IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Scientists at the Bhopal chapter of the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research have unravelled for the first time the genetic makeup of native Indian cow breeds Kasargod Dwarf, Kasargod Kapila, Vechur, and Ongole.
About genome sequencing:
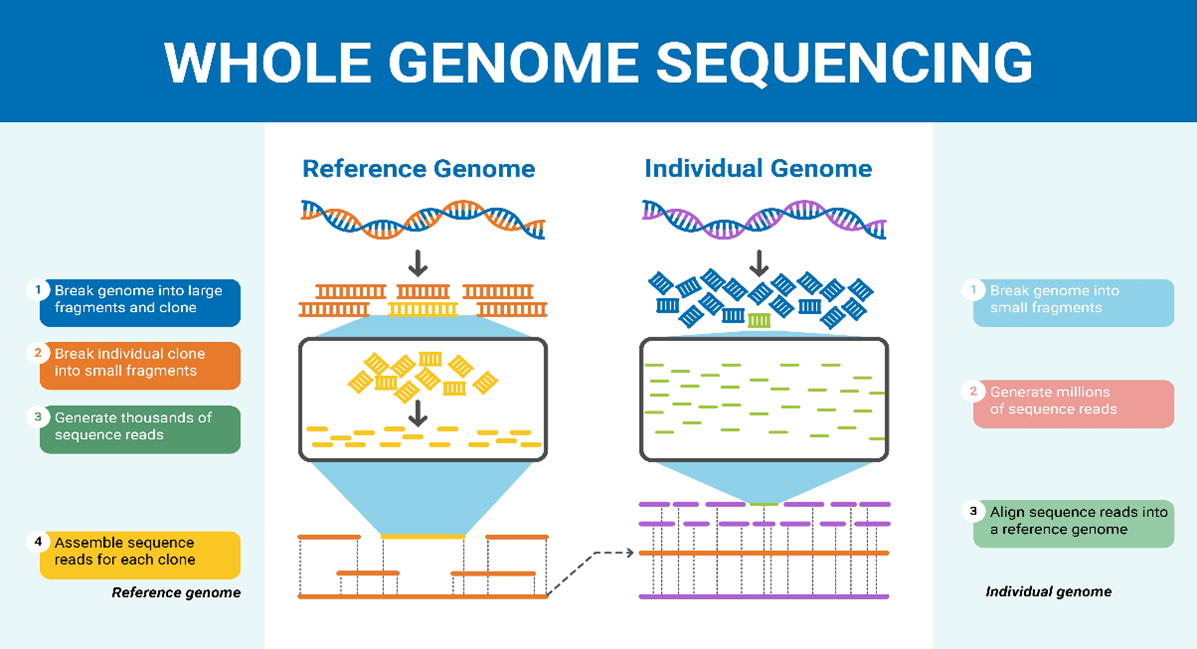
- A genome is a complete set of genetic instructions which are present in an organism in its DNA.
- Sequencing is the sequence of occurrences of the four nucleotide bases i.e., adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T).
- The human genome is made up of over 3 billion of these genetic letters.
- The whole genome can’t be sequenced all at once because available methods of DNA sequencing can only handle short stretches of DNA at a time.
- While human genomes are made of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid), a virus genome can be made of either DNA or RNA (Ribonucleic acid).
- Genome sequencing is a technique that reads and interprets genetic information found within DNA or RNA.
About the Cow Breeds:
Kasargod Dwarf
- It is originated in the mountain range of Kasaragod district, Kerala
- They are known for their excellent milking ability and give mineral-rich milk with a high feed-to-milk ratio.
- One among the four prime dwarf cattle in India- Kasargod Dwarf, Malnad Gidda, Punganur and Vechur Cattle.

Kasargod Kapila

- Native to Karnataka and Kasaragod.
- They possess golden hide of shining texture, golden eyes, and nose.
- Voluntarily shed their horns annually
- It contains a substance named “Go-rochana” and possess rare medicinal qualities according to ancient literature and traditional healers.
Vechur

- Smallest cattle breed in the world.
- Rare breed of Bos indicus cattle in Kerala.
- Listed on the Food and Agriculture Organization’s World Watch List of Domestic Animal Diversity.
Ongole

- Breed of cattle family Bos indicus in Andhra Pradesh.
- Known for their toughness, rapid growth rate, and natural tolerance to tropical heat and disease resistance.
- This breed is Famous for its bulls commonly used in bullfights in Mexico and East Africa.
