IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Recently, India scored 74.4 on the World Bank index on the life cycle of working women.
About the World Bank index on the life cycle of working women:
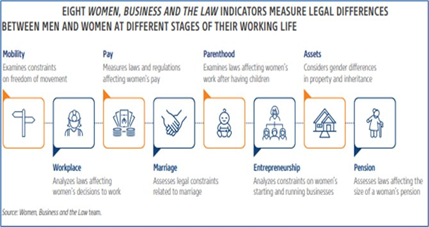
- The Index is an annual study conducted by the World Bank that measures the laws and regulations affecting women’s economic opportunities across 190 economies.
- The Index considers eight indicators measuring women’s interactions with the Law during their business. These are:
- Mobility
- Workplace
- Pay
- Marriage
- Parenthood
- Entrepreneurship
- Assets
- Pension.
- The index is divided into three categories:
- Starting a job,
- During employment, and
- After employment.
- Each category includes a set of indicators that measure the specific challenges and opportunities faced by women at different stages of their careers.
- Objective : The purpose of the index is to provide policymakers and stakeholders with data and insights that can be used to inform policies and programs aimed at improving women’s economic opportunities and outcomes.
India’s performance:
- India has scored 4 out of 100 in the World Bank Index on the life cycle of working women, which measures factors like laws, regulations, and practices affecting women’s economic participation.
- This score places India at 140th out of 190 countries surveyed in the index.
- India’s score on the index that assesses the life cycle of the working woman dropped to 74.4.
- In the 2023 index only 14 (Belgium, Canada, Denmark, etc) economies scored a perfect 100.
- The primary reason for this was that the laws concerning wages and pensions were not providing equality among men and women.
- India’s score was above the regional average for South Asia (63.7) but lower than that of Nepal (80.6), which was the highest in the region.
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which one of the following issues the ‘Global Economic Prospects’ report periodically? (2015)
- The Asian Development Bank
- The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development
- The US Federal Reserve Bank
- The World Bank
Q.2) India’s ranking in the ‘Ease of Doing Business Index’ is sometimes seen in the news. Which of the following has declared that ranking? (2016)
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
- World Economic Forum
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity (Government Schemes ), Economy
Context: Recently, the government announced its plans to rope in more industry partners to increase the pace of training under its flagship SAMARTH scheme for skill development in the textile sector.
About the SAMARTH scheme :
- Samarth is a demand-driven and placement-oriented umbrella skilling programme of the Ministry of Textiles.
- The implementation period of the scheme: is up to March 2024.
- The training programme and course curriculum have been rationalized keeping in view the technological and market demand of the domestic and international economies.
- In addition to the entry-level skilling, a special provision for upskilling/ re-skilling programme has also been operationalized under the scheme towards improving the productivity of the existing workers in the Apparel & Garmenting segments.
- Samarth also caters to the upskilling/ re-skilling requirement of the traditional textile sector such as handloom, handicraft, silk and jute.
Objectives :
- to incentivize and supplement the efforts of the industry in creating jobs in the organized textile and related sectors, covering the entire value chain of textiles, excluding Spinning and Weaving.
Implementation :
- The Samarth scheme is implemented through Implementing Partners (IPs) comprising of Textile Industry/ Industry Associations, State government agencies and Sectoral Organizations of the Ministry of Textiles like DC/ Handloom, DC/Handicrafts and Central Silk Board.
Advanced features :
- Aadhaar Enabled Biometric Attendance System (AEBAS), Training of Trainers (ToT), CCTV recording of the training programme, a dedicated call centre with helpline number, mobile app, Web-based Management Information System (MIS), on-line monitoring of the training process etc.
- The State, District, and Training Centre-wise information/ data in the dashboard is available in the public domain.
Source: THE ECONOMIC TIMES
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements : (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things, will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) ‘Recognition of Prior Learning Scheme’ is sometimes mentioned in the news with reference to (2017)
- Certifying the skills acquired by construction workers through traditional channels.
- Enrolling the persons in Universities for distance learning programmes.
- Reserving some skilled jobs to rural and urban poor in some public sector undertakings.
