IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Recently, NeGD organised the 36th CISO Deep-Dive Training Programme under Cyber Surakshit Bharat.
About CISO Deep-Dive Training Programme:-
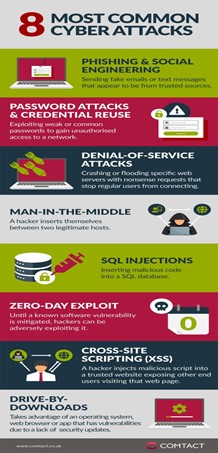
IMAGE SOURCE: Infographic: The 8 most common types of Cyber Attacks – CyberOne
- It’s a training programme, under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It is a five-day intensive training programme.
- The CISO training programme was launched in 2018 under the Public Private Partnership (PPP) model.
- NeGD has organized 36 sessions of CISO deep-dive training programs for more than 1,419 CISOs and IT officials since that time.
- Participants: it had 24 participants, including CISOs, technical wings of police and security forces, CTOs, and members of technical/PMU teams from Central Line Ministries and States/UTs.
- The purpose of the CISO Deep-Dive training programme is to provide CISOs with a comprehensive understanding of cyber-attacks, the latest safeguarding technologies, and how to communicate the benefits of a strong e-infrastructure to organizations and the public. (UPSC PRELIMS: India’s cyber infrastructure)
- Additionally, the training seeks to give a comprehensive view of legal provisions and help build concrete crisis management plans for cyber-attacks. (UPSC CSE: Cybercrime)
- Coverage of Topics:-
- Governance Risk and Compliance, the Landscape of Cyber Security Products in India, Security for Endpoints and Digital Workplaces, Network Security, Security for Applications and Data, Incident Response and CCMP, Mobile Security, Cryptography, Cyber Security Testing and Audit, Cyber Security related Provisions of IT Act and ISMS Standards such as ISO 27001, as well as Security Logging and Operation and Monitoring of Security Operation Centers.
Cyber Surakshit Bharat:-
- It is the initiative of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- It was conceptualised with the mission to spread awareness about cybercrime and build capacities of Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT officials, across all government departments, for ensuring adequate safety measures to combat the growing menace.
MUST READ: Cyber Attacks in India
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In India under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) Consider the following pairs of Terms sometimes seen in news vs Context /Topic: (2018)
- Belle II experiment: Artificial Intelligence
- Blockchain technology: Digital/ Cryptocurrency
- CRISPR — Cas9: Particle Physics
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council(GJEPC) launched India Jewellery Exposition 2023.
About Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council(GJEPC):-
IMAGE SOURCE: Gems and Jewellery Industry in India by 10rahulcc on DeviantArt
- The Gem & Jewellery Export Promotion Council is the apex body founded in 1966.
- It drives India’s export-led growth in the gem and jewellery sector. (UPSC MAINS: Export-oriented units)
- Headquartered in Mumbai.
- It has regional offices across the country and over 7,500 members in its fold.
- VISION: to make India the preferred source for quality gems and jewellery. (UPSC PRELIMS: India’s Gems & Jewellery sector )
Objectives:-
- PROMOTING BRAND INDIA:-
- Organising India’s biggest and second-biggest trade shows, IIJS Premiere and IIJS Signature
- Organising joint participation in international jewellery shows
- CONNECTING GOVERNMENT & TRADE:-
- Facilitating better interaction on trade-related issues between the industry and the Government of India, Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Ministry of Finance, DGFT, Dept of Commerce, Dept. of Finance
- UPHOLDING DIAMOND INTEGRITY:-
- Executing the Kimberly Process Certification Scheme in the country, as the Nodal Agency appointed by the Government of India
- SPREADING EDUCATION:-
-
- Running training institutes that impart manufacturing skills, technical and design excellence in six cities – Mumbai, Delhi, Surat, Jaipur, Varanasi and Udupi
- INNOVATION AND INFRASTRUCTURE:-
- Providing MSMEs with affordable modern machines and tools at Common Facility Centres
- Setting up Jewellery Parks across the country
- HEALTH AND WELL-BEING:-
- Providing health insurance for the employees of the Council’s member companies through the group mediclaim scheme called Swasthya Ratna
- PAYING BACK TO SOCIETY:-
- Founded by GJEPC in 2014, Jewellers for Hope has donated Rs.1 crore every year to one or more NGOs/charities doing exceptional work in supporting the underprivileged.
