Environment & Ecology
Context: India’s Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) framework for used tyres, batteries, and revised rules for e-waste and plastics kindled interest among the G20 countries.
About Extended Producer Responsibility:
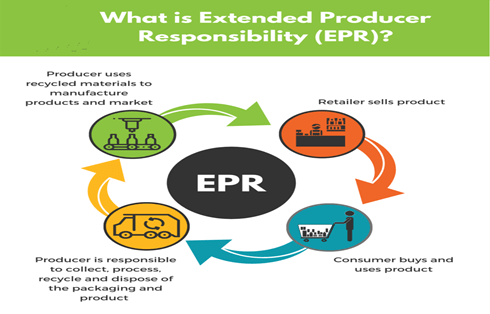
- Extended producers’ Responsibilities is a globally recognized policy used as an effective tool to put the onus on the producers for efficient end of life waste management of the plastic, electronic and electrical equipment.
- The concept of EPR responsibility is based on three foundation principles:
- Pollution prevention approach
- Life cycle thinking,
- Polluter pay principle
- EPR responsibility makes it the responsibility of the producers not only to take back products for recycling but also to design better and longer life products to minimize the amount of waste generated.
EPR in India:
EPR responsibility Certificate:
- EPR responsibility Certificate is authorized by Central Pollution Control Board which is mandatory for Producers/Importers of the Electronic products.
- Under these rules, the producers have a responsibility to delegate this responsibility to the third party or specialized organizations which manufacturers can financially aid for proper waste management.
EPR Responsibility Policies under E-Waste Management Rules:
- E-Waste (management and handling) Rules, 2016 adopted Extended Producers Responsibility for the first time in India.
- EPR responsibility under E-Waste (management) Rules, 2016 stipulates collection targets of E–Waste for producers.
- The producers are responsible for setting up collection centres for e-waste and financing and organizing a system for environmentally sound management of e-waste.
- The producers are required to have an arrangement with dismantlers and recyclers through either the Producers responsibility organization or the E-Waste exchange system.
- Marketing or selling any electronic equipment without EPR responsibility Authorization is considered a violation of the rules.
EPR responsibility Policy under Plastic Waste Management Rules:
- The Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2022 provide guidelines for strengthening the circular economy of plastic packaging waste as well as promoting alternatives to plastic.
- Producers of waste are mandated to ensure that generation of plastic waste is minimized, and plastic waste is not littered and stored at the source, which is then handed over to local bodies or authorized agencies.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) “Climate Action Tracker” which monitors the emission reduction pledges of different countries is a : (2022)
- Database created by coalition of research organisations
- Wing of “International Panel of Climate Change”
- Committee under “United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change”
- Agency promoted and financed by United Nations Environment Programme and World Bank
Q.2) Consider the following statements:
- The Climate Group is an international non-profit organisation that drives climate action by building large networks and runs them.
- The International Energy Agency in partnership with the Climate Group launched a global initiative “EP100”.
- EP100 brings together leading companies committed to driving innovation in energy efficiency and increasing competitiveness while delivering on emission reduction goals.
- Some Indian companies are members of EP100.
- The International Energy Agency is the Secretariat to the “Under2 Coalition”.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1,2, 4 and 5
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 2,3 and 5 only
- 1,2, 3, 4 and 5











