IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – POLITY
Context: Senior Congress leader K Suresh, as the seniormost member of the Lok Sabha, is expected to be appointed as pro-tem Speaker when the first session of the 18th Lok Sabha begins.
Background:-
- The 18th Lok Sabha will hold its first session from June 24 to July 3, during which the new Speaker of the House will be elected. Until this happens, a pro-tem Speaker will be chosen to swear in the new Members of Parliament.
What is a pro-tem Speaker?
- Being the Presiding Officer of the Lok Sabha, the Speaker has to fulfil certain key duties related to its day-to-day proceedings.
- Article 94 of the Indian Constitution states: “Whenever the House of the People is dissolved, the Speaker shall not vacate his office until immediately before the first meeting of the House of the People after the dissolution.”
- In the new Lok Sabha, the Speaker of the House is decided by a simple majority. Until her selection, the pro-tem Speaker is chosen to administer some important duties. ‘Pro-tem’ essentially means ‘for the time being’ or ‘temporarily’.
- The Constitution does not mention the post. However, the official ‘Handbook on the Working of Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs’ speaks about the ‘Appointment and Swearing in of Speaker pro term’.
How is the pro-tem Speaker chosen?
- The handbook states when the Speaker post falls vacant before a new Lok Sabha, “the duties of the Speaker are to be performed by a Member of the House appointed for this purpose by the President as Speaker pro tem”.
- Administering oaths to the new MPs is the pro-tem Speaker’s primary duty.
- Under Article 99 of the Constitution, “Every Member of the House shall, before taking his seat, make and subscribe before the President or some person appointed in that behalf by him, an oath or affirmation according to the form set out for the purpose in the Third Schedule of the Constitution.”
- Normally, three other elected members of the Lok Sabha are also appointed by the President for the MPs to take oath before them. According to the handbook, the seniormost members (in terms of number of years of membership of the House) are generally chosen for the purpose, though there have been exceptions.
- As soon as the new government is formed, the Legislative I Section of the Government of India prepares a list of the seniormost Lok Sabha members. It is then submitted to the Minister of Parliamentary Affairs or the Prime Minister for identifying an MP as Speaker pro-tem and another three members for oath-taking.
How are new MPs administered oaths?
- After the Prime Minister’s approval, the consent of these members is obtained by the Minister of Parliamentary Affairs. The Minister then submits a note to the President, seeking approval for the appointment of the Speaker pro-tem and the other three members. They also decide the date and time of the swearing-in ceremony.
- Following the approval of the President, the Ministry informs the Speaker pro-tem and other members about their appointments.
- Finally, the President administers the oath to the Speaker pro-tem in the Rashtrapati Bhawan. The other three members appointed by the President are administered the oath by the Speaker pro-tem in the Lok Sabha.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – CURRENT EVENT
Context: The Congress party has described the proposed Rs 72,000-crore infra upgrade at the Great Nicobar Island as a grave threat to the island’s indigenous inhabitants and fragile ecosystem, and demanded immediate suspension of all clearances and a thorough, impartial review of the proposed project.
Background:
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are a cluster of 836 islands, split into two groups — the Andaman Islands to the north and the Nicobar Islands to the south — by the 150-km wide Ten Degree Channel.