- Providing relief to victims of natural calamities and emergency situations through the Gem & Jewellery National Relief Foundation (GJNRF).
MUST READ: New Foreign Trade Policy
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana is aimed at (2016)
- bringing small entrepreneurs into the formal financial system
- providing loans to poor farmers for cultivating particular crops
- providing pensions to old and destitute persons
- funding the voluntary organizations involved in the promotion of skill development and employment generation
Q.2) What is/are the purpose/purposes of `District Mineral Foundations in India? (2016)
- Promoting mineral exploration activities in mineral-rich districts
- Protecting the interests of the persons affected by mining operations
- Authorizing State Governments to issue licences for mineral exploration
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the Finance Minister chaired the meeting of the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC).
About Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC):-
IMAGE SOURCE: What is the meaning of fiscal deficit? – OneMint
- The Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) was constituted by executive order in 2010.
- It is a non-statutory apex council.
- It works under the Ministry of Finance.
- The Council can invite experts to its meeting if required.
- The Raghuram Rajan committee (2008) on financial sector reforms first proposed the creation of FSDC.
- It is chaired by the Finance Minister.
- FSDC sub-committee is headed by the Governor of RBI.
- Its members include:-
- The heads of all Financial Sector Regulators (RBI, SEBI, PFRDA & IRDA)
- Finance Secretary
- Secretary of the Department of Economic Affairs (DEA)
- Secretary of the Department of Financial Services (DFS)
- Chief Economic Adviser
- Minister of State for the Department of Economic Affairs (DEA)
- Secretary of the Department of Electronics and Information Technology,
- Chairperson of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI)
- Revenue Secretary.
- Objectives:-
- To strengthen and institutionalize the mechanism for maintaining financial stability, enhancing inter-regulatory coordination and promoting financial sector development. (UPSC MAINS: Mechanism to address fiscal deficit)
- To monitor macro-prudential supervision of the economy. (UPSC MAINS: Macro-economic stability)
- It assesses the functioning of the large financial conglomerates.
MUST READ: Financial Stability Report
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements: (2022)
- If the inflation is too high, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is likely to buy government securities.
- If the rupee is rapidly depreciating, RBI is likely to sell dollars in the market.
- If interest rates in the USA or European Union were to fall, that is likely to induce RBI to buy dollars.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements (2018)
- The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Review Committee Report has recommended a debt-to-GDP ratio of 60% for the general (combined) government by 2023, comprising 40% for the Central Government and 20% for the State Government.
- The Central Government has domestic liabilities of 21% of GDP as compared to that of the war of GDP of the State 2 Governments.
- As per the Constitution of India, it is mandatory for a State to take the Central Government’s consent for raising any loan if the former owes any outstanding liabilities to the latter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, the Border Roads Organisation started constructing 6,100km of road on the China border.
About Border Roads Organisation:-
- BRO was conceived and raised in 1960 by Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru for coordinating the speedy development of a network of roads in the North and the North Eastern border regions of the country.
- It works under the administrative control of the Ministry of Defence. (UPSC PRELIMS: Umbrella scheme of Border Infrastructure & Management (BIM))
- Functions:-
- It develops and maintains road networks in India’s border areas and friendly neighbouring countries. (UPSC MAINS: Economic and strategic advantages of Border road infrastructure)
- Construction and development works comprising airfields, building projects, defence works and tunnelling and has endeared itself to the people.
- Staff:-
- It is staffed by officers and troops drawn from the Indian Army’s Corps of Engineers, Electrical and Mechanical Engineers, Army Service Corps, Military Police and army personnel on extra regimental employment.
- Officers from the Border Roads Engineering Service and personnel from the General Reserve Engineer Force (GREF) form the parent cadre of the Border Roads Organisation.
- Currently, the organisation maintains operations in twenty-one states, one UT (Andaman and Nicobar Islands), and neighbouring countries such as Afghanistan, Bhutan, Myanmar, and Sri Lanka.