- Certifying the skills acquired by trainees under the National Skill Development Programme.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography, Environment, and Ecology
Context: Recently, Yellowstone celebrated its 151st anniversary.
About Yellowstone national park :
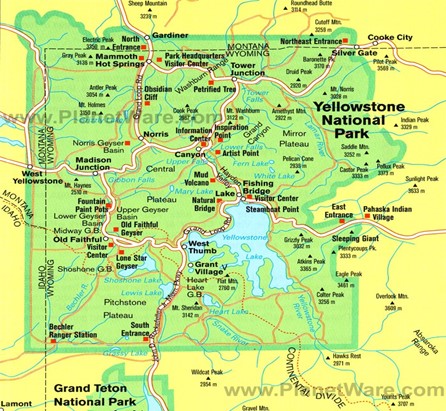
- Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States.
Salient features :
- Yellowstone National Park was the first national park in the US and is also widely held to be the first national park in the world.
- The park is known for its wildlife and its many geothermal features, especially the Old Faithful geyser, one of its most popular.
- The subalpine forest is the most abundant.
- It is part of the South-Central Rockies forests ecoregion.
- The rivers of the Snake-Columbia basin, Green-Colorado basin, and Missouri River Basin all begin as snow on the Continental Divide as it weaves across Yellowstone’s peaks and plateaus.
- Yellowstone Lake is one of the largest high-elevation lakes in North America and is centered over the Yellowstone Caldera, the largest supervolcanic on the continent.
- Caldera :
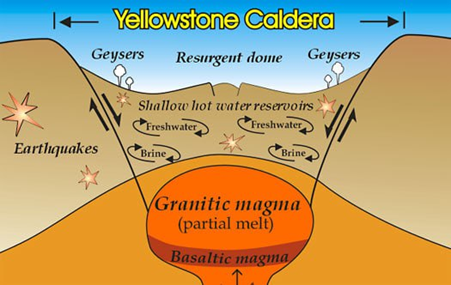
- A large bowl-shaped volcanic depressionis more than one kilometre in diameter and rimmed by in facing scarps.
- It is usually formed by the collapse of the top of a volcanic cone or group of cones because of the removal of the support formerly furnished by an underlying body of magma (molten rock).
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: ( 2020)
River Flows into
- Mekong – Andaman Sea
- Thames – Irish Sea
- Volga – Caspian Sea
- Zambezi – Indian Ocean
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1,2 and 4 only
Q.2) Consider the following pairs: (2019)
Sea Bordering country
- Adriatic Sea : Albania
- Black Sea: Croatia
- Caspian Sea: Kazakhstan
- Mediterranean : Sea Morocco
- Red Sea: Syria
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
- 1, 2, and 4 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
- 2 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims – Defence
Context: INS Trikand will be participating in the International Maritime Exercise/ Cutlass Express 2023 (IMX/CE-23) which will be held in the Gulf region.
About International Maritime Exercise/ Cutlass Express 2023 (IMX/CE-23):
- IMX/CE-23 is one of the largest multinational maritime exercises in the world.
- This is Indian Navy’s maiden IMX participation.
- The International Maritime Exercise is coordinated by the US-led Combined Maritime Forces (CMF).
- Combined Maritime Forces (CMF) – a 34-nation naval group that seeks to promote security, stability, and prosperity.
- India became an associate member of CMF in 2022.
- It marks the second occasion where an Indian Naval ship is participating in an exercise conducted by the CMF.
- Earlier, INS Trikand had participated in the CMF-led Operation Sea Sword 2 in 2022.
About INS Trikand:

- ‘INS Trikand’ is a Stealth Frigate.
- It was commissioned into the Indian Navy in 2013.
- It is the last of the three “Follow On Talwar Class” frigates built in the Russian Federation.
- The other ships of the class: INS Teg and INS Tarkash
- INS Trikand carries a state-of-the-art combat suite which includes the supersonic BRAHMOS missile system, advanced Surface to Air missiles Shtil, upgraded A190 medium range gun, Electro-optical 30 mm Close-in Weapon System, Anti-Submarine weapons such as torpedoes and rockets and an advanced Electronic Warfare system.
