IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the Finance Bill 2023 was approved with amendments.
About Finance Bill 2023:-
Key Highlights of the bill:-
- The withholding tax rate on royalties and fees for technical services paid to non-residents has been raised from 10% to 20%This may increase the cost of import of technology.
- Options contracts will now attract 0.021% STT from 0.017% earlier and futures will attract a levy of 0.0125%, up from 0.01%
- The Finance Bill has paved the way for setting up GST Appellate Tribunals across the country, with a principal bench in New Delhi and several State benches.
- The Tribunal will be headed by a former Supreme Court judge or a retired Chief Justice of a High Court.
- The stock market has seen an increase in Securities Transaction Tax (STT) on futures and options contracts from April 1, 2023.
- It is to discourage excessive trade in F&O.
Significance of the amendment:-
- This increase in STT will shore up revenues for the Government.
- The main idea behind this could be to discourage excessive trade in the F&O segment where a large number of retail traders end up losing money as per a recent SEBI study.
- An incidental effect of this could be shifting the F&O trades to SGX, Gift and other locations that do not attract such taxes for participants who have access to them.
- REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts) and InvITs (Infrastructure Investment Trusts):
- the government has tweaked the Budget proposal to tax distribution from business trusts as income from other sources.
- Any amount received in excess of the issue price would be taxable as income.
- The draft rules related to valuation shall be shared with the stakeholders for their input in April itself, and exclusions, currently provided to domestic Venture Capital Funds etc, shall also be considered for similar overseas entities.
- This will impact all mutual funds that offer schemes with nomenclatures such as conservative hybrid funds, that invest predominantly in debt but have an equity exposure of up to 35% in their portfolios.
- An arbitrage is being created right now where interest income from a debt mutual is not distributed and converted into long-term capital gains of 20% (with indexation).
- Debt mutual fund: where not more than 35% is invested in shares in the domestic company.
- Thus many taxpayers are able to reduce their tax liability through this arbitrage.
Money Bill vs Finance Bill:-
- A Finance Bill is a bill that deals with the country’s finances, as the name implies – it could be about taxes, government spending, government borrowings, revenues, and so on.
- The Union Budget is enacted as a Finance Bill because it deals with these issues.
- The finance bill is classified into two categories:
- Financial bill (I)
- Financial bill (II)
- Money Bills, as the name implies, are bills whose provisions are entirely concerned with all or any of the issues specified in Article 110(1).
- It includes issues such as the imposition, repeal, and regulation of taxes, the control of government borrowing, the protection of Consolidated or Contingency Funds and the influx or outflow of money from any such funds, the allocation of money from the Consolidated Fund of India, and so on.
Types of Financial Bills:-
- Financial bills (I)–Article 117 (1)
- A financial bill (I) is a measure that includes not only any or all of the subjects stated in Article 110, but also other general legislative provisions.
- A finance bill (I) is comparable to a money bill in two ways: (a) both can be introduced only in the Lok Sabha and not in the Rajya Sabha and (b) both can be introduced only on the president’s advice.
- In all other ways, a finance bill (I) follows the same parliamentary procedure as an ordinary bill.
- Financial bills (II)–Article 117 (3)
- A financial bill (II) has provisions affecting Consolidated Fund of India spending but does not include any of the items enumerated in Article 110.
- It is considered an ordinary bill and is subject to the same parliamentary procedure as an ordinary bill in all aspects.
- The single distinguishing element of this bill is that it cannot be enacted by either House of Parliament unless the President has requested that the measure be considered by that House.
- As a result, finance bill (II) can be filed in either House of Parliament, and the President’s approval is not required.
- In other words, the President’s suggestion is not necessary at the introduction stage but is required during the consideration step.
- Either the House of Parliament has the option of rejecting or amending it.
- If the two Houses disagree on such a law, the President might call a joint session of the two Houses to break the stalemate.
- When the measure is given to the President, he can either grant his consent to it, withhold his assent to it, or return it to the Houses for reconsideration.