Source: Times of India
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body? (2022)
- They protect the environmental allergens. body
- They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
- They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
- They protect the body from the diseases caused by pathogens.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Recently, 15 railway stations under Tiruchi Division Railway Division were selected to be developed under the Amrit Bharat Station Scheme.
About Amrit Bharat Station Scheme:
- The Union Ministry of Railways launched Amrit Bharat Station Scheme in December 2022 to modernize over 1,000 small stations over the coming years.
- The scheme will subsume all previous redevelopment projects where work is yet to begin.
- Key features for these proposed stations:
- provisions for roof top plazas,
- longer platforms,
- ballastless tracks; and
- 5G connectivity.
- Other Facilities Planned under this Scheme
- Smooth access by widening of roads, properly designed signages, dedicated pedestrian pathways, well planned parking areas, improved lighting.
- High level platforms(760-840 mm) shall be provided at all categories of stations.
- Provide good cafeteria/retail facilities.
- Space shall also be created for Executive Lounges and places for small business meetings.
- Drainage of platform areas.
- Ceremonial flags may be provided at appropriate space in the station.
- Special amenities for the disabled.
- Gradual shift to sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions as per availability of funds and condition of existing assets is considered.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity and Governance
Context: As the recent majority judgment of the Supreme Court on demonetisation comes under criticism, the minority judgment by J. Nagarathna is being hailed for its challenge to the RBI’s institutional acquiescence to the Central government.
About Judicial Majoritarianism:
- As opposed to standard matters heard by Division Benches consisting of two judges, numerical majorities are of particular importance to cases which involve a substantial interpretation of constitutional provisions.
- In such cases, Constitutional Benches, consisting of five or more judges, are set up in consonance with Article 145(3) of the Constitution.
- Such Benches usually consist of 5, 6, 9, 11 or even 13 judges.
- This is done to facilitate decision-making by ensuring numerical majorities in judicial outcomes.
- Article 145(5) of the Constitution: It states that no judgment in such cases can be delivered except with the concurrence of a majority of the judges but that judges are free to deliver dissenting judgments or opinions.
Differences among the judges and methodological fallacies:
- Any differences in judicial decisions can be attributed to a difference in either the methodology adopted and the logic applied by the judges.
- The differences can also be attributed to the judges’ own ‘judicial hunches’ which may be an outcome of their subjective experiences, outlook, and biases.
- In such circumstances, it is entirely possible that the majority may fall into either methodological fallacies and errors or be limited by their ‘judicial hunch’ respectively.
- In such situations, a meritorious minority decision, irrespective of the impeccability of its reasoning receives little weightage in terms of its outcomes.
- For example:
- The dissenting opinion of Justice H.R. Khanna in A.D.M. Jabalpur v. Shivkant Shukla (1976) upholding the right to life and personal liberty even during situations of constitutional exceptionalism.
- Dissenting opinion of Justice Subba Rao in the Kharak Singh v. State of U.P. (1962) case upholding the right to privacy which received the judicial stamp of approval in the K.S. Puttaswamy v. UOI (2017) case.
Dissenting opinions:
- The rate of judicial dissent at the height of the Emergency in 1976 was a mere 27% as opposed to 10.52% in 1980.
- The rate of dissent where the Chief Justice was a part of the Bench was lower than in those cases where the Chief Justice was not on the Bench.
- Such situations call into question the efficiency and desirability of head-counting procedures for a judicial determination on questions of national and constitutional importance.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) A legislation which confers on the executive or administrative authority an unguided and uncontrolled discretionary power in the matter of the application of law violates which one of the following Articles of the Constitution of India? (2021)
- Article 14
- Article 28
- Article 32
- Article 44
Q.2) With reference to Indian Judiciary, consider the following statements.
- Any retired judge of the Supreme Court of India can be called back to sit by the Chief Justice of India with prior permission of the President of India.
- A High court in India has the power to review its own judgement as the Supreme Court does.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2021)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: The Union Budget has proposed several measures to enhance business activities at Gujarat International Finance Tec-City – International Financial Services Centre (GIFT IFSC).
- A subsidiary of EXIM Bank for trade re-financing would be established at GIFT IFSC and IFSCA Act would be amended for statutory provisions for arbitration, ancillary services, and avoiding dual regulation under SEZ Act.
About International Financial Services Centre Authority:
- IFSCA is a statutory body established in 2020 under the International Financial Services Centres Authority Act, 2019 to ensure inter-regulatory coordination within the financial sector.