MUST READ: Sela Tunnel Project
SOURCE: TIMESOFINDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following countries : (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
- 1, 2, 4 and 5
- 3, 4, 5 and 6
- 1, 3, 4 and 5
- 2, 3, 4 and 6
Q.2) Consider the following countries (2015)
- China
- France
- India
- Israel
- Pakistan
Which among the above are Nuclear Weapons States as recognized by the Treaty on the Nonproliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonly known as the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT)?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 3, 4 and 5 only
- 2, 4 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Personalities
Context: Recently, the Prime Minister paid homage to Gopal Krishna Gokhale on his birth anniversary.
About Gopal Krishna Gokhale:-

IMAGE SOURCE: Gopal krishna gokhale (slideshare.net)
- Gopal Krishna Gokhale was a great social reformer and educationist who provided exemplary leadership to India’s freedom movement.
- Ideology:-
- He worked towards social empowerment, expansion of education, and struggle for freedom in India for three decades and rejected the use of reactionary or revolutionary ways.
- He joined Indian National Congress in 1889.
- He was associated with the Moderate Group of Indian National Congress. (UPSC MAINS: Key achievements of the moderates)
- He became president of INC in 1905 in Banaras’s session.
- Societies and Other Works:-
- Gokhale with the aid of M.G. Ranade established the Servants of India Society in 1905 for the expansion of Indian education.
- He was also associated with the Sarvajanik Sabha journal started by Govind Ranade.
- In 1908, Gokhale founded the Ranade Institute of Economics.
- He started an English weekly newspaper, The Hitavada (The People’s Paper).
- Role in Colonial Legislatures:-
- Between 1899 and 1902, he was a member of the Bombay Legislative Council followed by work at the Imperial Legislative Council from 1902 till his death (1915).
- Mahatma Gandhi was regarded as his political master. (UPSC MAINS: Non-Cooperation Movement)
- Gandhi wrote a book in Gujarati dedicated to the leader titled ‘Dharmatma Gokhale’.
MUST READ: Mahatma Gandhi
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following freedom fighters: (2022)
- Barindra Kumar Ghosh
- Jogesh Chandra Chatterjee
- Rash Behari Bose
Who of the above was/were actively associated with the Ghadar Party?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Q.2) Who among the following was associated as Secretary with Hindu Female School which later came to be known as Bethune Female School? (2021)
- Annie Besant
- Debandranath Tagore
- Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar
- Sarojini Naidu
Syllabus
- Prelims –Defence
Context: A MiG-21 fighter jet of the Indian Air Force (IAF) crashed near Rajasthan’s Suratgarh recently.
About MiG-21 fighter jet:-
- The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG 21 is a supersonic jet fighter and interceptor aircraft.
- It is designed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich Design Bureau in the Soviet Union.
- The MiG-21 is capable of performing a range of roles and can be used for both air-to-air and ground attacks.
- It has a single engine and can seat only one person.
- MiG is a product of the Soviet Union which entered into the service in 1959.
- India inducted the MiG-21 in 1963 and got full technology transfer and rights to license-build the aircraft in the country.
- The MiG-21 has proved its mettle in several wars fought by India, including the Bangladesh Liberation War of 1971. (UPSC CSE: 50 Years of Bangladesh Liberation War)
- It was also one of the mainstay fighter jets in the 1965 and 1999 Kargil conflicts with Pakistan
- In 2019, a MiG-21 Bison flown by Wing Commander Abhinandan Varthaman downed an F-16 aircraft of the Pakistan Air Force. (UPSC CSE: Balakot Airstrike )
- Russia stopped producing the aircraft in 1985.
- India continued operating the upgraded variants.
- India has procured over 700 MiG-21 aircraft of different variants since then, such as the Type-77, Type-96 and the BIS.
- The latest of them is the MiG-21 Bison.
- MiG-21 Bison: this is an upgraded aircraft with advanced missiles and radars and better avionics.
- Over 100 MiG-21s with the IAF have been upgraded to Bison since 2006.
- The IAF has three squadrons of MiG-21 Bison aircraft currently in service, planned to be phased out by 2025.
