IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: The Greater Horn of Africa is likely to get heavy rains from October to December 2023, according to the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD) Climate Prediction and Applications Centre (ICPAC).
Key Highlights:
- ICPAC attributed the wetter-than-usual conditions across most parts of the Greater Horn of Africa to El Nino.
- El Nino: a natural phenomenon wherein the ocean temperatures rise especially in parts of the Pacific Ocean.( El Nino and La Nina)
- Southern Ethiopia, eastern Kenya, and southern Somalia are very likely to experience wetter-than-usual rainfall, according to the forecast.
- In contrast, drier-than-usual conditions have been forecast for the isolated areas of southwestern Uganda and southwestern South Sudan.
- Below-average rainfall has been forecast until the end of the season for Eritrea, central and northern Ethiopia, Djibouti, Western Kenya, significant areas of South Sudan and Sudan, and Northern Uganda.
- October to December, the vital rainfall season, especially in the equatorial parts of the Greater Horn of Africa, may contribute 20-70 percent of the annual total rainfall.
About the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD):-
- Establishment: 1996.
- HQ: Djibouti, Africa.
- The IGAD in Eastern Africa was created to supersede the Intergovernmental Authority on Drought and Development (IGADD).
- Mission: Promote regional cooperation and integration to add value to Member States’ efforts in achieving peace, security, and prosperity.
About ICPAC:-
- Historical Background:-
- The Drought Monitoring Center-Nairobi (DCMN) was adopted as a specialized IGAD institution in the 10th Summit of the Heads of State and Governments IGAD in 2003.
- It changed its name to IGAD Climate Prediction and Applications Centre (ICPAC).
- HQ: Nairobi, Kenya.
- It is a Climate Center accredited by the World Meteorological Organization.
- It provides Climate Services to 11 East African Countries.
About Horn of Africa:-
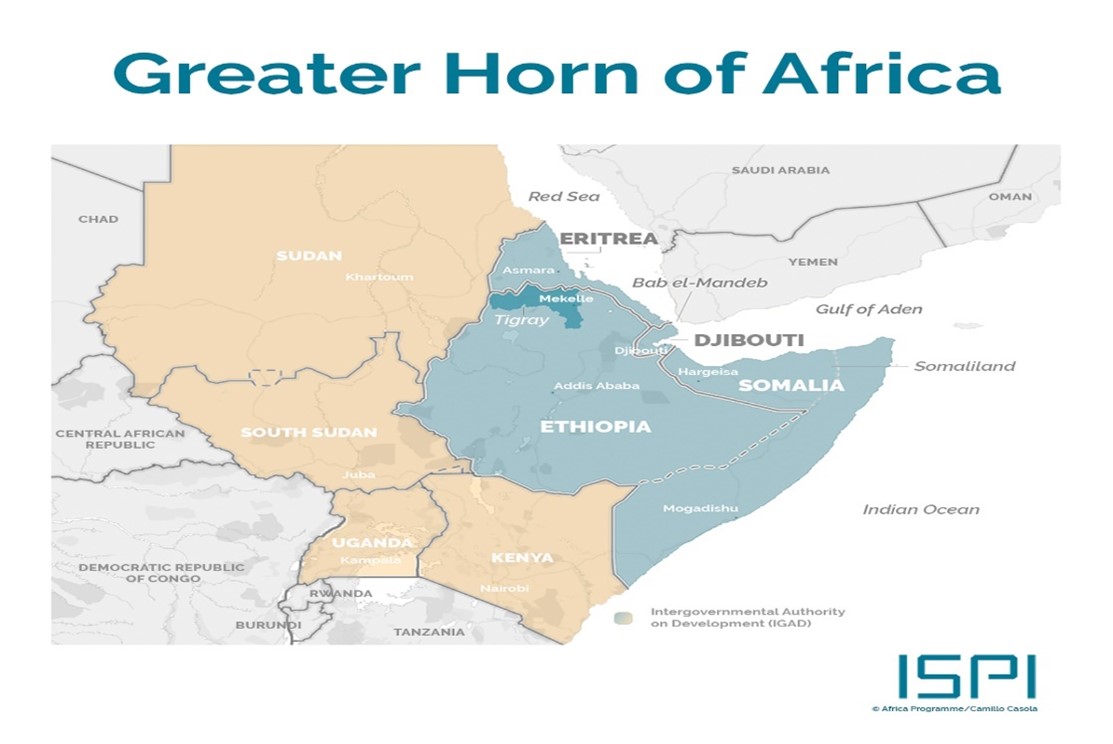
IMAGE SOURCE: is online
About Horn of Africa:-
- Countries: Somalia, Ethiopia, Eritrea and Djibouti.