- Headquarters: At GIFT City, Gandhinagar in Gujarat.
- Prior to the establishment of IFSCA, the domestic financial regulators, namely, RBI, SEBI, PFRDA and IRDAI regulated the business in IFSC.
- The IFSCA is a unified authority for the development and regulation of financial products, financial services and financial institutions in the International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) in India.
- The main objective of the IFSCA is to develop a strong global connect and focus on the needs of the Indian economy as well as to serve as an international financial platform for the entire region and the global economy as a whole.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) ‘Rapid Financing Instrument” and “Rapid Credit Facility” are related to the provisions of lending by which of the following: (2022)
- Asian Development Bank
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative
- World Bank
Q.2) In India, the Central Bank’s function as the “lender of last resort” usually refers to which of the following? (2021)
- Lending to trade and industry bodies when they fail to borrow from other sources
- Providing liquidity to the banks having a temporary crisis
- Lending to governments to finance budgetary deficits
Select the correct answer using the code given below
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 2 and 3
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Economic Survey 2022-23 has suggested measures like simplifying ESOP taxation, and easier corporate laws like in the US and Singapore to accelerate reverse-flipping among startups, namely moving domicile back to India.
About Flipping and Reverse-flipping:
- Flipping is the process of transferring entire ownership of an Indian company to an overseas entity.
- It is generally accompanied by a transfer of all intellectual property and data owned by an Indian company.
- Reverse Flipping is the process of shifting the domicile of those companies back to India who flipped earlier.
- Companies reverse flip because of easy access to capital from private equity and venture capital, changes in rules regarding round-tripping, and the growing maturity of India’s capital market.
Reasons for Flipping:
- Flipping happens at the early stage of the startups, driven by commercial, taxation and personal preferences of founders and investors.
- Some companies decide to ‘flip’ because the major market of their product is offshore.
- Sometimes, investor preferences like access to incubators drive the companies to ‘flip’ as they insist on a particular domicile.
- For easy access to capital from private equity and venture capital, changes in rules regarding round-tripping, and the growing maturity of India’s capital market.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to foreign-owned e-commerce firms operating in India, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2022)
- They can sell their own goods in addition to offering their platforms as market-places.
- The degree to which they can own big sellers on their platforms is limited.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements
Other things remaining unchanged, market demand for a good might increase if
- Price of its substitute increases
- Price of its complement increases
- The good is an inferior good and income of the consumers increases
- Its price falls
Which of the above statements are correct? (2021)
- 1 and 4 only
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
In News: The National Stock Exchange (NSE) placed Adani Enterprises, Adani Ports, and Ambuja Cements under the additional surveillance mechanism (ASM) in the wake of accusations of stock manipulation and fraud levelled against the group by New York-based short seller Hindenburg Research.
Additional surveillance mechanism (ASM):
- The ASM was introduced in 2018 with the intention to protect investors from market volatility and unusual changes in share price.
- It is placed on securities with surveillance concerns based on objective parameters viz. Price / Volume variation, Volatility etc. in addition to other surveillance measures.
- The shortlisting of securities for placing in ASM is based on criteria that are jointly decided by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and exchanges, covering the parameters of “high low variation, client concentration, PE, close to close price variation, market capitalisation, volume variation, delivery percentage, and number of unique PANs”.
- An ASM shortlisting signals to investors that the stocks have seen unusual activity.
- The shortlisting of securities under ASM is purely on account of market surveillance and it should not be construed as an adverse action against the concerned company / entity.
National Stock Exchange (NSE)
- NSE was incorporated in 1992.
- It was recognised as a stock exchange by SEBI in 1993 and commenced operations in 1994
- NSE was the first exchange in India to implement electronic or screen-based trading
- NSE is counted as one of the world’s largest exchanges and a catalyst for driving India’s economic growth.
- The products on the Exchange are organized into 3 asset classes for trading: Capital market for the listing and trading of equities, fixed income securities and the derivatives market.
Source: Indian express
Previous Year Question
Q1) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Retail investors through demat account can invest in ‘Treasury Bills’ and ‘Government of India Debt Bonds’ in primary market.
- The ‘Negotiated Dealing System-Order Matching’ is a government securities trading platform of the Reserve Bank of India.
- The ‘Central Depository Services Ltd.’ is jointly promoted by the Reserve Bank of India and the Bombay Stock Exchange.
Which of the statements given below is/are correct?