MUST READ: Tejas Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Mk-1A
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best reflects the idea behind the “Fractional Orbital Bombardment System” often talked about in media? (2022)
- A hypersonic missile is launched into space to counter the asteroid approaching the Earth and explode it in space.
- A spacecraft lands on another planet after making several orbital motions.
- A missile is put into a stable orbit around the Earth and deorbits over a target on the Earth.
- A spacecraft moves along a comet with the same surface. speed and places a probe on its
Q.2) Which reference to Agni-IV Missile, of the following statements is/are correct? (2014)
- It is a surface-to-surface missile.
- It is fuelled by liquid propellant only.
- It can deliver one-tonne nuclear warheads about 7500 km away.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Personalities
Context: Recently, a controversy arose pertaining to Saint Samarth Ramdas’s alleged connection to Marathi icon Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
About Saint Samarth Ramdas:-
- Saint Samarth Ramdas was an Indian Marathi Hindu saint, poet, philosopher, writer and spiritual master. (UPSC CSE: Swami Vivekananda )
- He was a devotee of Hindu deities Rama and Hanuman.
- He was previously famous as Narayan.
- He was born in Jamb, a village in the present-day Jalna district of Maharashtra.
- He was born on the occasion of Rama Navami, in 1608.
- His Works:-
- His literary works include Karunashtakas, Dasbodh, Yuddhakand, Sunderkand, Poorvarambh, Antarbhav, Chaturthman, Aatmaaram, Panchman, Panchsamasi, Manpanchak, Janaswabhawgosavi, etc.
- Ramdas is not deemed a pacifist.
- His writings include strong expressions encouraging nationalism to counter aggressive Muslim invaders.
- His Legacy:-
- Ramdas served as an inspiration for several Indian thinkers, historians and social reformers from the 19th and 20th-century, including Bal Gangadhar Tilak, Rajwade, Keshav Hedgewar, and Ramchandra Ranade. (UPSC MAINS: Contribution did Swami Vivekananda)
- A spiritual guru, Nana Dharmadhikari, promoted the views of Ramdas through his spiritual discourses.
MUST READ: Dayanand Saraswati
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Madanapalle of Andhra Pradesh, which one of the following statements is correct? (2021)
- Pingali Venkayya designed the tricolour Indian National Flag here.
- Pattabhi Sitaramaiah led the Quit India Movement of the Andhra region from here.
- Rabindranath Tagore translated the National Anthem from Bengali to English here.
- Madame Blavatsky and Colonel Olcott set up the headquarters of the Theosophical Society first here.
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2021)
- St. Francis Xavier was one of the founding members of the Jesuit Order.
- St. Francis Xavier died in Goa and a church is dedicated to him there.
- The feast of St. Francis Xavier is celebrated in Goa each year.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the phenomenon of the gold rush by central banks was observed.
About Gold Rush:-
- The Adding gold to its reserves at an unusual pace is commonly called the ‘gold Rush’. (PSC PRELIMS: Gold Reserve)
- Objective: to safeguard its returns amid global uncertainty and a rising inflation scenario.
- adding gold to its reserves, is considered a more safe, secure, liquid asset.
- Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) gold reserves showed an increase of nearly 5 per cent over fiscal 2022 when it held 760.42 metric tonnes of gold. (UPSC MAINS: Factors to maintain a healthy foreign exchange reserve)
- Global Scenario:-
- Many other central banks, including the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), the People’s Bank of China (PBoC) and the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey have been buying gold.
- In the calendar year 2022, central banks around the world purchased 1,136 tonnes of gold, which was a record high.
- During 2022, the central banks from the Middle East, including Egypt, Qatar, Iraq, the UAE, and Oman significantly boosted their gold reserves.
- The Central Bank of Uzbekistan ended 2022 as a net purchaser of gold, with its gold reserves rising by 34 tonnes.
- In January-March 2023, the Monetary Authority of Singapore was the largest single buyer of gold after it added 69 tonnes to its gold reserves
- The two key drivers of central banks’ decisions to hold gold are:-
- its performance during times of crisis, and
- its role as a long-term store of value
MUST READ: RBI relaxed norms to stem rupee slide and to Forex inflows
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements: (2022)
- An increase in Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) indicates the appreciation of the rupee.
