IASbaba's Press Information Bureau
IASbaba Press Information Bureau 3rd June to 9th June, 2018
GS-2
Launch of ‘JANAUSHADHI SUVIDHA’ – Oxo-biodegradable Sanitary Napkin
(Topic: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health)
Why: According to the National Family Health Survey 2015-16, about 58 percent of women aged between 15 to 24 years use locally prepared napkins, sanitary napkins and tampons. Further, about 78 percent women in urban areas use hygienic methods of protection during menstrual period; only 48 percent women in rural areas have access to clean sanitary napkins.
Under: Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP)
Affordable sanitary napkins at Rs. 2.50 per pad now available at over 3600 Janaushadhi Kendras functional in 33 States/UTs across India
Ensure Affordability, Hygiene as well as Ease of use and disposal for them
- Jan Aushadhi Suvidha comes with a special additive, which makes it biodegradable when it comes in contact with oxygen after being discarded. This would ensure ‘Swachhta, Swasthya and Suvidha’ for the underprivileged Women of India
- The average price of sanitary napkins available in the market today is around Rs. 8 per pad, whereas now with the launch of the SUVIDHA napkins at Rs. 2.50 per pad, this will go a long way in making the basic hygiene requirement aid for Women affordable for the underprivileged sections.
- One of the most important requirement in ensuring the Health Security to that section of Women in India who still use unhygienic aids during menstrual period due to non-affordability of some of the popular brands of sanitary napkins available in the market today. Such unhygienic aids cause fungal infections, Reproductive Tract Infection, Urinary Tract Infection, Cervical cancer and also make women vulnerable to infertility.
Ministries of MSME and Ayush Sign MoU for the Development of Ayush Enterprises
(Topic: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health)
The MoU will create synergies through the institutions and schemes of both ministries for the development of AYUSH enterprises in the country.
Objective: To position India as a world leader in “Holistic Healthcare”.
- AYUSH is a rising sector, having immense potential for preventive, curative and rehabilitative health and has been part of India’s socio-cultural heritage.
- AYUSH industry include the Ayurveda, Unani, Siddha and Homoeopathy drug manufacturing units as well as the healthcare delivery centers in public & private sectors and are essentially dominated by MSMEs, which need handholding support in the areas of entrepreneurship development, capacity building and financial assistance in order to grow and increase the market share of AYUSH.
- The domestic market for AYUSH sector has been increasing steadily over the past decade. There is also an acceptance of traditional medicines worldwide. Therefore, export of AYUSH products like food supplements, nutraceuticals and herbal extracts has increased significantly.
In order to benefit from this the Ministries of MSME and AYUSH have agreed to join hands for developing enterprises in this sector. Both Ministries will organize regional workshops for entrepreneurship development in AYUSH sector and Ministry of MSME will frame new schemes for AYUSH industries to get the benefits of SIDBI.
Cabinet Approves
Extension of Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between India and Netherlands on technical cooperation in the field of Spatial Planning, Water Management and Mobility Management: to promote and strengthen the collaboration between the signatories in the areas of Spatial Planning, Water Management and Mobility Management on the basis of equivalence, affordable housing, smart city development, geographical information system (GIS) for water supply & sewerage system, waste water reuse and recycle, conservation of fresh water by artificial recharge of aquifer, integrated solid waste management and heritage conservation and mutual benefit, taking into account the practical needs of both the countries.
Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between India and Denmark on technical cooperation in the field of Sustainable and Smart Urban Development: To promote bilateral cooperation in the field of sustainable and smart urban development on the basis of reciprocity and mutual benefit through exchange of knowledge, institutional cooperation, research & development and commercial relations on related issues. Areas of cooperation include smart urban solutions, liveability, sustainable and integrated urban planning, re-development and land use, integrated solid waste management including waste to energy, sustainable transport systems, water and sanitation management, energy efficiency, resource mobilization and other related areas mutually agreed upon.
Between India and United Kingdom on technical cooperation in the field of Sustainable Urban Development: To facilitate and strengthen India-UK institutional cooperation in the field of sustainable urban development. The areas of cooperation include smart cities development, solid waste management, green affordable housing, waste water management, capacity building of urban institutions, skill development in urban areas, urban mobility, intelligent transport system and transit-oriented development, innovative access to finance and other related areas as mutually agreed upon by the Contracting Parties.
Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark-III Continuation Programme – Phase 6 – Thirty Operational Flights of PSLV: The Programme will also meet the launch requirement of satellites for Earth observation, Navigation and Space Sciences. This will also ensure the continuity of production in Indian industry.