- The weapons and sensors are integrated through a Combat Management System ‘Trebovanie-M’, which enables the ship to simultaneously neutralize multiple surfaces, sub-surface and air threats.
- The ship also incorporates innovative features to reduce radar, magnetic, and acoustic signatures, which have earned this class of ships the sobriquet of ‘Stealth’ frigates.
- The ship is powered by four gas turbines and is capable of speeds in excess of 30 knots.
- The ship can carry an integrated Kamov 31 helicopter which is best suited for airborne early warning roles.
Source: PIB
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following in respect of the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS): (2017)
- Inaugural IONS was held in India in 2015 under the chairmanship of the Indian Navy.
- IONS is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime cooperation among navies of the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements : (2018)
- IRNSS has three satellites in geostationary and four satellites in geosynchronous orbits.
- IRNSS covers entire India and about 5500 sq. km beyond its borders.
- India will have its own satellite navigation system with full global coverage by the middle of 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Agencies and reports , Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, the International Energy Agency (IEA) released its annual Methane Global Tracker report.
About Methane Global Tracker report:
- It is an annual report published by the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Background :
- Methane is a greenhouse gas responsible for 30% of warming since preindustrial times, second only to carbon dioxide.
- Methane is 80 times more potent at warming than carbon dioxide.
Key Findings of the report :
- The report shows that 75% of methane emissions can be reduced with cheap and readily available technology.
- Global Methane Pledge – 150 countries have joined the Global Methane Pledge which aims to reduce methane emissions from human activity by 30% from 2020 levels by 2030.
- India has committed to reducing the emissions intensity of its GDP by 33-35% below 2005 levels by 2030.
- The energy sector accounts for around 40% of total average methane emissions.
- 80% of available options to curb methane emissions can be implemented at net zero cost.
- Implementing methane reduction measures would cost less than 3% of the net income received by the oil and gas industry in 2022.
- Reduction of 75% of natural gas wastage could lower global temperature rise by nearly 0.1 degree Celsius by mid-century.
About the International Energy Agency (IEA) :
- It is an intergovernmental organization established in 1974.
- Headquarters: Paris
- The IEA is made up of 31 member countries.
- Objective: to promote reliable, affordable, and clean energy for its member countries and the rest of the world.
- The Agreement on an International Energy Program (IEP Agreement) established the mandates and structure of the IEA under the umbrella of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
Eligibility Criteria for membership:
- A candidate country to the IEA must have crude oil and/or product reserves (Strategic Oil Reserves) equivalent to 90 days of the previous year’s net imports, to which the government has immediate access (even if it does not own them directly) and could be used to address disruptions to global oil supply.
- India became an Associate member of IEA in 2017.
- India inked a Strategic Partnership Agreement with the IEA to strengthen cooperation in global energy security, stability, and sustainability in 2021.
- India’s current strategic oil reserves equal 9.5 days of its requirement.
- India is not a member of the OECD but a key economic partner.
- IEA invited India to deepen its cooperation with IEA by becoming a full Member.
Key publications of IEA :
- World Energy Outlook (WEO)
- Net Zero by 2050: a roadmap for the global energy sector
- Energy Technology Perspectives (ETP)
- Global EV Outlook (GEVO)
- Oil Market Report
- World Energy Investment
- Clean Energy Transitions Programme
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Climate Group is an international non-profit organisation that drives climate action by building large networks and runs them.
- The International Energy Agency in partnership with the Climate Group launched a global initiative “EP100”.
- EP100 brings together leading companies committed to driving innovation in energy efficiency and increasing competitiveness while delivering on emission reduction goals.
- Some Indian companies are members of EP100.
- The International Energy Agency is the Secretariat to the “Under2 Coalition”.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1,2, 4 and 5
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 2,3 and 5 only
- 1,2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) The term ‘West Taxes Intermediate’, sometimes found in news to a grade of (2020)
- Crude oil
- Bullion
- Rare earth elements
- Uranium
Q3. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
- Argentina Mexico, South Africa and Turkey.
- Australia Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
- Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
- Indonesia Japan Singapore and South Korea
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity
Context: Recently, the National Commission for Minorities rescued stranded Indians from Libya.