Key Takeaways
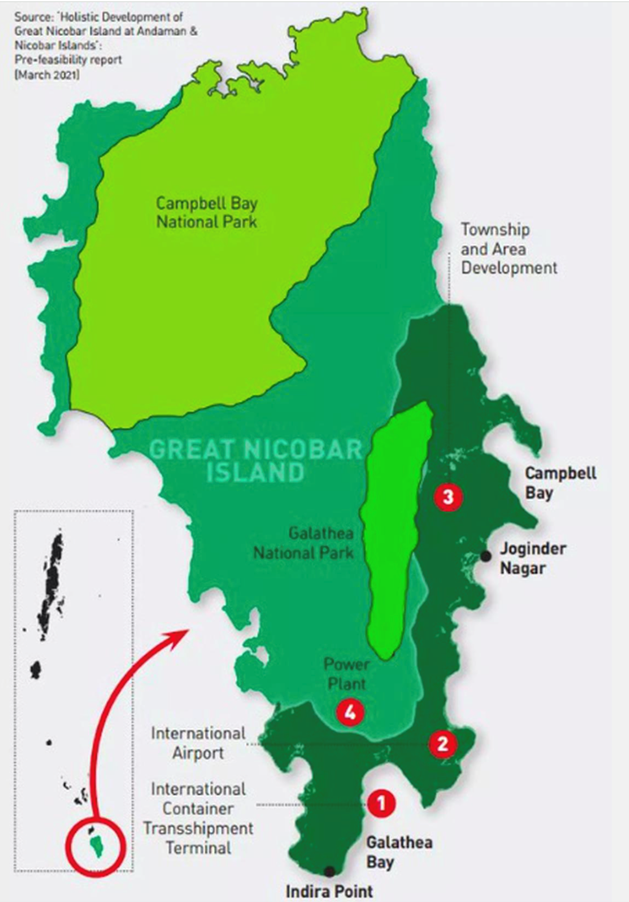
- Great Nicobar is the southernmost and largest of the Nicobar Islands, a sparsely inhabited 910-sq-km patch of mainly tropical rainforest in southeastern Bay of Bengal. Indira Point on the island, India’s southernmost point, is only 90 nautical miles (less than 170 km) from Sabang at the northern tip of Sumatra, the largest island of the Indonesian archipelago.
- Great Nicobar has two national parks, a biosphere reserve, small populations of the Shompen and Nicobarese tribal peoples, and a few thousand non-tribal settlers.
- The Great Nicobar Island has tropical wet evergreen forests, mountain ranges reaching almost 650 m above sea level, and coastal plains.
- The leatherback sea turtle is the island’s flagship species.
- The project for the “holistic development” of Great Nicobar Island was implemented after a report by NITI Aayog. A pre-feasibility report flagged the opportunity to leverage the strategic location of the island, which is roughly equidistant from Colombo in Sri Lanka to the southwest and Port Klang (Malaysia) and Singapore to the southeast.
- It is close to the Malacca Strait, the main waterway that connects the Indian Ocean to the Pacific, and the infrastructure project is expected to allow Great Nicobar to participate in the regional and global maritime economy by becoming a major player in cargo transshipment.
- It has been alleged that the project violates the rights of the tribal population, and will impact the island’s ecology with the felling of nearly a million trees.
- The opposition — by wildlife conservation researchers, anthropologists, scholars, and civil society apart from the Congress — has focused on the potentially devastating impact on the Shompen, a particularly vulnerable tribal group (PVTG) of hunter-gatherers with an estimated population of a few hundred individuals who live in a tribal reserve on the island.
- It is feared that the port project will destroy coral reefs with spinoff effects on the local marine ecosystem, and pose a threat to the terrestrial Nicobar Megapode bird and leatherback turtles who nest in the Galathea Bay area.
For Your Information:
- The Great Nicobar project is to be implemented in three phases over the next 30 years.
- The proposal: A “greenfield city” has been proposed, including an International Container Transhipment Terminal (ICTT), a greenfield international airport, a power plant, and a township for the personnel who will implement the project.
- The site for the proposed ICTT and power plant is Galathea Bay on the southeastern corner of Great Nicobar Island.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – ECONOMY
Context: Amid a sharp decline in funding for startups and consequent job losses, Indian Inc has sought the removal of Angel Tax that has been a subject of heated debate between the industry and the government ever since the scope of the controversial tax was expanded in the Finance Bill 2023.
Background:
- The Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) in its Union Budget recommendation on Tuesday suggested the removal of Section 56(2)(viib) of the Income-tax Act colloquially known as the ‘Angel Tax’ stating that the step would greatly aid capital formation in the country.
About Angel Tax
- Angel Tax was first introduced in 2012 to deter the generation and use of unaccounted money through the subscription of shares of a closely held company at a value that is higher than the fair market value of the firm’s shares.
- Angel tax – which is income tax at the rate of 30.6 per cent – is levied when an unlisted company issues shares to an investor at a price higher than its fair market value.
- Earlier, it was imposed only on investments made by a resident investor. However the Finance Act 2023 proposed to extend Angel Tax even to non-resident investors from April 1, 2024, meaning that when a start-up raises funding from a foreign investor, that too will now be counted as income and be taxable.