Memorandum of Understanding between India and Oman on Cooperation in the peaceful uses of outer space: Enable the following areas of cooperation such as, space science, technology and applications including remote sensing of the earth; satellite based navigation; Space science and planetary exploration; use of spacecraft and space systems and ground system; and application of space technology.
Agreement between India and France on technical cooperation in the field of Sustainable Urban Development: To promote technical cooperation in the areas of smart cities development, development of urban mass transportation systems, urban settlements and utilities (water supply and sewerage systems), disposal and treatment of solid waste, landfill remediation, management of non-revenue water, water reuse & recycle, technology transfer, conservation of fresh water by artificial recharge of aquifer, circular economy, mass housing, green housing, urban planning, heritage, human resource development, capacity building and other related areas as mutually agreed by the Contracting Parties.
GS-3
Achievements of Power Ministry during last 4 years
(Topic: Infrastructure: Energy)
(i) Generation capacity-
- 1 Lakh MW generation capacity added. (2,43,029 MW in March 2014 to 3,44,002 MW in March 2018)
- India emerges as net exporter of electricity. 7203 MU supplied to Nepal, Bangladesh and Myanmar in FY 2017-18.
- Energy deficit reduced from 4.2 per cent (in FY 2013-14) to 0.7 per cent (in FY 2017-18)
(ii) One Grid One Nation-
- Expansion of transmission grid by 1 lakh ckm
- Highest ever transformation capacity addition of 86,193 MVA in FY 2017-18
- 26 projects worth Rs. 48,427 crore awarded through Tariff Based Competitive Bidding
- Inter-regional transfer capacity addition more than tripled (16,000 MW in FY 2010-14 and 50,500 MW in FY 2014-18)
(iii) Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGKY)
- 100 per cent of village electrification
- Outlay of Rs. 75,893 crore
- Funds to states increased by 2.5 times (Rs. 10,873 crore in FY 2010 -14 and Rs 24,890 crore in 2014-18)
- 2,56,750 km HT and LT lines
- 4,09,989 distribution transformers
(viii) Integrated Power Development Scheme (IPDS)
- Outlay of Rs. 65,424 crore
- 1376 towns IT enabled
- 1900 additional towns under progress
- 1156 towns reported reduction in AT&C losses
- 1,29,093 km HT and LT lines
- 66,947 distribution transformers
(vii) UDAY
- More than Rs 20,000 crore interest cost saved by DISCOMs under UDAY
- Reduction in AT&C losses in 17 states within one year of operation
- Revenue gaps bridged by 33 per cent in one year of operation
- India’s rank improved to 29 in 2018 from 111 in 2014on World Bank’s Ease of Getting Electricity Ranking.
(vi) SAUBHAGYA
- Launched for universal electrification
- Camps organised at village level. Minimum documentation required
- Special drive for economically weaker sections under Gram Swaraj Abhiyan
- 60.34 lakh households electrified since 11th Oct, 2017
(ix) Power for All 24*7 –
- Joint initiative of Govt. of India and State Govts.
- Roadmap for 24*7 power supply prepared. States ready to ensure 24*7 Power for all from 1st April, 2019.
(x) Focus on North-East region-
- Electrification of 5855 villages and intensive electrification of 9004 villages completed.
- 130 towns IT enabled.
- 52.28 lakh LED bulbs distributed under UJALA
- Rs. 9866 crore projects undertaken for strengthening/development of intra-state transmission
(iv) UJALA
- 107 crore LED bulbs distributed
- 30.01 crore LED bulbs distributed under UJALA resulting in saving of 15,500 crore per year
- 77.99 crore additional LED bulbs distributed by industry.
- 87 per cent reduction in LED bulb procurement cost through demand aggregation.
(v) 4376 MW hydel capacity addition (FY 2014-18)
Innovations and Initiatives-
Electric vehicles –
- No licence required for charging stations
- Procurement of 10,000 e-vehicles for Government institutions
Smart Metering-
- Procurement of 50 lakh smart meters done.
- 1 crore prepaid meters under procurement
Energy efficiency-
- Star labelling program saved energy worth Rs. 22,500 crore.
- Energy efficiency measures through PAT in large industries saved energy worth Rs. 9500 crore
- Energy Conservation Building Code for energy efficient buildings launched in June, 2017
Digital initiatives-
- e-Bidding and e-Reverse Auction for short and medium term procurement of power.
- Enabling payments through NPCI platforms such as BHIM, BBPS, Bharat QR etc. More than 24 crore digital transactions in FY 2017-18 for electricity bill payments.
