IASbaba's Mains Strategy, Mains Examination
Civil Services (Mains) Examination – General Studies
Strategy for Paper 2
Essay Strategy- Click here
Model Essay by IASbaba– Click here
Marks allotted- 250
Paper 2 comprises of Indian Constitution, Governance issues and International Relations. It is one of the most interesting papers of General Studies-Mains. What makes it distinct and interesting is its evolving and dynamic nature.
Many aspirants misinterpret the syllabus and spend too much time on static aspects. For a beginner and naive aspirant, the syllabus is intriguing in much sense. First, for basic understanding a beginner will have to spend quality time in learning the basics that takes substantial time. Second, when the aspirant is done with the basic books, the real challenge awaits as how to answer the questions asked by UPSC?
This happens to most of the aspirants since the change of pattern in 2013, UPSC has stopped asking static questions. If you go through previous year papers, 2013 and 2014, almost all the questions are dynamic though require basic understanding. But if you are well versed with contemporary developments around that issue, you can answer the questions very well.
The strategy given below is a blend of both, static and contemporary aspects.
Please note that, there are 2 most important things a beginner should do, before one starts off with his/her preparation:
- Firstly, memorize all the aspects of the syllabus
- Secondly, go through last 5 year’s UPSC (Mains) question papers
One has to be well versed with all the dimensions of the topics given in the syllabus. If you are able to understand them, then half the battle is won! While reading a newspaper or going through any material, it will help you in picking up the relevant issues from the exam perspective. Most of the topics and sub-topics are interconnected. This is explained as you read further.
Must: IASbaba has made the first part of your preparation simpler by innovatively explaining the various dimensions of the Syllabus through Mind Maps. This will help you to memorize the syllabus in less time. Once you have browsed through for say 5 times, most of the aspects of the syllabus will be visually imprinted in your mind.
For the second part of your preparation (which is dynamic in nature), refer our
- Think & Learn Perform (TLP) – Mains initiative
- IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs
- Monthly Magazine
- Yojana/Kurukshetra Gist
The whole syllabus of Paper 2 can be broadly divided into three parts-
- Indian Constitution and Polity
- Governance and Social Justice
- International Relations
Now, let’s go through each Topic and Sub-topics in detail.
Constitution, Polity
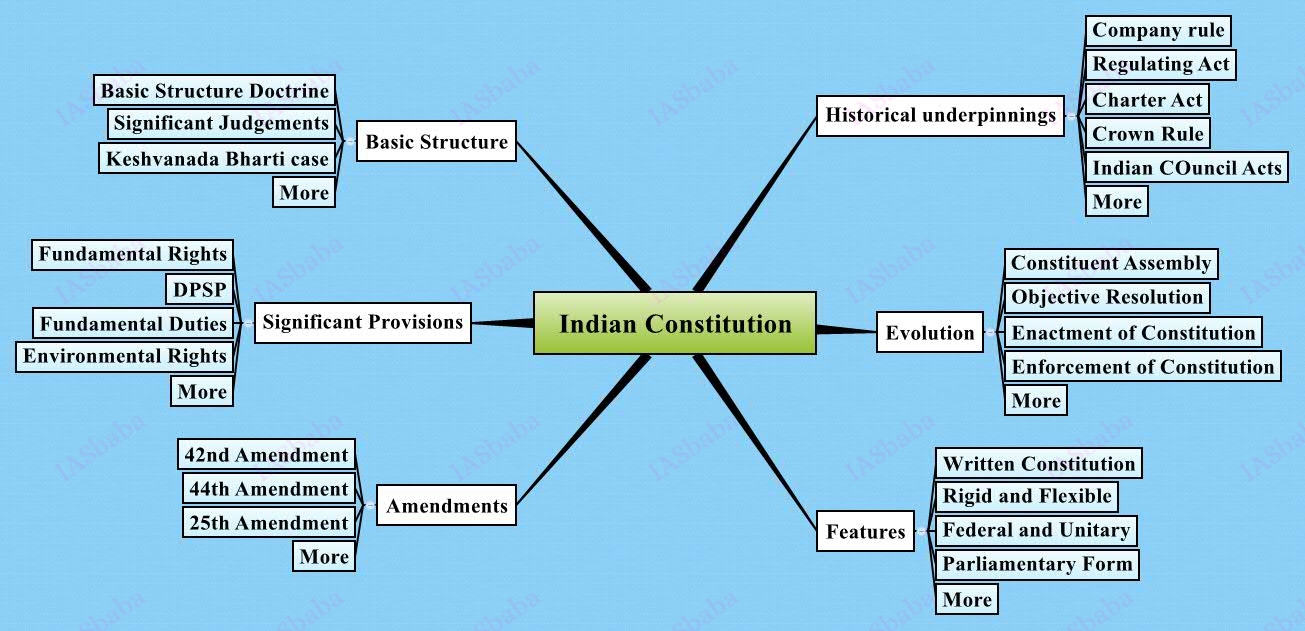
Indian Constitution- historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions and basic structure.
- Historical Underpinnings–means the events/acts/laws which led to strengthening the foundation of Indian Constitution right from Regulation Act of 1773 to Government of India Act of 1919.
- Evolution of the Constitution – starts from for the first time the ‘demand for Constitution’ was laid down by Motilal Nehru in 1924 to its adoption in 1950.
- Salient Features of the Indian Constitutionlike forms of government, Federal System with unitary bias, Fundamental Rights (FR), Fundamental Duties, DPSP, Supremacy of the Constitution, Integrated and Independent Judiciary etc. Have a basic understanding on how basic structure of the Constitution evolved, important cases involved.
- You would have covered the above topics while reading for Prelims. For MAINS, brush up the concepts and focus more on the current happenings related to these topics.
- Example: 66A of IT Act was in news because it curtailed the ‘freedom of expression’ (Article 19).
NOTE: Make note of the recent ‘Amendments’ and rationale behind these amendments. Example: With 97th Amendment Act forming a Co-operative Society became a Fundamental Right (FR). Why was it made a FR, what were the issues involved?
Now, let us relate these topics from previous years UPSC questions
Important Points to Focus
- Though the above topics may seem factual and static, but the questions asked by UPSC can only be answered if one is having a track of recent issues not news.
- What we mean by issues? Follow the news but study the issue. A news when completes its entirety becomes an issue. An issue has several dimensions and UPSC loves to ask a question on any one such dimension or an issue comprehensively.
- If you are done with your basics, a relative study and understanding of the issue is a cake walk.
- It will also lessen your time that is consumed for newspaper reading.
The below comparison is done to show how you can cover this part of the syllabus smartly by inter-linking the static with the current issues.
Check these questions from UPSC
Discuss Section 66A of IT Act, with reference to its alleged violation of Article 19 of the Constitution. (2013)
Recent directives from Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas are perceived by the Nagas’ as a threat to override the exceptional status enjoyed by the State. Discuss in light of Article 371A of the Indian Constitution. (2013)
What do you understand by the concept “freedom of speech and expression”? Does it cover hate speech also? Why do the films in India stand on a slightly different plane from other forms of expression? Discuss. (2014)
Reference: A general topic of debate and discussion that is sort of evergreen in Indian media. You can find number of articles with respect to this.
Sources/Books to Refer:
- Indian Polity by LAXMIKANTH-4th Edition
- “Introduction to The Constitution Of India” – D.D. Basu:- The first 4 chapters in this book give a good insight on this topic.
- We consider that you have read NCERT, Polity books of class 9th, 10th and 11th as part of Prelims preparation. If not, then try to finish it as soon as possible and get back to above mentioned sources.
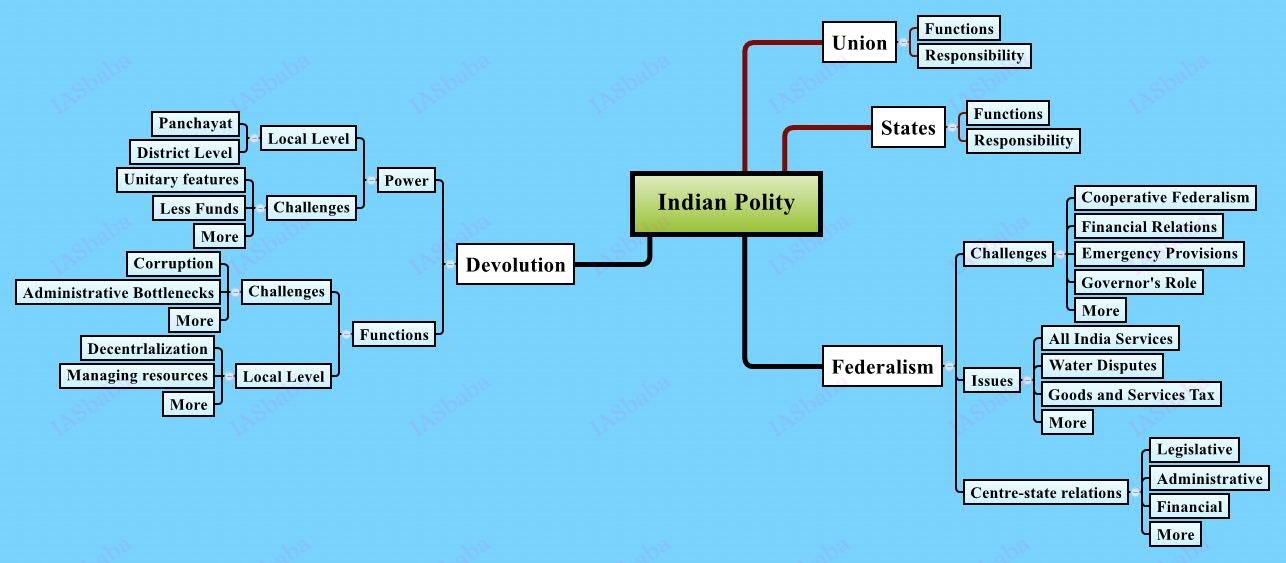
Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein.
