IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) recently informed that several states and Union territories (UTs) are yet to implement the Incident Response System (IRS), which is crucial for disaster response.
About Incident Response System (IRS):
- IRS is a combination of facilities, equipment, personnel, procedure and communications operating within a common organizational structure, with responsibility for the management of assigned resources to effectively accomplish stated objectives pertaining to an incident.
Functions of IRS:
- In line with administrative structure and DM Act 2005, Responsible Officer (RO) is designated at the State and District level as overall in charge of the incident response management.
- RO may delegate responsibilities to the Incident Commander (IC), who in turn will lead/manage the incident through Incident Response Teams (IRTs).
- IRS functions through Incident Response Teams (IRTs) in the field. An IRT is a team comprising all positions of IRS organization; headed by Incident Commander (IC).
- On receipt of Early Warning, RO activates IRTs.
- In case of a disaster without any warning, local IRT will respond and contact RO for further support, if required.
- IRTs pre-designated at all levels, i.e. State, District, Sub-Division and Tehsil/Block.
- IRT’s lowest administrative unit (Sub-Division / Tehsil / Block) will be the ‘first responder’.
- If the incident becomes complex and beyond the control of local IRT, higher level IRT will be informed / take over the response management.
- In such cases the lower level IRT will merge with the higher level IRT.
- When lower level of IRT merges with a higher level, IC of lower level may play the role of Deputy IC or Operations Sections Chief (OSC) or any other duty that the IC of higher authority assigns.
Source: Hindustan Times
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity and Governance
Context: Recently, the Union Home Minister chaired the 38th meeting of the Committee of Parliament on Official Language.
About Committee of Parliament on Official Language:
- The Committee of Parliament on Official Language was set up in 1976 under Section 4 of the Official Languages Act, 1963.
- With the active promotion of Hindi being mandated by Article 351 of the Constitution, the Official Language Committee was set up to review and promote the use of Hindi in official communications.
- The first Report of the Committee was submitted in 1987.
- The Committee is constituted and chaired by the union home minister, and has, in accordance with the provisions of the 1963 Act, 30 members (20 MPs from Lok Sabha and 10 MPs from Rajya Sabha).
- Unlike the other Parliamentary, panels submit its report to Parliament, this panel submits its report to the President, who “shall [then] cause the report to be laid before each House of Parliament, and sent to all the State Governments”.
- The purpose of the Committee is
- To review the progress made in the use of Hindi for official purposes, and
- To make recommendations to increase the use of Hindi in official communications.
Constitutional Status of Hindi and other languages:
- Schedule 8 of the Indian Constitution has 22 Official Languages, including Hindi as well. ( UPSC CSE: Languages of India)
- Article 351 states that, it is the duty of the Union to encourage the spread of the Hindi language to make it lingua franca (a shared language of communication used by people who are speakers of different languages) in India without interfering with its genius, style and expressions.
- Article 348 (2) provides that the Governor of the State may, with the previous consent of the President, authorize the use of the Hindi language or any other language used for any official purpose of the State, in the proceedings of the High Court having its principal seat in that State provided that decrees, judgments or orders passed by such High Courts shall be in English.
- As per Article 343(1) of the Constitution of India, Hindi in Devanagari script shall be the official language of the Union.
- The Official Language Act, 1963 provides under Section 7 that the use of Hindi or official language of a State in addition to the English language may be authorized, with the consent of the President of India, by the Governor of the State for the purpose of judgments, decrees etc. made by the High Court for that State. (UPSC CSE: Three language formula)
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Miscellaneous
Context: The Grandmaster D. Gukesh has recently overtook Chess legend Viswanathan Anand as the highest-rated Indian player in International Chess Federation (FIDE) rankings.
About the International Chess Federation (FIDE):
- The International Chess Federation (FIDE) is the governing body of the sport of chess, and it regulates all international chess competitions. Constituted as a non-governmental institution, it was recognized by the International Olympic Committee as a Global Sporting Organization in 1999.
- FIDE currently has its headquarters in Lausanne, but it was initially founded in 1924 in Paris under the motto “Gens una Sumus” (Latin for “We are one Family”).