MUST READ: Angel Tax
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements (2022)
- An increase in Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) indicates the appreciation of the rupee.
- An increase in the Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) indicates an improvement in trade competitiveness.
- An increasing trend in domestic inflation relative to inflation in other countries is likely to cause an increasing divergence between NEER and REER.
Which of the above statements is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which one of the following situations best reflects “Indirect Transfers” often talked about in media recently with reference to India? (2022)
- An Indian company investing in a foreign enterprise and paying taxes to the foreign country on the profits arising out of its investment
- A foreign company investing in India and paying taxes to the country of its base on the profits arising out of its investment
- An Indian company purchases tangible assets in a foreign country and sells such assets after their value increases and transfers the proceeds to India
- A foreign company transfers shares and such shares derive their substantial value from assets located in India
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently,2,660 Labour Rooms and 1989 Maternity Operation Theatres certified facilities under the LaQshya programme conduct the sensitization/ orientation of the latest Labour Room Protocols.
About LaQshya Programme:-
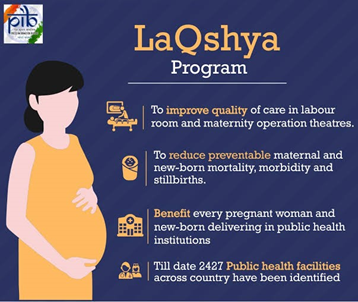
IMAGE SOURCE: PIB
- LaQshya is a quality improvement initiative under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- It focuses on improving the quality of care in the labour room and maternity Operation Theatre (OT).
- It aims to ensure Quality of Care during intrapartum and immediate post-partum periods in Labour Room and Maternity OT.
- It targets all Government Medical College Hospitals, District Hospitals & equivalent health facilities, designated FRUs as well as high case load CHCs.
- All the targeted facilities (which include 2660 Labour Rooms and 1989 Maternity Operation Theatres) for LaQshya certification and certified facilities under the LaQshya programme conduct the sensitization/ orientation of the latest Labour Room Protocols.
- Goal – To reduce preventable maternal and newborn mortality, morbidity and stillbirths associated with the care around delivery in the Labour room and Maternity OT and ensure respectful maternity care.
- Under the purview of LaQshya, one of the facility-level targets is to achieve a 5% or less Surgical Site Infection Rate in Maternity OT or at least a reduction of 30% from the baseline.
- At the time of LaQshya certification, compliance with the above-mentioned requirement is verified by the independent empanelled NQAS assessors.
MUST READ: Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) of India
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Maternity Benefit Amendment Act, 2017? (2019)
- Pregnant women are entitled to three months of pre-delivery and three months of post-delivery paid leave.
- Enterprises with creches must allow the mother a minimum of six creche visits daily.
- 3) Women with two children get reduced entitlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) The endeavour of the ‘Janani Suraksha Yojana’ Programme is (2012)
- to promote institutional deliveries
- to provide monetary assistance to the mother to meet the cost of delivery.
- to provide for wage loss due to pregnancy and confinement
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Art and Culture
Context: Recently, the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has sealed the road between Khandagiri and Udaygiri caves.
About Khandagiri Udayagiri caves:-
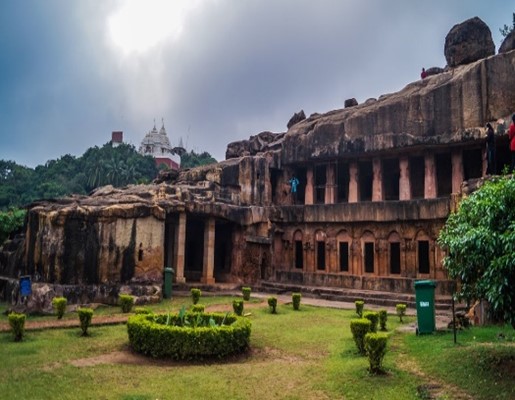

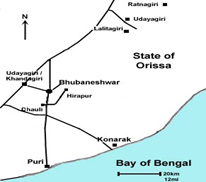
IMAGE SOURCE: Ancient India (art-and-archaeology.com)
- These caves had been created during the reign of Kalinga King Kharavela in the first and second centuries BC.