- 1 Only
- 1 and 2 Only
- 3 Only
- 2 and 3 Only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
In News: The Kashmir Valley has bucked the trend of Asiatic black bear attacks on humans rarely reported throughout the animal’s global range.
Asiatic Black Bear

- Scientific name – Ursus thibetanus
- It is also called Himalayan bear, Tibetan bear, or moon bear
- It has a glossy black (sometimes brownish) coat with a whitish mark shaped like a crescent moon on the chest.
- Its long, coarse neck and shoulder hair forms a modified mane.
- It is omnivorous, eating insects, fruit, nuts, bees and honey, small mammals, and birds as well as carrion.
- It occasionally attacks domestic animals.
- They are generally nocturnal, sleeping in caves or tree hollows during the day
- During the summer the Asiatic black bear lives mainly in forested hills and mountains at elevations up to 3,600 metres (11,800 feet).
- Becoming fat by fall, it spends the winter at elevations of 1,500 metres (5,000 feet) or less and may sleep for much of the time.
- An adult male weighs 100–200 kg (220–440 pounds), a female about half as much; its length averages about 130–190 cm (51–75 inches), in addition to a 7–10-cm (3–4-inch) tail.
- Asiatic black bears may live as long as 25 years in the wild and up to 39 years in captivity.
- IUCN status – Vulnerable
- All Indian Bear species are listed under Appendix I in CITES and Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- This provides complete protection to the species from hunting and trade.
Distribution
- Afghanistan; Bangladesh; Bhutan; Cambodia; China; India; Iran, Islamic Republic of; Japan; Korea, Democratic People’s Republic of; Korea, Republic of; Lao People’s Democratic Republic; Myanmar; Nepal; Pakistan; Russian Federation; Taiwan, Province of China; Thailand; Viet Nam
Reproduction
- Males and females become sexually mature between ages three and four.
- Mating occurs between June and October, and pregnancies typically produce two cubs some seven to eight months later.
Sources: The hindu
Previous Year Question
Q1) consider the following statements: (2019)
- Asiatic lion is naturally found in India only.
- Double-humped camel is naturally found in India only.
- One-horned rhinoceros is naturally found in India only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
In News: In the Union Budget 2023-24, Deep Ocean Mission has been allocated Rs 600 crore
Deep Ocean Mission:
- It aims to explore marine biodiversity for the sustainable use of resources
- It is overseen by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)
- It includes myriad of activities such as a manned submersible, ship-building, exploration and conservation of deep-sea biodiversity and identification of mineral deposits in the deep ocean
- A manned submersible will be developed to carry three people to a depth of 6,000 metres in the ocean
- In 2016, India was awarded a 15-year contract to explore an area of 75,000 square kilometres for mining polymetallic nodules from the Central Indian Ocean Basin at depths of 5,000-6,000 metres.
- The other components of the mission include developing ocean climate change advisory services and designing offshore Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) powered desalination plants.
Significance
- Oceans are storehouses of food, energy, minerals, and medicines.
- It also modulates weather and climate.
- Deep-sea mining involves extracting ores rich in cobalt, manganese, zinc and other rare metals from the sea floor.
- They contain critical minerals needed to build batteries for electric vehicles and renewable energy capacity, smartphones and laptops.
Source: DTE
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Qaumi Waqf Board Taraqqiati Scheme (QWBTS)
- Implemented by The Ministry of Minority Affairs through the Central Waqf Council (CWC)
- Under this scheme, a dedicated online portal has been developed.
- This dedicated online portal is the Waqf Assets Management System of India (WAMSI) for computerization, digitization of records of Waqf properties and Geographic Information System (GIS) mapping of Waqf properties to prevent encroachment.
- The Waqf property details on WAMSI have been entered by the respective State Waqf Boards (SWBs).
- As per Section 40 of the Waqf Act 1995 (as amended in 2013) the State Waqf Board is empowered to decide any question which arises as to whether a particular property is a Waqf property or not or whether a Waqf is a Sunni Waqf or a Shia Waqf.
- The decision of the Board on a question, unless revoked or modified by the Tribunal, be final.
Central Waqf Council (CWC)
Vision
- Protection, Retrieval & E-monitoring of Auqaf under the provision of The Waqf Act
- Proactive role in protection development of Auqaf & to work closely with the State Waqf Boards to improve their functioning.
About
- It is a statutory body under the Ministry of Minority Affairs.
- It was set up in 1964 as per the provision given in the Waqf Act, 1954 as Advisory Body to the Central Government on matters concerning the working of the Waqf Boards and the due administration of Auqaf.