About the National Commission for minorities :
- It was established by the Union Government in 1992 under the National Commission for Minorities Act.
- Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists, Zoroastrians (Parsis), and Jains are six religious communities that have been designated as minority communities by the Union Government in India’s Gazette.
- Sikhs, Buddhists, Parsis, Christians, and Muslims were notified in 1993
- Jains were added later in 2014.
- According to the 2001 Census, these six communist countries account for 18.8% of the country’s population.
Composition:
- NCM consists of a Chairperson, a Vice-Chairperson, and five members.
- All the members shall be from amongst the minority communities.
- A total of 7 persons to be nominated by the Central Government should be from amongst persons of eminence, ability, and integrity.
- Tenure: Each Member holds office for a period of three years from the date of assumption of office.
- The Chairperson or a member can resign from office by writing to the Central Government.
Removal of Office of Chairperson
- The Central Government shall remove a person from the office of Chairperson or the member if they:
- Become an undischarged insolvent.
- Are declared having an unsound mind by a competent court.
- He refused to act or become incapable of acting.
- Have been convicted and sentenced to imprisonment for an offense which in the opinion of the Central Government involves moral turpitude.
- Absent from three consecutive meetings without obtaining leave of absence.
- Abused the position of chairperson or member in the opinion of the Central Government.
- Detrimental to the interest of minorities or public interest.
- However, No person shall be removed under this clause until the person has been given a reasonable opportunity of being heard in the matter.
Functions:
- Recommending Union and State Government regarding Implementation of Safeguards for the minorities.
- Address the complaints regarding the deprivation of rights of minorities and take up such matters with the rightful authorities.
- The commission shall perform any of the functions mentioned above and have all powers of civil court.
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which of the following are associated with ‘Planning’ in India? (2014)
- The Finance Commission
- The National Development Council
- The Union Ministry of Rural Development
- The Union Ministry of Urban Development
- The Parliament
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1, 2, and 5 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
- 2 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) Which of the following bodies does not/do not find mention in the Constitution? (2013)
- National Development Council
- Planning Commission
- Zonal Councils
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Recently, former RBI Governor ,Raghuram Rajan claimed that India is ‘dangerously close’ to the Hindu rate of growth.
About Hindu growth rate :
- Hindu rate of growth is a term describing low Indian economic growth rates from the 1950s to the 1980s, which averaged around 4%.
- The term ‘Hindu rate of growth’ was coined by Professor Rajkrishna, an Indian economist, in 1978 to characterize the slow growth and to explain it against the backdrop of socialistic economic policies.
- The term came into being to show India’s contentment with the low growth rate, post-independence.
- The word “Hindu” in the term was used by some early economists to imply that the Hindu outlook of fatalism and contentedness was responsible for the slow growth.
- Many economists believed that the so-called Hindu rate of growth was a result of socialist policies implemented by the then-staunch secular governments and had nothing to do with Hinduism.
- A small growth rate alone does not characterize the Hindu rate of growth.
- A prolonged low growth rate, albeit not an economic contraction, is not sufficient to be deemed as the Hindu rate of growth.
- In addition to growth being low and extending over a long period of time, the term also captures a low per-capita GDP, by factoring in the population growth.
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), consider the following statements: (2022)
- They enable the digital representation of physical assets.
- They are unique cryptographic tokens that exist on a blockchain.
- They can be traded or exchanged at equivalency and therefore can be used as a medium transaction. of commercial
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- c) 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) The money multiplier in an economy increases with which one of the following? (2021)
- Increase in the Cash Reserve Ratio in the banks.
- Increase in the Statutory Liquidity Ratio in the banks
- Increase in the banking habit of the people
- Increase in the population of the country
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Rupee gained 8 paise to close at 82.50 against the U.S. dollar recently.
About depreciation :
- Currency depreciation is a fall in the value of a currency in a floating exchange rate system.
- Rupee depreciation means that the rupee has become less valuable with respect to the dollar.
- It also means that the rupee is now weaker than what it used to be earlier.
Factors affecting depreciation :
- Wear and Tear due to Use or Passage of Time:
- It is the deterioration that is followed by a decrease in the value of an asset, resulting from its use in business operations to earn revenue.