These topics are overlapping and dynamic in nature:
- Have a basic understanding on Seventh Schedule– Division of Powers between the Union and the States in terms of Union List, State List and the Concurrent List.
- Issues with the powers and functions of State and the Central government like – dealing with State Subjects – Agriculture, Law & Order, Statehood issues etc.
- Issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure– Distribution of Legislative, Executive and Financial powers between the Centre and the States.
Issues range from:
- Administration: Co-operative Federalism, Role of Governor, NITI Ayog replacing Planning Commission, Formation of New States, National Counter terrorism Centre (NCTC), FDI in retail, AFSPA,Misuse of Article 356 (President’s Rule), River water disputes, Emergency Provisions, All-India Civil Services etc.
- Finance: Goods and Service Taxes (GST), The role of Finance Commission; distribution of taxes among States and between States and the Centre. etc.
- Legislation: Circumstances under which Parliament can legislate in the State field like when Rajya Sabha passes a resolution (A-249), during national emergency (A-352) etc.
- Devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges: Though Constitutional Status has been granted to Local Self Governments – Panchayat’s and Urban Local bodies- there are Issues with the transfer of Functions, Funds and Functionaries from the State Government to the Central Government. Various structural, operational and socio cultural factors affecting the effective functioning of the panchayats have to be dealt with.
Let us go through previous years UPSC questions
Constitutional mechanisms to resolve the inter-state water disputes have failed to address and solve the problems. Is the failure due to structural or process inadequacy or both? Discuss. 2013
Reference: Cauvery Water Dispute
Many State Governments further bifurcate geographical administrative areas like Districts and Talukas for better governance. In light of the above, can it also be justified that more number of smaller States would bring in effective governance at State level? Discuss. 2013
Reference: Formation of Telangana, Rise in Demands of separate State. This was the basis of this question. One can find many articles from newspapers.
Though the federal principle is dominant in our Constitution and that principle is one of its basic features, but it is equally true that federalism under the Indian Constitution leans in favour of a strong Centre, a feature that militates against the concept of strong federalism. Discuss. 2014
Reference: A very basic question. After going through polity books, one can easily answer this question. However, it is required to substantiate your arguments with several examples from current happening. It will add value to your answer.
Books/Sources to Refer:
- For getting your Basics right refer “Introduction to The Constitution of India” – D.D. Basu (Chapters 5, 11, 12, 13, 14, 17, 18 and 19) OR ‘’Indian Polity” –Laxmikanth 4th edition. (Chapters 12, 13, 14, 30 and 31).
- To get a Critical Perspective of this topic refer ‘Administrative Reforms Committee’s (ARC II)’ 13threport on ‘Organizational Structure of Government of India’ and if you ‘re on a time crunch then go through the summary of the report
- For ‘devolution of powers and finances’ refer ‘Administrative Reforms Committee’s (ARC II)’ 6th report on ‘Local Governance’. If you ‘re on a time crunch then go through the summary of the report
- A must read for Decentralization in Rural Governance
- Read it to understand the issues and dimensions to Urban Governance
NOTE: These topics should be supplemented with Committee recommendations like Sarkaria Committee, Punchhi Committee, Administrative Reforms Committee (ARC II).
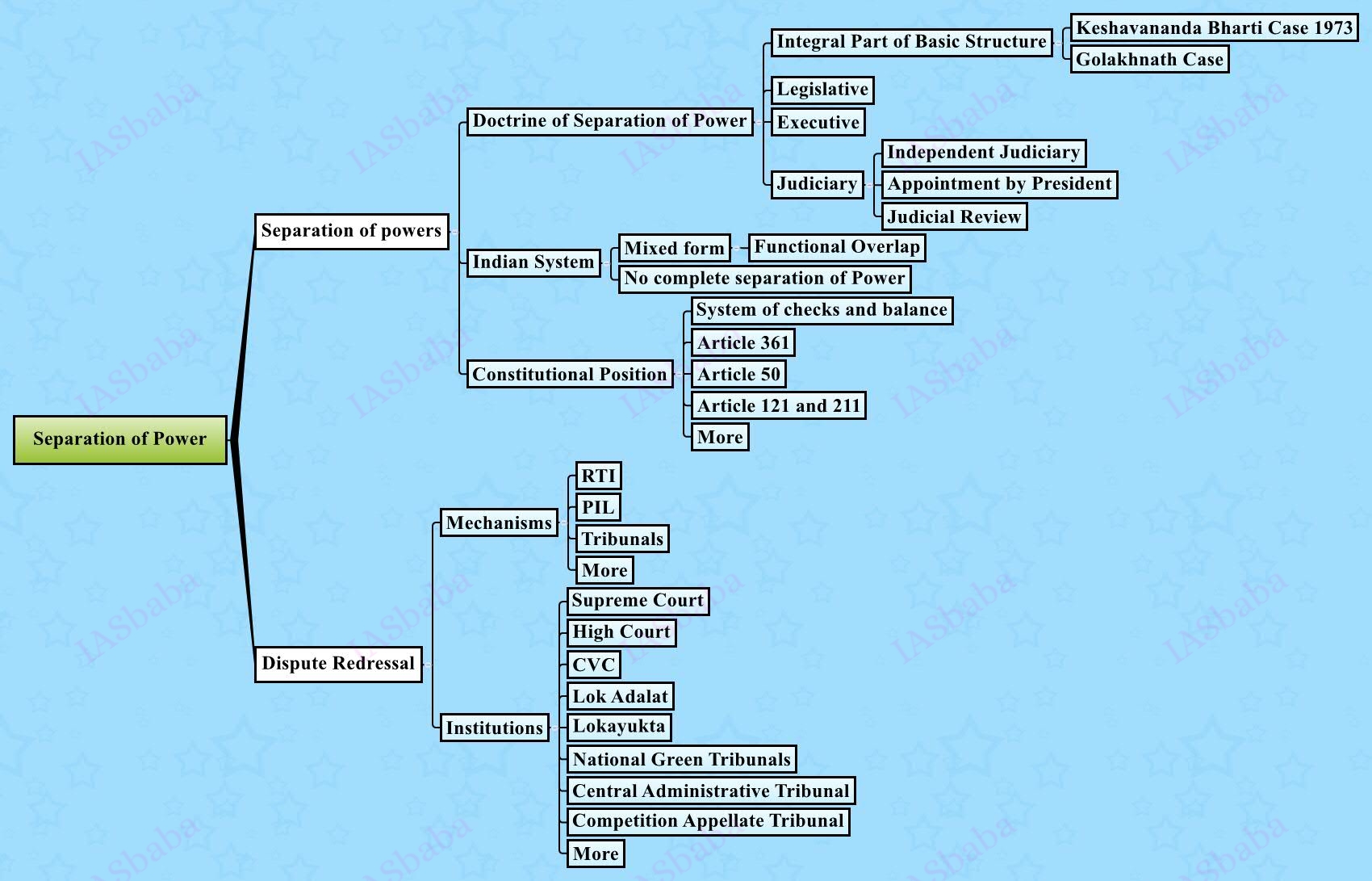
Separation of powers between various organs, Dispute redressal mechanisms and institutions.
- Have a basic understanding of Various Organs of the State – Legislative, Executive and the Judiciary;
- Issues like overlapping functions of the three organs of the State; Concept of Checks and balance; Judicial Activism, Judicial Overreach.
- Issues between other organs like UPSC and CVC, Planning Commission (obsolete) Verses NITI Ayog and Finance Commission or between Constitutional Bodies or between a Constitutional Body and a Statutory Body.
- Dispute Redressal mechanisms and Institutions– Judiciary, Tribunals, Central Vigilance Commission (CVC), Lok Adalat, Lokayukta, Inter-State Council, Zonal Councils, NDC.
- Public Redressal mechanisms like Right to Information (RTI), Public Interest litigation (PIL), Citizen’s Charter, Sakala in Karnataka etc
Books/Sources to Refer:
- Once you have read through the topics mentioned under Topic 2, for Conceptual Understanding refer “Introduction To The Constitution Of India” – D.D. Basu (Chapters 21, 22 and 23) OR ‘’Indian Polity”– Lakshmikanth 4th edition. (Chapters 23, 28, 35, 37, 41, 44, 45, 46 , 48 and 54).
- ‘Administrative Reforms Committee’s (ARC II)’ 7th report on ‘Capacity Building for Conflict Resolution’ will give you more insights on the issues like Regional Disparities, North East conflicts, Left Wing Extremism, River water disputes, SC and ST issues etc. and Operational and Institutional Arrangements for Conflict Resolution like Inter-State Council, Zonal Councils, NDC, National Human Rights Commission, National Commissions for SCs, STs etc.
