IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Defense
Context: In recent times, the Assam Rifles personnel have been facing increased hostility in Manipur.
Background:-
- Normally, there are 20 battalions of the Assam Rifles in Manipur, with the primary mandate of counter-insurgency and border guarding.
- Since ethnic violence erupted in the state on May 3, 2023, two more battalions were moved in.
- Due to being tasked with manning “buffer zones” between Meitei- and Kuki-Zomi-dominated territories in Manipur, the Assam Rifles has been facing heat from the Meiteis, with some even demanding its removal from the state.
About Assam Rifles:-
- Establishment:1835.
- Ministry: Ministry of Home Affairs.
- It is a Central Paramilitary Force under the Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF).
- CAPF: the collective name of central police organizations in India under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- It includes 7 forces: Assam Rifles (AR), Border Security Force (BSF), Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP), Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB), Central Industrial Security Force (CISF), Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) and National Security Guard (NSG).
- Assam Rifles is the oldest Central Para Military Force in India.
Historical Background:-
- The Assam Rifles was set up as Cachar Levy in 1835 to protect British Tea estates and their settlements against tribal raids.
- Post-Independence, role of the Assam Rifles continued to evolve ranging from:-
- Conventional combat role: during Sino-India War in 1962
- Operating in a foreign land: as part of the Indian Peace Keeping Force (IPKF) to Sri Lanka in 1987 (Op Pawan)
- Peacekeeping role: in the North-Eastern areas of India.
Structure of Assam Rifles:-
- The Force is commanded by an officer of the rank of Lieutenant General of the Army. (UPSC CSE: Administration of Assam Rifles)
- HQ Directorate General of Assam Rifles: Shillong.
MUST READ: Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Home Guards, consider the following statements: (2023)
- Home Guards are raised under the Home Guards Act and Rules of the Central Government.
- The role of the Home Guards is to serve as an auxiliary force to the police in the maintenance of internal security.
- To prevent infiltration on the international border/ coastal areas, the Border Wing Home Guards Battalions have been raised in some states.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Consider the following statements (2023)
- Ballistic missiles are jet-propelled at subsonic speeds throughout their flights, while cruise missiles are rocket-powered only in the initial phase of flight.
- Agni-V is a medium-range supersonic cruise missile, while BrahMos is a solid-fuelled intercontinental ballistic missile.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: The Kerala Assembly has passed the resolution to rename state as Keralam.
Background:-
- The resolution, moved by Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan, was passed unanimously, with the Congress-led Opposition not suggesting any changes.
Formation of Kerala:-
- 1949: Travancore and Kochi was merged, forming the Travancore-Cochin State. ( Integration of the princely states)
- State Reorganization Commission recommended the creation of Kerala as a state for Malayalam-speaking people.
- The state of Kerala came into being on November 1, 1956.
- In Malayalam, the state was referred to as Keralam, while in English it was Kerala.
Origin of the name:-
- There are several theories about the origin of the name ‘Kerala’.
- Earliest epigraphic record: Asoka’s Rock Edict II of 257 BC.
- The inscription refers to the local ruler as Keralaputra (Sanskrit for “son of Kerala”), and also “son of Chera” referring to the Chera dynasty.
- About ‘Keralam’, scholars believe it could have originated from ‘Cheram’.
- Significance of the name: ‘Keralam’ aligns more closely with the native pronunciation, historical roots, and cultural identity of the region’s people.
Process to rename a state in India:-
- The proposal has to first come from the state government.
- Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) Approval: The Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) then takes over and gives its consent after it receives No Objection Certificates (NOCs) from several agencies.
- These agencies include the Ministry of Railways, Intelligence Bureau, Department of Posts, Survey of India, and Registrar General of India.
- Parliamentary proceedings: If the MHA finds the proposal acceptable and all the necessary NOCs are obtained, a Constitutional amendment bill is initiated.
- The Bill goes through the usual legislative process in both the Lok Sabha (Lower House) and the Rajya Sabha (Upper House).
- The Bill requires a simple majority to be passed in each house.
- After it is passed by both houses if the President gives his assent, the Bill becomes law.
- Implementation: With the President’s assent, the name change becomes official and the name of the state is changed thereafter.
Constitutional provisions for renaming a State:-
- The renaming of an existing state requires Parliamentary approval under Articles 3 of the Constitution.
