IASbaba's Press Information Bureau
Press Information Bureau (PIB) IAS UPSC – 18th March to 24th March – 2019
GS-2
Health Ministry reviews the preparedness on West Nile Fever
(Topic: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources)
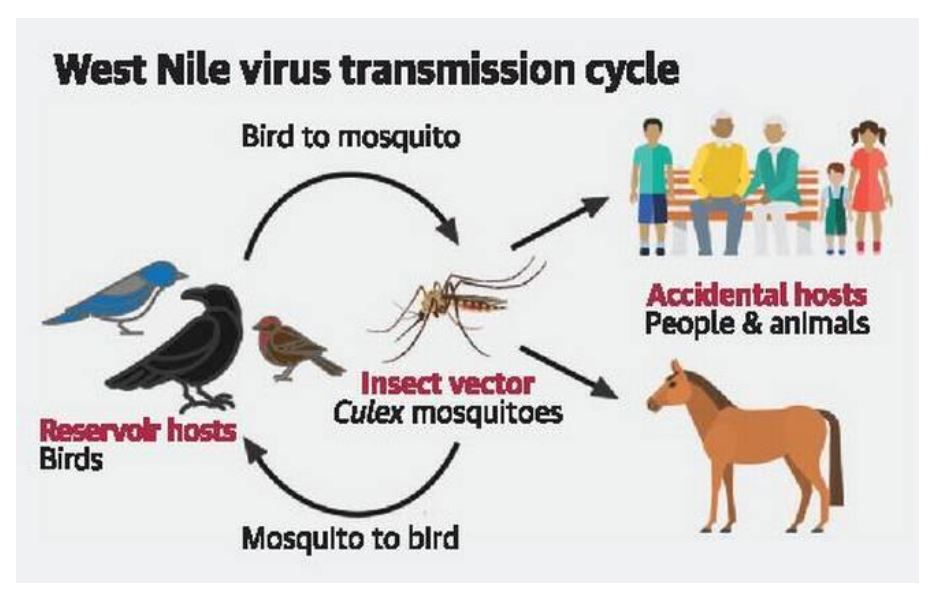
The State has been advised to follow the National Vector Borne Disease Control Program (NVBDCP) guidelines of personal protective measures to prevent mosquito bites. The Ministry has also recommended vector surveillance and control to be carried out in coordination with NVBDCP.
West Nile Fever is a mosquito borne zoonotic disease caused by a flavivirus -West Nile Virus (WNV). This virus is related to viruses that cause Japanese Encephalitis, yellow fever and St. Louis encephalitis. Human infection is most often due to bites from infected mosquitoes. To date, no human-to-human transmission of WNV through casual contact has been documented. Infection with WNV is either asymptomatic (no symptoms) in around 80% of infected people, or can lead to West Nile fever or severe West Nile disease.
Do you know?
- West Nile virus can cause a fatal neurological disease in humans.
- Approximately 80% of West Nile virus infections in humans have few or no symptoms.
- WNV is found in temperate and tropical regions of the world.
- The virus was discovered in Uganda in 1937 and was first detected in North America in 1999.
- West Nile fever is spread by Culex mosquitoes and the infection could be confirmed only if the second samples test positive. Symptoms include fever, headache, tiredness, and body aches, nausea, vomiting, occasionally with a skin rash on the trunk of the body, and swollen lymph glands.
Pic: https://iasbaba.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/PIB.jpg
World Water Day
(Topic: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation)
Theme: Leaving no one behind – Whoever you are, wherever you are, water is your human right.
600 million people face acute water shortage and 200,000 die each year because they have no access to clean water. By 2020, 21 cities will run out of groundwater. Just over a decade from now, water woes could cause a 6% loss in GDP.
What is ‘safe water’?
Safe water means water that is free from contamination, and available whenever needed. The world cannot grow and prosper if there are people without access to safe water. When they are forced to use unsafe or contaminated water, they risk contracting deadly diseases.