- It was one of the very first International Sports Federations, alongside the governing bodies of the sports of Football, Cricket, Swimming, and Auto Racing.
- It is now one of the largest, encompassing 199 countries as affiliate members, in the form of National Chess Federations.
- Chess is nowadays a truly global sport, with dozens of millions of players in all the continents, and more than 60 million games on average played every day.
- Each month, FIDE publishes the lists such as-
- Top 100 Players
- Top 100 Women
- Top 100 Juniors
- Top 100 Girls
- It also publishes rankings of countries according to the average rating of their top 10 players and top 10 female players.
- It uses the Elo rating system for ranking purpose.
- The Elo rating system is a method for calculating the relative skill levels of players in zero-sum games such as chess.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims: Art and Culture
In News: The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has sought permission to inspect the inner chamber of the Ratna Bhandar (treasury) of the Shree Jagannath Temple in Puri.
Background:
- About 1.2 quintal of gold jewellery is stocked in the Ratna Bhandar
- The previous inventory of the jewellery in the Ratna Bhandar was carried out in 1978.
About Puro Jagannath Temple:
- The Shree Jagannath Temple of Puri is an important Hindu temple dedicated to Lord Jagannath, a form of Vishnu,in Puri in the state of Odisha on the eastern coast of India.
- The present temple was rebuilt from the 10th century onwards, on the site of an earlier temple, by King Anantavarman Chodaganga Deva, first of the Eastern Ganga dynasty.
- The Jagannath Temple in Puri is called the “White Pagoda”.
- The temple is a part of Char Dham (Badrinath, Dwaraka, Puri, Rameswaram) pilgrimages that a Hindu is expected to make in one’s lifetime.
- The Puri temple is famous for its Annual Ratha yatra, or chariot festival, in which the three principal deities are pulled on huge and elaborately decorated temple cars.
- These gave their name to the English term Juggernaut.
- Unlike the stone and metal icons found in most Hindu temples, the image of Jagannath is made of wood and is ceremoniously replaced every twelve or nineteen years by an exact replica.
Architecture of Jagannath temple:
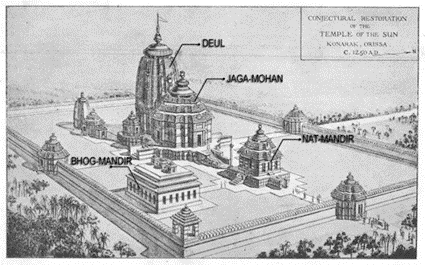
- The temple is built in the Kalinga style of architecture, with the Pancharatha (Five chariots) type consisting of two anurathas, two konakas and one ratha.
- Jagannath temple is a pancharatha with well-developed pagas.
- ‘Gajasimhas’ (elephant lions)carved in recesses of the pagas, the ‘Jhampasimhas’ (Jumping lions) are also placed properly.
- The perfect pancharatha temple developed into a Nagara-rekha temple.
- The temple is built on an elevated platform, as compared to Lingaraja temple and other temples belonging to this type.
- This is the first temple in the history of Kalingaan temple architecturewhere all the chambers like Jagamohana, Bhogamandapa and Natyamandapa were built along with the main temple.
- There are miniature shrines on the three outer sides of the main temple.
Archaeological Survey of India:
- The ASI is the premier organization for the archaeological researches and protection of the cultural heritage of the country.
- The prime objection of ASI is to maintain the archaeological sites, ancient monuments, and remains of national importance.
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
- Established: 1861 by Alexander Cunningham.
- It regulates all archaeological activities as per the provisions of the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958.
- It functions under the aegis of the Union Ministry of Culture.
- It also regulates Antiquities and Art Treasure Act, 1972.
SOURCE: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims: Indian Economy
In News: A new online dispute resolution (ODR) system involving institutions, conciliators and arbitrators for the capital market is on its way.
- It will harness online conciliation and online arbitration for the resolution of disputes arising in the securities market.
The Dispute Resolution Process
- At the initial stage, an investor would be required to lodge a complaint with the market participant directly.