- For latest issues regarding Conflict of various Bodies and Dispute redressal mechanisms ‘Newspapers’ are the best source.
UPSC Previous Year Questions
The Supreme Court of India keeps a check on arbitrary power of the Parliament in amending the Constitution. Discuss critically. 2103
Starting from inventing the ‘basic structure’ doctrine, the judiciary has played a highly proactive role in ensuring that India develops into a thriving democracy. In light of the statement, evaluate the role played by judicial activism in achieving the ideals of democracy 2014
Reference: It is a mixed question. You need to know the Basic Structure Doctrine and the role of Judiciary. Here examples from past judicial pronouncements as well as recent cases in this regard have to be mentioned. Check these articles published in mid 2014
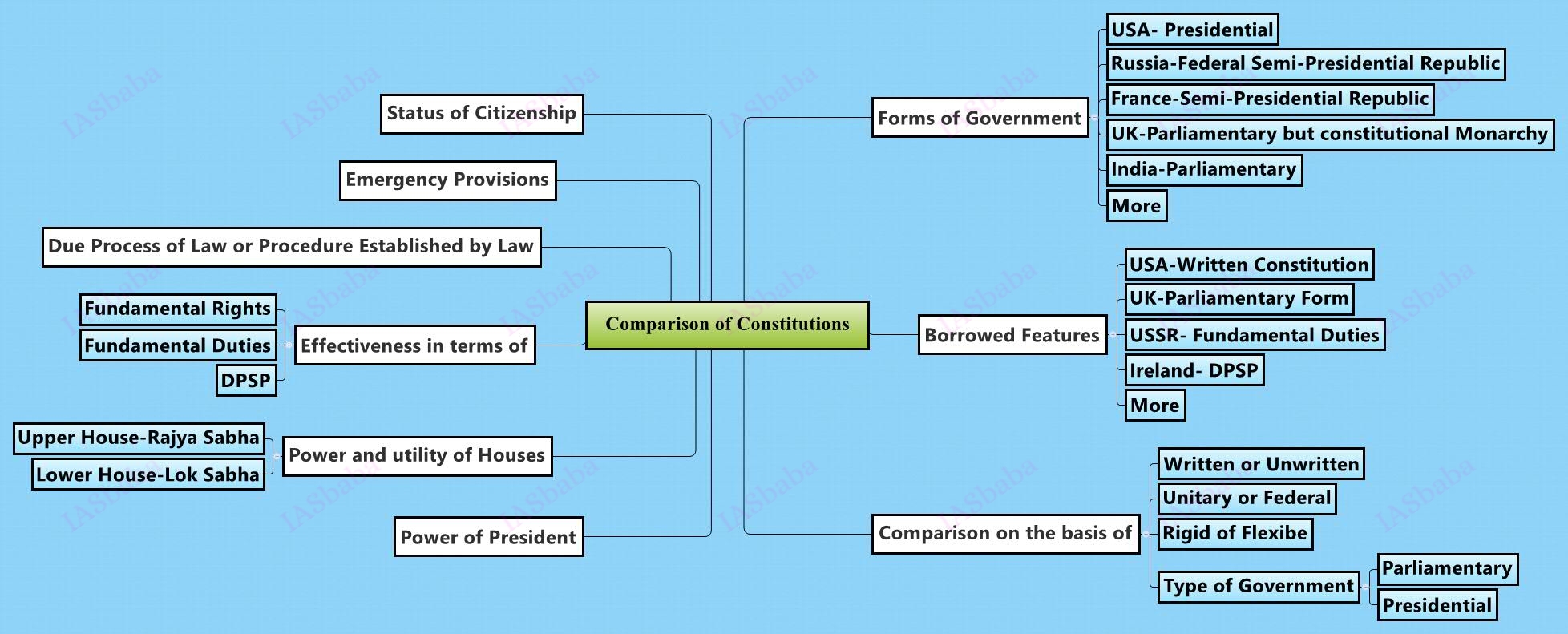
Comparison of the Indian constitutional scheme with that of other countries.
- Basic idea about the salient features of Constitutions across the World – US, UK, Russia, France, German, Japan.Salient features like form of government, fundamental rights, supremacy of organs of state, separation of powers, federalism/unitary etc
- Borrowed features of Indian Constitution like Written Constitution, Rigidity or flexibility of the Constitution, Parliamentary form of Government, Federal Features, FR’s, FD’s, DPSP, Emergency provisions, etc.
- For understanding the scope of this topic, refer the below link
NOTE: Keep a note of the New Constitutions framed/being framed in Pakistan, Bhutan, Nepal and Myanmar.
Books/Sources to Refer:
- Considering the cost benefit, one should avoid rushing for books and bulky notes.
- More dependency should be on various newspapers and current developments.
- UPSC will never ask purely static question that require a comprehensive follow through to various Constitutions.
- Even if UPSC asks you such a question, it will be more wise to ignore it and move on J
- You can update and follow IASbaba’s new initiative, Think Learn & Perform (TLP) for such topics.
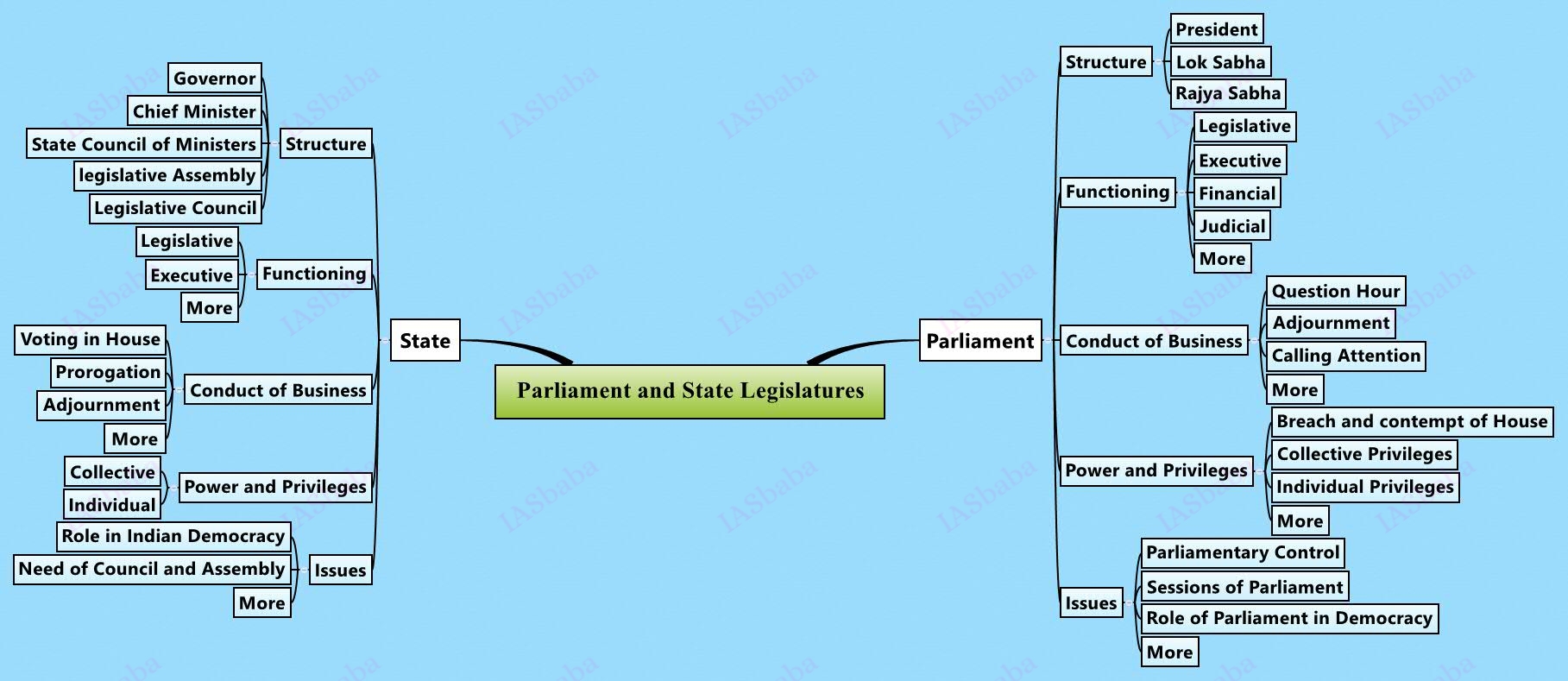
Parliament and State Legislatures – structure, functioning, conduct of business, powers & privileges and issues arising out of these.
- Once the basic functioning of the Parliament is understood, focus on the Issues like the Composition of the Parliament – Women Representatives (both at the Centre and State constitute only about 10% of the total strength),
- Quality of debates that go on in the Parliament, number of bills passed, procedure of passage of the bills like Money Bill, Ordinary Bill and the time spent on discussion of the Bills- compare this with the initial phases of our democracy;
- The role of Opposition (the status of Opposition Leader was in recent news), anti-defection, horse-trading, Role of parliament for a functioning democracy,
- Criminalization of members of legislatures, accountability measures in parliament through various committees and procedures, misuse of the privileges of the parliament, attendance, etc.
- Relevance and functioning of Parliament.