Women, children, refugees, and disabled people sometimes face discrimination when they try to access water. This is against the basic human right to water — which entitles everyone to water for drinking, personal sanitation, washing clothes, food preparation, and household hygiene. This year’s World Water Day will focus on the reasons why so many people are being left behind.
Composite Water Management Index: Seventy per cent of the water resources in the country is polluted, 75 per cent households do not have drinking water and more than 600 million people in the country face high to extreme water distress.
The Mihir Shah Committee argued that there is little “understanding of river systems or their interconnections with the health of catchment areas or groundwater”. There needs to be a paradigm shift in the country’s water governance: From a predominantly engineer-centred approach of the CWGB to one involving hydrologists, geologists, agronomists, and ecologists.
Water scarcity is a clear and present danger, not a distant threat, and global warming heightens this threat.
World Tuberculosis Day
(Topic: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources)
24th March marks the day in 1882 when Dr Robert Koch announced that he had discovered the bacterium that causes TB, which opened the way towards diagnosing and curing this disease.
TB remains the world’s deadliest infectious killer. Each day, nearly 4500 people lose their lives to TB and close to 30,000 people fall ill with this preventable and curable disease.
Global efforts to combat TB have saved an estimated 54 million lives since the year 2000 and reduced the TB mortality rate by 42%. To accelerate the TB response in countries to reach targets – Heads of State came together and made strong commitments to end TB at the first-ever UN High Level Meeting in September 2018.
Theme of World TB Day 2019 – ‘It’s time’ – puts the accent on the urgency to act on the commitments made by global leaders to:
- Scale up access to prevention and treatment
- Build accountability
- Ensure sufficient and sustainable financing including for research;
- Promote an end to stigma and discrimination
- Promote an equitable, rights-based and people-centered TB response.
India’s War on TB – The Way Forward
Countering Delay in Diagnosis:
- To block transmission, treatment should begin as soon as a symptom shows up. As cough is a very common symptom of many diseases, doctors don’t think of TB until other treatments fail.
- Partnership with the private sector is essential for early diagnosis of TB.
- Universal primary health care, a basic human right, and a diagnostic algorithm for early diagnosis are essential for TB control.
- To retard progression: Employ the biomedical method is drug treatment of latent TB. Experts recommend an age window of 5-10 years when all children must be screened with TST; those with latent TB must be treated to prevent progression.
Private Sector: The private sector has a very crucial role to play in checking the rise of TB as it is the first place a patient from an urban area visits. We need to make them a partner in this fight.
- Strict guidelines need to be followed to report cases of TB to government.
- Developing a comprehensive set of national guidelines could strengthen private sector engagement in TB
- Efforts should be made to map and categorise private practitioners based on the nature of their education, experience and services provided.
- Private hospitals need to be penalised for failure to report early TB cases to government. This will enhance the accountability of the private players.
- If cannot provide free treatment, it needs to refer the patient to a government clinic.
Strengthening research: We urgently require rapid and cost-effective point-of-care devices that can be deployed for TB diagnosis in different settings across the country.
- Additionally, new drug regimens are necessary for responding to the spread of drug-resistant strains as is an effective vaccine for preventing TB in adults. It is a big challenge in current times, which is due to irregular treatment.
- Operational research for optimising service delivery is also critical because it is often the case that diagnostics and drugs do not reach those who need them the most.
- TB with other disease like HIV is difficult to treat and the research needs to be strengthened in this field.
- The India TB Research and Development Corporation launched in 2016 must play a pivotal role in accelerating these efforts.
Technology: Technology has to be introduced and utilized in the most effective manner to ensure early access and monitoring.
Ending social stigma: TB is not a health issue alone. It is a broader societal challenge. Patients often hesitate to seek treatment or deny their condition altogether for fear of losing social standing. The consequence is that TB becomes a death sentence for many even though it is a fully curable illness. Women are disproportionately affected with estimates suggesting that 100,000 Indian women are asked to leave their homes every year after being diagnosed with TB.