- There are both man-made and natural caves in the cave complex.
- Udayagiri has 18 caves and Khandagiri has 15.
- They were formerly known as the Kattaka Caves or Cuttack Caves.
- The twin hills Udayagiri and Khandagiri (Lat. 20.16 N; Long. 85.47E) are located in the vicinity of Bhubaneswar town. National Highway No.5 passes through the close proximity of the hills.
- These two hills represent one of the earliest groups of Jaina rock-cut architecture in eastern India.
- These hills are honeycombed with excavated rock-cut caves, essentially meant for the dwelling retreats of the Jaina recluses.
- On the basis of inscriptional evidence, these caves were first excavated by king Kharavela of the Chedi dynasty and his successors who were devout Jainas during the first century B.C.
- The Jain temple on the top of the Khandagiri hill was constructed in the late 19th century and is under worship even at present, preserving the continuity and tradition of the glorious past of the hill.
- Ranigumpha and Swargapuri-Manchapuri caves are double-storied and the largest in size.
- The Rani and Hathi Gumpha in the Udayagiri has description of the culture of dance in Orissa- Odissi among others beyond the 2nd century B.C.
- Ranigumpha or the queen’s palace is the architectural marvel of the entire complex.
- Architecturally the Hathi gumpha is insignificant but its historical importance lies in the famous inscription of king Kharavela engraved on its brow.
- The 17-line inscription records the expeditions of king Kharavela including the victory of Magadha and the retrieval of the Jaina cult image taken away by the Nanda king long before.
- The depiction of 24 Tirthankaras along with Sasanadevis in the Barabhuji cave, Surya Gajalaksmi and Jaina symbols in the Ananta Gumpha of Khandagiri in relief are a notable achievement of early medieval Indian art.
- Besides, remains of an apsidal structure were unearthed in 1958 atop the Udayagiri is the first earliest structure of its kind in eastern India.
MUST READ: Ancient rock paintings
SOURCE: THE NEW INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Indian history, consider the following texts: (2022)
- Nettipakarana
- Parishishtaparvan
- Avadanashataka
- Trishashtilakshana Mahapurana
Which of the above are Jaina’s texts
- 1,2 and 3
- 2 and 4 only
- 1,3 and 4
- 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) Consider the following pairs: (2021)
Historical place Well-known for
- Burzahom Rock-cut shrines
- Chandraketugarh Terracotta art
- Ganeshwar Copper artefacts
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
- 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations and Economy
Context: Former Brazilian President Dilma Rousseff has been “unanimously elected” as the head of the New Development Bank (NDB) recently.
About New Development Bank (NDB):-
IMAGE SOURCE: BRICS Culture Ministers Meeting (10pointer.com)

IMAGE SOURCE: ndb BRICS countries – Bing
- It is a multilateral financial institution set up by the five BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa)
- It was founded at the 6th BRICS Summit in Fortaleza, Brazil in 2014.
Objective: It was formed to support infrastructure and sustainable development efforts in BRICS and other underserved, emerging economies for faster development through innovation and cutting-edge technology.
- It is headquartered in Shanghai, China.
- The NDB President is elected on a rotational basis from one of the founding members.
- K. V. Kamath, from India, is the first elected president of the NDB.
- The New Development Bank has an initial subscribed capital of US$50 billion and an initial authorized capital of US$100 billion.
- The initial subscribed capital is equally distributed among the founding members.
- The five founding members of the Bank include Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
- The Bank’s Articles of Agreement specify that all members of the United Nations could be members of the bank.
- However, the share of the BRICS nations can never be less than 55% of the voting power.
- The NDB’s credit rating is AA+.
Major Projects funded by NDB in India:-
- Mumbai Metro rail
- Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut Regional Rapid Transit System and many Renewable Energy projects.
- The NDB has so far approved 14 Indian projects for an amount of nearly USD 4.2 billion.
