IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: District Legal Services Authority in West Tripura recently organized Door-to-Door Legal Aid Campaign.
About District Legal Services Authority:-
- Legal Services Authorities are statutory bodies that are formed in the various states of India under the Legal Services Authorities Act, of 1987.
- Objective: to provide free legal aid and services to the weaker sections of this society to make sure that opportunities for securing justice are not denied to any citizen because of economic or other disabilities.
- It is organized at the district level to provide effective monitoring of legal aid programmes and their composition.
- Related Constitutional provision:
- Article 39-A: Deals with the provision of providing free legal services to the citizens of India.
- The provision applies to the citizens if they are unable to bear the expenditure of legal services.
- It also helps the defendant by appointing a lawyer to act for him in legal aspects.
- Composition of DLSA:-
- The State Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of the High Court constitutes it. (UPSC CSE: Judicial appointments)
- Chairman: District Judge
- Other members: must have the experience and qualifications as prescribed by the State Government.
- The Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of the High Court may nominate these members.
- The person to be appointed shall belong to the State Judicial Service and not lower than rank than that of a Subordinate Judge or Civil Judge posted at the seat of the District Judiciary as Secretary of the District Authority.
- Member Secretary of the District Authority: Assistant Commissioner of the concerned District
- The officers and other employees of the District Authority are entitled to salary and allowances and shall be subject to such other conditions of the services as the State Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of the High Court prescribes.
- Article 39-A: Deals with the provision of providing free legal services to the citizens of India.
Legal Services Institutions at Various Levels:-
The Legal Services Authorities Act, of 1987 mandates the establishment of the following at various levels;
National Level: National Legal Services Authorities (NALSA)
- The NALSA was founded in 1995 under the Legal Services Authorities Act of 1987.
- Objective: to monitor and review the effectiveness of legal aid programs and to develop rules and principles for providing legal services under the Act.
- Patron-in-Chief: Chief Justice of India
- It distributes funding and grants to state legal services authorities and non-profit organisations to help them execute legal aid systems and initiatives.
State Level: State Legal Services Authority
- Patron-in-Chief: Chief Justice of the State High Court
At District Level: District Legal Services Authority.
- ex-officio Chairman: District Judge of the District
At Taluka/Sub-Division Level: Taluka/ Sub-Divisional Legal Services Committee.
- A senior Civil Judge heads it.
Eligibility for free legal service:-
- Women and children
- Members of SC/ST
- Industrial workmen
- Victims of mass disasters, violence, flood, drought, earthquake, and industrial disasters.
- Disabled persons
- Persons in custody
- Those persons who have an annual income of less than the amount prescribed by the respective State Government, if the case is before any court other than the Supreme Court, and less than Rs. 5 Lakhs if the case is before the Supreme Court.
- Victims of Trafficking in Human beings or begar.
Nyaya Bandhu’s (Pro Bono Legal Services)
- It is a primary initiative to establish a framework for the dispensation of pro bono (free of cost) legal services across the country.
- Under Nyaya Bandhu, practising advocates, interested to volunteer their time and services, are connected, via mobile technology, with eligible marginalised beneficiaries.
- Nyaya Bandhu Mobile application (Android/IOS) has been developed in collaboration with technical partner Common Services Centres (CSC) e-Governance Pvt. Ltd.
- Common Services Centres (CSC) are the access points for the delivery of various e-governance and business services to citizens in rural and remote areas of the country. (UPSC MAINS: Risks in e-governance)
- CSC e-Governance Services India Limited, a Special Purpose Vehicle set up under the Companies Act, 1956.
- Ministry: Ministry of Electronics & IT
- Objective: to oversee the implementation of the CSC scheme.
- It provides a centralized collaborative framework for the delivery of services to citizens through CSCs, besides ensuring the systemic viability and sustainability of the Scheme.
- Nyaya Bandhu Mobile application has been on boarded on the UMANG platform.
- UMANG (Unified Mobile Application for New-age Governance) is developed by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and the National e-Governance Division (NeGD).
MUST READ: Judicial Accountability
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Judicial custody means an accused is in the custody of the concerned magistrate and such an accused is locked up in a police station, not in jail.