Books/Sources to Refer:
- For Basic Understanding refer “Introduction to the Constitution of India” – D.D. Basu (Chapters 22 and 23) OR ‘’Indian Polity” –Lakshmikanth4th edition. (Chapters 22 and 27).
- Newspaper is the best source for dynamic nature of the issues related to Parliament.
Read these articles about Parliamentary Reforms- Read in sequence
Do read Monthly Policy Review given by PRS Legislative- Download
Previous Year Questions
The role of individual MPs (Members of Parliament) has diminished over the years and as a result healthy constructive debates on policy issues are not usually witnessed. How far can this be attributed to the anti-defection law, which was legislated but with a different intention? 2013
Reference: The issue is about the functioning of MP’s and MLA’s. It is rooted in the occurrence of some events and Lok Sabha’s poor performance on many parameters like: few sittings, low number of Bills passed and a significant proportion passed without deliberation, the higher proportion of time wasted on disruption etc.
Moreover, if you followed PRS Legislative Research (highly recommended for Paper 2) you would have directly got the essence and importance of this issue. Here is the reference
The ‘Powers, Privileges and Immunities of Parliament and its Members’ as envisaged in Article 105 of the Constitution leave room for a large number of un-codified and un-enumerated privileges to continue. Assess the reasons for the absence of legal codification of the ‘parliamentary privileges’. How can this problem be addressed? 2014
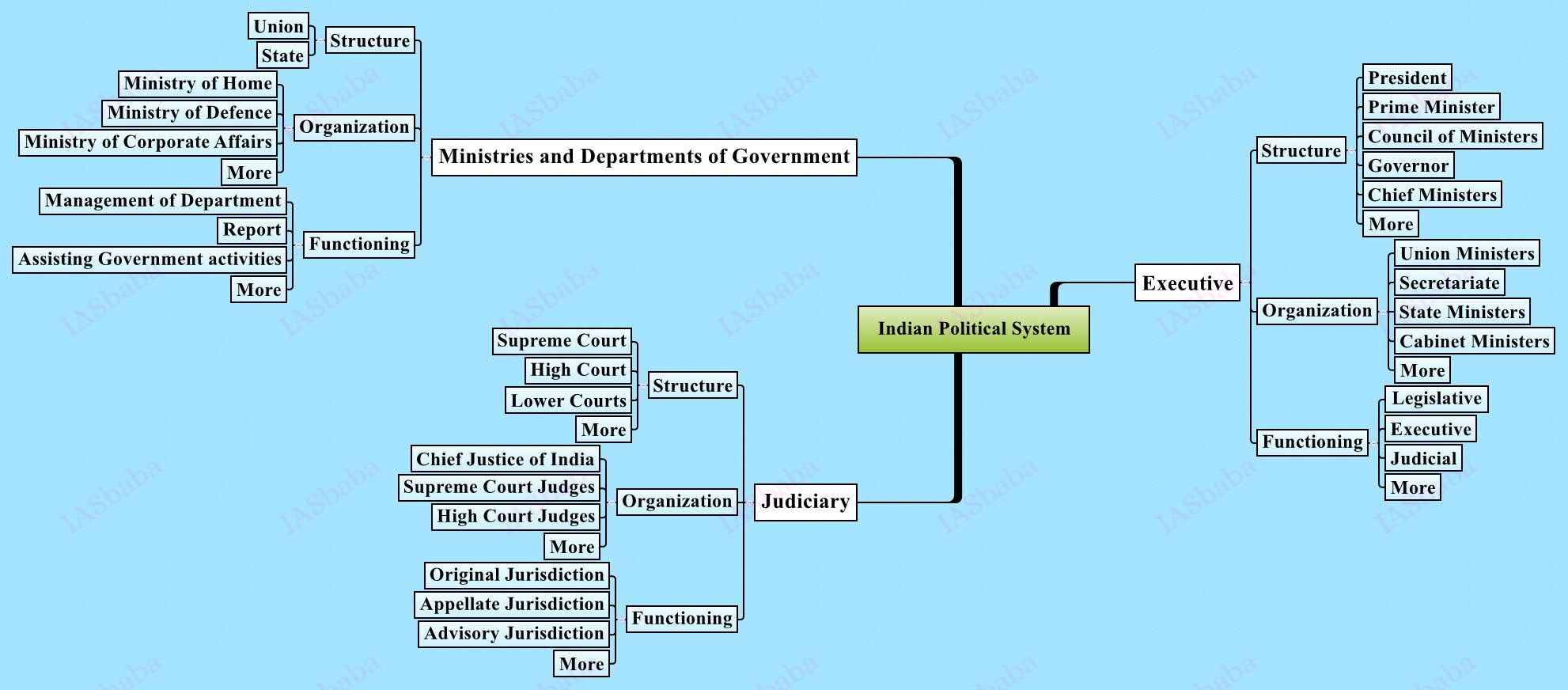
Structure, organization and functioning of the Executive and the Judiciary, Ministries and Departments of the Government; pressure groups and formal/informal associations and their role in the Polity.
- The Executive will comprise of President, Vice-President , Prime Minister, Governor, Chief Minister, Attorney General, Advocate General of the State, Cabinet Ministers, Council of Ministers both at the Centre and the State. You would have read about the powers, functions, responsibilities, of the executive for
- Once you are done with the basics, focus on the issues like President’s rule ( Article – 356), appointment and removal of Governor, Capital Punishment/Death Sentence etc.
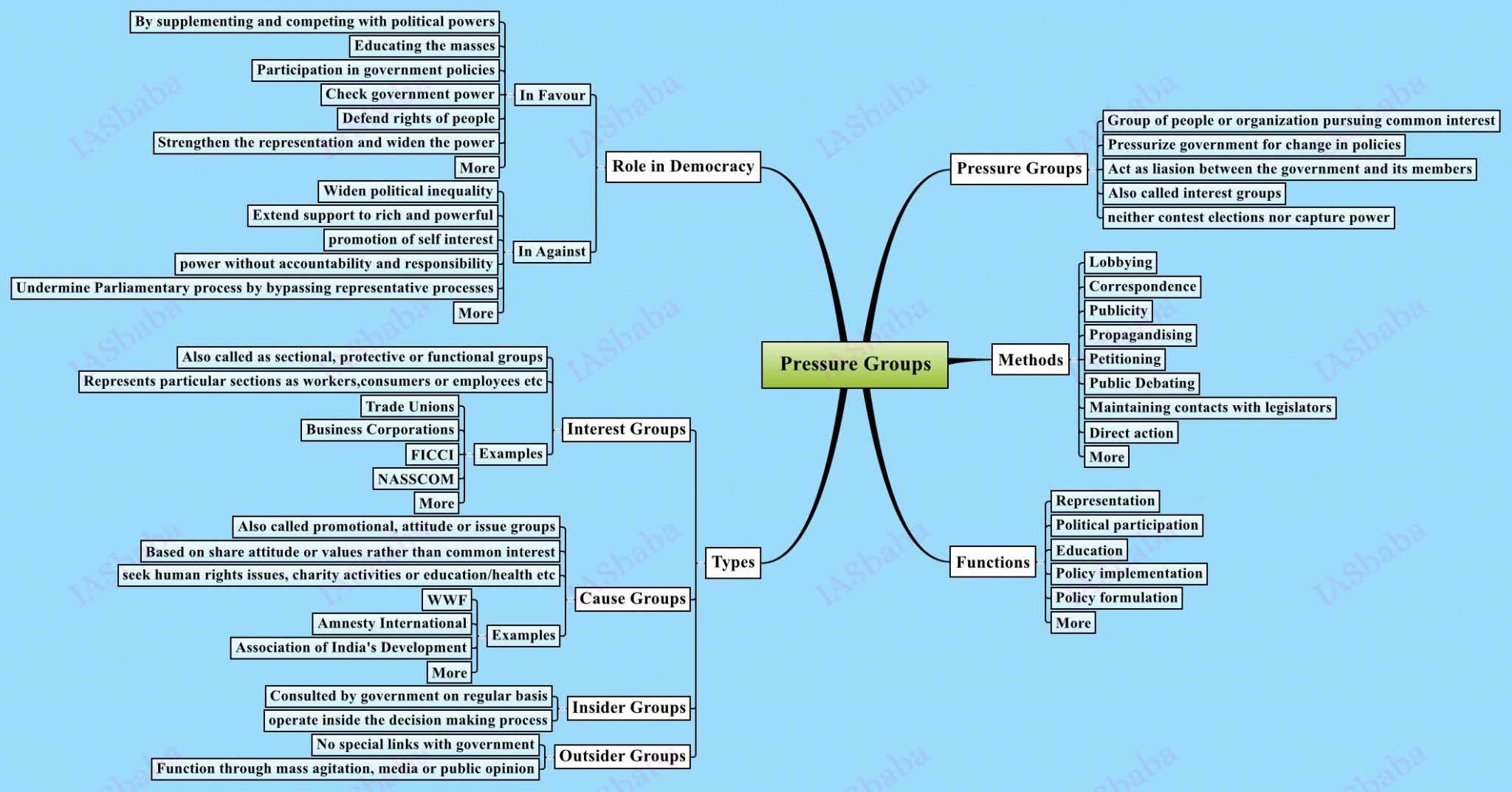
- Pressure groups can range from Business Groups (FICCI , ASSOCHAM), Trade Unions, Agrarian Groups (All India Kisan Sabha), Professional Associations (Indian Medical Associations), Student Organisations (Akhila Bharatiya Vidyarthi Parishad (ABVP)), Religious Organisation (RSS), Caste, Linguistic Groups, Tribal Organisations , Ideology based Groups (Environmental protection, Civil liberties, Women Rights). This is a very dynamic
- When you come across these groups in the Newspaper understand how they function, what are its objectives and issues involved.