To bring transparency and to disseminate information to public at large following Apps are launched by the Ministry of Power:
- SAUBHAGYA – App for tracking household electrification.
- VidyutPravah – The Mobile/Web App provides real time information of current demand met, shortages if any, surplus power available and the prices in Power Exchange.
- UJALA (UnnatJyoti by Affordable LED`S for All) – App provides real time updates on the LED distribution happening across the country.
- UrjaMitra – monitoring of power availability and sending power cut information through SMS
- MERIT– information pertaining to marginal variable cost and source wise purchase of electricity.
- UDAY- Allows people to compare DISCOMs on the basis of 26 major performance parameters.
- URJA (Urban Jyoti Abhiyaan) – It is an informative App for Urban Distribution Sector. It captures Consumer centric parameters from the IT systems created under IPDS.
- TARANG (Transmission App for real time monitoring & Growth) – It is an IT Web/mobile based platform to provide status of both inter and intra state Transmission Projects in the country. This platform also shows the prospective interstate as well as intra state Transmission Projects.
- DEEP e-bidding (Discovery of Efficient Electricity Price) – The portal will provide a common e-bidding platform with e-reverse auction facility to facilitate nation-wide power procurement through a wider network so as to bring uniformity and transparency in the process of power procurement.
- Ash Track- linking fly ash users and power plants for better ash utilisation.
“Methanol Economy”: NITI Aayog
(Topic: Infrastructure: Energy)
What is it?
- Methanol Economy is the “Bridge” to the dream of a complete “Hydrogen based fuel systems”.
- Methanol is a scalable and sustainable fuel, that can be produced from a variety of feedstocks like Natural Gas, Coal (Indian High Ash Coal), Bio-mass, Municipal Solid waste and most importantly from CO2.
- The Concept of “Methanol Economy” is being actively pursued by China, Italy, Sweden, Israel, US, Australia, Japan and many other European countries. 10% of fuel in China in transport Sector is Methanol.
Why?
- Methanol is an alternative fuel for internal combustion and other engines, either in combination with gasoline or directly (“neat”).
- Methanol is less expensive to produce sustainably and is a less expensive way to reduce the carbon footprint.
- Methanol burns efficiently in all internal combustion engines, produces no particulate matter, no soot, almost nil SOX and NOX emissions (NEAR ZERO POLLUTION). The gaseous version of Methanol – DME can blended with LPG and can be excellent substitute for diesel in large buses and trucks. To adopt Methanol as a transport fuel, it requires minimal infrastructure modifications and capital both in vehicles and in terminal and distribution infrastructure.
Why does Methanol have the potential to be an enduring solution to human energy needs?
Because the beltched out C02 (greenhouse gas emission) both from using Methanol and while producing Methanol can be tapped back to produce Methanol. Thereby a seamless loop of CO2 sequestration cycle is created to perpetually burn fuels without polluting the environment at all.
NITI Aayog’s plan
NITI Aayog has drawn out a comprehensive plan to replace 20% of crude imports from Methanol alone. Adopting Methanol in this scale would bring down pollution in the country by more than 40% and not to forget the benefits from import substitution.
Indian Railways alone burns three billion litres of diesel every year. Plans are in place to convert 6000 diesel railway engines to work on 100% Methanol and make railways a carbon neutral organisation.
India by adopting Methanol can have its own indigenous fuel at the cost of approximately Rs. 19 per litre at least 30% cheaper than any available fuel. Methanol fuel can result in great environmental benefits and can be the answer to the burning urban pollution issue.