- Mass awareness campaigns like ‘TB Harega Desh Jeetega’ can play an important role in breaking social taboos.
- Local communication channels such as community radios and street plays must also be leveraged.
- Children should be engaged through anganwadis and schools for disseminating accurate messages about TB to their families.
- Paediatric TB is often a neglected area. Children come from low socio-economic strata with social stigma and discrimination which needs to be de-stigmatised.
Major initiatives taken by India–
Shift to Daily regime of medication: With DOT Centres, the treatment will be at individual door level leading to no defaulter.
Cash benefit for TB patients & Medical Practitioner:
- About 35 lakh identified Tuberculosis patients across the country will soon get Rs. 500 every month from the Centre as social support. The cash benefit for social support will cover loss of wages, travel and mainly nutrition.
- INR 500/- to the private medical practitioner for notification of the disease
Will this work: Need to incentivise both the patients and the private practitioners as both the sides will ensure that they stand to gain from the treatment, which, in the long term, might lead to behavioural change.
Web-based Application – Nikshay: To enable health functionaries at various levels across the country to monitor TB cases in their areas
- Patients receive daily SMSes to ensure they continue their medication.
- The medicines come with a toll free number that is visible only after the medicine has been taken out of the foil pack; patients are required to give the number a missed call.
- Every missed call is tracked, and when there are too many gaps, the patient is traced, often by treatment supervisors who travel to remote areas on bikes that the programme pays for.
Introduction of Cartridge-Based Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (CBNAAT): It is a revolutionary rapid molecular test which simultaneously detects Mycobacterium tuberculosis and rifampicin drug resistance. This test is fully automated and provides results within two hours. It is a highly sensitive diagnostic tool and can be used in remote and rural areas without sophisticated infrastructure or specialised training.
Connect the Dots:
- TB remains one of the leading causes of death from any single infectious agent worldwide. Comment on the national and global efforts to eliminate the disease by 2035.
- TB is still one of the major cause of deaths across the world. To eliminate this epidemic, understanding the private sector and designing the corresponding strategies is one of the important solutions. Elucidate.
- To outsmart TB bacilli, we must intercept infection, progression and transmission concerted use of all interventions — biomedical and socio-behavioural- is required. Analyze.
GS-3
Strong Action against Terrorism in Jammu & Kashmir
(Topic: Security challenges and their management in border areas; linkages of organized crime with terrorism)
Central Government has followed the policy of ‘Zero Tolerance’ against terrorism and has acted strongly against terrorists. Central Government in its pursuit of strong action against terrorism, has declared JKLF (Yasin faction) as an unlawful association under the provisions of Section 3(1) of the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967.
- Securities Forces have been given free hand to deal with terrorism.
- Government is committed to relentlessly pursuing the policy of curbing the activities of secessionist organizations which are threat to unity and integrity of the country. NIA and Enforcement Directorate are taking strong action against these organizations.
- With above objective, Government has declared ‘Jamaat-e-Islami (J&K)’ as an unlawful association under the provisions of Section 3(1) of the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967. It was made clear at that time that ‘Jamaat-e-Islami (J&K)’ is separate from ‘Jamaat-e-Islami Hind’. In 1953, it made its own constitution. JeI (J&K) is responsible for formation of Hizbul Mujahidin (HM), the biggest terrorist organization active in Jammu & Kashmir. JeI (J&K) has been providing all kind of support to HM in terms of recruits, funding, shelter, logistics, etc
- Jammu & Kashmir Liberation Front led by Md. Yasin Malik has spearheaded the separatist ideology in the valley and has been at the fore-front of separatist activities and violence since 1988. Murders of Kashmiri Pandits by JKLF in 1989 triggered their exodus from the valley. Md. Yasin Malik was the mastermind behind the purging of Kashmiri Pandits from the Kashmir valley and is responsible for their genocide.