- In this regard, listed companies, regulated entities and specified intermediaries in the securities market are referred to as market participants collectively.
- In case the grievance is not satisfactorily redressed, they have the option to raise it to the SEBI Complaints Redress System (SCORES) online portal.
- However, if an investor is dissatisfied with the outcome at this level, they will have the option to go in for dispute resolution via the ODR portal.
- The conditions in this regard are:
- The complaint is not under consideration by the market participants and the SCORES platform.
- The matter should not be pending before a court, consumer forum, or tribunal.
The New System
- Markets Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs), which include stock exchanges, and clearing corporation’s depositories, will be required to identify and empanel one or more ODR institutions.
- A common ODR portal will be established and operated by MIIs in consultation with their empaneled ODR institutions.
- The ODR institution that gets the reference of the complaint will be responsible for appointing qualified conciliators and arbitrators.
- Coverage: ODR will cover a wide array of intermediaries, including
- Alternate investment funds (AIFs), investment advisors, mutual funds, portfolio managers, research analysts, and more.)
- Disputes arising from different types of cases involving investors or clients, along with listed companies, including their registrar and share transfer agents, could involve the implementation of ODR.
- Applicable to disputes that involve specified intermediaries or regulated entities in the securities market.
About SEBI (The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) :
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India was established as a statutory body in the year 1992.
- Headquarters: Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Ministry: Ministry of Finance
- Chairperson: Madhabi Puri Buch
- The chairman is nominated by the Union Government of India.
- Appointment of other members:
- Two members, i.e., Officers from the Union Finance Ministry.
- One member from the Reserve Bank of India.
- The remaining five members are nominated by the Union Government of India, out of them at least three shall be whole-time members.
SOURCE: Livemint
Syllabus
- Prelims: Technology
In News: Direct-to-home (DTH) service provider Tata Play has started beaming of television channels from its dedicated GSAT-24 satellite which it has leased from Indian space agency ISRO.
GSAT-24 satellite – Ushering in a new era of satellite television for India
GSAT-24 is a 4-tonne 24-Ku band communication satellite built by ISRO only to cater to the requirement of Tata Play’s DTH application needs.
- It is the first demand-driven communication satellite mission undertaken by NSIL post space sector reforms.
- As a testament to the success of the Make In India initiative, this satellite would support domestic broadcasting services with advanced digital TV transmission capabilities
Working of a Communication satellite
- A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunications signals through a transponder. It basically creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on earth.
- Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. There are currently 2,134 communications satellites in the earth’s orbit and these comprise both private and government organizations. Several are in geostationary orbit 22,236 miles (35,785 km) above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky.
- The orbital period of these satellites is the same as the rotation rate of the Earth, which in turn allows the satellite dish antennas of ground stations to be aimed permanently at that spot; they do not have to move along and track it.
- Since the high-frequency radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight, they get obstructed by the curve of the earth. What these communications satellites do is they relay the signal around the curve of the earth thus making possible communication between widely removed geographical points.
- Communications satellites use a wide range of radio and microwave frequencies. To avoid signal interference, international organizations have regulations stating which frequency ranges (or bands) certain organizations are permitted to use. This allocation of bands reduces the chances of signal interference.
SOURCE: Business Standard
Starlink: New Sovereign of Low-earth Orbit
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology)
Context: Starlink’s importance in Ukraine has highlighted how high-speed satellite Internet access is quickly becoming the most valuable strategic resource in a conflict or war-stricken region.
About the Starlink Project:
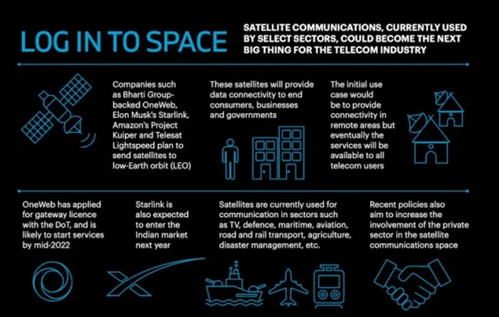
- Starlink is a satellite constellation that comprises thousands of small satellites in low-Earth orbit (LEO).
