IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography/Economy
Context: The Parliament has passed the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023.
Background:-
- The Bill puts six minerals, including lithium — used in electric vehicle batteries and other energy storage solutions — into a list of “critical and strategic” minerals.
About Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023: –
- Bill passed: 2023.
- Objective: to attract private sector investment in the exploration of critical and deep-seated minerals in the country.
- Critical Minerals: natural resources that are essential for various industries, including technology, manufacturing, and clean energy.
- Example: Lithium, nickel, cobalt, etc.
- Deep-Seated Minerals: minerals that are found deep within the Earth’s crust and are typically more challenging and costly to explore and mine. ( Mines & Minerals Amendment Bill)
- g., Gold, Copper, Diamonds, etc.
Historical Background:-
- The MMDR Act, of 1957 has undergone several amendments to address various issues in the mineral sector.
- Amendments in 2015: introduced auction-based mineral allocation, established District Mineral Foundation (DMF) for community welfare, and NMET for exploration promotion.
- DMF: As per the Mine and Minerals Development Regulation (Amendment) Act, 2015, in every district affected by mining-related operations, the state government shall, by notification, establish a trust as a non-profit body to be called the District Mineral Foundation.
- Funds every mining lease has to pay a fraction of royalty, not exceeding one-third of the royalty, to the DMF as per rates prescribed by Central Government.
- This fund will be used for welfare of the people affected in the mining affected areas.
- National Mineral Exploration Trust (NMET): NMET is a Trust set up as a non-profit body by the Central Government for the purposes of regional and detailed exploration of minerals using the funds accrued to it and in such manner as prescribed by the Central Government.
- Amendments in 2016, 2020, and 2021: focused on emerging challenges and reforms, including removing the captive vs. merchant mine distinction.
- Need for further Amendment: The mineral sector requires more reforms, particularly in exploring and mining Critical Minerals since the limited availability and extraction concentration of these minerals pose supply chain vulnerabilities and disruptions. Minor mineral plunder)
Salient features of Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023:-
Private Sector to Mine Atomic Minerals:-
- The new bill allows the private sector to mine 6 atomic minerals- lithium, beryllium, niobium, titanium, tantalum, and zirconium.
- The central government can auction mining leases and composite licenses for critical minerals.
Auction for Exploration Licence: –
- The Bill allows the state government to grant licenses through competitive bidding, while the Central government prescribes auction details.
Incentive for Exploration Licence: –
- The Bill allows the state to conduct auctions for mining leases if resources are proven after exploration.
- Licensee receives a share in the auction value of the mining lease for prospected minerals.
MUST READ: Indian Bureau of Mines
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding mercury pollution: (2023)
- Gold mining activity is a source of mercury pollution in the world.
- Coal-based thermal power plants cause mercury pollution.
- There is no known ·safe level of exposure to mercury.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) In India, what is the role of the Coal Controller’s Organization (CCO)? (2022)
- CCO is the major source of coal Statistics in the Government of India.
- It monitors the progress of the development of Captive Coal/ Lignite blocks.
- It hears any objection to the Government’s notification relating to the acquisition of coal-bearing areas.
- It ensures that coal mining companies deliver the coal to end users in the prescribed time.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 3
- 3 and 4 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recent reports show that the RISC V- Semiconductor technology can give India a chance to challenge global domination.
Background:-
- India has thrown its weight behind the open-source RISC-V architecture.
- The aim is to be self-reliant in semiconductor design.
About RISC V- Semiconductor:-

IMAGE SOURCE: SlideServe
- Invented by: David Patterson.
- The term RISC stands for “reduced instruction set computer” which executes few computer instructions whereas ‘V’ stands for the 5th generation.
- It is a free and open ISA (instruction set architecture).
- It follows the open-source model with a modular design.
- In this, all the base instructions are frozen, which means the hardware is stable and the software will be able to work on RISC-V chips everywhere and forever, in theory. (India Semiconductor Mission)
- They excel in space-constrained designs and complex computational tasks.