- For Example, Recently an Environmental group- ‘Green Peace’ was caught in the controversy of getting funding from foreign countries to stop the functioning of Nuclear and coal-based plants in India and this has slowed down India’s energy policy implementation.
Books/Sources to Refer:
- For basic understanding refer “Introduction To the Constitution Of India” – D.D. Basu or ‘’Indian Polity” – Lakshmikanth 4th edition (Chapters 18, 19, 20, 21, 24, 25, 26, 42, 43)
- For Pressure Groups refer Chapter 61 of
- Pressure Group- Read this
- Again, Newspapers are an important source to refer for the dynamic aspects of this topic.
Previous year Questions
Pressure group politics is sometimes seen as the informal face of politics. With regards to the above, assess the structure and functioning of pressure groups in India.
Reference: With due knowledge of basic concepts regarding Pressure Groups, you will be able to answer such questions. But it is advised to go through newspapers and gather quality facts and develop opinion.
Instances of President’s delay in commuting death sentences have come under public debate as denial of justice. Should there be a time limit specified for the President to accept/reject such petitions? Analyse. 2014
- Bhullar Death Sentence
- Commutation of Death Sentence by Supreme Court citing Delay
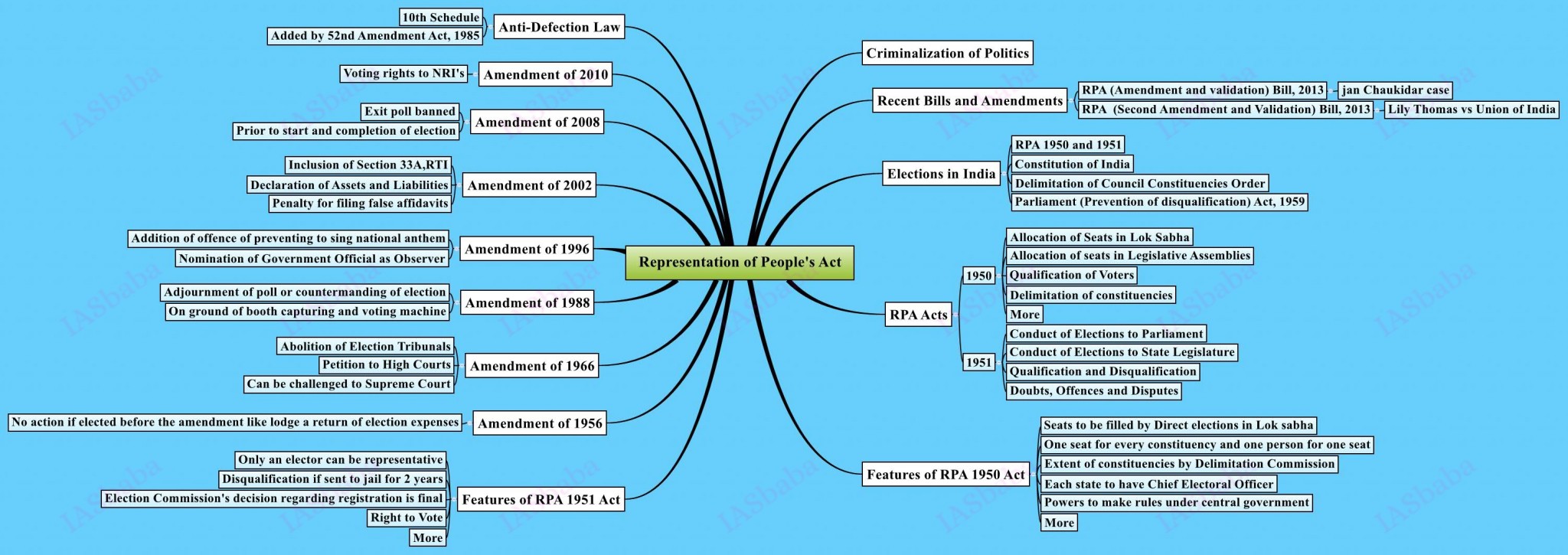
Salient features of the Representation of People’s Act.
Read the important provisions of
- RPA Act, 1950– Allocation of seats in Lok Sabha and Legislative Assemblies, Qualification of voters, Delimitation of Constituencies.
- RPA Act, 1951- Conduct of elections to Parliament and State Legislature, Qualification and Disqualification of the MP’s and MLA’s etc
- Issues related to RPA Act, has always been a hot topic of discussion be it Electoral reforms, Qualification and Disqualification of the MP’s and MLA’s, Office of profit, Anti-defection , etc.
- Every election year, Election Commission comes up with various electoral reforms on Qualification, disqualification, paid news, funding of elections etc.
- Even Supreme court has given its ruling on disqualification of MPs and MLAs with criminal background, and the recent landmark judgement on Convicted MP’s and MLA’s all have given a new scope to this topic.
Books/Sources to Refer:
- No need to refer any book or bulky notes.
- Just go through Mind Maps first and then gather related contents from internet and newspapers.
- UPSC is not going to ask decade old articles or amendments in detail.
- Look for related aspects in newspapers, any issue like recent SC Judgements, Election Commission’s initiatives, role and relevance.
- UPSC has not asked any question from this section in 2013 and 2014 hence important for next year.
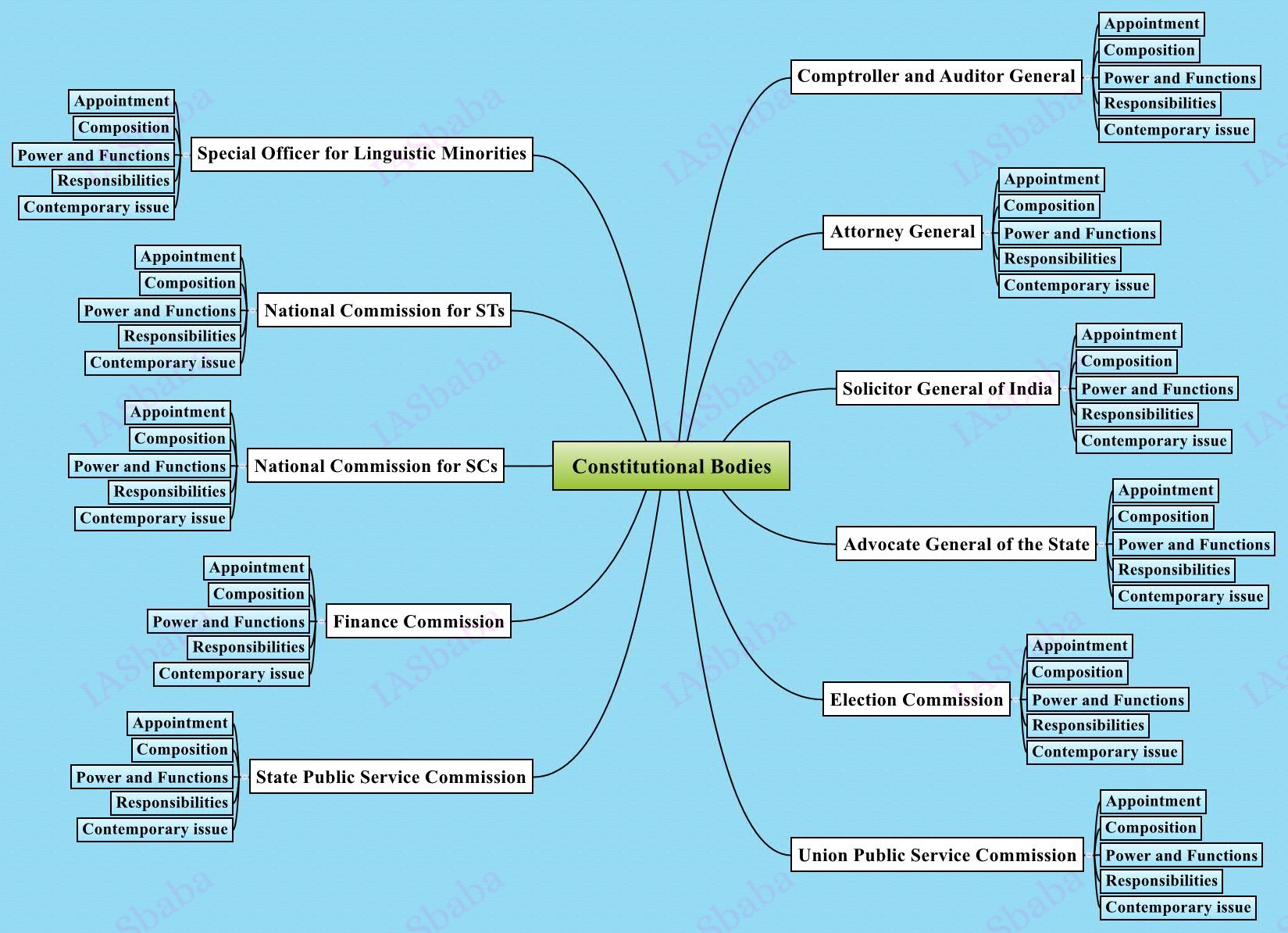
Appointment to various Constitutional posts, powers, functions and responsibilities of various Constitutional Bodies.