- During judicial custody, the police officer in charge of the case is not allowed to interrogate the suspect without the approval of the court.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to Indian Judiciary, consider the following statements. (2021)
- Any retired judge of the Supreme Court of India can be called back to sit by the Chief Justice of India with the prior permission of the President of India.
- A High Court in India has the power to review its own judgement as the Supreme Court does.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
: The National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) Rankings 2023 were released recently.
About National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) Rankings 2023:-
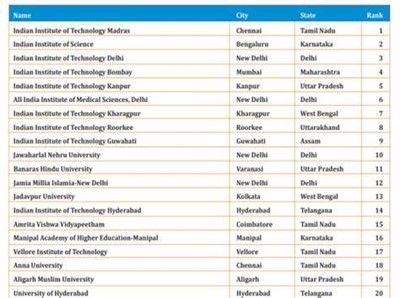
IMAGE SOURCE: findhow.net
- The National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) is a methodology to rank institutions of higher education in India.
- Ministry: Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD)
- Objective: help universities to improve their performance on various ranking parameters and identify gaps in research and areas of improvement.
- There are separate rankings for different types of institutions depending on their areas of operation like universities and colleges, engineering institutions, management institutions, pharmacy institutions and architecture institutions.
- Five broad categories of parameters identified in the NIRF: Teaching, learning and resources (TLR); research and professional practice; graduation outcome; outreach; and inclusivity and perception.
Key findings of NIRF 2023:-
- Indian Institute of Technology Madras: retains its first position in Overall Category and Engineering.
- Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru: tops the Universities Category and stood first in Research Institutions Category.
- IIM Ahmedabad: tops in Management subject retaining its first position.
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi: top slot in Medical.
- National Law School of India University, Bengaluru: retains its first position.
- Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi: takes the top slot in Agriculture and Allied Sectors.
- Three distinct additions to the 2023 edition of India Rankings are as follows:-
- Introduction of a new subject namely Agriculture & Allied Sectors. (UPSC CSE: Agriculture Reforms)
- Integration of the “Innovation” ranking to reduce the burden on institutions of providing similar data to two different agencies.
- Expansion of scope of “Architecture” to “Architecture and Planning” to include institutions imparting courses in Urban and Town Planning. (UPSC CSE: Transforming Indian Cities)
- With the addition of these, the existing portfolio of India Rankings has increased to 13 categories and subject domains that have been ranked in India Rankings 2023.
- It ranks Overall, Universities, Colleges, and Research Institutions & Innovation.
- It ranks 8 subject domains: Engineering, Management, Pharmacy, Architecture & Planning, Medical, Law, Dental Agriculture and Allied Sectors.
MUST READ: Education & Nation Building
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) What is the purpose of ‘Vidyanjali Yojana’? (2018)
- To enable famous foreign educational institutions to open their campuses in India.
- To increase the quality of education provided in government schools by taking help from the private sector and the community.
- To encourage voluntary monetary contributions from private individuals and organizations to improve the infrastructure facilities for primary and secondary schools.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
Q.2) What is the aim of the programme ‘Unnat Bharat Abhiyan’? (2018)
- Achieving 100% literacy by promoting collaboration between voluntary organizations and the government’s education system and local communities.
- Connecting institutions of higher education with local communities to address development challenges through appropriate technologies.
- Strengthening India’s scientific research institutions in order to make India a scientific and technological power.
- Developing human capital by allocating special funds for health care and education of rural and urban poor, and organizing skill development programmes and vocational training for them.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Art and Culture
Context: Recently, debates on who built the Agra Fort has started again.
About Agra Fort:-
- The Agra Fort is a UNESCO World Heritage site that attracts people from all over the world.
- This fort has been occupied by several dynasties, including the Rajputs, Mughals, Jats, and Marathas.
- The fort underwent a construction of eight years under the reign of Akbar in 1565.
- However, the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) lacks knowledge about who built the Agra Fort first and what changes it underwent during Akbar’s reign.
- It is made of red sandstone.
- It comprises the Jahangir Palace and the Khas Mahal (built by Shah Jahan), Diwan-i-Khas and two very beautiful mosques.
- It was the main residence of the emperors of the Mughal Dynasty until 1638 when the capital was shifted from Agra to Delhi.