Uses of RISC V- Semiconductor:-
- It is used for the development of custom processors targeting a variety of end applications.
- It is used in ( Semiconductors)
- It is used in wearables, IoT, smartphones, automotive, aerospace, and more, offering power efficiency, performance customization, and security.
MUST READ: Silicon Diplomacy
SOURCE: THE TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following communication technologies:(2022)
- Closed-circuit Television
- Radio Frequency Identification
- Wireless Local Area Network
Which of the above are considered Short-Range devices/technologies?
- 1 and 2 only.
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which one of the following is the context in which the term “qubit” is mentioned? (2022)
- Cloud Services
- Quantum Computing
- Visible Light Communication Technologies
- Wireless Communication Technologies
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography/Environment and Ecology
Context: Recent reports show that locals in Assam are taking initiatives to save the dying Deepor Beel Lake.
Background:-
- Some initiatives, along with bettering the health of the beel, have also provided employment to women from the community.
- One such initiative is – Simang, which is a collective initiative by six women from Keotpara has successfully transformed the invasive weed, water hyacinths into beautiful artefacts and yoga mats.
About Deepor Beel:-

IMAGE SOURCE: researchgate.net
- Location: Southwest of Guwahati, Assam.
- it is the erstwhile water channel of River Brahmaputra.
- Area: up to 30 sq. km in summer and about 10 sq. km in the winter.
- The Deepor Beel Wildlife Sanctuary measures 1 sq. km within this wetland (beel).
- Name: ‘Deep’ is an Assamese term for elephants, while the word deepor comes from the Sanskrit word dipa, which means elephants.
- Beel means lake in Assamese.
- Deepor Beel means lake of elephants.
- Deepor Beel is a permanent freshwater lake. (Deepor Beel)
- It was designated a Ramsar site in 2002.
- It is the Assam’s only Ramsar site.
- It has been selected as one of the Important Bird Area (IBA) sites by Birdlife International.
- It has also been a patch for the elephant movement for ages.
Significance:-
- It is considered a vital aspect of Guwahati tourism.
- It provides a means of livelihood for a number of local families.
- It constitutes a unique habitat for aquatic flora and avian fauna.
Fauna:-
- Birds (Avifauna): Deepor Beel is the natural habitat of as many as 219 species of birds that also includes over 70 species of migratory birds.
- Animals: Wild Asian elephants, barking deer, leopards, elephants, sambar, and Chinese porcupine.
- Aquatic animals: it is home to around 12 lizard species, 20 kinds of amphibians, 6 tortoise and turtle species, along with 18 species of snakes.
- Other animals: the wetlands and rivers here are called home by more than 50 species of fish.
Issues:-
- Its water has become toxic and it has lost many of its aquatic plants that elephants would feed on.
- It has for decades been threatened by a railway track — set to be doubled and electrified.
MUST READ: Community fishing prohibited in Deepor Beel
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Under Ramsar Convention, it is mandatory on the part of the Government of India to protect and conserve all the wetlands in the territory of India.
- The Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 were framed by the Government of India based on the recommendations of the Ramsar Convention.
- The Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 also encompass the drainage area or catchment regions of the wetlands as determined by the authority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Modern Indian History
Context: Recently, the Anniversary of the Quit India Movement was celebrated.
About Quit India Movement:-
- Launched on: August 8, 1942.
- The slogan ‘Quit India’ was coined by Yusuf Meherally who was a socialist and also a trade unionist.
Historical Background:-
- It was launched during World War II, when the British government’s involvement in the war had strained its resources and the Indian people’s patience with continued colonial rule had grown thin.
- Aim: to demand an immediate end to British rule in India and to establish an independent and sovereign nation.
- Leadership: The movement was led by Mahatma Gandhi and supported by the Indian National Congress.
- On August 8, 1942, Mahatma Gandhi gave his famous “Do or Die speech, urging the Indian people to engage in nonviolent civil disobedience and to be prepared to sacrifice their lives for the cause of independence.