- Location: northeast of the African
- It lies along the southern boundary of the Red Sea.
- It extends hundreds of kilometers into the Guardafui Channel, the Gulf of Aden, and the Indian Ocean.
- It is equidistant from the equator and the Tropic of Cancer.
- It extends out into the Arabian Sea for hundreds of kilometers.
- It is located along the south of the Gulf of Aden.
- The Horn of Africa is a UNESCO Biodiversity Hotspot and one of the two entirely arid ones.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: To qualify as a biodiversity hotspot, an area must meet two strict criteria:-
- Contain at least 1,500 species of vascular plants found nowhere else on Earth (known as “endemic” species).
- Have lost at least 70 percent of its primary native vegetation.
- The Greater Horn of Africa region includes Burundi, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda, Somalia, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda.
MUST READ: India-Africa: Challenges & Way Ahead
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the lakes of West Africa has become dry and turned into a desert? (2022)
- Lake Victoria
- Lake Faguibine
- Lake Oguta
- Lake Volta
Q.2) With reference to the ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting the Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct (2017)
- The IOD phenomenon is characterized by a difference in sea surface temperature between the tropical Western Indian Ocean and the tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, a rare black eagle was spotted at Chail Wildlife Sanctuary.
About Chail Wildlife Sanctuary:-
- Location: Solan & Shimla districts of Himachal Pradesh.
- Terrain: encompasses hills, valleys, forests, and grasslands.
- Flora: oak, pine, cedar, rhododendron, and grasslands.
- Fauna: pheasants, Himalayan bears, deer, langurs, and porcupines.
- Water Bodies: It comprises part of the catchment area of a tributary of the Giri River.
- Conservation programs: Established a pheasant breeding program in 1988. (Wildlife Protection)
- Chail Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected area.
- Protected areas: in which human presence or the exploitation of natural resources (e.g. firewood, non-timber forest products, water, etc.) is limited. (Eco-sensitive Zones (ESZ))
Black eagle:-
- Characteristics feature: This Eagle is dark black in color and has a striking yellow beak.
- Habitat: It soars over forests and is mostly found in hilly regions.
- Food: They mainly hunt for mammals and small birds, especially the ones in the nest.
- Family: Accipitridae.
- Genus: Ictinaetus.
- It is the only member of the genus.
- Distribution: tropical and subtropical South and Southeast Asia, as well as southeastern China.
- Distribution in India: Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir, forests of the Eastern and Western Ghats in peninsular India.
- Conservation status:-
- IUCN: Least concern
MUST READ: Rare migratory eagle
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding the Indian squirrels: (2023)
- They build nests by making burrows in the ground.
- They store their food materials like nuts and seeds in the ground.
- They are omnivorous.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Consider the following fauna: (2023)
- Lion-tailed Macaque
- Malabar Civet
- Sambar Deer
How many of the above are generally nocturnal or most active after sunset?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: The government’s flagship scheme for financial inclusion Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana recently completed nine years of implementation.
Background:-
- Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman has said that Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana-led interventions and digital transformation have revolutionized financial inclusion in the country in the last nine years
About Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY):-
- Launched: 28th August in 2014.
- Ministry: Ministry of Finance.
- Objectives: ensuring access to various financial services like availability of basic savings bank account, access to need based credit, remittances facility, insurance, and pension to the excluded sections i.e. weaker sections & and low-income groups.
Salient Features of PMJDY:-
- The PMJDY is a National Mission on Financial Inclusion.
- It encompasses an integrated approach to bring about comprehensive financial inclusion of all the households in the country.
- The plan envisages:-
- Universal access to banking facilities: with at least one basic banking account for every household
- Financial literacy: Promoting savings, use of ATMs, getting ready for credit, availing insurance and pensions, and using basic mobile phones for banking.
- Access to credit: Creation of Credit Guarantee Fund to provide banks some guarantee against defaults.
- Insurance: Accident cover and life cover.
- Accident cover: up to Rs. 1,00,000.
- Eligibility: People holding a RuPay Debit Card under PMJDY will be eligible for this insurance. (RuPay Debit Cards and BHIM UPI)
- Life cover: Rs. 30,000 on account opened between 15 Aug 2014 to 31 January 2015.
- Eligibility: It will only apply to people opening bank accounts for the first time under Jan Dhan Yojana with a debit card.
- The person should also be the head of the family or a major earning member.
- Pension facility: for the Unorganized sector.
- Overdraft Facility: Beneficiaries can avail of an overdraft facility for up to ₹10,000.
- However, this is only available against one account per household.