- Constitutional Bodies – Election Commission, UPSC, SPSC, Finance Commission, National Commission for SCs and ST’s, Special officer for Linguistic Minorities, Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG), Attorney General and Solicitor General, Advocate General of the State
- Non- Constitutional Bodies like National Development Council, National Human Rights Commission, and Central Vigilance Commission etc.
- You would have read about the mode of appointment, powers and functions of these bodies while preparing for Prelims. For MAINS, read these topics from analytical perspective.
- For example: In 2012, the appointment of CVC Commissioner, PJ Thomas was held illegal because of pending corruption case against him in the palmolein oil import scam. Though the Leader of Opposition (LoP) (who is one of the three-member committee that is constituted for the appointment of CVC Commissioner) had given a dissenting vote, he was still appointed as the Commissioner. Supreme Court, nullified the appointment and came up with the concept of ‘institutional integrity’, which should be followed in the appointment of Constitutional and Non-Constitutional Bodies.
- Or the Recent, National Judicial Appointments Commission (NJAC) all come under this topic of discussion.
Books/Sources to Refer:
- For Basics refer ‘’Indian Polity” – Lakshmikanth 4th edition (Parts VII and Part VIII)
- Newspaper for the dynamic part.
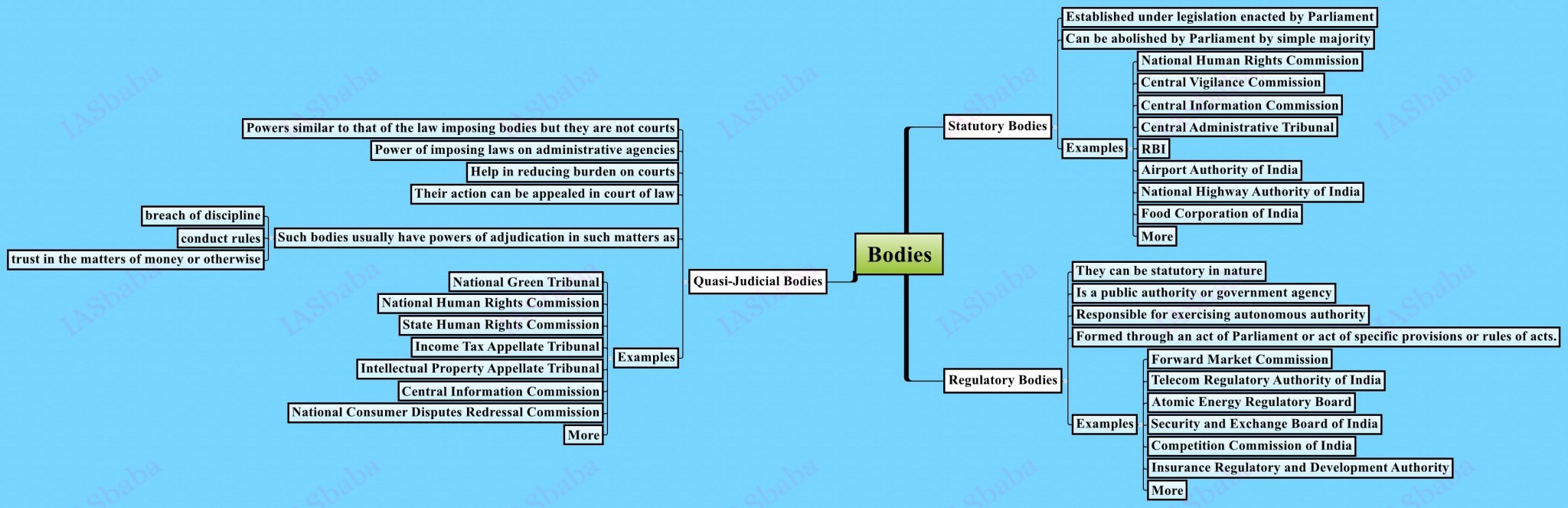
Statutory, regulatory and various quasi-judicial bodies.
- Statutory Bodies– NHRC, CVC, CIC, Lokpal, Lokayukta,
- Regulatory– SEBI, RBI, AERC, Food Safety and Standards Authority of India, TRAI, CCI, PFRDA, IRDA etc.
- Quasi-judicial bodies– NHRC, CIC, Tribunals- National Green tribunal, Appellate Tribunal for Electricity and CIC, National Consumer Dispute Redressal Commission etc.
- As you can see the Quasi-Judicial bodies overlap with the Statutory and Regulatory bodies as these bodies have quasi-judicial function too like NHRC, CIC etc.
- The Prescribed books give you enough content for the powers and functions of these bodies. But questions from this section will be framed based on the contentious issues of the bodies like overlapping functions of the regulatory bodies, jurisdictional issues, advisory nature of recommendations (not binding on the government) etc.
- Few Examples: Jurisdictional issue between SEBI and IRDA, Sri Krishna’s Committee recommendation on Unified regulatory body for financial sector.
Books/Sources to Refer:
- Only Laxmikant, Indian Polity
- Must– The Hindu, Business Standard and Economic Times
Previous Year UPSC Questions :
The product diversification of financial institutions and insurance companies, resulting in overlapping of products and services strengthens the case for the merger of the two regulatory agencies, namely SEBI and IRDA. Justify 2013
Reference: This issue was in news in 2013. You can refer to the given links for assurance.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) in India can be most effective when its tasks are adequately supported by other mechanisms that ensure the accountability of a government. In light of the above observation assess the role of NHRC as an effective complement to the judiciary and other institutions in promoting and protecting human rights standards 2014
Reference: This is a broader question. To answer this, one need to know the basic of NHRC functioning as well as the essence of the first statement, ‘NHRC in India can be most effective when its tasks are adequately supported by other mechanisms that ensure the accountability of a government’.
NHRC has always been at the opposite end of government. From revocation of AFSPA, human rights management in communally hit areas to role in Communal law and many other, it has come to stiff resistance for government.
You can only answer such questions if following a mixed strategy. There is no other way to update and generate content for such questions other than following a dynamic cum static study.
Governance and Social Justice
Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Various governmental development interventions like rural development, urban development, regional development, infrastructural development, MSME and other various industrial interventions by government etc.
- Interventions in various sectors would include allowing FDI in railways, defence etc. or bringing out reforms in Education, Health Sector, Power Sector, Agriculture sector etc.
- The emphasis must also be on the schemes launched by government like make in India, MNREGA etc and their success stories and weaknesses if any. For e.g MNREGA has been hailed as one of the successful programme in independent India and at the same time it has its criticisms. Focus on both the pros and cons and any suggestions for betterment of these programmes.
Books/Sources to Refer:
- Do not fall prey to any notes or book for preparing this topic. As you can see the evolving nature of the topic and further UPSC questions asked in previous years, you will come to know the cost of spending time reading a book for this.
- For Government Policies and Schemes under this topic- refer to Press Information Bureau and any newspapers- Hindu, Economic Times or Business Line.
- We would recommend, Business Standard and Economic Times
- Also, refer to India Year Book- Selected chapters for topic wise study only
Previous Year UPSC Questions :
Though 100 percent FDI is already allowed in non-news media like a trade publication and general entertainment channel, the Government is mulling over the proposal for increased FDI in news media for quite some time. What difference would an increase in FDI make? Critically evaluate the pros and cons. 2013
Reference: The links given below will present a good insight to answer this question.
The setting up of a Rail Tariff Authority to regulate fares will subject the cash strapped Indian Railways to demand subsidy for obligation to operate non-profitable routes and services. Taking into account the experience in the power sector, discuss if the proposed reform is expected to benefit the consumers, the Indian Railways or the private container operators.
Reference: A direct question from current affairs. Check the links below
Topics- 2, 3 and 4 are overlapping
Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections.
- Empowerment mechanisms by Government on vulnerable population like women, children, disabled, poor, transgender etc.
- Various initiatives by Government in protecting and promoting the interests of these sections like Janani Shishu Suraksha karyakram, widow and disability pension scheme, ICDS etc. Functioning of these schemes, effectiveness of these schemes in empowering the weaker sections and enabling them to be equal participants in societies etc.
- Various institutions by GOI in promoting interests of weaker sections like national commission for women, National commission for backward classes, national commission for protection of child rights etc and statutes like protection of women from domestic violence act, protection of child rights act etc.
- Basic idea about all the above mechanisms and their effectiveness in achieving their objectives must be looked at.