- SpaceX first began sending them into space in 2019.
- SpaceX is an American aerospace manufacturer and space transport services company founded by Elon Musk.
- Currently, there are more than 3,000 of these satellites that send internet signals to designated ground receivers.
- Unlike traditional internet providers, Starlink doesn’t require any ground infrastructure.
- One just needs to have a small satellite dish or a receiver device to access high-speed internet, much like satellite TV.
Significance of Starlink:
- Global Connectivity: Starlink aims to offer high-speed internet to users worldwide, including those living in remote and rural areas with limited or no access to traditional broadband services.
- Low Latency: LEO satellites offer low latency, reducing the signal delay experienced with traditional geostationary satellites, making activities like online gaming and video conferencing smoother.
- Reliable and Redundant: The large number of satellites in the constellation allows for redundancy, minimizing service disruptions in case of satellite failures.
- Emergency Connectivity: Starlink has shown its potential in providing emergency internet access during natural disasters and crises, offering communication lifelines to affected communities.
Challenges
- Space Debris: With thousands of satellites in LEO, concerns have been raised about space debris and its impact on the space environment and other satellite operations.
- Astronomy Interference: Starlink satellites have been criticized for interfering with ground-based astronomical observations due to their brightness and impact on the night sky.
- Monopoly Concerns: As Starlink expands its dominance in the satellite internet market, concerns arise about potential monopolistic control over global internet access.
- Regulatory and Legal Challenges: Operating a massive satellite constellation involves navigating complex international regulations, spectrum management, and coordination with other satellite operators.
- Russia Ukraine – Operations controlled by company: After the Russia-Ukraine war broke out in 2022, fibre network lines and cell towers were the first pieces of infrastructure to be destroyed, rendering Starlink as the lifeblood of Ukraine’s communication network.
- When Internet connectivity is deployed in a region, the nature of the technology is such that its operations aren’t controlled by the user, but by the company.
- So when the Ukrainian government wanted to switch on/off access in a particular area.
- For example, if a piece of territory had fallen into Russian hands and a few Starlink dishes or terminals had been lost – it had to call up Starlink each time.
Comparison with internet through Geostationary Satellites:
- The internet services obtained from Geostationary Satellites have the advantage
- Better coverage with lesser number of satellites. Roughly, 3 or 4 satellites is enough to cover whole earth.
- Since, these satellites appear to be stationary, linkage is easier.
Way Forward:
- In 2022, the European Union earmarked EUR 2.4 billion to set up a “sovereign” satellite constellation to be rolled out by 2027. China has its own plans to deploy a 13,000-satellite LEO mega constellation to rival Starlink.
- Starlink’s disputes with Ukraine and other countries should serve as a wake-up call of how the power of the stars is quickly being concentrated in the hands of just one man, and a worrying lesson for any country or government looking to depend on Elon Musk for connectivity.
- Source: The Hindu
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: According to recent data, around three lakh patients wait for organ donation in the India.
Key highlights of the data:
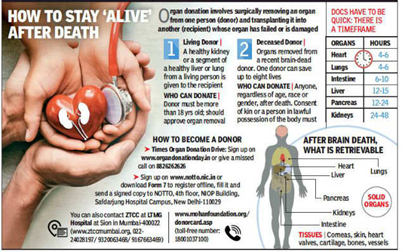
- Health Ministry’s data: The number of donors (including deceased) only grew from 6,916 in 2014 to about 16,041 in 2022.
- The country registered 1,589 kidney transplants, 761 liver and 250 heart transplants in the deceased category in 2022.
- Kidney and pancreas transplants grew from three in 2014 to 22 in 2022.
- Statistics indicate around 70%-75% of donors are female. Wives, mothers, and sisters have emerged as most prevalent sources of donation.
- Global Data: Even worldwide, only 10% of patients needing organs get them in time. Spain and the U.S. have better organ donation systems clocking 30-50 donations per million.
Organ transplant: Scenario in INDIA
- The number of organ transplants has increased by over three times from 4,990 in 2013 to 15,561 in 2022.