- This scheme also provides loans of up to ₹5,000 to beneficiaries after completing six months of account transactions.
Eligibility:-
- Citizenship: The applicant should be an Indian National.
- Age: aged between 18 and 59 years.
- If minors above ten years apply, they will require support from their legal guardians to administer their PMJDY account.
Benefits of PMJDY:-
- The plan envisages channeling all Government benefits (from Centre / State / Local Body) to the beneficiaries’ accounts.
- It pushes the Direct Benefits Transfer (DBT) scheme of the Union Government.
Challenges:-
- Technological issues like poor connectivity, and online transactions.
MUST READ: Digital Banks
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in relation to Janani Suraksha Yojana : (2023)
- It is a safe motherhood intervention of the State Health Departments.
- Its objective is to reduce maternal and neonatal mortality among poor pregnant women.
- It aims to promote institutional delivery among poor pregnant women.
- Its objective includes providing public health facilities to sick infants up to one year of age.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) With reference to the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Private and public hospitals must adopt it.
- As it aims to achieve universal health coverage, every citizen of India should be part of it ultimately.
- It has seamless portability across the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: The Kampala Declaration on climate change, and human mobility recently, got 48 African countries as members.
Background:-
- Representatives from 48 African countries gathered in Nairobi, Kenya, for the Conference of States on the continental expansion of the Kampala Ministerial Declaration on Migration, Environment, and Climate Change.
- The continental expansion of the KDMECC was discussed at a three-day Conference of States that began August 23, 2023.
- It was co-hosted by the Governments of Kenya and Uganda with support from the International Organization for Migration (IOM) and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
IOM:-
- Established: 1951.
- HQ: Geneva,
- It currently has 175 Member States.
- It is a United Nations agency that provides services and advice concerning migration to governments and migrants, including internally displaced persons, refugees, and migrant workers
- The International Organization for Migration (IOM) governing bodies are comprised of the Council, which is the highest authority, and the Standing Committee on Programmes and Finance, a sub-committee of the Council.
About Kampala Ministerial Declaration on Migration, Environment, and Climate Change (KDMECC):-
- Signed: 2022.
- Signed at Kampala, Uganda.
- Signed by: 15 African states.
- Objective: to address the nexus of human mobility and climate change in the continent.
- The Declaration is the first comprehensive, action-oriented framework led by Member States to address climate-induced mobility in a practical and effective manner.
- Need: Africa is one of the world’s most vulnerable continents to the impacts of climate change. ( Global Risks due to Climate Change)
- There were over 7.5 million new internal disaster displacements in 2022, according to a 2023 report by the Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre.
- If nothing is done, as many as 105 million people could become internal migrants within the African continent.
- Progress: An Expert Working Group (EWG) was formed in May 2023 to ensure that the signatory states of the KDMECC receive the necessary support they need to meet their commitments.
- The EWG comprises climate and migration experts and youth climate advocates from the signatory countries and regional bodies.
- Significance: It will ensure that all voices, including those of youth, women, and persons in vulnerable situations are the priority of the expanded declaration.
Signatory countries of the KDMECC:-
- The Republic of Burundi
- The Republic of Djibouti
- The Democratic Republic of Congo
- The Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia
- The Republic of Kenya
- The Republic of Rwanda
- The Federal Republic of Somalia
- The Republic of South Sudan
- The Republic of the Sudan
- United Republic of Tanzania
- The Republic of Uganda
- The Arab Republic of Egypt
- People’s Democratic Republic of Algeria
- The Republic of Senegal
- The Republic of Zambia
MUST READ: Mitigating Climate Change
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to coal-based thermal power plants in India, consider the following statements: (2023)
- None of them uses seawater.
- None of them is set up in a water-stressed district.
- None of them is privately owned.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Which one of the following has been constituted under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986? (2022)
- Central Water Commission
- Central Ground Water Board
- Central Ground Water Authority
- National Water Development Agency
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: iPhone and Android users were recently warned against a new fraud called ‘Smishing’.
About Smishing:-
- Smishing” is a combination of “SMS” (Short Message Service) and “phishing.”
- It is a type of phishing attack.
- It involves sending fraudulent text messages to individuals.
- Objective: tricking them into divulging sensitive personal information, such as passwords, credit card numbers, or other confidential data.
- Cybercriminals send fraudulent emails that seek to trick the recipient into clicking on a malicious link.
- It uses text messages instead of email. ( Cyberattacks)
- It often involves messages that appear to be from legitimate sources, such as banks, government agencies, or well-known companies.
Working mechanism:-
- Smishing messages typically contain urgent or enticing content to persuade recipients to take immediate action.