- The Council has been empowered to advise the Central Government, State Governments and State Waqf Boards.
- It will now issue directives to the boards/ State Government to furnish information to the Council on the performance of the board particularly on their financial performance, survey, revenue records, encroachment of Waqf properties, Annual and Audit report etc
- The 12th Council was constituted in 2019
Composition
- The Council consists of Chairperson – Union Minister In charge of Waqf
- Such other members, not exceeding 20 in number, as may be appointed by the Government of India.
- Presently Union Minister of Minority Affairs is the ex-officio Chairperson of the Central Waqf Council.
Major functions
- To monitor the implementation of the provisions of Waqf (Amendment) Act, 2013 in States and UTs.
- To render legal advice on protection and retrieval of the Waqf Properties and for removal of encroachment etc.
- To implement the Scheme for Development of Urban Waqf Properties & Identification of potential Waqf land for development by National Waqf Development Corporation Ltd.
- To undertake awareness programmes to promote the interest of the Council and to sensitize the Waqf institutions about their new roles and responsibilities.
Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 International Relations
Context:

- The talks between India’s National Security Advisor Ajit Doval and his American counterpart Jake Sullivan have concluded with the announcement of a new road map for deeper military and techno-economic cooperation between the two countries.
- The bilateral Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET) could lend a new strategic depth and breadth to the expanding engagement between India and the United States.
- The idea was first mooted in the meeting between Prime Minister Narendra Modi and President Joe Biden on the margins of the Tokyo summit of the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad) in 2022
Bilateral relations
- The U.S.-India strategic partnership is founded on shared values including a commitment to democracy and upholding the rules-based international system.
- The United States and India have shared interests in promoting global security, stability, and economic prosperity through trade, investment, and connectivity.
- India and the United States cooperate closely at multilateral organizations, including the United Nations, G-20, Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) Regional Forum, International Monetary Fund, World Bank, and World Trade Organization.
- India is an ASEAN dialogue partner, an Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development partner, and an observer to the Organization of American States.
- Together with Australia and Japan, the United States and India convene as the Quad to promote a free and open Indo-Pacific and provide tangible benefits to the region.
- India is also one of twelve countries partnering with the United States on the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) to make our economies more connected, resilient, clean, and fair.
- India is a member of the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), at which the United States is a dialogue partner.
Political relations
- President Biden and Prime Minister Modi have participated in multiple engagements of the Quad Leaders mechanism with Japan and Australia
- The 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue between the U.S. Secretaries of State and Defense and their Indian counterparts is the premier recurring dialogue mechanism between the United States and India.
- The United States hosted the fourth 2+2 Dialogue in 2022.
- The United States welcomed India joining the UN Security Council in 2021 for a two-year term and supports a reformed UN Security Council that includes India as a permanent member.
- Various working groups – Civil Space Working Group, the Education and Skills Development Working Group, Trade Policy Forum, Defense Policy Group, and Counternarcotics Working Group.
Economic relations
- In 2021, overall U.S.-India bilateral trade in goods and services reached a record $157 billion.
- The United States is India’s largest trading partner and most important export market.
- Indian companies seek to increase their presence in U.S. markets and at the end of 2020, Indian investment in the United States totaled $12.7 billion, supporting over 70,000 American jobs.
- USA accounts for 16 percent in the exports of goods exports and 50 percent of IT and BPO services.
- Major items of exports to USA are apparels, diamonds, marine products and footwear – These industries are labour intensive and hence will pave the way for more employment opportunities in the sectors
Environment
- India and USA launched the “Climate Action and Finance Mobilization Dialogue (CAFMD)”.
- Under the Climate and Clean Energy Agenda 2030 partnership
- It was launched at the Leaders’ Summit on Climate in 2021
- In 2021, the United States joined the International Solar Alliance headquartered in India
- In 2022 the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) Administrator Samantha Power became Co-chair of the Governing Council of the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) where India is a permanent co-chair.
- In 2021, The India-USA Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (SCEP) was launched in accordance with the US – India Climate and Clean Energy Agenda 2030 Partnership announced by both countries at the Leaders’ Summit on Climate
Technological
- The Indo-US Science and Technology Forum (IUSSTF) – is a bi-national autonomous organization established to promote cooperation in Science, Technology and Innovation has continued to play an important role in strengthening cooperation in this field.
- The iCET involves collaboration in a range of areas including quantum computing, semiconductors, 5G and 6G wireless infrastructure, and civilian space projects such as lunar exploration.