- It became a UNESCO World Heritage site in 1983. (UPSC MAINS: Mandate and significance of UNESCO)
Important Structures Inside the Agra Fort:-
- Jahangir’s Hauz: This is a monolithic tank, and was built by Jahangir.
- The tank was initially used for bathing.
- It is now a part of Akbar’s Bengali Mahal.
- Shahjahani Mahal: The Shahjahani Mahal is probably one of the earliest attempts of Emperor Shah Jahan to turn a red sandstone palace into a palace of white marble.
- Babur’s Baoli (step well): Babur built a stone step well, which took care of the water needs in the ancient fort of Agra.
- Nagina Masjid: Nagina Masjid is a mosque, which was built by Shah Jahan.
- The mosque was built using white marble only and was considered a private place of worship.
- Diwan-I-Am (Hall of Public Audience): This hall was built by Shah Jahan.
- Interestingly, the hall was first built using red sandstone but was later shell-plastered, giving it a look of white marble.
- Ghaznin Gate: The Ghaznin Gate actually belongs to the tomb of Mahmud of Ghazni, one of the rulers of the Ghaznavid Empire.
- Bengali Mahal: This palace was built by Akbar and was later modified by Shah Jahan.
- Akbar’s Mahal: The ruins of Akbar’s famous palace remain in the fort. (UPSC CSE: Akbar)
- Akbar breathed his last in this very palace.
- The entire palace was built using red sandstone.
MUST READ: Dholavira: India’s 40th World Heritage Site
SOURCE: INDIA TODAY
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the cultural history of India, consider the following statements (2018)
- White marble was used in making Buland Darwaza and Khankah at Fatehpur Sikri
- Red sandstone and marble were used in making Bara Imambara and Rumi Darwaza at Lucknow
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) The painting of Bodhisattva Padmapani is one of the most famous and oft-illustrated paintings (2017)
- Ajanta
- Badami
- Bagh
- Ellora
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) particle-smasher at CERN, in Europe, reported that they had detected a Higgs boson decaying into a Z boson particle and a photon.
About Higgs boson:-
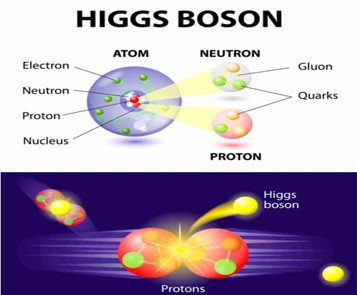
IMAGE SOURCES: scalarlight.com
- The Higgs boson is a type of boson, a force-carrying subatomic particle.
- It carries the force that a particle experiences when it moves through an energy field, called the Higgs field.
- Higgs field: a field that gives mass to other fundamental particles such as electrons and quarks.
- It is believed to be present throughout the universe.
- The Higgs boson is often called “the God particle”because it’s said to be what caused the “Big Bang” that created our universe many years ago.
- The Higgs boson is an extremely short-lived particle.
- Characteristic property: It decays rapidly into other particles, making its direct detection challenging.
- Scientists at the LHC used high-energy particle collisions to produce the Higgs boson and observed its decay products to confirm its existence.
- The Higgs boson has a mass of 125 billion electron volts.It is 130 times more massive than a proton.
- It is also chargeless with zero spin. Spin: a quantum mechanical equivalent to angular momentum. The Higgs Boson is the only elementary particle with no spin.
- It has a short lifespan.
- It sticks around for merely less than a trillionth of a billionth of a second or, more precisely, 6 x 10-22 seconds.
Timeline:-
- Peter Higgs, François Englert, and four other theorists to explain why certain particles have mass proposed the existence of Higgs boson in 1964.
- Scientists confirmed its existence in 2012 through experiments at the Large Hadron Collider at CERN in Switzerland.
- This discovery led to the 2013 Nobel Prize in Physics being awarded to Higgs and Englert.
Significance:-
- The Higgs boson can provide significant insights into the nature of our universe.
- Scientists hope to use the Higgs Boson as a tool to learn more about dark matter. (UPSC CSE: International Space Station (ISS))
- Its decay process can help test the predictions of the Standard Model of physics.
- Standard model of elementary particles: it is a theoretical framework in physics that explains the particles of matter and their interactions.