- This can be clicking on a malicious link, calling a phone number, or providing sensitive information.
- Once the victim opens and clicks on the link or dials the phone number listed in the message, they are taken to a fraudulent website or a mobile phone line that’s designed to resemble a legitimate source.
- The victim might be asked to enter sensitive information, such as login credentials, social security numbers, credit card information, or personal identification numbers (PINs).
- Once the victim’s sensitive information is divulged, the attacker might steal it to commit fraud.
MUST READ: Cybercrime
SOURCE: TIMES NOW
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In India under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant willfully damages it, if proven so
- Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defense in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, and 4 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2020)
- Aadhaar metadata cannot be stored for more than three months.
- State cannot enter into any contract with private corporations for the sharing of Aadhaar data.
- Aadhaar is mandatory for obtaining insurance products.
- Aadhaar is mandatory for getting benefits funded out of the Consolidated Fund of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: Recently, Magic Rice got Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
About Magic Rice:-
- Magic rice also known as Chokuwa rice.
- It is a part of Assam’s culinary heritage.
- This unique rice has been a staple of the troops of the mighty Ahom dynasty.
- It is cultivated around the Brahmaputra area.
- It is a semi-glutinous winter rice, known as Sali rice.
- The sticky and glutinous variety is categorized as Bora and Chokuwa based on their amylose concentration.
- The low amylose Chokuwa rice variants are used to make soft rice, which is known as Komal Chaul or soft rice.
- This rice variety is widely consumed for its convenience of preparation and nutritional value.
MUST READ: GI tag for Narasinghapettai nagaswaram
SOURCE: ECONOMIC TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the “Tea Board” in India, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Tea Board is a statutory body.
- It is a regulatory body attached to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- The Tea Board’s Head Office is situated in Bengaluru.
- The Board has overseas offices in Dubai and Moscow.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 4
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 4
Q.2) System of Rice Intensification” of cultivation, in which alternate wetting and drying of rice fields is practiced, results in: (2022)
- Reduced seed requirement
- Reduced methane production
- Reduced electricity consumption
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Inmates’ right to conjugal visits
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: A Public Interest Litigation (PIL) was filed in Delhi High Court on the issue of prison inmates’ right to conjugal visits.
- ‘Do prison inmates have fundamental right to conjugal visits by spouses?’ – is a petitioner’s question.
About Conjugal Rights:
- They are rights created by marriage, that is, the right of the husband or the wife to the company of their spouse.
- In the context of prisons, however, conjugal visits refer to the concept of allowing a prisoner to spend some time in privacy with his spouse within the precincts of a jail.
- Through such instruments, prisoners are guaranteed the right to life and inherent dignity.
- The right to maintain family relations including conjugal visits are included in these treaties.
- However, section nine of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955 deals with restitution of conjugal rights by recognising the right to consortium and protects it by allowing a spouse to move court to enforce the right.
Advantages of the conjugal rights:
- Prisoner rights: The conjugal visits are a fundamental right of the spouses of the prisoners that are internationally recognized through the United Nations Standard Minimum Rules for the Treatment of Prisoners, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights
- Prisoners are guaranteed the right to life and inherent dignity, and to maintain family relations including conjugal visits.
- Most prison Acts and Rules across the country accept the importance of maintenance of continuity in family and social relations.
- Preserving family ties and marital stability: If conjugal visits are allowed, the inmates will be able to continue their family ties.
- Many activities are undertaken in prisons, such as meditation and music, but at the end of the day, nothing can replace the pleasure of seeing one’s family.
- Health benefits: The conjugal visits can have positive impacts in the form of psychological health benefits for prisoners, preservation of marital ties and, reduction in the rates of homosexuality and sexual aggression within prisons.
- These generate positivity among prisoners, de-stress the inmates and help them on their journey towards reformation.
Arguments against the conjugal rights:
- Practicability: In July 2019, the then Director-General (Prisons) of Delhi, in an affidavit before the High Court, remarked, in accordance with established policy, the right to procreation is desirable, however, not practicable in the present prison scenario.
- Negative impact on family ties: Options like parole/furlough/interim bails, etc are available to inmates to preserve family ties and marital stability, but they are not always easy to get.
- Overcrowding with limited infrastructure: Official data showed that prison complexes in Delhi, Tihar, Mandoli, and Rohini are currently hold nearly 20,500 inmates, more than twice their total sanctioned strength.
- It highlighted that the allowing conjugal visits in prisons may not be feasible in light of the limited infrastructure available with the prisons.
Views of judiciary on conjugal visits:
- Sunil Batra vs Delhi Administration (1979): In this case, the SC judge Justice Iyer observed that visits to prisoners by family and friends are solace in isolation.