- Some orders of means lose their value after the agreement directing their use in business comes to an end after the expiry of the predetermined period.
- Obsolescence
- It is another factor driving the depreciation of fixed assets.
- It means being “out-of-date”.
- An actual asset that is becoming outdated on account of the availability of a better type of asset is referred to as obsolescence.
- Abnormal factors that are responsible for the drop in the use of the asset like accidents due to the earthquake, fire, cataracts, etc., Accidental loss is endless but not continuing.
About appreciation :
- It is an increase in the value of one currency in relation to another currency in a floating exchange rate system.
- Currencies appreciate against each other for a variety of reasons, including government policy, interest rates, trade balances and business cycles.
- Currency appreciation discourages a country’s export activity as its products and services become costlier to buy.
Factors affecting appreciation :
- Appreciation is directly linked to demand.
- If the value of the currency appreciates (or goes up), demand for the currency also rises.
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2021)
The effect of the devaluation of a currency is that it necessarily
- Improves the competitiveness of the domestic exports in the foreign markets
- Increase the foreign value of the domestic currency
- Improves the trade balance
Which of the above statements is/are
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
Q.2) Which one of the following is not the most likely measure the Government/RBI takes to stop the slide of the Indian rupee? (2019)
- Curbing imports of non-essential goods and promoting exports
- Encouraging Indian borrowers to issue rupee-denominated Masala Bonds
- Easing conditions relating to external commercial borrowing
- Following an expansionary monetary policy
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently the Government of India and World Bank signed two complimentary loans worth $1 billion to support and enhance India’s healthcare infrastructure.
About India’s healthcare sector at glance:
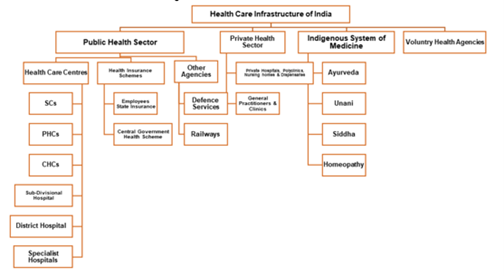
- In the Economic Survey of 2022, India’s public expenditure on healthcare stood at 1% of GDP in 2021-22 against 1.8% in 2020-21 and 1.3% in 2019-20.
- India had 7 physicians per 1,00,000 people in 2017 (in contrast to 98 in Pakistan, 100 in Sri Lanka and 241 in Japan).
- 53 beds per 1,00,000 people(in contrast to 63 in Pakistan, 79.5 in Bangladesh, 415 in Sri Lanka and 1,298 in Japan).
- 7 nurses and midwives per 1,00,000 people(in contrast to 220 in Sri Lanka, 40 in Bangladesh, 70 in Pakistan, and 1,220 in Japan).
- India has among the highest out-of-pocket (OOP) expenditures of all countries in the world- 62% of the total health expenditure in India is OOP.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), India ranks 184 out of 191 countries in health spending.
- The US spends over 16% of its total GDP on healthcare, while Japan, Canada, Germany etc. spend over 10% of their GDP on healthcare.
Health Index for states developed by Niti Aayog:
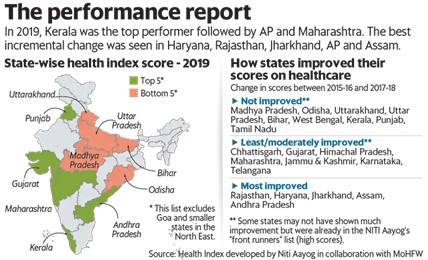
- The Health Index for States developed by Niti Aayog in consultation with the health ministry and the World Bank has rankings for large states, smaller states and Union territories.
- It is based on 23 health parameters ranging from mortality rate and sex ratio to functioning cardiac care units.
- In 2019, Kerala was the top performer followed by Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra.
- The index results indicated that states even with a lower economic output are performing better on health and well-being.
Challenges associated with India’s healthcare sector:
- Low Budget Spending: India’s public expenditure on healthcare is only 2.1% of GDP in 2021-22 while Japan, Canada and France spend about 10% of their GDP on public healthcare.