- An increase in the Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) indicates an improvement in trade competitiveness.
- An increasing trend in domestic inflation relative to inflation in other countries is likely to cause an increasing divergence between NEER and REER.
Which of the above statements is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements: (2022)
- If the inflation is too high, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is likely to buy government securities.
- If the rupee is rapidly depreciating, RBI is likely to sell dollars in the market.
- If interest rates in the USA or European Union were to fall, that is likely to induce RBI to buy dollars.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Context: China has maintained its stance on the UN Security Council reforms, saying there should be more representation for developing countries, but avoided a direct response to India and other countries’ call for its expansion and their inclusion.
About United Nations Security Council:
- The UNSC was established by the UN Charter in 1945.
- It is one of the 6 principal organs of the United Nations.
- UNSC has 15 members: 5 permanent members (P5) and 10 non-permanent members elected for 2-year terms.
- The 5 permanent members are: United States, Russian Federation, France, China and the United Kingdom.
- India has served seven times in the UNSC as a non-permanent member and in January 2021, India entered the UNSC for the eighth time.
UNSC elections:
- Each year the General Assembly elects five non-permanent members (out of 10 in total) for a two-year term.
- The 10 non-permanent seats are distributed on a regional basis as follows:
- Five for African and Asian States.
- One for the Eastern European States.
- Two for the Latin American and Caribbean States;
- Two for Western European and other States
- To be elected to the Council, candidate countries need a two-thirds majority of ballots of the Member States that are present and voting in the Assembly.
- The UNSC elections were traditionally held in the General Assembly hall with each of the 193 member states casting its vote in a secret ballot.
Need:
Changing world order:
- In the 77-year-old history of the UN, the composition of the Security Council has been altered only once.
- e., In 1963 when the General Assembly decided to expand the Council from 11 to 15 members, with the addition of four non-permanent seats.
- Since then, the world has changed. The geopolitical relations in the world have altered, the economic responsibilities in the world in countries have also changed.
Equitable World Order:
- There is a need for a more equitable world in order to uphold the principles of democracy at the global level.
- Developing countries like the African countries, need to be made stakeholders in the multilateral institutions and involved in the decision-making process.
Mitigation of New Threats:
- With rising protectionism, increased incidents of terrorism and the threat of climate change, the multilateral system must become more resilient and responsive.
Issues with regard to UNSC:
Lack of Adequate Representation:
- The UN Security Council is less effective because it is less representative, the most pertinent absence being that of Africa, a continent of 54 countries.
- Current global issues are complex, and interconnected.
- Lack of representation of geopolitical and geo-economically important countries is leaving out a large segment of global opinion to have a voice in the highest security summit.
Misuse of Veto Power:
- Veto power has been always criticized by many experts as well as by most States calling it a” self-chosen club of the privileged” and non-democratic and not allowing the Council to make necessary decisions whenever it displeases any one of the P-5.
- It is also not appropriate for the current global security environment to be guided by elite decision-making structures.
Geopolitical Rivalry within P5:
- The geopolitical rivalry among the permanent members has prevented the UNSC from coming up with effective mechanisms to deal with global issues.
- Taking the current world order as an example, the P5 members: United States, Russia, and China are three poles on the periphery of the globe having several geopolitical issues revolving around them (Taiwan Issue and Russia-Ukraine War).
Threat to State’s Sovereignty:
- As the principal organ of international peacekeeping and conflict resolution, the UNSC is responsible for keeping peace and managing conflict.
- Its decisions (referred to as resolutions) are binding on all member countries, unlike the General Assembly’s.
- This means that any state’s sovereignty can be encroached upon, if necessary, by acting, such as imposing sanctions.
Significance of India as a permanent UNSC member:
- Global decision-making: As a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC), India would have a more significant role in shaping global decision-making and playing a prominent role in maintaining international peace and security.
- Representation of the global south: It would address the issue of under-representation of developing countries in the Council.