Large Hadron Collider (LHC)
- The LHC is a huge experiment that collides two beams of particles to study physics at very high energies.
- It is the world’s largest and most powerful particle accelerator.
- It is the largest science experiment in the world.
- Operated by: CERN (European Organisation for Nuclear Research)
- CERN: the world is largest nuclear and particle physics laboratory.
- It is best known as the operator of the Large Hadron Collider.
- It is based in Geneva on the French-Swiss border.
- It has 22 member states.
India and CERN:-
- India in 2016 became an associate member of the European Organisation for Nuclear Research (CERN).
- India’s association with CERN goes back decades with active involvement in the construction of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC).
- India was inducted as an ‘Observer’ at CERN in 2004.
- The associate membership would cost India Rs. 78 crores annually though it still would not have voting rights on decisions of the Council.Indian scientists have played a significant role in the Large Ion Collider Experiment (ALICE).
MUST READ: IN-SPACe
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following is the context in which the term “qubit” is mentioned? (2022)
- Cloud Services
- Quantum Computing
- Visible Light Communication Technologies
- Wireless Communication Technologies
Q.2) Which one of the following is a reason why astronomical distances are measured in light-years? (2021)
- Distance among stellar bodies does not change
- The gravity of stellar bodies does not change
- Light always travels in a straight line
- The speed of light is always the same
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: As per recent reports of the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE), parts of New Delhi and South Delhi were worst affected this summer by ground-level ozone pollution.
Ozone Pollution

IMAGE SOURCE: Climate Central
- Ozone occurs both in the Earth’s upper atmosphere (stratosphere) and at ground level (troposphere).
- It can be good or bad, depending on where it is found.
- Good Ozone: Ozone occurs naturally in the Earth’s upper atmosphere (Stratosphere).
- It forms a protective layer that shields from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays.
- Ozone-depleting gases like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), HCFCs, and halons, destroy this protective shield and causes a hole in the ozone.
- Bad Ozone: found in the Earth’s lower atmosphere (troposphere) near ground level.
- It is formed when pollutants emitted by cars, power plants, industrial boilers, refineries, chemical plants, and other sources react chemically in the presence of sunlight.
- It is a harmful air pollutant. (UPSC CSE: Air Pollution)
- It causes damage to crops and forests.
- It can increase the risk and susceptibility to pulmonary inflammation like Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
- It may reduce lung function and make breathing difficult.
About the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE):-
- It was established in 1980
- It is a public-interest research and advocacy organisation.
- HQ: New Delhi
- It works as a think tank on environment-development issues in India.
- It researches into, lobbies for and communicates the urgency of development that is both sustainable and equitable.
- It creates awareness about problems and proposes sustainable solutions.
- In 2018, the CSE was awarded Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament and Development.
MUST READ: India’s uphill battle to bring down air pollution
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the Guidelines, statements: the context of WHO consider the Air Quality following (2022)
- The 24-hour mean of PM2.5 should not exceed 15 ug/m³ and the annual mean of PM 2.5 should not exceed 5 µg/m³.
- In a year, the highest levels of ozone pollution occur during periods of inclement weather.
- PM10 can penetrate the lung barrier and enter the bloodstream.
- Excessive ozone in the air can trigger asthma.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1 and 4 only
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1 and 2 only
Q.2) Consider the following: (2022)
- Carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen oxide
- Ozone
- Sulphur dioxide
Excess of which of the above in the environment is/are the cause(s) of acid rain?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2 and 4 only
- 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, a 15-year-old tiger died after being found in an injured condition near the Kanha Tiger Reserve (KTR), Madhya Pradesh.
About Kanha Tiger Reserve (KTR):-
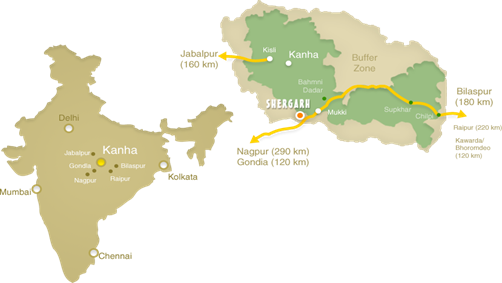
IMAGE SOURCE: shergarh.com
- Kanha Tiger Reserve stretches over the two districts: Mandla and Balaghat – of Madhya Pradesh.