- Introduction: A bill for renaming a state may be introduced in the Parliament on the recommendation of the President
- State assembly consultation: Before the introduction of the bill, the President shall send the bill to the respective state assembly for expressing their views within a stipulated time.
- The views of the state assembly are not binding, neither on the President nor on the Parliament.
- Parliamentary approval: On the expiry of the period, the bill will be sent to the Parliament for deliberation.
- The bill in order to take the force of a law must be passed by a simple majority.
- Presidential Approval: The bill is sent for approval to the President.
- After the approval of the said bill, the bill becomes a law and the name of the state stands modified.
MUST READ: Asymmetrical federalism
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- A bill amending the Constitution requires a prior recommendation of the President of India.
- When a Constitution Amendment Bill is presented to the President of India, it is obligatory for the President of India to give his/her assent.
- A Constitution Amendment Bill must be passed by both the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha by a special majority and there is no provision for joint sitting.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which one of the following in Indian polity is an essential feature that indicates that it is federal in character? (2021)
- The independence of the judiciary is safeguarded
- The Union Legislature has elected representatives from constituent units
- The Union cabinet can have elected representatives from regional parties
- The Fundamental rights are enforceable by Courts of Law
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: Recently, a Bill was listed to be introduced in the Rajya Sabha on the appointment of the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and Election Commissioners (ECs).
Background:-
- The Centre’s Bill seeks to establish a committee of,
- the Prime Minister,
- the Leader of the Opposition in the Lok Sabha,
- A Cabinet Minister nominated by the PM for selecting members of the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- In March this year, a Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court had ruled that the Election Commissioners should be selected by a committee comprising the Prime Minister, the Leader of Opposition and the Chief Justice of India.
- The bench led by Justice KM Joseph passed the direction to ensure the independence of the Election Commissioners from the independence. While passing the direction, the bench noted that there is no Parliamentary law at place in terms of Article 324(2) of the Constitution laying down the selection procedure for Election Commissioners.
About Election Commission India:-
- Establishment: 25th January 1950.
- It is a constitutional body responsible for administering Union and State election processes in India.
- It administers elections to Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha, State Legislative Assemblies, State Legislative Councils, and the offices of the President and Vice President of the country.
Composition of Election Commission:-
- Originally the commission had only a Chief Election Commissioner. (Chief Election Commissioner (CEC))
- It currently consists of the Chief Election Commissioner and two Election Commissioners.
- 1989: For the first time, two additional Commissioners were appointed.
- Since 1993 the concept of a multi-member Commission has been in operation.
Appointment, Tenure, and Privileges of Commissioners:-
- Appointment Procedure as of now: Under Article 324(2) the appointment of the CEC and other Election Commissioners shall be made by the President.
- The Law Minister suggests a pool of suitable candidates to the Prime Minister for consideration.
- The President makes the appointment on the advice of the PM.
- Tenure: six years, or up to the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
- Salary: They enjoy the same status and receive salary and perks as available to Judges of the Supreme Court of India.
Removal of Election Commissioners:-
- They can resign anytime or can also be removed before the expiry of their term.
- The CEC can be removed from office only by the order of the President, just like a judge of the Supreme Court.
The issue in Removal of Other Commissioners:-
- The Constitution is silent about the procedure for the removal of the two Election Commissioners.
- The Constitution has not specified the term of the members of the Election Commission.
- The Constitution has not debarred the retiring election commissioners from any further appointment by the government.
MUST READ: Impartiality of the Election Commission
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2021)
- In India, there is no law restricting the candidates from contesting in one Lok Sabha election from three constituencies.
- In the 1991 Lok Sabha Election, Shri Devi Lal contested from three Lok Sabha constituencies.
- As per the existing rules, if a candidate contests in one Lok Sabha election from many constituencies, his/her party should bear the cost of bye-elections to the constituencies vacated by him/her in the event of him/her winning in all the constituencies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the Union Government, consider the following statements: (2017)
- The Election Commission of India is a five-member body.
- Union Ministry of Home Affairs decides the election schedule for the conduct of both general elections and by-elections.
- Election Commission resolves the disputes relating to splits/mergers of recognized political parties.
Select the correct code:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) Academy joined the Interpol Global Academy Network.