- In 2020, India announced a 1 billion USD loan pact with NDB to boost rural employment and infrastructure.
MUST READ: BRICS
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) The ‘Fortaleza Declaration’ recently in the news, is related to the affairs of:(2015)
- ASEAN
- BRICS
- OECD
- WTO
Q.2) With reference to a grouping of countries known as BRICS, consider the following statements: (2014)
- The First Summit of BRICS was held in Rio de Janeiro in 2009.
- South Africa was the last to join the BRICS grouping.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, a sacred Hopi site in Arizona was awarded the ICOMOS Water and Heritage Shield.
About the Hopi site in Arizona:-
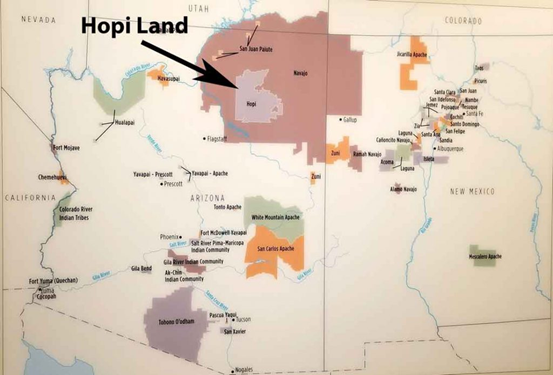
IMAGE SOURCE: Looming power plant closure leaves Hopi seeking new energy and revenue sources – Medill Reports Chicago (northwestern.edu)
- It is located in northeastern Arizona.
- It encompasses lands that the Hopi people have inhabited for more than a thousand years.
- Hopi shrines and sacred sites are essential in the practice of the Hopi religion.
- Without them, the Hopi people cannot fulfil their religious obligation to serve as stewards of the land.
About International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS):-
- ICOMOS is a non-governmental international organisation.
- It is dedicated to the conservation of the world’s monuments and sites.
- The International Secretariat is located at the headquarters of ICOMOS in Greater Paris.
- It is the only global non-government organisation of this kind, which is dedicated to promoting the application of theory, methodology, and scientific techniques to the conservation of architectural and archaeological heritage.
- ICOMOS is a network of experts that benefits from the interdisciplinary exchange of its members, among which are architects, historians, archaeologists, art historians, geographers, anthropologists, engineers and town planners.
- The members contribute to improving the preservation of heritage, the standards and the techniques for each type of cultural heritage property: buildings, historic cities, cultural landscapes and archaeological sites
- The members of ICOMOS (December 2020):-
- 10 489 Individual Members in 151 countries
- 248 Institutional Members
- 104 National Committees
- 30 International Scientific Committees
Mission:-
- support the development of ICOMOS’s network.
- disseminate knowledge about heritage conservation, notably through its Documentation Centre.
- provide advisory and evaluation services to State Parties required for the implementation of the World Heritage Convention.
MUST READ: UNESCO Heritage Sites in Maharashtra
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following statements is correct? (2021)
- Ajanta Caves lie in the gorge of the Waghora river.
- Sanchi Stupa lies in the gorge of the Chambal river.
- Pandu – lena cave shrines lie in the gorge of the Narmada river.
- Amaravati Stupa lies in the gorge of the Godavari river.
Q.2) What is/are common to the two historical places known as Ajanta and Mahabalipuram? (2016)
- Both were built in the same period.
- Both belong to the same religious denomination.
- Both have rock-cut monuments.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- None of the statements given above is correct
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, ‘the world’s first 3D-printed rocket Terran 1 launched successfully on its third attempt failed to achieve orbit during second-stage separation.
About Terran 1:-
- It is the world’s first 3D-printed rocket.
- It is an expendable two-stage small-lift launch vehicle.
- It is developed by Relativity Space, a private sector company
- It’s 85% 3D-printed except for moving parts such as rubber seals, computers, and electrical circuitry.
- Objective: to show that the 3D-printed vehicle can endure Max Q or maximum dynamic pressure condition.