- It is located in the central Indian highlands.
- The reserve is situated on the Maikal range, which is a part of the Satpura mountain range.
- Prominent Rivers: Banjar and the Halon Rivers.
- Kanha National Park was created in 1955.
- Kanha National Park is the largest National Park in Central India.
- It was made the Kanha Tiger Reserve in 1973. (UPSC CSE: Global Conservation Assured|Tiger Standards (CA|TS))
- It is the first tiger reserve in India to officially introduce a mascot, “Bhoorsingh the Barasingha”.
- Fauna: The State animal of Madhya Pradesh – Hard Ground Barasingha (Swamp deer or Rucervus duvaucelii) is found exclusively in Kanha Tiger Reserve.
- Protection Status of Swamp Deer:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I
- Other Species: Tiger, Leopard, Dhole, Bear, Gaur and Indian Python etc.
- Flora: It is best known for its evergreen Sal forests (Shorea Robusta).
MUST READ: Kali Tiger Reserve
SOURCE: DECCAN HERALD
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following Protected Areas are located in the Cauvery basin? (2020)
- Nagarhole National Park
- Papikonda National Park
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) Which one of the following protected areas is well-known for the conservation of a sub-species of the Indian swamp deer (Barasingha) that thrives well on hard ground and is exclusively graminivorous: (2020)
- Kanha National Park
- Manas National Park
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
- Tal Chhapar Wildlife Sanctuary
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: The Commission of Railway Safety (CRS) is investigating the recent Odisha rail accident.
About the Commission of Railway Safety (CRS):-
- The Commission of Railway Safety deals with matters pertaining to the safety of rail travel and trains.
- Ministry: Ministry of Civil Aviation
- HQ: Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh
- The operation is charged with certain statutory functions as laid down in the Railway Act (1989).
- Its functions are of an inspectorial, investigatory & advisory nature. (UPSC CSE: Mobile Train Radio Communication (MTRC))
- Investigating serious train accidents is one of the key responsibilities of the CRS. (UPSC MAINS: Indian railways accidents)
- It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA).
- The reason or principle behind this, put simply, is to keep the CRS insulated from the influence of the country’s railway establishment and prevent conflicts of interest.
MUST READ: Shramik Kalyan Portal
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Who among the following can join the National Pension System (NPS)? (2016)
- Resident Indian citizens only.
- Persons of age from 21 to 55 only.
- All State Government employees joining the services after the state of notification by the respective State Governments.
- All Central Government employees including those of Armed Forces joining the services on or after 1st April 2004.
Q.2) Which one of the following is the purpose of `UDAY’, a scheme of the Government? (2017)
- Providing technical and financial assistance to start-up entrepreneurs in the field of renewable sources of energy.
- Providing electricity to every household in the country by 2018.
- Replacing the coal-based power plants with natural gas, nuclear, solar, wind and tidal power plants over a period.
- Providing for financial turnaround and revival of power distribution companies.
Pulses Production in India
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context: There are two agricultural commodities in which India is significantly import-dependent: Edible oil and pulses.
About pulses production in India:
- Pulses are annual leguminous crops yielding between one and 12 grains or seeds of variable size, shape and colour within a pod, used for both food and feed.
- Bengal Gram (Desi Chick Pea / Desi Chana), Pigeon Peas (Arhar / Toor / Red Gram), Green Beans (Moong Beans), Chick Peas (Kabuli Chana), Black Matpe (Urad / Mah / Black Gram), Red Kidney Beans (Rajma), Black Eyed Peas (Lobiya), Lentils (Masoor), White Peas (Matar) are major pulses grown and consumed in India.
- February 10 is a designated global event to recognize and emphasize the importance of pulses and legumes as a global food.
- The UN General Assembly adopted 2016 as the International Year of Pulses (IYP).
- According to the Agriculture Ministry, India’s pulses output has increased from 19.26 MT in 2013-14 to 27.50 MT in 2022-23.
- The reduction in pulses imports have come essentially on the back of higher domestic production.
- It can be seen that imports of two items have recorded dramatic drops: Yellow/white peas (matar) and chickpea (chana).