- As the world’s largest democracy, with a population of over 1.3 billion people and a growing economy, India’s permanent membership would ensure that the voices and interests of the global South are better represented in the UNSC.
- Larger role in dealing with the new age challenges: India’s permanent membership would give it greater leverage in dealing with regional and international issues.
- India could play a more active role in addressing challenges such as terrorism, climate change, and nuclear disarmament.
- Peace Keeping efforts: India has consistently contributed to the UN peacekeeping efforts. Despite this, it has no say in how the peace-making forces will be deployed and how the mandate will be exercised.
- India’s inclusion in the UNSC would also give India more say in decisions regarding peacekeeping operations and interventions in conflict zones.
- Recognition as an emerging power: India’s permanent membership would also be a recognition of its growing global importance and its commitment to multilateralism.
- India’s permanent membership in the UNSC would be an affirmation of its place as a key player in shaping the future of the world.
Suggestive Measures:
- the Security Council should better reflect on the current global realities and incorporate more geographically diverse perspectives.
- It must demonstrate flexibility and willingness to compromise in the name of greater credibility and legitimacy.
- Developing countries vision of development for the South and the role on the UN in promoting and achieving such vision needs to be strongly and consistently articulated.
- The UN’s role as the core global governance institution should not be undermined by the UN reform Rather, such process should result in a strengthened mandate for the UN as the primary global governance institution to be able to exercise coordinative functions over the work of the major multilateral economic policymaking institutions like the World Bank, the IMF and the WTO.
- India should continue to push hard for UNSC reforms. Foreign Policy experts suggest that a pragmatic approach should be to accept a permanent status without the power to veto.
Way Forward:
India’s claim for permanent membership is a genuine demand in the changed geo politics of 21st century as we have discussed before. India is possibly the most obvious and least controversial option to add as a permanent member, and probably long overdue for a seat.
However it is under constant criticism for its plans and actions. It is said to be performing in unilateral way with unquestioned authority, working only for vested interests and not making non-permanent members inclusive in their decision making.
Source: Times of India
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recent failures of Indian manufactured drugs overseas (like the Gambia incident) have brought attention to the issue of absence of a drug recall law in the pharmaceutical industry in India.
About Drug Recall:
- Drug recall refers to the action of removing or withdrawing a batch of product from distribution or use, to be returned to the manufacturer.
- This action is generally done in cases where deficiencies are discovered in the safety, quality, or efficacy of drugs.
- The Organization of Pharmaceutical Producers of India (OPPI) defines recall as,
- “An action is taken to resolve a problem with therapeutic goods for which there are established deficiencies in quality, efficacy or safety.”
Status of Drug Recall Law in India:
- India has been considering the creation of a mandatory recall law for substandard drugs since 1976, but still no law exists that mandates such medicine be removed from the market.
- In 1976, the Drugs Consultative Committee (DCC), discussed the issue of drug recalls with the various state regulators, however, none of them resulted in amendments to the Drugs & Cosmetics Act to create a mandatory recall mechanism.
- In 2012, the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) proposed a set of draft recall guidelines but the national regulator lacks the power to convert guidelines into a binding law.
- The issue of recalls resurfaced in 2016 at meetings of the DCC and at another committee, called the Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB).
- Nothing changed on the ground. The same issue came up again in 2018 and 2019 at the meetings of the DCC, but India still lacks a recall law, 46 years on.
Reasons for Absence of Drug Recall Law in India:
- Incompetence of authorities: The Drug Regulation Section of the Union Health Ministry is unable to tackle complex drug regulatory issues due to a combination of factors including apathy, lack of expertise etc.
- Vested interests: There have been indications that Ministry of Health has greater interest in enabling the growth of the pharmaceutical industry than protecting public health.
- It is believed that tighter regulation could slow the growth of the pharmaceutical industry.
- Fragmented regulatory structure: India has one of the most fragmented regulatory structures with each State having its own drug regulator.
- One regulator cannot inspect facilities in another jurisdiction.
- Opposition to centralized authority: There must be a central authority that has legal powers to hold companies liable for failures to recall drugs.
- However, pharmaceutical industry and state drug regulators have opposed centralization of regulatory powers.
