabha, the Congress held both the Speaker and Deputy Speakers positions.
- In the fifth Lok Sabha, whose term was extended due to the Emergency, an independent member, Shri G G Swell, was elected the Deputy Speaker.
- The tradition for the post of the Deputy Speaker going to the Opposition party started during the term of Prime Minister Morarji Desai’s government.
Historical background of Deputy Speaker:
- The history of the office of Deputy Speaker goes back to the government of India Act of 1919 when he was called Deputy President as the Speaker was known as the president of the central legislative assembly.
- This tradition was continued after Independence, when a Deputy Speaker was elected to chair, besides the Speaker, the meetings of the Constituent Assembly (Legislative).
- The first Speaker was G V Mavlankar and the first Deputy Speaker was M Ananthasayanam Ayyangar who was elected by the Constituent Assembly (Legislative) on September 3, 1948.
- Later under the new Constitution, he was elected the first Deputy Speaker of the House of the people on May 28, 1952.
- Thereafter, every Lok Sabha had a Deputy Speaker who would be elected after a few days after the election of the Speaker.
Power of Deputy Speaker:
- The Deputy Speaker has the same power as the Speaker when he presides over a sitting of the House.
- Similarly no appeal lies to the Speaker against a ruling given by the Deputy Speaker.
- So the Speaker is powerless in the matter of revising or overruling a decision of the Deputy Speaker.
- Under Article 95(1) of the Constitution, the Deputy Speaker gets all the powers of the Speaker when the office of the Speaker is vacant, so the Deputy Speaker can also determine the petitions relating to disqualification under the 10th Schedule of the Constitution.
- Although the Deputy Speaker gets to exercise these powers only in the absence of the Speaker his decisions are final and binding when he gives a ruling.
- In the eventuality of the Speaker remaining absent for a longer time due to illness or otherwise the government will have to grapple with the unpredictability of a ruling or an adverse decision by a Deputy Speaker who comes from the Opposition ranks.
Need for Deputy Speaker:
- Unprecedented Move: It is quite unfortunate that the Deputy Speaker has not been appointed for more than two years now (for the first time in the history of independent India).
- Decreasing Discussion in recent times: Parliament is viewed as a temple of deliberation and discussion. But, in the recent Lok Sabha Monsoon session, there has been zero discussion on any policy issue.
- Falling productivity: In 2020-21, Lok Sabha functioned for 34 days while Rajya Sabha functioned for 33 days. It was the lowest ever in India.
- Winter session 2020 was not conducted completely. Even Budget Session 2021 was reduced by two weeks because of election campaigning.
- Hasty legislation: No bill was passed to the Parliamentary Committee. Every bill introduced in this Monsoon Session was passed within the same session.
- Surprisingly, 18 bills were passed in Lok Sabha with only one bill being discussed over 15 minutes.
Issues associated with the role of Deputy Speaker:
- No specific timeline for Deputy Speaker’s appointment: Article 93 for Lok Sabha and Article 178 for state Assemblies state that these Houses “shall, as soon as may be”, choose two of its members to be Speaker and Deputy Speaker.
- The Constitution and the Assembly rules do not specify a time-frame for filling a vacancy in the post.
- Maintaining Neutrality: It would be unrealistic to expect a Presiding Officer to completely abjure all party considerations while functioning as there are structural issues regarding the manner of appointment of the Speaker and his/her tenure in office.
Way Forward:
The office of the Deputy Speaker is as important as the office of the speaker. The constitution has created this office for the smooth functioning of the house. Therefore, in the present circumstances, the post of Deputy Speaker is desirable to maintain neutrality and smooth functioning of the Parliament.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha, consider the following statements:
- As per the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha, the election of Deputy Speaker shall be held on such date as the Speaker may fix.
- There is a mandatory provision that the election of a candidate as Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha shall be from either the principal opposition party or the ruling party.
- The Deputy Speaker has the same power as of the Speaker when presiding over the sitting of the House and no appeal lies against his rulings.
- The well-established parliamentary practice regarding the appointment of Deputy Speaker is that the motion is moved by the Speaker and duly seconded by the Prime Minister.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
Q.2) Consider the following statements:
- In the election for Lok Sabha or State Assembly, the winning candidate must get at least 50 percent of the votes polled, to be declared elected.