- It will be monitored and driven from the PMO in Delhi and the White House in Washington
- GE Aerospace has applied for an export licence for jet engine production and phased transfer of technology to Indian entities.
- ISRO and NASA are working together to realize a joint microwave remote sensing satellite for Earth observation, named NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR).
Defence and Security
- The Defense Policy Group (DPG) provides a platform for a comprehensive review of defense dialogues/mechanisms.
- The last DPG was held in 2021.
- The defense procurement activities are monitored through the Defense Production and Procurement Group (DPPG)
- In August 2022, a U.S. Navy Ship (USNS) Charles Drew visited in Chennai for repairs and allied services. This was the first ever repair of a U.S. Navy ship in India.
- US designating India as “Major Defence Partner,” a status unique to India, India is now at par with its closest allies.
- There is a new panorama for elevated Indo-US cooperation, like signing of Defence Technologies and Trade Initiative (DTTI), BECA, COMCASA, LEMOA etc
- The signing of Communication Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA) – paved the way for supply of equipment with transfer of technology.
- The decision to start exchanges between US Naval Forces Central Command (NAVCENT) and Indian navy was another milestone for strengthening maritime cooperation in the Western Indian Ocean.
- Bilateral exercises include: Yudh Abhyas (Army); Vajra Prahar (Special Forces), a tri-services exercise– Tiger Triumph (inaugurated in 2019).
- India joined the multilateral Combined Maritime Force (CMF) based in Bahrain, as an Associate Partner in 2022.
- S. participated in India’s multilateral Exercise Milan 2022.
Indian Diaspora
- The 3.5-million-plus strong Indian American community is an important ethnic group in the U.S., accounting for about 1% of the total population in the country
- Almost 21% of total international students in the U.S. are Indians. In 2022 close to 82000 student visas were issued in India, mostly for graduate (Masters) programs
- The nearly 200,000 Indian students in the United States contribute $7.7 billion annually to the U.S. economy.
- With two Indian Americans occupying high level posts of Governor and several representatives of the people, the Indian Diaspora has assimilated into their adopted country and is acting as a catalyst to forge closer and stronger ties between India and the U.S.
- An MOU has been signed in June 2016 to facilitate India’s joining of the Global Entry Programme for expedited immigration for eligible Indian citizens at U.S. airport
Suggestion for future
- Enhance cooperation in emerging technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) as data regulation, information sharing, and privacy protection become increasingly salient issues crucial to the preservation of national security.
- Strengthen coordination multilaterally and on international issues, including prioritising two multilateral strategic dialogues that have gained prominence in recent years—i.e., the Quad and the West Asian Quad or I2U2.
- Pursue greater cooperation on counterterrorism, including coordinating strategies for managing a Taliban-led Afghanistan and leading multilateral efforts to apply pressure on the Pakistani military-intelligence complex to abandon support for terrorist groups such as the Taliban and Haqqani Network, and Kashmir-focused groups like Jaish-e-Mohammed and Lashkar-e-Taiba.
- Strengthen and integrate Global Value Chains(GVCs), using FDI in each other’s economies to strengthen bilateral trade and integrate GVCs as well as incentivise multinational corporations to participate in these initiatives.
- Seek greater coordination between line ministries working on cybersecurity, especially identifying relevant counterparts on specific issues.
- Embed security and defence issues into their emerging technology agenda, focusing for instance on identifying common principles for defence applications of artificial intelligence.
Way forward
- In recent years, exigencies such as the COVID-19 pandemic have redirected the relationship to a forward-looking assessment of regional and global geopolitics
- The sectors that will be key to shaping the arc of a strong Indo-US relationship in the years ahead are the following: emerging technologies; national security and defence cooperation; counterterrorism; and trade.
Source: Indian express
Practice MCQs
Q.1) consider the following statements:
- Asiatic black bear is naturally found in India only.
- Asiatic black bear lives up to 25 years of age.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to ‘Additional surveillance mechanism (ASM)’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It aims to protect investors from market volatility
- It is jointly decided by Reserve Bank of India and Exchanges.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following pairs:
Indigenous cattle breed and state
- Kasargod Dwarf – Tamil Nadu
- Vechur Cattle – Kerala
- Ongole Cattle – Telangana
- Malnad Gidda – Maharashtra
How many pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- One pair only
- Two pairs only
- Three pairs only
- All four pairs
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 3rd February 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 2nd February – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – b