- Muslim League, the Communist Party of India, and the Hindu Mahasabha did not support the movement.
- Repression: The British colonial government responded with a heavy hand, imposing severe repressive measures to suppress the movement. ( Quit India Movement)
Popular leaders of the Quit India Movement:-
- Key leaders of the Indian National Congress, including Mahatma Gandhi Jawaharlal Nehru, and Sardar Patel were arrested.
- Other leaders took charge of the movement at ground level. These include:-
- Aruna Asif Ali: Also known as the Grand Old Lady of India, she unfurled the tricolor at Gowalia Tank Maidan in Bombay.
- Ram Manohar Lohia
- Usha Mehta ( 75 years of Quit India Movement)
- Biju Patnaik
- Sucheta Kriplani
- Jai Prakash Narayan
Causes of Quit India Movement:-
- Immediate cause: the collapse of Cripps Mission.
- The anti-British sentiments and demand for full independence had gained popularity among the Indian masses.
Phases of the Quit India Movement
First Phase of Quit India Movement:
- In the first phase, there were strikes and demonstrations across the country. Mahatma Gandhi was imprisoned in the Aga Khan Palace in Pune. Several other leaders were also detained by the Britishers.
Second Phase of Quit India Movement:
- The second phase of the Quit India Movement saw many peasant rebellions marked by the destruction of communication systems, such as railway tracks and stations
Third Phase of Quit India Movement:
- The third and final phase of the Quit India Movement witnessed the formation of national governments or parallel governments in isolated pockets such as Ballia, Tamluk, Satara, etc.
MUST READ: Mahatma Gandhi
SOURCE: TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the proposals of Cripps Mission, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Constituent Assembly would have members nominated by the Provincial Assemblies as well as the Princely States.
- Any Province, which is not prepared to accept the new Constitution would have the right to sign a separate agreement with Britain regarding its future status.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to 8th August 1942 in Indian history, which one of the following statements is correct? (2021)
- The Quit India Resolution was adopted by the AICC.
- The Viceroy’s Executive council was expanded to include more Indians.
- The Congress ministries resigned in seven provinces.
- Cripps proposed an Indian Union with full Dominion Status once the Second World War was over.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the Agricultural and Processed Foods Exports Development Authority (APEDA) stated that India’s agricultural produce exports fell 14 percent in value terms during the April-June (2023) quarter as against April-June (2022).
Key highlights of the report:-
- Agricultural exports worth $6.321 billion in the April-June quarter (2023), as against $7.397 billion in 2022.
- Basmati shipments, on the other hand, registered a 12 percent growth in dollar terms during the quarter.
- Non-basmati rice, comprising the largest chunk of the export basket, fell 2.69 percent in dollar value.
- Exports of buffalo meat, the main livestock product, fell 4.5 percent.
- Fresh fruits and vegetables registered a 16 percent increase in exports.
About Agricultural and Processed Foods Exports Development Authority (APEDA):-
- Establishment:1985.
- Ministry: Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- It is a statutory body under the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority Act of 1985.
- Objective: To develop and promote the export of scheduled products.
Functions:-
- Setting the standards and specifications for the scheduled products.
- Registration of exporters of the scheduled products on payment of required fees.
- Improving packaging and marketing of the Scheduled products.
- Carrying out an inspection of products to ensure the quality of such products.
- Training in various aspects of the industries connected with the scheduled products.
- Collection of statistics from the owners of factories or establishments and publication of such statistics.
MUST READ: Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
SOURCE: BUSINESS LINE
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- The Government of India provides Minimum Support Price for niger (Guizotia aoyssinica) seeds.
- Niger is cultivated as a Kharif crop.
- Some tribal people in India use niger seed oil for cooking.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Which of the following factors/policies were affecting the price of rice in India in the recent past? (2020)
- Minimum Support Price
- Government’s trading
- Government’s stockpiling
- Consumer subsidies
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, and 4 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –Government Schemes
Context: Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone for the redevelopment of 508 railway stations across the country, under the Amrit Bharat Station Scheme.