Background:-
- The CBI Academy has become the 10th member of the Interpol Global Academy Network.
About Interpol Global Academy Network:-

IMAGE SOURCE: INTERPOL
- Launched: 2019.
- Objective: supporting Interpol in leading a global approach to Law Enforcement Training.
- The Interpol Global Academy Network is a network of trusted law enforcement education institutions.
- Members: The Network has members in all regions and supports academic collaboration amongst Law Enforcement Training Institutions across the globe.
- Significance: It seeks to promote academic excellence and innovation in law enforcement training by establishing quality standards, accreditation mechanisms, and recognition systems.
- Working mechanism: Its members support the creation and delivery of select digital and face-to-face training courses.
- These cover INTERPOL’s tools and services, crime areas, and other law enforcement topics.
- They also help identify and coordinate responses to training needs.
- They contribute to a knowledge exchange platform to advance law enforcement education through cutting-edge training tools and methodologies.
About INTERPOL:-
- Establishment:1923.
- HQ: Lyon, France.
- Full name: International Criminal Police Organization and we are an inter-governmental organization.
- Members: 195 countries.
- India is one of the oldest members of Interpol. It joined Interpol in 1949.
- Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) represents Interpol in India as the country’s national central bureau.’ (CBI and ED)
MUST READ: Operation Garuda
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements is correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps the Public Sector Banks develop strategies and capital raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company.
- Brickwork Ratings is an Indian credit rating agency.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, the members of the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO), met in Brazil to come up with a roadmap to protect tropical rainforests.
Background:-
- Leaders and Ministers from eight Amazon nations signed a declaration on August 8, 2023, in Belem, Brazil.
- Belem Declaration laid out plans to drive economic development in their countries while preventing Amazon’s ongoing demise from reaching a point of no return.
- The summit aimed to address sustainable development in the Amazon Basin but fell short of achieving consensus on crucial environmental targets.
About Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO):-
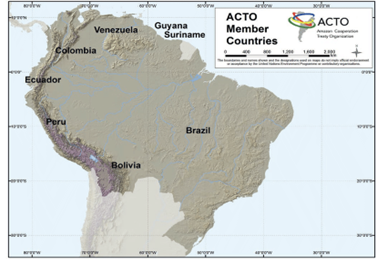
IMAGE SOURCE: ResearchGate
- Establishment: 1978.
- HQ: Brasilia, Brazil.
- Official languages: Dutch, English, Portuguese, and Spanish.
- Members: Eight countries- Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela.
- ACTO is an intergovernmental organization formed by the eight Amazonian countries which signed the Amazon Cooperation Treaty (ACT).
- ACT: it was signed in 1978, and gave rise to the ACTO.
- It is the only socio-environmental block in Latin America.
- The Directorate of the Permanent Secretariat and the coordination of the projects plan and execute their activities.
Objective of ATCO:-
- Promote the harmonious development of the Amazonian territories
- Sustainable development of the Amazon Region. ( Deforestation in Amazon Basin)
MUST READ: India and Brazil: Bilateral Investment Treaty
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the context of India’s preparation for Climate-smart Agriculture, consider the following statements: (2021)
- The ‘Climate-Smart Village’ approach in India is part of a project led by climate change, Agriculture, and food security (CCAFS), an international research program.
- The project of CCAFS is carried out under the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) headquartered in France.
- The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) in India is one of the CGIAR’S research centres.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Climate Group is an international non-profit organization that drives climate action by building large networks and running them.
- The International Energy Agency in partnership with the Climate Group launched a global initiative “EP100”.
- EP100 brings together leading companies committed to driving innovation in energy efficiency and increasing competitiveness while delivering on emission reduction goals.
- Some Indian companies are members of EP100.
- The International Energy Agency is the Secretariat to the “Under2 Coalition”.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1,2, 4 and 5
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 2,3 and 5 only
- 1,2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims –Defense
Context: Australia will host Exercise Malabar for the first time in 2023.
Exercise Malabar 2023:-
- Location: Sydney, Australia.
- Date: August 11-21(2023).
- Participating countries: India, USA, Japan, and Australia.
- An Indian multi-role frigate, INS Sahyadri, and a guided missile destroyer, INS Kolkata, will represent the Indian Navy.