- Only a dehumanized system can deprive prison inmates of this humane amenity.
- Jasvir Singh vs State of Punjab: In this case, the High Court held that this right to conjugality is available to prisoners under Article 21, subject to restrictions.
- Meharaj vs State of TN (2022): The Madras HC observed that there have to be differential standards in enforcement of Article 21 for law abiders and law violators.
- Conjugal visits could not be held as a fundamental right.
- The prisoner would still be eligible to avail leave for conjugal visits if there are extraordinary reasons such as infertility treatments.
Way Forward: Punjab model for conjugal visits
The Punjab govt. recently introduced the Parivar Mulakat/Family Visit programme in the Ludhiana Central Jail, allowing inmates to have face-to-face meetings with their loved ones in specially designated rooms within the prison premises. The State guidelines clarify that conjugal visits are a matter of privilege rather than a right.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology)
Context: In recent years, several states in the U.S. have enacted ‘right to repair’ laws.
About Right to repair:

- It refers to government measures that forbid manufacturers to impose barriers that deny consumers the ability to repair consumer products.
- The sectors identified for the right to repair include farming equipment, mobile phones/tablets, consumer durables, and automobiles/automobile equipment.
- Government has launched a unified portal, https://righttorepairindia.gov.in, to onboard leading brands and reliable third-party technicians to provide easy access to overhauling services.
- The portal has on boarded leading brands such as Apple, Samsung, Honda, Kent RO Systems, Havells, Hewlett Packard, and Hero MotoCorp.
- The portal seeks to streamline trade between original equipment manufacturers and third-party sellers.
- The right to repair has been recognized in many countries across the globe, including the USA, UK, and European Union.
Significance of Right to repair for India:
- Lowering costs for consumers: By providing access to third-party technicians, the right to repair can reduce costs for consumers who may not be able to afford expensive repairs or replacement devices.
- Reducing electronic waste: India is one of the largest generators of electronic waste in the world, and the right to repair can help reduce e-waste by extending the lifespan of electronic devices and appliances.
- Supporting small businesses: The right to repair can also support small businesses that provide repair services, by creating a level playing field with manufacturers who may have previously had a monopoly on repairs.
- Empowering consumers: By giving consumers the ability to repair their own devices or choose where to have them repaired, the right to repair empowers consumers to make informed choices and take control of their own devices.
- Promoting transparency and collaboration: The right to repair framework aims to build a consumer-centric ecosystem that promotes transparency and collaboration between manufacturers, sellers, and consumers.
Challenges associated with implementing right to repair in India
- Limited Access to Information: Many manufacturers do not provide adequate information to consumers about repair options or how to repair devices, which can make it difficult for consumers to exercise their right to repair.
- Lack of Awareness: Consumers lack awareness about their rights to repair and the benefits of repairing their devices leading to a lack of demand for repair services, limiting the growth of the repair industry.
- Opposition from manufacturers: Some manufacturers may oppose the right to repair, arguing that it could compromise their intellectual property rights or lead to safety concerns making it difficult to pass legislation or regulations to support the right to repair.
- Limited availability of spare parts: The availability of spare parts is often limited in India, particularly for older or less common models of devices makes it difficult for repair technicians to perform repairs or for consumers to find reliable repair services.
- Lack of regulatory mechanism: Currently, there is no comprehensive regulation in India that governs the right to repair which can lead to confusion among consumers and repair technicians about their rights and responsibilities, and may limit the growth of the repair industry.
Right to repair across the world:

Way Forward:
Many countries around the world have been attempting to pass effective ‘right to repair’ laws. But the movement has faced tremendous resistance from tech giants such as Apple and Microsoft over the years.
The New York legislation is a reminder that it is time to not only acknowledge the right to repair of consumers but also respond to the corresponding rights of the manufacturers. This warrants some expedited policy changes to recognise the ‘right to repair’, be it through amendments in the Consumer Protection Act, 2019 or through a separate law.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Eagle species | IUCN Status |
| 1.Bald eagle | Least Concern |
| 2.Steppe Eagle | Endangered |
| 3.Black Eagle | Critically Endangered |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Magic rice is also known as Chokuwa rice.
Statement-II:
It is cultivated around the Yamuna Basin area.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
The Horn of Africa includes Somalia, Ethiopia, Eritrea, and Djibouti only.
Statement-II:
The Horn of Africa is equidistant from the equator and the Tropic of Cancer.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Question
Q.1) What do you mean by right to repair? Discuss how will it be beneficial for both the consumers and the environment. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 29th August 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 28th August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – c