About Amrit Bharat Station Scheme:-
- Launched:2023.
- Ministry: Ministry of Railways.
- Objectives: development of stations on a continuous basis with a long-term vision to enhance the facilities. ( Indian Railway Management Service (IRMS))
Benefits of Amrit Bharat Station Scheme:-
- Elegant Station Building: A new station building will redefine Station’s architectural landscape.
- Focus on Swachh Bharat: Keeping in step with the Swachh Bharat mission, the station will introduce a modular Sewage Treatment Plant, ensuring efficient sewage treatment and a cleaner environment.
- Aesthetic Platforms: Platforms will undergo a resurfacing and aesthetic uplift.
- Passenger Amenities: Travelers will enjoy improved amenities, including better seating, drinking water facilities, and enhanced lighting.
- Enhanced Connectivity: A revamped foot-over bridge, supplemented by additional lift and escalator facilities.
- Guidance and Information: Modernized train indication boards and passenger-friendly signages will facilitate seamless navigation within the station premises.
- Functional Upgrades: The existing booking office and other administrative buildings will undergo a thorough renovation.
- Inclusivity: All improvements will be designed to be divyangjan (specially-abled) friendly, ensuring equal access and convenience for all.
MUST READ: Restructuring of Railways
SOURCE: BUSINESS TODAY
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in the context of interventions being undertaken under the Anaemia Mukt Bharat Strategy: (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for preschool children, adolescents, and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of childbirth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anemia in endemic pockets with a special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies, and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following markets : (2023)
- Government Bond Market
- Call Money Market
- Treasury Bill Market
- Stock Market
How many of the above are included in capital markets?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
E20 PETROL
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology)
Context: Minister of State, Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas informed the Rajya Sabha about the E20 programme of the government.
About E20 fuel:
- The number “20” in “E20” refers to the percentage of ethanol in the gasoline blend.
- Simply put, the higher the number, the higher the percentage of Ethanol in the gasoline.
- India’s current ethanol-to-petroleum mix is 10%, the highest it has ever been.
- Because it is made from biomass, ethanol does not require crude oil.
- Ethanol is primarily produced from crops such as corn and sugarcane.
- India already produces significant quantities of grain and sugarcane. It may allow automobiles to use a higher proportion of Ethanol.
Ethanol blending:
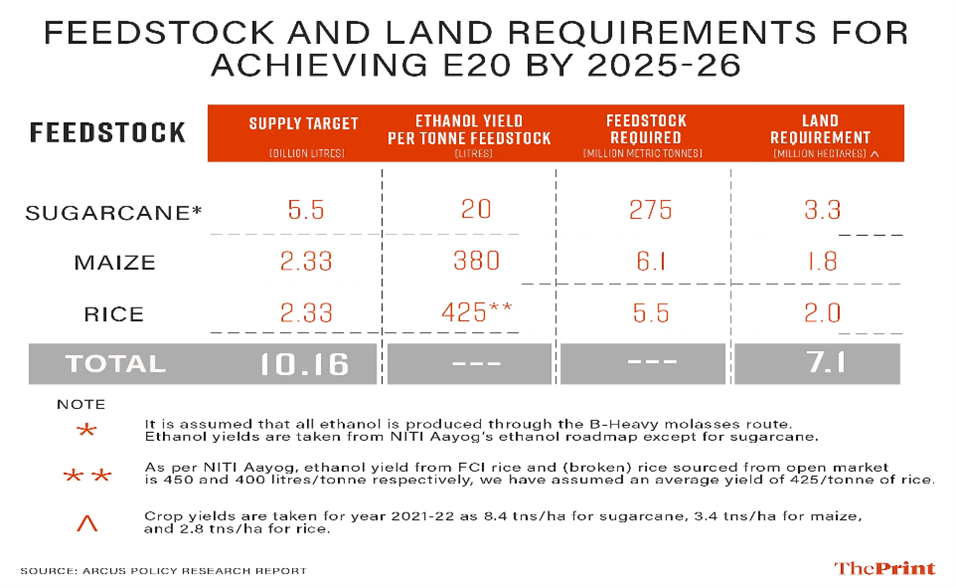
- Naturally, Produced– Ethanol is a biofuel, naturally produced by the fermentation of sugars by yeasts or by petrochemical processes like ethylene hydration.