Significance of pulses:
- Pulses are rich in nutritional and protein values and are an important part of a healthy diet.
- Pulses and legumes (lentils, peas, chickpeas, beans, soybeans, and peanuts) play an equally important role in health maintenance and overall improvement.
- Pulses also contribute majorly to achieving the goals of the 2030 Agenda of Sustainable Development.
- Pulses play a critical role in marking challenges of poverty, food chain security, degraded health, and climate change.
- Pulses and legume crops help in improving the feasibility of agricultural production systems.
- The nitrogen-fixing properties of pulses improve soil fertility, which increases the productivity and fertility of the farmland.
- Pulses are important for a healthy diet.
Challenges to the Pulse Production:
- Infrastructure: Poor and inadequate storage facilities
- Prices: Volatility in the prices due to rainfed dependency of the crops
- Decrease in the cultivation area, farmers opting Higher Yielding Crops with higher MSP.
- Inconsistencies in Minimum Support Price (MSP) like the Agricultural Costs and Prices Commission who fixes MSP is by status a department whose recommendations are only advisory.
- Representation of farmers is minimal.
- The so-called 50 per cent profit to the farmer is not per the government’s intended formula, and so it is relatively low. The farmers do not even get the declared MSP.
- The pulses are imported at prices lower than the domestic ones.
- Vulnerability to pests is also a major hindrance in the production of pulses.
- Farmers lack crop Insurance and credit facilities.
Government of India Initiatives to boost pulses production:
- National Food Security Mission: Launched by the Government of India during 2007-08 at the beginning of the 11th five-year plan.
- To expand the area under cultivation of pulses, and;
- To enhance productivity by bridging the gap between the actual and potential yield.
- Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana programme: It is a continuing scheme under implementation from the 11th Five Year Plan period of National Development Council (NDC).
- The scheme will incentivize States in enhancing more allocation to Agriculture and Allied Sectors.
- PM-POSHAN: The Indian government has urged states to procure pulses (for Mid-day meals) under the PM-POSHAN (Prime Minister’s Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nutrition) program from NAFED (National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India Ltd.).
Way Forward:
India is moving closer to AatmaNirbharta on pulses with consistent efforts by the government. It is vital to raise awareness about the benefits of eating pulses that are high in macronutrients for both sustainability and dietary needs.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Environment)
Context: Every year, June 5 is celebrated as World Environment Day. The day called for global solutions to combat the pandemic of plastic pollution.
- The date was chosen by the UN General Assembly during the historic 1972 Stockholm Conference on the Human Environment – considered to be the first world conference to make the environment a major issue.
- Over the years, it has grown to become the largest global platform for environmental outreach, with millions of people from across the world engaging to protect the planet.
- 2023 marks the 50th anniversary of the World Environment Day.
- #BeatPlasticPollution: Hosted by Côte d’Ivoire and supported by the Netherlands, this year’s World Environment Day campaign is aimed towards discussing and implementing solutions to the problem of plastic pollution.
About Plastic Pollution:
- Plastic refers to a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient with their defining quality being their plasticity – the ability of a solid material to undergo permanent deformation in response to applied forces.
- These include Polyethylene terephthalate or PET, High-density polyethylene or HDPE, Polyvinyl chloride or PVC, Low-density polyethylene or LDPE, Polypropylene or PP, and Polystyrene or PS.
- Each of these have different properties and can be identified by their resin identification code (RIC) denoted by symbols found on plastic products.
- Plastic pollution occurs when plastic has gathered in an area and has begun to negatively affect the natural environment and create problems for plants, wildlife, and even the human population.
- This includes killing plant life and posing dangers to local animals.
- Plastic is an incredibly useful material, but it is not biodegradable.
- According to UN data, more than 400 million tonnes of plastic is produced every year worldwide, half of which is designed to be used only once.
- Of that, less than 10 per cent is recycled. Consequently, an estimated 19-23 million tonnes end up in lakes, rivers and seas annually.
- Around the world, one million plastic bottles are purchased every minute, while up to five trillion plastic bags are used worldwide every year.
- In total, half of all plastic produced is designed for single-use purposes – used just once and then thrown away.