- US Navy (USN), the Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF), and the Royal Australian Navy (RAN).
- Phases of the Exercise:-Malabar 2023 will be conducted in two phases.Phase I:It is the Harbour Phase and Phase II is the Sea Phase.
About Exercise Malabar:-
- Started in 1992.
- Objective: to coordinate for a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific.
- It is conducted annually.
Timeline of Exercise Malabar:-
- First Malabar Exercise: Bay of Bengal, 2007. ( Malabar naval exercise)
- It began as a bilateral naval exercise between India and US Navy.
- 2015: It was expanded into a trilateral format with the inclusion of Japan.
- 2020: Australian Navy joined the Malabar Exercise, making it a quadrilateral naval exercise.
- Location: It takes place in the Indian Ocean and Pacific Oceans
- This exercise includes a diverse range of activities such as fighter combat operations and maritime interdiction operations.
Significance of Exercise Malabar:-
- Enhanced Strategic Partnership.
- Sustainable Indo-Pacific Coalition.
- Ensuring peace and security in the Indo-Pacific Region.
MUST READ: Exercise Talisman Sabre
SOURCE: BUSINESS STANDARD
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Home Guards, consider the following statements: (2023)
- Home Guards are raised under the Home Guards Act and Rules of the Central Government.
- The role of the Home Guards is to serve as an auxiliary force to the police in the maintenance of internal security.
- To prevent infiltration on the international border/ coastal areas, the Border Wing Home Guards Battalions have been raised in some states.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (2019)
- Japan
- Russia
- The United Kingdom
- The United States of America
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: Recently, Rajya Sabha Chairman Jagdeep Dhankhar referred complaints related to the privilege of the House against TMC’s Derek O’Brien and AAP’s Raghav Chadha to the privileges committee.
About Privileges Committee:-
- This committee consists of 15 members in Lok Sabha (LS) and 10 members in Rajya Sabha(RS).
- Nominated by: Speaker or Chairman of LS and RS respectively.
- Function: The committee examines every question involving a breach of privilege of the House or of the members or of any Committee referred to it by the Speaker/Chairman and makes suitable recommendations in its report. (LS Privileges Committee)
- Once presented, a motion has to be passed for the consideration of the report and amendments can be suggested.
- The right to raise a question of privilege must satisfy the following two conditions:-
- the question shall be restricted to a specific matter of recent occurrence and
- the matter requires the intervention of the Council.
- The Speaker/RS Chairman is the first level of scrutiny of a privilege motion.
- The Speaker/Chairman can decide on the privilege motion himself or herself or refer it to the privileges committee of Parliament. (Privilege Motion)
MUST READ: Received privilege motion against Minister: Speaker
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- A bill amending the Constitution requires a prior recommendation of the President of India.
- When a Constitution Amendment Bill is presented to the President of India, it is obligatory for the President of India to give his/her assent.
- A Constitution Amendment Bill must be passed by both the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha by a special majority and there is no provision for joint sitting.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2021)
- In India, there is no law restricting the candidates from contesting in one Lok Sabha election from three constituencies.
- In the 1991 Lok Sabha Election, Shri Devi Lal contested from three Lok Sabha constituencies.
- As per the existing rules, if a candidate contests in one Lok Sabha election from many constituencies, his/her party should bear the cost of bye-elections to the constituencies vacated by him/her in the event of him/her winning in all the constituencies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
Sponge cities
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Disaster management)
Context: Recently China has been hit by devastating floods, inundating cities and causing deaths and infrastructural damage, as well as raising questions about the effectiveness of its 2015 “sponge city” initiative aimed at reducing urban flood risks.
About Sponge cities:
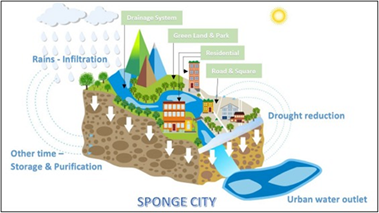
- A sponge city is a city that is designed to passively absorb, clean and use rainfall in an ecologically friendly way that reduces dangerous and polluted runoff.
- Associated techniques include permeable roads, rooftop gardens, rainwater harvesting, rain gardens, green space and blue space such as ponds and lakes.