- Unequal distribution: India’s health care system is concentrated in urban areas with very little presence in the rural areas where majority of the population lives.
- Lack of Medical Research: In India, R&D and cutting-edge technology-led new projects receive little attention.
- Low doctor-patient ratio: The doctor patient ratio in India is about 1:1500 much higher than the WHO norm of one doctor for every 1,000 people.
- Lack of Affordability: The contribution of private sector in healthcare expenditure in India is around 80 percent while the rest 20 percent is contributed by Public Sector.
- The private sector also provides for 58 percent of the hospitals and 81 percent of the doctors in India.
Govt of India Initiatives to improve healthcare sector in the country:
- Pradhan Mantri-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM): it aims to strengthen India’s health infrastructure and improve the country’s primary, secondary and tertiary care services.
- Ayushman Bharat : Follows a two- pronged approach by Creation of health and wellness centres to bring health care closer to homes.
- formulation of a Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) to protect poor and vulnerable families against financial risk arising out of health episodes.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission: aims to connect the digital health solutions of hospitals across the country. Under this, every citizen will now get a digital health ID and their health record will be digitally protected.
- National Ayush Mission: it is a centrally sponsored scheme for the development of traditional medicines
- Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY):aims to correct regional imbalances in the availability of affordable/reliable tertiary healthcare services and also to augment facilities for quality medical education in the country.
Way Forward:
There is an urgency to focus on all the three levels of primary, secondary and tertiary healthcare, it is imperative that the government look towards improving primary health care as a public good.
The lesson emerging most unequivocally from the pandemic experience is that if India does not want a repeat of the immeasurable suffering and the social and economic loss, we need to make public health a central focus.
There is also a need to declutter policy dialogue and provide clarity to the nomenclatures. India needs to move beyond the doctor-led system and Para medicalise several functions. India should focus on technology upgradation and preventive care to further its march towards healthy India.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following:
- Aarogya Setu
- COWIN
- DigiLocker
- DIKSHA
Which of the above are built on top of open-source digital platforms? (2022)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) With reference to recent developments regarding ‘Recombinant vector Vaccines’, consider the following statements:
- Genetic engineering is applied in the development of these vaccines.
- Bacteria and viruses are used as vectors.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2021)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Geography) and GS 3 (Economy)
Context: India has taken several steps to boost the output, create a niche brand for Indian tea, and ensure the welfare of the families associated with the tea industry.
About Indian Tea Industry:
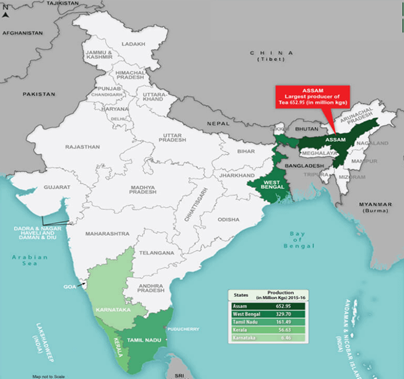
- India is the 2nd largest tea producer and largest black tea producer after China and 4th largest exporter of Tea in the world.
- India is also the largest consumer of black tea and accounts for 18% of the total World tea consumption.
- The main tea-growing regions are in the Northeast (including Assam) and in north Bengal (Darjeeling district and the Dooars region).
- Tea is also grown on a large scale in the Nilgiris in south India.
Ideal climate condition for tea cultivation:
- Originate in tropical and subtropical climates.
- Major tea growing regions are mainly concentrated in Asia, Africa, South America.
- Tea requires cool to warm temperatures with at least 5 hours of sunlight per day.
- The average annual temperature for tea plants to grow well is in the range of 15 – 23°C.
- The rainfall needed is between 150-200 cm.
Market Size of Tea Industry in India:
- In 2020, nearly 10 million tons of tea was consumed in the country.
- The market in the country is projected to witness a further growth in the forecast period of 2022-2027, growing at a CAGR of 4.2%.
- In 2026, the tea industry in India is expected to attain 1.40 million tons.
Tag for Geographical Indication (GI)
- The first GI tag product was Darjeeling Tea, also known as the “Champagne of teas” due to its floral aroma.