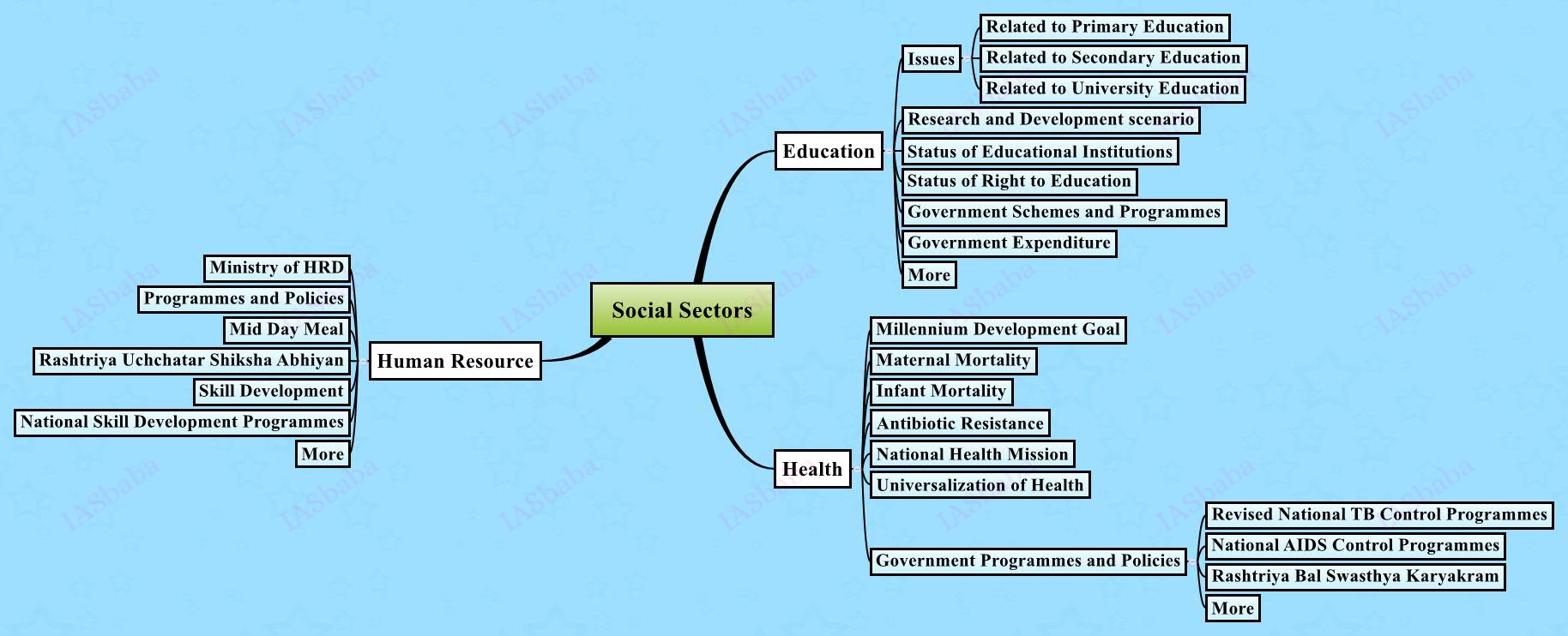
Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector or Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
- Government initiatives on promotion of health, education, skill development to utilise the human capabilities.
- Schemes like Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, Mid Day Meals programme, National Health Mission, National Skill Development Programme and various other initiatives.
- The percentage GDP spent on various sectors vis a vis other nations, rationale in spending huge sums on social services, their effectiveness, measures of accountability instilled in various programmes like school management committees in RTE act to monitor functioning of schools etc.
- Status of RTE Act
- Universalisation of Health and Education
- Status of higher education and scientific research in India.
- Reasons for poor achievement of results in various interventions and other accountability enhancing measures etc.
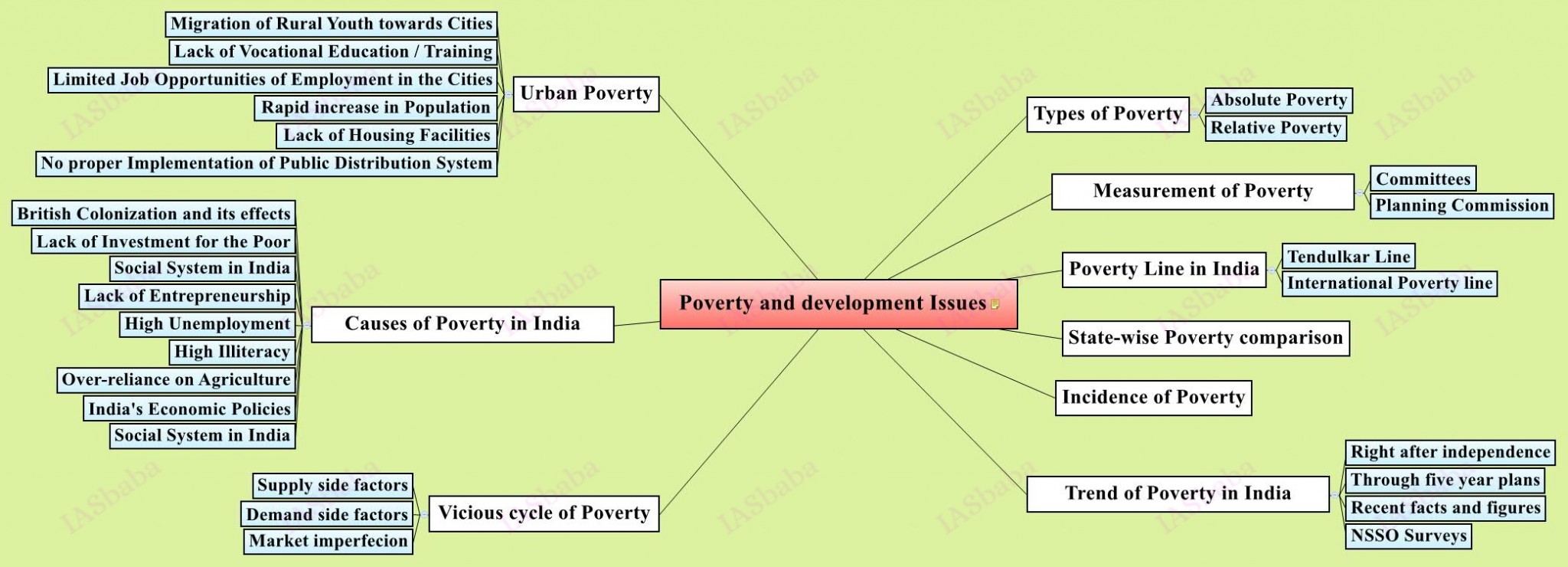
Issues relating to poverty and hunger.
- Definition of poverty, official measurement of poverty, recommendations of committees like S. Tendulkar and C. Rangarajan on deciding the poverty line and measurement of poverty, reasons for poverty etc.
- Various poverty alleviating measures like Income augmentation, PDS, National food security act etc. Their broad principles, objectives, effectiveness in functioning, operational deficiencies, weaknesses like ghost beneficiary leakages poor targeting etc.
Books/Sources to Refer:
- Topic, 2 ,3 and 4- No book recommended other than India Year Book
- Since you must have covered basic polity from mentioned books, there is no need to separately prepare for these topics. Moreover the questions are opinion based that will assess your analytical perspective.
- The above topics are solely current affair based. You will already be covering these topics from daily current events.
- If you want some background and facts, refer to Economic Survey and 12th Plan
For above topics – Questions are also of overlapping nature
Do government’s schemes for up-lifting vulnerable and backward communities by protecting required social resources for them, lead to their exclusion in establishing businesses in urban economics? 2014
Reference: Opinion based but you will find many articles in newspapers to build content.
Should the premier institutes like IITs/IIMs be allowed to retain premier status, allowed more academic independence in designing courses and also decide mode/criteria of selection of students. Discuss in light of the growing challenges. 2014
Reference: Status of higher Education in India. Since a report came highlighting the poor performance of Indian Institutes on global level, there were several articles and debates surrounding it.
Two parallel run schemes of the Government viz. the Aadhar Card and NPR, one as voluntary and the other as compulsory, have led to debates at national levels and also litigations. On merits, discuss whether or not both schemes need run concurrently. Analyse the potential of the schemes to achieve developmental benefits and equitable growth. 2014
Reference: The hint for this question is here in this article published in The Hindu in July, 2014
The concept of Mid Day Meal (MDM) scheme is almost a century old in India with early beginnings in Madras Presidency in pre-independent India. The scheme has again been given impetus in most states in the last two decades. Critically examine its twin objectives, latest mandates and success. 2013
Reference– Mid Day Meal Mishap in Bihar
The Central Government frequently complains on the poor performance of the State Governments in eradicating suffering of the vulnerable sections of the society. Restructuring of Centrally sponsored schemes across the sectors for ameliorating the cause of vulnerable sections of population aims at providing flexibility to the States in better implementation. Critically evaluate.
Reference: in 2013, Government restructured CSS by merging 147 schemes into 66. You can find several articles from newspapers.
Electronic cash transfer system for the welfare schemes is an ambitious project to minimize corruption, eliminate wastage and facilitate reforms. Comment
Reference: Electronic Cash Transfer was announced in 2013. Several articles came in favour and against too. Since the question asked for comment, you need to give both side arguments and your views. These articles will be handy
Identify theMillennium Development Goals (MDGs) that are related to health. Discuss the success of the actions taken by the Government for achieving the same. 2013
Reference: Since the target for achieving MDG is 2015 and India has not fared well in Health indicators like MMR and IMR, this question requires current affairs updates. Several articles can be found from various newspapers.