- Derived from agricultural products– In ethanol blending, a blended motor fuel containing ethyl alcohol derived from agricultural products is blended with petrol specifically.
- High in oxygen content– Ethanol is high in oxygen content, allowing an engine to combust fuel more thoroughly. (Ethanol blending)
Ethanol Blended with Petrol (EBP) programme:
- EBP programme was launched by the government in 2003 to promote the use of alternative and environmentally friendly fuels.
- This intervention also aimed to reduce import dependency for energy requirements, and give boost to the agriculture sector (supply of straw, additional income to farmers).
- Oil marketing companies (OMCs) were mandated to sell ethanol-blended petrol with percentage of ethanol up to 10 per cent.
- The government allowed procurement of ethanol produced from non-food feed stocks, like cellulosic and ligno-cellulosic materials, including petrochemical route.
- Ligno-cellulosic materials: It describes the main constituents in most plants, namely cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin. Lignocellulose is a complex matrix, comprising many different polysaccharides, phenolic polymers and proteins.
- Cellulose, the major component of cell walls of land plants, is a glucan polysaccharide containing large reservoirs of energy that provide real potential for conversion into biofuels.
- It is the non-starch based fibrous part of plant material.
Advantages of E20 fuel
- Environmentally friendly: Pointing out that vehicular emissions such as carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC) and oxides of nitrogen (NOx) are currently under regulation in India.
- Ethanol blended gasoline decreases these emissions.
- Cost savings: About 85% of India’s fuel needs are met by imports.
- The use of petrol with a 20% ethanol mix in India would result in significant cost savings for the nation.
- Employment generation: When innovative technologies are put into practice, new employment possibilities emerge.
- New positions will be created in the original equipment manufacturing (OEM) sector, as well as in the component supplier and aftermarket service provider sectors.
- Benefit to agriculture: India’s government believes that reaching its goal of 20% ethanol in gasoline would benefit the country’s agricultural industry.
- The government asserts that farmers’ incomes would rise because of these measures.
Challenges:
- Consumer acceptance: Consumer acceptance of new technology is subject to be tested.
- The anxiety about using new technology will remain a concern.
- Huge investment: A new technology implementation on a mass scale certainly requires a huge sum of investment from the industry stakeholders.
- After spending a huge amount of money on BS-VI migration from BS-IV in record time, it will be hard for the auto industry stakeholders to invest another huge sum.
- Farmers acceptance: Farmers who have been traditionally farming sugarcanes can be benefitted from the strategy.
- However, it is hard to believe that a large scale of farmers will opt for sugarcane farming, which is the main ingredient for ethanol production.
- Timeframe: With the Covid-19 and subsequent troubling situations disrupting the auto industry operations, achieving the target by the set deadline could be a challenge.
Present utilisation of E20 Fuels in India:
- India’s Creta, Venue, and Alcazar SUVs from Hyundai Motor are said to be capable of running on E20 gasoline as of the 2023 MY model year.
- Tata Motors debuted two new turbocharged petrol engine sat the Auto Expo 2023. (1.2-litre and 1.5-litre).
- Tata has stated that its vehicles longer than 4 meters will soon be equipped with E20 fuel-compatible engines.
- Similar developments are planned for vehicles manufactured by Mahindra, Maruti Suzuki, Kia, and others.
Way Forward
India being a large agricultural economy, there is a large amount of agricultural residues available; therefore, the scope of producing biofuels is immense in the country. Biofuels can help in rural and agricultural development in the form of new cash crops.
Source: LiveMint
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context: PM Modi recently addressed the ninth National Handloom Day in Delhi in order to promote India’s rich heritage of handloom.