- Bad publicity to pharma companies: A drug recall will mandate companies to publicize the product in media, which will generate bad publicity for pharma companies.
- This will not only harm them individually but will dent India’s image on the global scale.
Present Laws Regulating the Drugs and Pharmaceutical Sector in India:
- Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation: It is the National Regulatory Authority (NRA) of India.
- The Drugs & Cosmetics Act,1940 and rules 1945 have entrusted various responsibilities to central & state regulators for regulation of drugs & cosmetics.
- It envisages uniform implementation of the provisions of the Act & Rules made there under for ensuring the safety, rights and wellbeing of the patients by regulating the drugs and cosmetics.
- CDSCO along with state regulators, is jointly responsible for grant of licenses of certain specialized categories of critical Drugs such as blood and blood products, I. V. Fluids, Vaccine and Sera.
- The Drugs & Cosmetics Act, 1940: It regulates the import, manufacture, distribution and sale of drugs in India.
- The Pharmacy Act,1948: It is meant to regulate the profession of Pharmacy in India.
- The Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisement) Act, 1954: It provides to control the advertisements regarding drugs; it prohibits the advertising of remedies alleged to possess magic qualities.
- The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985: It is an act concerned with control and regulation of operations relating to Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances.
- National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority: It is an organization of the Government of India which was established, inter alia, to fix/ revise the prices of controlled bulk drugs and formulations and to enforce prices and availability of the medicines in the country, under the Drugs (Prices Control) Order, 1995.
- The organization is also entrusted with the task of recovering amounts overcharged by manufacturers for the controlled drugs from the consumers. It also monitors the prices of decontrolled drugs in order to keep them at reasonable levels.
Suggestive Measures
A national drug recall law:
- It is crucial for India to have a national drug recall law to guarantee that once a drug is known to be Not of Standard Quality (NSQ), the entire batch is withdrawn from the market.
A central drug regulator:
- There needs to be a central drug regulator who can execute and coordinate national recall.
Inspections of manufacturing facilities:
- Drug inspectors are required to carry out inspections of manufacturing facilities on an annual basis to ensure compliance with the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) code.
- It is possible that in many states, there is a lack of capacity and training to do so.
- But the larger problem, is a reluctance to actually enforce the GMP standards because it would put several SME pharma companies out of business.
Health Activism
- As with any other aspect of Indian society, activism can help move the needle on any policy issues.
- Health activists need to accept there is a problem with drug regulation and ask for systemic reform.
- Right now, there appears to be a reluctance to even accept there is a problem with drug quality in India.
Source: The Hindu
About Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation(CDSCO)
- CDSCO comes under Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
- It is the National Regulatory Authority (NRA) of India for Drugs.
- The Drugs & Cosmetics Act, 1940 and Rules 1945 have entrusted various responsibilities to central & state regulators for regulation of drugs & cosmetics.
- Under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, CDSCO is responsible for approval of Drugs, Conduct of Clinical Trials.
- Further CDSCO along with state regulators, is jointly responsible for grant of licenses of certain specialized categories of critical Drugs such as blood and blood products, I. V. Fluids, Vaccine etc.
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation(CDSCO):
- CDSCO comes under the Department of Pharmaceuticals
- It is the National Regulatory Authority (NRA) of India for Drugs.
- Under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, CDSCO is responsible for approval of Drugs, Conduct of Clinical Trials.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Q.2) He was a great social reformer and educationist who provided exemplary leadership to India’s freedom movement. He became president of INC in 1905 in Banaras’s session. With the aid of M.G. Ranade, He established the Servants of India Society in 1905 for the expansion of Indian education. Between 1899 and 1902, he was a member of the Bombay Legislative Council.
Which of the following freedom fighters described in the above paragraph?
- Lala Lajpat Rai
- Bal Gangadhar Tilak
- Gopal Ganesh Agharkar
- Gopal Krishna Gokhale
Q,3) Consider the following statements regarding the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC):
- It is a statutory apex council.
- It works under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- It aims to strengthen and institutionalize the mechanism for maintaining financial stability, enhancing inter-regulatory coordination and promoting financial sector development.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 10th May 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 9th May – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – c