- Max Q: a condition that happens during the first few minutes of flight when the rocket is exposed to the greatest forces and stresses.
- It passed max q and reached space but failed to achieve Low Earth Orbit due to a failure of the second stage.
- It is powered by Aeon engines using liquid oxygen and liquid natural gas as propellants.
- It has nine 3D-printed Aeon 1 engines in its first stage and one 3D-printed Aeon Vacuum engine in its second stage.
- The rocket will eventually be capable of putting up to 2,755 pounds (1,250 kilograms) into low Earth orbit.
MUST READ: LVM3-M2 rocket
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best reflects the idea behind the “Fractional Orbital Bombardment System” often talked about in media? (2022)
- A hypersonic missile is launched into space to counter the asteroid approaching the Earth and explode it in space.
- A spacecraft lands on another planet after making several orbital motions.
- A missile is put into a stable orbit around the Earth and deorbits over a target on the Earth.
- A spacecraft moves along a comet with the same surface. speed and places a probe on its
Q.2) Which one of the following is a reason why astronomical distances are measured in light-years? (2021)
- Distance among stellar bodies does not change
- The gravity of stellar bodies does not change
- Light always travels in a straight line
- The speed of light is always the same
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the MoD inked Rs 3,700 crore contracts with BEL for Medium Power Radars ‘Arudhra’ & 129 DR-118 Radar Warning Receivers.
About Arudhra:-
- The radar has been indigenously designed.
- It is developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and will be manufactured by BEL.
- Its successful trials have already been conducted by the Indian Air Force.
- It is a 4D multi-function phased array radar with electronic steering in both azimuth and elevation for surveillance, detection and tracking of aerial targets.
- The system will have target identification based on interrogations from co-located Identification Friend or Foe system.
- The project will act as a catalyst for the development of manufacturing capability in the industrial ecosystem.
About DR-118 RWR:-
- The DR-118 Radar Warning Receiver is a Radar Warning Receiver.
- It will considerably enhance the Electronic Warfare (EW) capabilities of Su-30 MKI aircraft.
- Majority of sub-assemblies and parts will be sourced from indigenous manufacturers.
Significance:-
- The project will boost and encourage active participation of Indian Electronics and associated industries, including MSMEs.
- It will generate employment of approx. two lakh man-days over a period of three and half years.
- The DR-118 RWR is a significant leap forward in developing indigenous EW capabilities and making the country ‘Aatmanirbharta’ in defence.
MUST READ: Smart anti-airfield weapon and Atmanirbhar Bharat 3.0
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
- Department of Science and Technology
- Ministry of Labour and Employment
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Q.2) In The context of digital technologies for entertainment, consider the following statements : (2019)
- In Augmented Reality (AR), a simulated environment is created and the physical world is completely shut out.
- In Virtual Reality (VR), images generated from the computer are projected onto real-life objects or surroundings.
- AR allows individuals to be present in the world and improves the experience using the camera of a smartphone or PC.
- VR closes the world, and transposes an individual, providing a complete immersion experience.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 and 4
- 1, 2 and 3
- 4 only
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context: International Monetary Fund (IMF) recently confirmed a $3 billion bailout plan for Sri Lanka’s struggling economy.
- Bailout is a general term for extending financial support to a company or a country facing a potential bankruptcy threat.
- It can take the form of loans, cash, bonds, or stock purchases.
- A bailout may or may not require reimbursement and is often accompanied by greater government oversee and regulations.
About International Monetary Fund (IMF):

Source: IMF
- IMF was set up in 1945 out of the Bretton Woods conference.
- It is governed by and accountable to the 190 countries that make up its near-global membership.
- Headquartered in Washington, D.C.
- India became a member in December 1945.
- Publications:
- World Economic Outlook
- Global Financial Stability Report
- Fiscal Monitor
- Global Policy Agenda
- When a country borrows from the IMF, the government agrees to adjust its economic policies to overcome the problems that led it to seek financial assistance.