- According to the provisions laid down in the Constitution of India, in Lok Sabha, the Speaker’s post goes to the majority party and the Deputy Speaker’s to the Opposition.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2017)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance) and GS 3 (Science and Technology)
Context: Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) has held in a judgment that children cannot be subjected to DNA tests in each and every case to establish proof of infidelity.
About Genetic Privacy:
- It is a term that seeks to prevent a third party from using a person’s genetic data without his permission.
- A person’s genes are the blueprint of his or her physical or biological being, personal life and information about the future, present and history.
- Other information that can be abstracted: alcoholism, depression, aggressiveness, sexual orientation, mental productivity etc.
- When a person’s genetic data is used for testing, medical purposes, or other purposes, his privacy should be protected.
- Genetic data is made up of a person’s deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and chromosomes.
- DNA sample sources: hair, teeth, blood etc.
SC rulings on genetic information:
- Genetic information is personal and intimate.
- Thus, a child’s genetic information is part of his fundamental right to privacy.
- Children have the right to not have their legitimacy questioned before a court of law.
- DNA tests would harm the reputation and dignity of the mother.
- The children should not to be subjected to forensic/DNA testing during the divorce proceedings.
- Family courts should direct for a DNA test only in the situations where it is a last resort and in the interest of justice.
Status of Genetic Privacy in India:
- In 2018, The Delhi High Court stated that discrimination in health insurance against people based on their genetic origin, in the absence of genetic test is unconstitutional.
- Genetic discrimination breaches Article 14, which guarantees equality before the law.
- In Justice KS Puttaswamy (Retd.) & Anr. v. Union of India, SC stated that the Right to Privacy is a fundamental Right under Article 21.
Genetic discrimination in other countries:
- In 2008, the United States had passed the Genetic Information Non-discrimination Act (GINA), to protects people from genetic discrimination in health care and jobs.
- Council of Europe has adopted the Guidelines on the use of genetic knowledge for insurance purposes.
- Under Canada’s Genetic Non-discrimination Act, it is illegal for insurers or employers to request DNA testing or findings.
Advantages of genetic information:
- Genetic information may disclose information about a disease, illness, or a person’s health status.
- It can make a person more aware of his or her health.
- A person can learn about his ancestors and distant relatives.
- One’s data can be used in medical research.
- If a person learns about his illness early on, he would be able to take more preventative steps to treat it.
Disadvantages of genetic Information:
- Based on the profile available in the domain, genetic evidence can be fabricated in any crime scene through engineered DNA samples not taken from a real individual.
- Data such as person’s personal life, health, family members, and other private information when assessed by a third party can be misused.
- If such information is revealed, it can negatively impact individuals lives, such as discrimination from employers, insurance providers, the government, and others.
UN Convention on the Rights of the Child:
- It is a treaty adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 1989.
- It recognises a child as every human being under 18 years old.
- It is an international agreement that is legally binding on the members.
- It sets out the civil, political, economic, social and cultural rights of every child, regardless of their race, religion or abilities.
- It includes rights such as Right to Education, Right to Rest and Leisure, Right to Protection from Mental or Physical Abuse including Rape and Sexual Exploitation.
- It has been ratified by all members of the UN except for the United States.
- It is the most widely ratified human rights treaty in the history of the world.
Way Forward:
Thus with improvements in encryption, safe storage, and data transfer protocols, there may be potential to improve privacy protections technologically. From an ethical standpoint, it will be crucial to keep educating the public about the benefits and dangers of genetic testing and data sharing. It may entail activities to provide fair access to genetic testing and benefits as well as efforts to support transparency, openness, and accountability around the collection, use, and sharing of genetic data.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding Indian Council of Historical Research (ICHR):
- It is an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Culture.
- It is statutory body established under the Societies Registration Act 1980.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to India’s biodiversity, consider the following statements:
- Assam has more than 90 % of the total Rhino in India.
- Only the Great One-Horned Rhino is found in India.
- One -horned Rhinos are listed under Schedule II of the Wildlife Protection Act.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding Nagoya protocol:
- This protocol was established at the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity.
- India signed the Nagoya Protocol in 2011.
- Protocol is an international agreement that aims to fairly and equitably distribute the advantages that result from the use of genetic resources.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 25th February 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 24th February – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – b