- JKLF has many serious cases registered against it. This organisation is responsible for murder of 4 Indian Air Force personnel and kidnapping of Dr. Rubaiya Sayeed (daughter of the then Home Minister Mufti Mohammad Sayeed in Shri V. P. Singh’s Government). This organization, alongside, is also responsible for illegal funnelling of funds for fomenting terrorism. JKLF is actively involved in raising of funds and its distribution to Hurriyat cadres and stone-pelters to fuel unrest in the Kashmir valley as well as for subversive activities.
- Activities of JKLF (Y) pose a serious threat to the security of the country and are prejudicial to the territorial integrity and sovereignty of India. The organization has been actively and continuously encouraging, feelings of enmity and hatred against the lawfully established Government as well as armed rebellion.
- 37 FIRs have been registered by J&K Police against JKLF. Two cases including the case of murder of IAF personnel were registered by CBI. NIA has also registered a case, which is under investigation. It is evident from these that JKLF continues to be actively engaged in supporting and inciting secessionism and terrorism including terror financing.
- A large number of secessionist leaders were being provided security by the State. Government, after review, has withdrawn the security of many such persons. This process will continue further.
- The Government has re-vitalized grass-root democracy in J&K by conducting elections peacefully for the first time in 2018 for Urban Local bodies after 2005 and for Panchayats after 2011. There was active participation of the people in these elections and overall polling percentage was 74%. More than 3,652 Sarpanches and 23,629 Panches were elected in these elections. Panchayats have been empowered and made more accountable towards public. Direct elections were held for Sarpanches. Financial powers of Panchayats have been increased 10 times. About 20 Departments have been brought under Panchayati Raj. Government is committed for integrated and coordinated development of all the three regions of the State, Jammu, Kashmir and Ladakh.
Please Note:
AFINDEX-19: Africa-India Field Training Exercise-2019 for India and African nations
Exercise MITRA SHAKTI: Conducted annually as part of military diplomacy and interaction between armies of India & Sri Lanka
Quotes:
The Vice President of India, Shri M. Venkaiah Naidu
On Media and Elections
- Advised the media to present a report card on the performance of parties in an objective manner to enable people make an informed choice during elections.
- If the media can present report card and the people can demand accountability from political party’s vis-a-vis their promises, raising resources and how they intend to spend them, our country can boast of not only being the largest democracy in the world but also one of the most vibrant, cleanest democracies in the world.
- Media should act as a mirror that reflects the reality, neither magnifying nor diminishing, neither distorting nor mystifying facts.
- Advised the media to “shun this tendency lest ‘money power’ is used to influence voters through ‘manufactured’ views and opinions of paid news”.
- To make elections more credible and inclusive the pitfalls such as money and muscle power, breaching the limits of election expenditure, invoking caste and religion, criminal antecedents of candidates, paid news and fake news, violating the Model Code of Conduct, inadequate representation of women in legislatures need to be addressed in quick time.
- As an old saying goes ‘facts are sacred and opinion is free’. So, stick to facts, present them fearlessly and give opinions fearlessly but when giving opinion don’t ‘change’ the facts.
- We must foresee that these 4C’s are coming and must be careful – Cash, Community, Caste and Criminality.
- Must Read: Link 1 + Link 2
On Blue Economy
-
- The objective of the Blue Economy is to promote smart, sustainable and inclusive growth and employment opportunities through maritime economic activities.
- There is a need to focus on ocean centric technology to harness the marine resources for sustained growth of India. Development of technologies for deep sea mining, underwater vehicles and underwater robotics for extraction of minerals should be initiated. NIO should also undertake research on development of drugs from the sea.
- A focused approach in some of the areas such as minerals from the ocean, energy from ocean can make India a global leader and serve our national goals. However, while pursuing the “blue growth”, every effort must be made by all the stakeholders, including private and public sectors, to prevent further degradation of the ocean and its ecosystems.
- Must Read: Link 1