- These policy adjustments are conditions for IMF loans and help to ensure that the country adopts strong and effective policies.
Functions of IMF
- Financial assistance: Providing loans to member countries that are experiencing actual or potential balance-of-payments problems is a core responsibility of the IMF.
- Surveillance: In order to maintain stability and prevent crises in the international monetary system, the IMF monitors member country policies as well as national, regional, and global economic and financial developments through a formal system known as surveillance.
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs): The IMF issues an international reserve asset known as Special Drawing Rights, or SDRs, that can supplement the official reserves of member countries participating in the SDR Department (currently all members of the IMF).
- Resources: Member quotas are the primary source of IMF financial resources.
- A member’s quota broadly reflects its size and position in the world economy.
- The IMF regularly conducts general reviews of quotas.
- IMF Members: Any other state, whether or not a member of the UN, may become a member of the IMF in accordance with IMF Articles of Agreement and terms prescribed by the Board of Governors.
- Membership in the IMF is a prerequisite to membership in the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development.
Reasons for nations seeking an IMF bailout:
- Countries seek help from the IMF usually when their economies face a major macroeconomic risk, mostly in the form of a currency crisis.
- For instance in the case of Sri Lanka and Pakistan, both countries have witnessed domestic prices rise rapidly and the exchange value of their currencies drop steeply against the U.S. dollar.
- A rapid, unpredictable fall in the value of a currency can destroy confidence in said currency and affect economic activity as people may turn hesitant to accept the currency in exchange for goods and services.
- When a country’s domestic economic policies can also have an adverse impact on its currency’s exchange rate and foreign exchange reserves.
- For example, economic policy that imperils productivity can affect a country’s ability to attract the necessary foreign exchange for its survival.
- In the case of Sri Lanka, a decrease in foreign tourists visiting the country led to a steep fall in the flow of U.S. dollars into the nation.
Conditions laid out by IMF for recent bail-out
- The IMF is willing to support Sri Lanka but has some conditions regarding macroeconomic reforms.
- It wants Sri Lanka to be transparent about its debt situation.
- The IMF usually imposes conditions on countries before it lends any money to them. For example, a country may have to agree to implement certain structural reforms as a condition to receive IMF loans.
- The IMF’s conditional lending has been controversial as many believe that these reforms are too tough on the public.
- Some have also accused the IMF’s lending decisions, which are taken by officials appointed by the governments of various countries, to be influenced by international politics.
- Supporters of the IMF’s lending policies, however, have argued that conditions are essential for the success of IMF lending.
- For one, countries that seek an IMF bailout are usually in a crisis due to certain policies adopted by their governments that turned out to be inimical to economic growth and stability.
- It may thus not make sense for the IMF to throw money at a country when the policies that caused its crisis remain untouched.
- So, for instance, the IMF may demand a country affected by high price inflation to ensure the independence of its central bank.
- The IMF basically lends money, often in the form of special drawing rights (SDRs), to troubled economies that seek the lender’s assistance.
- SDRs simply represent a basket of five currencies, namely the U.S. dollar, the euro, the Chinese yuan, the Japanese yen, and the British pound.
Way Forward:
IMF’s stated mission is working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world. Therefore, It is important for the Government of Sri Lanka in collaboration with the IMF to work for the betterment of its economic and fiscal situation while securing transparency.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance) and GS 3 (Economy)
Context: India has called upon G20 countries to adopt multilateral action for faster extradition of fugitive economic offenders and recovery of assets both on domestic front as well as from abroad, during the first anti-corruption working group meeting in Delhi.
About India’s Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018:
- India has put in place specialized legislation in the form of the Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018.
- The ‘fugitive economic offender’ (FEO) is defined as an individual against whom a warrant of arrest in relation to scheduled offence has been issued by any court in India and who has left the country so as to avoid criminal prosecution; or the FEO abroad, refuses to return to face criminal prosecution.
- The Act aims to help confiscate assets of high-value economic offenders absconding from India till they submit to the jurisdiction of the appropriate legal forum.