- The theme of the National Handloom Day 2023 is “Handlooms for Sustainable Fashion”, focusing on the sustainable and environmentally beneficial alternative to machine-made fabrics.
Handloom Sector in India
- The greatest cottage industry in the nation is the handloom industry.
- It is the second biggest employer in the rural area.
- A total of 35, 22,512-handloom workers were employed nationwide as per Handloom Census 2019–20.
- Women make up the majority of the workforce in this sector, accounting for 72.29% of all handloom employees.
- Production of hand-woven fabric from India constitutes 95 per cent of the global production.
Significance of the sector:
- Women empowerment: Apart from being a significant employment source in rural areas, the handloom sector is also a key player in the field of women empowerment as roughly 70 percent of all weavers and allied workers are women.
- Exports: The Indian handloom sector exports its products to more than 20 countries across the globe, including the USA, the UK, Germany, France, and South Africa.
- Handloom weaving community: The National Handloom Day is celebrated to honour the handloom weaving community and to highlight the contribution of the community in various sectors of the country, including rural employment.
- Protection of India’s rich handloom heritage: The day also stands for the protection of India’s rich handloom heritage and to empower the handloom community with bigger and better opportunities.
Problems in the industry:
- The lack of effective policy support: Combined with the fragmented nature of the sector has given rise to many problems.
- Weaver and supply chain problems: Most of the problems concerning the sector can be broadly categorised into weaver and supply chain problems.
- Lack of financial viability: According to the Handloom Census, approximately 67 per cent of the weavers still earn less than 5,000 a month, which is less than the amount that an unskilled worker earns as per the minimum wage rule.
- Handing the tradition over: Existing weavers are not showing an interest in handing the tradition over to their next generations.
- Indirect sources of credit: Most of the weavers depend on indirect sources of credit with high rates of interest. This is due to the low penetration of banking facilities among the weaver community.
- Fewer profits: The price fluctuations in the open market eat up the profit margins of the weavers.
Govt. Schemes for Handloom Sector
- Handloom Weavers’ Comprehensive Welfare Scheme: Weavers Comprehensive Welfare Scheme (HWCWS) is providing life, accidental and disability insurance coverage under the components
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): In order to support operations, the initiative provides small businesses with loans upto Rs. 10 lakhs.
- The National Handloom Development Programme (NHDP) aims to provide handloom weavers with financial assistance so they can advance their technology, market their products, and nurture their abilities.
- Micro and small businesses’ Credit Guarantee Fund Trust (CGTMSE): This initiative intends to provide operating cash and term loans to micro and small businesses without the need for collateral.
- The Yarn Supply Scheme: With partial modification, it is renamed as Raw Material Supply Scheme (RMSS) and has been approved for implementation during the period from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
Way Forward:
National Handloom Day serves as a reminder of the invaluable contribution of the handloom sector to India’s cultural heritage and rural livelihoods. The Government of India’s interventions play a crucial role in supporting and empowering handloom weavers and allied workers. By continuing to invest in skill development, infrastructure, and marketing opportunities, India can preserve its handloom heritage while ensuring a sustainable and prosperous future for the weaver community.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Ramsar site | Location |
| 1.Bakhira Wildlife Sanctuary | Gujarat |
| 2.Haiderpur Wetland | Uttar Pradesh |
| 3.Deepor Beel | Arunachal Pradesh |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
RISC V- Semiconductor is used for the development of custom processors.
Statement-II:
It follows the open-source model.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Amrit Bharat Station Scheme was launched in 2017.
Statement-II:
It envisions a comprehensive transformation of railway stations, creating modern and passenger-friendly spaces.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) “Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)”.Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (250 words)
Q.2) Discuss the significance of the handloom industry in India and the challenges it faces. How can the government promote and revitalize this traditional sector to preserve India’s cultural heritage and promote sustainable development? (250 Words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 10th August 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 9th August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – c
Q.3) -d