Common sources of Plastic pollution:
- Merchant ships expel cargo, sewage, used medical equipment, and other types of waste that contain plastic into the ocean.
- The largest ocean-based source of plastic pollution is discarded fishing gear (including traps and nets).
- Continental plastic litter such as Food Wrappers and Containers, Bottles and container caps, Plastic bags, Straws etc. enters the ocean largely through storm-water runoff.
Issues Associated with Plastic-Waste in India:
More Plastic per Person:
- Like much of the world, India is struggling to dispose of its growing quantities of plastic waste given how ubiquitous it has become- from our toothbrushes to debit cards.
- A little over 10,000 tonnes a day of plastic waste remains uncollected.
Unsustainable Packaging:
- India’s packaging industry is the biggest consumer of plastics.
- A 2020 study on packaging in India projects a loss of almost 133 billion dollars’ worth of plastic material value over the next decade due to unsustainable packaging.
- Unsustainable packaging involves general packaging through single use plastic.
Online Delivery:
- The popularity of online retail and food delivery apps, though restricted to big cities, is contributing to the rise in plastic waste.
- India’s biggest online delivery startups Swiggy and Zomato are each reportedly delivering about 28 million orders a month.
- E-commerce companies too have come under fire for excess use of plastic packaging.
Upsets the Food Chain:
- Polluting plastics can affect the world’s tiniest organisms, such as plankton.
- When these organisms become poisoned due to plastic ingestion, this causes problems for the larger animals that depend on them for food.
- Larger items, such as plastic bags and straws, can choke and starve marine life, while smaller fragments (microplastics) can cause liver, reproductive, and gastrointestinal damage in animals and it can directly affect the blue economy as well.
Impact on Human Health:
- The World Health Organisation published shocking research in 2018 that exposed the presence of micro plastics in 90% of bottled water.
- We absorb plastic through our clothes, 70% of which are synthetic and the worst fabric for the skin.
- We even breathe plastic when due to poor waste management by burning the trash in the open air.
- Plastic toxicity in humans can lead to hormonal disruption and adverse reproductive and birth outcomes.
Govt Initiatives to tackle plastic pollution:
National Dashboard on Elimination of Single Use Plastic and Plastic Waste Management:
- India launched a nationwide awareness campaign on Single Use Plastics on World Environment Day in June 2022.
- A mobile app for Single Use Plastics Grievance Redressal was also launched to empower citizens to check sale/usage/manufacturing of SUP in their area and tackle the plastic menace.
Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2022:
- It prohibits the manufacture, import, stocking, distribution, sale and use of several single-use plastic items as of July 1, 2022.
- It has also mandated Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) that incorporates circularity by making manufacturers of products responsible for collecting and processing their products upon the end of the products’ lifetime.
India Plastics Pact:
- It is the first of its kind in Asia. The Plastics Pact is an ambitious and collaborative initiative to bring stakeholders together to reduce, reuse and recycle plastics within the material’s value chain.
Mascot ‘Prakriti’:
- To spread awareness among masses about small changes that can be sustainably adopted in lifestyle for a better environment.
Project REPLAN:
- Project REPLAN (stands for REducing PLastic in Nature) launched by Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) aims to reduce consumption of plastic bags by providing a more sustainable alternative.
Way Forward: Adaptation of the 3R’s +E Strategy
- Reduce: To efficiently reduce plastic pollution, there is an evident need of reducing our usage of plastic.
- Reuse: Many plastic items can be reused or used for different purposes. Before throwing plastic items, it is important to consider how they can be reused.
- Recycle: Plastic recycling consists of collecting plastic waste and reprocessing it into new products, to reduce the amount of plastic in the waste stream.
- Educate: Another crucial solution is education in order to increase awareness and behavioural change.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q1) With reference to Ozone pollution, consider the following statements.
- Ozone in the stratosphere is a pollutant.
- India is a party to the Kigali Agreement.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q2) With reference to the Commission of Railway Safety, consider the following statements.
- It is under the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
- Its primary function is to investigate rail accidents.
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q3) With reference to the Kanha Tiger Reserve, consider the following statements.
- Banjar and the Halon rivers flow through it.
- It passes through the Satpura Hills.
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 7th June 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 6th June – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – d
Q.3) -a