Salient features of the act:
- Its purpose is to take the assets of economic criminals who have left the country to escape prosecution or refuse to return to face charges.
- Statement of FEO: After hearing the application, a special court (created under the PMLA, 2002) may designate someone as a fugitive economic offender.
- It has the right to take any property, whether in India or abroad, including Benami assets and criminal gains.
- Upon confiscation, the central government will become the only owner and own all rights and titles to the property (such as any charges on the property).
- Prohibition Against Filing or Defending Civil Claims: The Act permits any civil court or tribunal to bar a designated fugitive economic offender from filing or defending any civil claim.
Significance of the act:
- Recovering Loan Defaults: The key provision of confiscation of properties of fugitive economic offenders has helped in recovering loan defaults, which has been a major problem for Indian banks.
- For instance, in 2019, the Enforcement Directorate (ED) confiscated assets worth over Rs 18,000 crore belonging to fugitive economic offender Vijay Mallya.
- This helped in recovering a significant portion of the loans owed by him to Indian banks.
- International Cooperation: The act provides a mechanism for international cooperation in the investigation and prosecution of economic offenses.
- This has helped in the extradition of economic offenders who have fled the country.
- For instance, fugitive economic offender Nirav Modi was arrested in the UK and is currently facing extradition to India for his alleged involvement in the PNB scam.
- Transparency and Accountability: The act has helped in bringing transparency and accountability to the Indian banking sector by ensuring that economic offenders are held responsible for their actions.
- For instance, the act requires economic offenders to disclose all their assets, which helps in tracking and confiscating their properties.
- A deterrence for Economic Offenders: The act has acted as a strong deterrence for economic offenders from absconding.
- In the past, many economic offenders fled the country to escape prosecution, leaving Indian banks to suffer significant losses.
Criticisms of the Act:
- Under the Act, any court or tribunal may prohibit FEO from initiating or defending civil cases in its court or tribunal.
- It seems that excluding these individuals from initiating or defending civil claims would violate Article 21 of the Constitution, which protects the right to life.
- The property of an FEO may be seized and transferred to the central government.
- It permits the Special Court to exclude properties in which third parties may have an interest (e.g., secured creditors). It does not define, however, whether the central government would split sale revenues with other claimants who do not have such an interest, e.g., those who do not own the land (secured creditors).
- Before conducting a search, the Act does not require authorities to acquire a search warrant or verify the presence of witnesses.
- Other statutes, such as the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC) of 1973, incorporate comparable protections.
- These measures provide protection against harassment and abuses such as evidence planting.
- It permits the forfeiture of an FEO’s property. This varies from other regulations, such as the Criminal Procedure Code of 1973, where confiscation is final two years after an absconder is declared.
- The time period ensures due process without jeopardizing the defendant’s legal interests.
Way Forward:
Thus the government can consider introducing measures to ensure that the act is not misused, providing greater clarity on the definition of economic offenses, and improving the efficiency of the legal system to ensure speedy trials. India can improve transparency and accountability in its financial system to prevent FEOs from exploiting loopholes and engaging in illegal activities.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q.1) With reference to India, consider the following statements:
- All money bills are financial bills, but not all financial bills are money bills.
- A bill shall be deemed to be a Money Bill if it contains only provisions dealing with all or any of the matters mentioned in the article 112 of the constitution.
- The President of India is authorised to decide whether the Bill is a Money Bill or not.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 only
- 1 and 3 only
Q.2) Consider the following statements regarding the Khandagiri Udayagiri caves:
- These caves are located near Pune, Maharashtra
- These caves built by the Kalinga emperor Kharavela in first century B.C.
- The Rani and Hathi Gumpha in the Udayagiri has description of the culture of Odissi.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding the International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS):
- ICOMOS is a United Nations specialised organisation.
- It is the only global organisation, which is dedicated to promoting the application of theory, methodology, and scientific techniques to the conservation of architectural and archaeological heritage.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 27th March 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 25th March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) - c
Q.2) - b
Q.3) - d
[/su_box