Main reasons for Urban Floods:
- Inadequate Drainage Infrastructure: Cities like Hyderabad and Mumbai rely on a century-old drainage system, covering only a small part of the core city.
- In the last 20 years, the Indian cities have grown manifold with its original built-up area.
- As the city grew beyond its original limits, not much was done to address the absence of adequate drainage systems.
- Terrain Alteration: Lasting irreversible damage has been done to the city by property builders, property owners, and public agencies by flattening terrain and altering natural drainage routes.
- Reducing Seepage: Indian cities are becoming increasingly impervious to water, not just because of increasing built up but also because of the nature of materials used (hard, non-porous construction material that makes the soil impervious).
- Lax Implementation: Even with provisions of rainwater harvesting, sustainable urban drainage systems, etc., in regulatory mechanisms like the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA), adoption at user end as well as enforcement agencies remains weak.
- Encroaching Natural Spaces: The number of wetlands has reduced to 123 in 2018 from 644 in 1956. The green cover is only 9%, which ideally should have been at least 33 per cent.
Significance of Sponge cities:
- It is a new way of thinking about storm water, not as a problem but as an opportunity and a resource to augment our water supply.
- In the long run, sponge cities will reduce carbon emissions and help fight climate change.
- Sponge cities also come with wider social benefits.
- Properly implemented sponge city can reduce the frequency and severity of floods and improve water quality.
- By capturing storm water, we are preventing beach pollution.
- Greening the city by planting new plants.
- Associated strategies such as green space can improve quality of life, improve air quality and reduce urban heat islands.
- Water can be used to keep green spaces verdant, provide an outdoor area for the people who live and work in the building, and even be used to grow food.
- This in-turn can improve urban eco-system diversity by providing new habitats for a wider range of organisms.
China’s Sponge Cities: Case study
- Nowhere has embraced the idea of sponge cities as enthusiastically as China.
- The Chinese government is building water-absorbent projects in 30 cities as part of its “sponge city initiative.”
- The plan is to manage 60% of rainwater falling in the cities.
- Develop ponds, wetlands; build permeable roads and public spaces that enable storm water to soak into the ground.
- By 2020, China hopes that 80% of its urban areas will absorb and re-use at least 70% of rainwater.
- However, transforming entire cities into sponges will require massive investment.
- With growing urbanisation in India and increasing urban floods, it is time for India to move towards sponge cities.
India’s Schemes/Programmes Related to Urban Development:
- Smart Cities Mission
- AMRUT Mission
- Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban
- HRIDAY
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban
- Aspirational district programme
Way Forward:
Acknowledging the role of different actors in the city can create a practical space to begin this work. Doing so will not just help control recurring floods but also respond to other fault lines, provide for water security, and more green spaces, and will make the city resilient and sustainable. The constant search for a scapegoat to blame, while a few people try what they can, limits our capacities and only creates cycles of devastation.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance), GS 4 (Ethics)
Context: An amendment to the New Drugs and Clinical Trial Rules (2023) was passed by the Government with the aim of stopping the use of animals in research, especially in drug testing.
Key-highlights of the Amendment:
- The amendment grants researchers the authority to use alternative techniques that do not include animals and are more applicable to humans.
- These methods encompass technology such as 3D organoids, organs-on-chip, and sophisticated computational approaches, which are utilized to assess the safety and effectiveness of novel pharmaceuticals.
- The aforementioned regulations provide that any Contract Research Organization (CRO) doing a clinical trial or bioavailability/bioequivalence research involving novel or experimental medications in human participants must get registration from the Central Licensing Authority prior to commencing such investigations.
Clinical Trials module in India:
- Every drug goes through a long journey of tests, designated to check whether it can treat the disease for which it was created and its harmful effects.
- The first step of the process for drug testing involves candidate molecule in at least two animal species: a rodent (mouse or rat) and a non-rodent, such as canines and primates.
- However, humans are more complex creatures, and biological processes and their responses often vary from person to person as well, based on factors such as age, sex, pre-existing diseases, genetics, diet, – and a lab-bred animal species reared in controlled conditions may not fully capture the human response to a drug.
Technologies suggested as alternatives:
- Technologies developed using human cells or stem cells: These include millimeter-sized three-dimensional cellular structures that mimic specific organs of the body, called “organoids” or “mini-organs”.