Development processes and the development industry- the role of NGOs, SHGs, various groups and associations, donors, charities, institutional and other stakeholders.
- Augmentation role played by Civil society organisations like NGOs, SHGs
- Their potential in alleviating poverty, creating employment, development initiatives, awareness generation programs on various schemes of government and the supplementary role played by NGOs in resource generation, acting as eyes and ears of government, extending the reach of government etc.
- Emphasis must be on case studies of success stories of SHG and NGOs in various sectors etc.
- Weaknesses of SHGs like socio cultural restrictions, poor resources etc and the measures taken by government in strengthening these institutions must be known.
- Issues related to various NGOs and Charity institutions, criticisms of promoting interests of a section of people, slowing the developmental initiatives of government through environmental blockages, lack of transparency in foreign funding, issues related to FCRA act must be covered.
- Emphasis must be on current issues from newspaper.
Books/Sources to Refer:
- No separate book is required.
- SHG – Link 1 and Link 2
- NGO and Development issues
- Focus on current affairs and newspapers you are following
Previous Year Questions
The penetration of Self Help Groups (SHGs) in rural areas in promoting participation in development programmes is facing socio-cultural hurdles. Examine 2014
Reference: A very broad question. No book will come to your rescue other than current affairs. You need to create dimensions to answer such question. Even if you go blank just sit and think for some time. Once you develop the habit of relating current aspects to static, these questions will never bother you. All you need is various view points and thought process.
The legitimacy and accountability of Self Help Groups (SHGs) and their patrons, the micro-finance outfits, need systematic assessment and scrutiny for the sustained success of the concept. Discuss 2013
Reference: Same as above
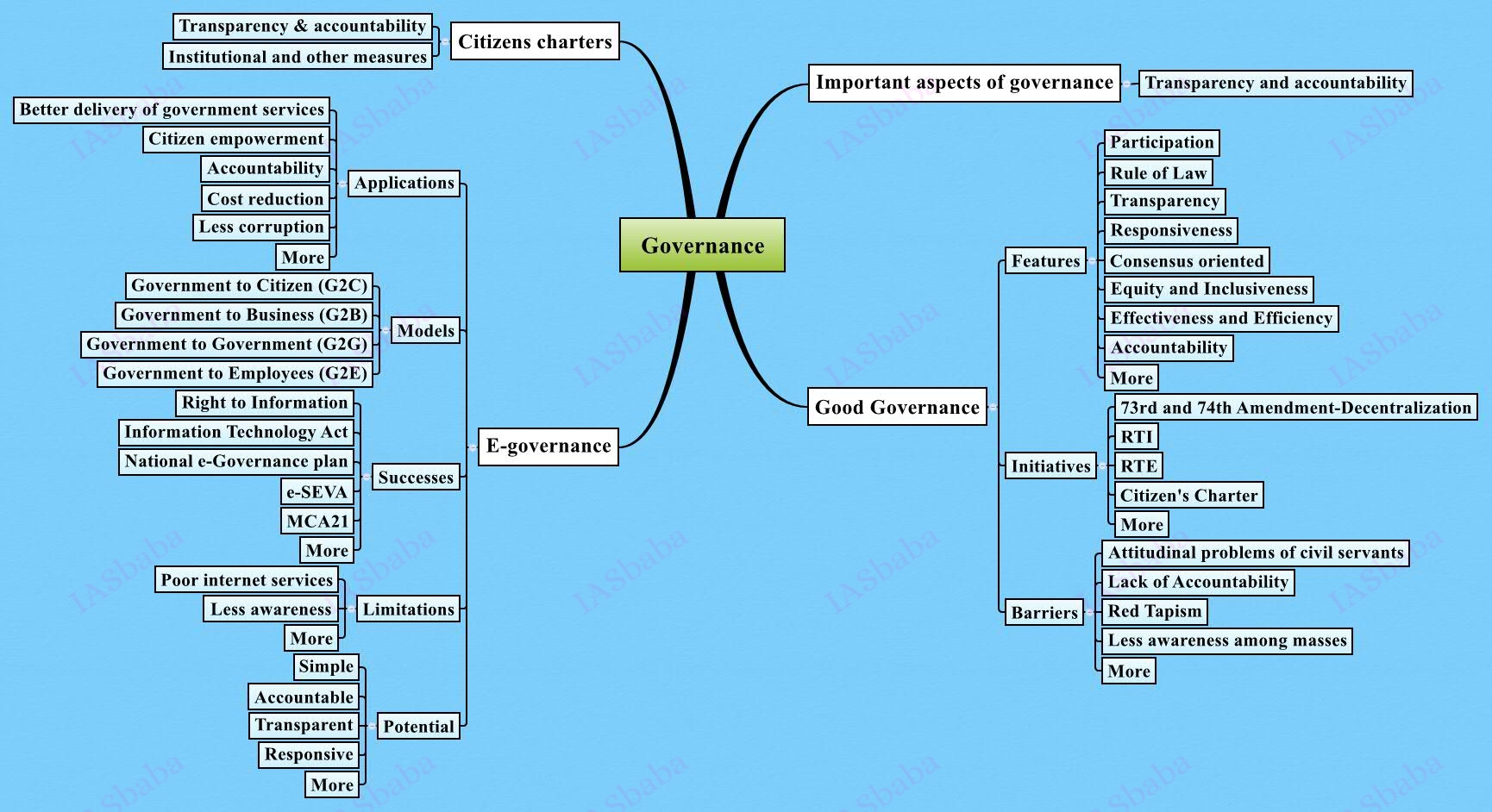
Important aspects of governance, transparency and accountability, e-governance- applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential; citizens charters, transparency & accountability and institutional and other measures.
- Measures taken by Government in enhancing transparency, accountability, participation, effectiveness of governance like RTI, Citizens charter, right to service delivery and grievance redressal mechanisms, whistle blowers act etc.
- Their effectiveness and weaknesses like delay in disposing of RTI related queries, delay in appointment of heads of information commissions, pendency of cases, security of RTI activists, poor enforcement of decisions by information commissions, vague commitments and lack of enforcement mechanisms of commitments in citizens charter etc.
- Concentrate on the recent cases which were instrumental in enhancing transparency in government and also cases of non commitment by various organs to the orders of CIC.
Books/Sources to Refer:
- Governance in India– Laxmikanth
- ARC 12th Report- Citizen Centric Administration
- ARC 11th Report- Promoting e- Governance
- Report- Open India– Read selectively
- Focus on newspapers, Yojana and Kurukshetra magazines
- Websites of respective ministries for update.
Previous Year Questions
Though Citizen’s charters have been formulated by many public service delivery organizations, there is no corresponding improvement in the level of citizens’ satisfaction and quality of services being provided? Analyze 2013
Reference: A basic question. Once you read the basics about Citizen Charter and Public Service Delivery Mechanism and follow the current affairs updates, you can easily chalk out several points to write an effective answer.
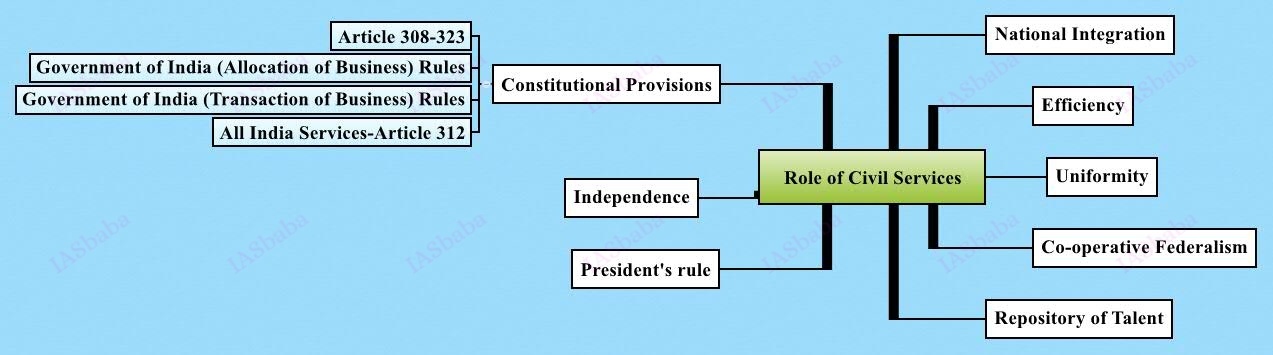
Role of civil services in a democracy.
- The role played by civil services in maintaining the stability of government, developmental role, regulatory role and implementing the constitutional obligations of the country etc.
- For e.g the functions of DC which involves developmental role like implementing various government schemes and assisting panchayats in carrying out their functions etc, law and order like maintaining prisons in district and issuing gun licenses, regulatory etc must be aware of.
- Relation between political executives and permanent executive, external and internal pressures in performing the functions etc.
Books/Sources to Refer:
- Read this for Civil Services reforms
- Governance in India– Laxmikanth
- Newspapers
Previous Year Question
Has the Cadre based Civil Services Organisation been the cause of slow change in India? Critically examine. 2014
Reference: In 2014, new rule for minimum 2 years of posting for IAS, IFoS and IPS came into existence. However this question is very broad one. There are other prominent reasons for the slow change, cadre based is among one of them.
International Relations- Click on the next Tab above (next to Paper 2)
All the best
IASbaba