- The industry has argued that the government is wrong in citing the difference between valuations and actual performance as a sign of money laundering, adding that investors fund startup based on their future potential. Taxes levied on the difference between issue price of unlisted securities and its fair market value (FMV) has hurt funding, it said.
- The changes in the Angel Tax provisions came at a time when an estimated 100 Indian startups laid off over 15,000 employees in 2023, as funding winter that began in 2022 persisted.
- Moreover, Indian startups witnessed over 60 per cent decline in funding in terms of value in 2023.
- With the latest amendment, the government had proposed to also include foreign investors in the ambit, meaning that when a start-up raises funding from a foreign investor, that too will now be counted as income and be taxable.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: The European Commission (EC) has proposed anti-dumping duties on Indian optical fibre cable (OFC) manufacturers.
Background:
- If implemented, the duties would increase the cost of Indian OFC exports, potentially limiting their competitiveness in the European market. India exported nearly Rs 39,600 crore worth of OFC in 2024, with Europe being a major destination.
About EUROPEAN COMMISSION (EC) :
- The European Commission (EC) is a crucial institution within the European Union (EU).
- It serves as the EU’s executive arm, overseeing day-to-day operations and policy implementation.
- Composition:
- The EC consists of a College of Commissioners, with each member representing one of the 27 EU member states.
- The College of Commissioners is composed of the President of the Commission, eight Vice-Presidents, including three Executive Vice-Presidents, the High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy, and 18 Commissioners, each responsible for a portfolio.
- The day-to-day running of Commission business is performed by its staff (lawyers, economists, etc.), organised into departments known as Directorates-General (DGs), each responsible for a specific policy area.
What does the Commission do?
- Proposes new laws: The Commission is the sole EU institution tabling laws for adoption by the Parliament and the Council that –
- protect the interests of the EU and its citizens on issues that can’t be dealt with effectively at national level
- Manages EU policies & allocates EU funding
- sets EU spending priorities, together with the Council and Parliament
- draws up annual budgets for approval by the Parliament and Council
- supervises how the money is spent, under scrutiny by the Court of Auditors
- Enforces EU law
- together with the Court of Justice, ensures that EU law is properly applied in all the member countries
- Represents the EU internationally
- speaks on behalf of all EU countries in international bodies, in particular in areas of trade policy and humanitarian aid
- negotiates international agreements for the EU
Source: Economic Times
Syllabus
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: Punjab Chief Minister Bhagwant Mann recently conducted an on-site review of flood-prone areas along the Ghaggar River.
Background:
- This proactive move aims to mitigate flood risks in Punjab and assess the preparedness for the upcoming monsoon season. Notably, this approach represents a significant shift from past practices, where state visits occurred post-flooding.
About GHAGGAR RIVER
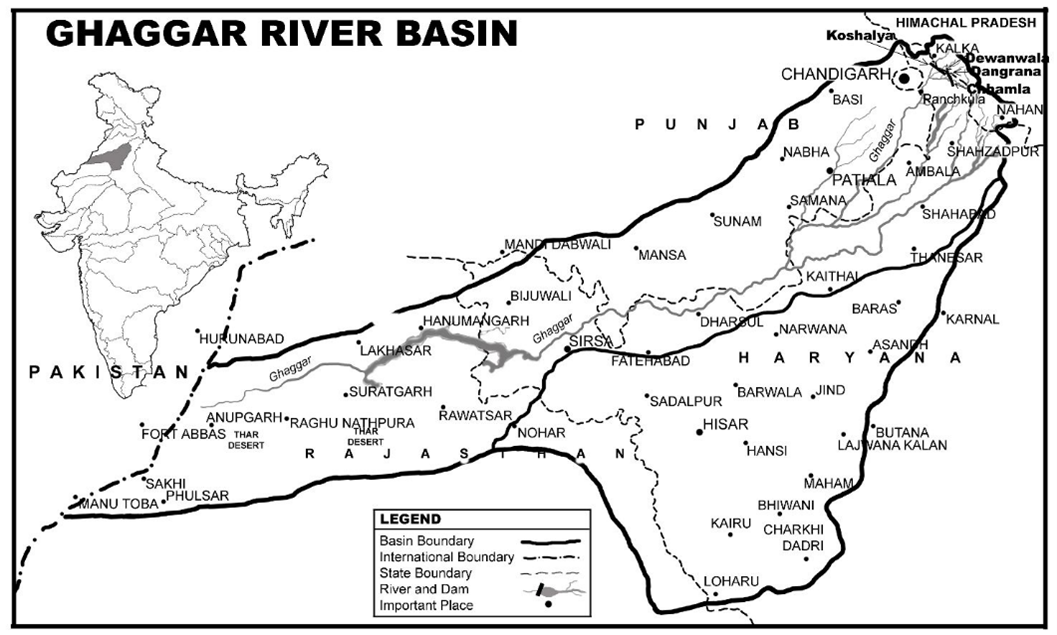
- The Ghaggar river rises from the Shivalik Range in northwestern Himachal Pradesh.