- ‘Organ-on-a-chip’ Technology: These are AA-battery-sized chips lined with human cells connected to micro channels, to mimic blood flow inside the body.
- These systems capture several aspects of human physiology, including tissue-tissue interactions and physical and chemical signals inside the body.
- USING 3D Bioprinter: Bio printers are used to ‘print’ biological tissues using human cells and fluids as ‘bio-ink’.
- Since they can be built using patient-specific cells, they can also be used to personalise drug-tests.
Challenges:
- Developing an organ-on-a-chip system: It typically requires multidisciplinary knowledge and expertise in cell biology to recreate the cellular behaviour in the lab.
- Materials science to find the right material to ensure that the chip does not interfere with biological processes.
- Fluid dynamics to mimic blood flow inside the microchannels; electronics to integrate biosensors that can measure pH, oxygen etc. in the chip; engineering to design the chip; and pharmacology and toxicology to interpret action of the drugs in the chips.
- Resources for research and development: Most of the reagents, cell-culture related materials and instruments are currently imported from the U.S., Europe, and Japan.
- There is a huge gap and opportunity in several diverse areas related to cell culture, material science and electronics, to develop an end-to-end ecosystem in India.
- Variability in the data arising from differences in lab-to-lab protocols and expertise.
- For example, one lab may create a system with only liver cells, while another lab attempting to study the immune system and liver may also incorporate immune cells in its liver-on-a-chip.
- It means there can be no ‘standard’ or ‘universal’ liver-on-a-chip to study all liver diseases.
Status of regulations worldwide:
- United States: FDA Modernization Act 2.0 was passed in December 2022, allowing researchers to use these systems to test the safety and efficacy of new drugs.
- South Korea: A ‘Vitalization of Development, Dissemination, and Use of Alternatives to Animal Testing Methods’ bill was introduced in December 2022.
- European Union: In 2021, a resolution was passed on an action plan to facilitate transition towards technologies that do not use animals in research, regulatory testing, and education.
- Canada: The Environmental Protection Act was amended in June 2023 to replace, reduce or refine the use of vertebrate animals in toxicity testing.
- India: In March 2023, the government embraced these systems in the drug-development pipeline by amending the New Drugs and Clinical Trials Rules 2019.
- It did so after inviting comments from the people and in consultation with the Drug Technical Advisory Board, the statutory body that advises Central and State governments on drug-related technical matters.
Way Forward:
India’s drug development law change reduces animal experimentation and promotes ethical principles for safer and more effective pharmaceuticals. India establishes a foundation for responsible drug development by promoting alternative approaches, animal welfare, and international criteria. It’s a truly interdisciplinary endeavour and needs focused training and human-resource building, which is lacking in the country at present.
Source: The Hindu
Additional information:
Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB):
- DTAB serves as the supreme statutory decision-making authority concerning technical aspects of drugs within the nation.
- It is established in accordance with the Drugs and Cosmetics Act of 1940.
- DTAB operates under the umbrella of the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO), which operates within the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO):
- CDSCO is India’s top regulatory authority for pharmaceuticals and medical devices.
- Established under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- Operates under the Directorate General of Health Services (DGHS) in the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Mandate and Functions:
- Ensures safety, efficacy, and quality of drugs, cosmetics, and medical devices.
- Reviews new drug approvals, clinical trials, and import/export licenses.
- Regulates manufacturing, sale, distribution, labelling, and packaging.
- Monitors adverse reactions, conducts post-market surveillance.
- Collaborates with state authorities, industry, global regulators.
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Exercise | Countries |
| 1.JIMEX | India and Jordan |
| 2.SANGAM | India and US |
| 3.Pitch Black | India and Australia |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, provides for freedom from arrest and detention of members under civil process during the continuance of the meeting of the House.
Statement-II:
Article 194 of the Indian constitution deals with the powers, privileges, and immunities of the State Legislatures.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Renaming a state is under Articles 3 and 4 of the Indian constitution.
Statement-II:
Such a bill in order to take the force of law must be passed by a special majority.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Question
Q.1) Discuss the significance of rainwater harvesting and sponge cities concept in reducing urban flooding. How can community engagement play a role in flood preparedness and water body conservation? (250 Words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 11th August 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 10th August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – b
Q.3) -d