- Green and white tea, the other two Darjeeling tea varieties, also have GI tags.
- The Indian tea industry is being developed and promoted by the Tea Board of India.
About Tea Board of India:
- The genesis of the Tea Board India dates back to 1903 when the Indian Tea Cess Bill was passed.
- The present Tea Board was set up under Section 4 of the Tea Act 1953.
- It is functioning as a statutory body of the Central Government under the Ministry of Commerce.
- The Board is constituted of 31 members (including Chairman) drawn from Members of Parliament, tea producers, tea traders, tea brokers, consumers, and representatives of Governments from the principal tea producing states, and trade unions .
- HQ: Kolkata
- The Board is reconstituted every three years.
- Earlier, the Tea Board had offices in Cairo and Kuwait.
- But these two offices were relocated to Dubai.
Issues associated with the Indian Tea sector:
- Stiff competition and improved standards in the world market – due to low product prices from Kenya and other countries – increasing demand for organic tea and quality assurance that entails environmental justice.
- Decline in productivity and quality – Tea bushes must be replanted every five years, but most Tea bushes older than 20 yrs.; uneven rainfall due to climate change – is affecting the productivity and quality of Indian Tea leading to lower prices at Tea auctions.
- Poor worker conditions and low wages – despite the provisions of the Plantation Labor Act, 1951 most workers and their families live in unsanitary conditions and receive low wages – this issue needs to be addressed given the fact that “starvation deaths” in North Bengal caught the international media attention.
- Small Tea Growers – the challenges faced by the Small Tea Growers’ sector is as follows
- Not getting the right green leaf price
- Unlike large estates, STG’s are not able to capitalize on scale and marketing of product as a collective is difficult – since it is unorganized
- Issue of workers’ rights – since STG’s are not governed by the PLA, 1951
- Most of them are not recognized by the Tea Board of India due to landownership regulations and related procedural problems – this means lesser data available on the state of the STG’s making it difficult for policy coordination
- Some global factors like the decline in demand from European markets in the wake of the Russia-Ukraine war have compounded the problem.
Suggestive measures:
- The One District and One Product (ODOP) program can aid in promoting Indian Tea’s fame.
- The “AROMA” of tea needs to be improved in order for the industry to become profitable, viable, and sustainable.
- Support small farmers to raise production to satisfy domestic and international demand while improving quality and sustainability.
- Create infrastructure to boost exports and concentrate on high value markets like the EU, Canada, South America, and the Middle East to re-energize.
- Promote GI tea and organic tea using brand marketing and promotion.
- Modernization: To help local supply networks be strengthened and tea producers to become self-sufficient
- Adaptability: Focus on the importance of a risk proof ecosystem, that is, the need for sustainable solutions to make tea plantations meet the challenges of climate change.
India being the second largest producer of Tea has numerous opportunities to develop the Tea Industry as it is providing employment to a huge number of people in the north eastern states. A win-win for all and therefore a truly sustainable and transparent model — is the key requirement for a highly labour-centric industry like tea plantations.
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following States:
- Andhra Pradesh
- Kerala
- Himachal Pradesh
- Tripura
How many of the above are generally known as tea-producing States? (2022)
- Only one State
- Only two States
- Only three States
- All four States
Q.2) With reference to the “Tea Board” in India, consider the following statements:
- The Tea Board is a statutory body.
- It is a regulatory body attached to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- The Tea Board’s Head Office is situated in Bengaluru.
- The Board has overseas office at Dubai and Moscow.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1 and 4 only
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Which of the following organizations recently released Index on the life cycle of working women?
- World Bank
- Ministry of Women and Child Development
- Un Women
- NITI Aayog
Q.2) Consider the following statements regarding the International Energy Agency (IEA):
- It is an intergovernmental organization established in 1974.
- Presently the IEA is made up of 61 member countries.
- India became a member of IEA in 2017.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 only
- 1 and 3 only
Q.3) The Yellowstone national park often mentioned in the news is in
- Australia
- United States of America
- Japan
- Brazil
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’6th March 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 4th March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – c