- It is a seasonal river that flows only during the monsoon season.
- The Ghaggar River flows through four states in India: Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan
- The Hakra, which flows in Pakistan, is the continuation of the Ghaggar River in India, and they are together called the Ghaggar – Hakra River.
- Before reaching the Ottu barrage, it is known as the Ghaggar.
- Downstream of the barrage, it becomes the Hakra and flows through the Thar Desert in Pakistan.
- It dries up in the Great Indian (Thar) Desert.
- Historical Significance:
- In pre-Harappan times, the Ghaggar was a tributary of the Sutlej River.
- The Sutlej changed its course around 8,000-10,000 years ago, leaving the Ghaggar-Hakra as a system of monsoon-fed rivers terminating in the Thar Desert.
- The Indus Valley Civilization thrived along the dried-up Hakra riverbed in Pakistan.
- Sarasvati River Connection:
- Scholars have suggested that the Ghaggar-Hakra might be the defunct remains of the Sarasvati River mentioned in the Rig Veda.
- Despite drying up, it still holds historical and cultural significance.
Source: Business Standard
Syllabus
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: Recently, the Prime Minister of India granted certificates to over 30,000 women from Self Help Groups (SHGs) as ‘Krishi Sakhis’ under the Krishi Sakhi Convergence Programme (KSCP).
Background:
- This certification course aligns with the objectives of the “Lakhpati Didi” Program.
About KRISHI SAKHI CONVERGENCE PROGRAM (KSCP)
- Krishi Sakhi convergence program (KSCP) aims to transform rural India through the empowerment of rural Women as Krishi Sakhi, by imparting training and certification of Krishi Sakhis as Para-extension Workers.
- This certification course aligns with the objectives of the “Lakhpati Didi” Program.
- Under the ‘Lakhpati Didi’ program, the aim is to create 3 crore Lakhpati Didis, one dimension of which is Krishi Sakhi.
- Training Modules:
- Krishi Sakhis undergo comprehensive training, including modules on agro-ecological practices, farmer field schools, soil health, livestock management, and more.
- After training, Krishi Sakhis take a proficiency test. Those who qualify become certified Para-extension Workers, enabling them to undertake various agricultural activities.
- Employment Opportunities:
- Krishi Sakhis can engage in activities related to soil health, crop demonstrations, crop insurance, horticulture awareness, and rainfed area development, earning resource fees for their services.
Source: PIB
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Consider the following statements:
- European Commission is the EU’s politically independent executive arm.
- Ursula von der Leyen is the current president of European Commission.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q2.) With reference to the Krishi Sakhi Convergence Programme (KSCP), consider the following statements:
- It aims to transform rural India through the empowerment of rural Women as Krishi Sakhi, by imparting training and certification of Krishi Sakhis as Para-extension Workers.
- Krishi Sakhis undergo comprehensive training, including modules on agro-ecological practices, farmer field schools, soil health, livestock management, and more.
- This certification course aligns with the objectives of the “Lakhpati Didi” Program.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Q3.) Consider the following states:
- Himachal Pradesh
- Punjab
- Haryana
- Rajasthan
The Ghaggar river flows through how many of the above – mentioned states in India?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 20th June 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 19th June – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – d