- The most common organ transplant is for the kidney, followed by liver, heart, lung, pancreas, and small bowel transplants.
- In 2022 alone, nearly 12,791 living donor transplants and 2,765 deceased donor transplants were conducted.
- Only 1,743 (14%) of the organs were from deceased donors, while the majority of organs harvested were from living donors, specifically kidney and liver donations.
- Nearly all deceased organ donations in 2021 were in 15 states, with the top five accounting for over 85% of the total.
Need for Increased Organ Donations in India:
- India conducts the third highest number of transplants in the world, but the number of organs needed is still much higher than the number of transplants.
- Lifestyle diseases are increasing the demand for organs as heart and lungs can only be retrieved from deceased donors.
- Nearly 1.5 lakh persons die in road traffic accidents every year in India, many of whom can ideally donate organs.
- Organ transplantation also helps to reduce the burden on the healthcare system by reducing the need for hospitalization, repeat surgeries, and long-term treatment.
- India has an organ donation rate of 0.52 per million population, much lower than the rate in Spain (49.6 per million).
- Organ donation can help save the lives of multiple people, as one donor can donate several organs and tissues.
Challenges of Organ Transplantation:
- Lack of awareness: There is a lack of awareness among people about the importance of organ donation and transplantation, which leads to a shortage of donated organs.
- Shortage of donors: Despite increasing awareness, there is still a shortage of organ donors due to several reasons, including religious beliefs, and lack of trust in the medical system.
- Legal and ethical issues: There are several legal and ethical issues surrounding organ donation, including consent, allocation of organs, and the fair distribution of organs.
- Transportation and preservation: Organs need to be transported and preserved under specific conditions to ensure their viability for transplantation which has logistical challenges, especially for organs that have a short shelf life.
- Medical suitability: Not all donated organs are suitable for transplantation due to medical conditions or other factors, which can limit the number of available organs for transplant.
- Costs: The costs associated with organ transplantation can be high, which can limit access to treatment for some patients.
Government Steps to facilitate Organ Transplant in India
- Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues Act (THOTA): It was enacted in 1994 and governs organ transplantation in India.
- The act also establishes the National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO) and State Organ and Tissue Transplant Organizations (SOTTO) to oversee organ donation and transplantation activities.
- National Organ Transplant Programme (NOTP): It was launched in 2014 to create a national registry of organ donors and recipients, establish more organ transplant centers, and raise awareness about organ donation.
- Deceased Organ Donation Program: It was launched by Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to encourage organ donation from deceased individuals.
- National Organ Donation Day: The government of India has designated November 27 as National Organ Donation Day to raise awareness about the importance of organ donation and encourage people to pledge to donate their organs.
- Swasth Bharat Yatra: It is a government-led campaign to promote healthy living, prevent lifestyle diseases, raise awareness about organ donation and encourages people to pledge to donate their organs.
- National Organ and Tissue Transplant Registry: It has established a National Organ and Tissue Transplant Registry to maintain records of organ donations and transplantation in the country to help in the development of policies and strategies to promote organ donation and transplantation.
- Organ Retrieval Banking Organization: It is a part of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) in New Delhi and is responsible for the retrieval, preservation, and distribution of organs for transplantation in the Delhi-NCR region.
Way Forward:
Presently, India has greater awareness about organ donation and doctors say more families are coming forward for this noble deed. There is a need for awareness, building trust, and increasing the number of medically qualified transplant coordinators to help increase the deceased donations. Overall, organ transplant plays a critical role in the medical field by offering hope to patients suffering from organ failure and improving their quality of life.
Source: The Hindu
Q.1) Discuss the global debates and implications arising from Starlink’s satellite integration in the Russia-Ukraine conflict. Analyze the significance of relying on a single entity for satellite internet services and the potential challenges faced by countries and governments in such scenarios. (250 Words)
Q.2) Discuss the issues and challenges of Organ Transplantation in India? What steps has the government taken in this regard? (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR 7th August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – b
Q.3) -a