Please Note:
June 21st: International Yoga Day
June 5th: World Environment Day; Prime Minister’s ‘mantra’ of 6 Rs –
- Reduce
- Recycle
- Reuse
- Retrieve
- Recover
- Redesign
- Remanufacture
First World Bicycle Day: 3rd June
Gulf of Aden
- Also known as the Gulf of Berbera
- Amidst Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea and Guardafui Channel to the east, Somalia to the south, and Djibouti to the west
- In the northwest, it connects with the Red Sea through the Bab-el-Mandeb strait, and in the southeast, it connects with the Indian Ocean through the Guardafui Channel
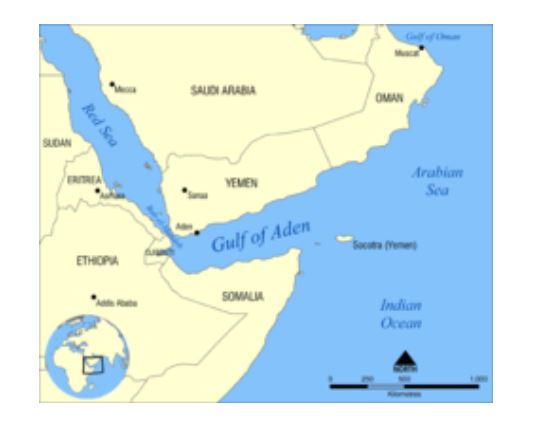
Socotra, Yemen – A very Severe Cyclonic Strom Mekenu – Operation NISTAR
Agni-5 missile: Long range ballistic missile
- Intercontinental ballistic missile developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of India
- Other intercontinental missile countries: P5+Israel
- Canister based (Road mobility, all weather, flexible launching) [Others: Shaurya, Brahmos (Only supersonic cruise missile in the world)]
- Range: >5ooo km
- 3 stage solid propellant
- Nuclear warhead
- Usage: small satellites, shoot down enemy satellites in short range
Ganga Praharis: A new grassroot-level volunteer workforce is out there to protect the bio-diversity of river Ganga. A group of 427 trained volunteers are reaching to each and every house in areas along river Ganga to educate them about the importance of protecting river’s bio-diversity. They are spread over Ganga basin states of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, Bihar and West Bengal.
Zigzag technology: To reduce carbon emissions from burning of bricks in brick kilns
As part of the Nationally Determined Contributions, India is committed to reducing thirty-three to thirty-five percent of emission intensity of its GDP during 2005 to 2030.
India’s Journey in Renewable Energy
- Globally, India stands 4th in wind power 5th in renewable power and 6th in solar power installed capacity.
- India is well on track to achieving 175 GW target of installed renewable energy capacity.
- KUSUM – Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan Scheme
- SRISTI – Sustainable Rooftop Implementation for Solar Transfiguration of India – new scheme for solar rooftop
- Transparent bidding and facilitation for procurement of solar and wind power through tariff based competitive bidding process have led to significant reduction in cost of solar and wind power.
Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission (JNNSM)
- One of the several initiatives that are part of the National Action Plan on Climate Change
- To establish India as a global leader in solar energy, by creating the policy conditions for its diffusion across the country as quickly as possible
- 21 MW Solar PV projects have been undertaken with meticulous planning by Indian Navy towards achieving the GOI target of 100 GW by 2022
Ministry of Railways PSU IRCTC introduces bagasse based food packaging to commemorate World Environment Day 2018 – Bagasse, the fibrous remains left behind after extracting sugarcane juice, is being used to make disposable cutlery and containers in which meals will be served. Provision will be made to collect the used packaging which will then be processed for disposal through composting to ensure environmental sustainability.
Under the Swachh Bharat Mission, the largest behavior change programme in the world, the rural sanitation coverage of India has now risen to 85%. Through mobilization of rural communities, 7.4 crore toilets have been built across rural India, and as an outcome, over 3.8 lakh villages and 391 districts have been declared Open Defecation Free (ODF). This is significant because, under the Swachh Bharat Mission (Grameen), sanitation coverage has increased to more than double the coverage at the time of the launch of the Mission.
Krishi kalyan Abhiyaan: To aid, assist and advice farmers on how to improve their farming techniques and raise their incomes
- Will be undertaken in 25 Villages with more than 1000 population each in Aspirational Districts identified in consultation with Ministry of Rural Development as per directions of NITI Ayog.
- In districts where number of villages (with more than 1000 population) is less than 25, all villages will be covered.
- Various activities to promote best practices and enhance agriculture income:
- Distribution of Soil Health Cards to all farmers
- 100% coverage of bovine vaccination for Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) in each village
- 100% coverage of Sheep and Goat for eradication of Peste des Petits ruminants (PPR )
- Distribution of Mini Kits of pulses and oilseeds to all
- Distribution of Horticulture/Agro Forestry/Bamboo plant @ 5 per family(location appropriate)
- Making 100 NADAP Pits in each village
- Artificial insemination saturation
- Demonstration programmes on Micro- irrigation
- Demonstrations of integrated cropping practice
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana –
- For extending the coverage of irrigation ‘Har Khet ko pani’ and improving water use efficiency ‘More crop per drop’ in a focused manner with end to end solution on source creation, distribution, management, field application and extension activities
- PMKSY has been formulated amalgamating ongoing schemes viz.
- Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP) of the Ministry of Water Resources,
- River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation (MoWR,RD&GR)
- Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP) of Department of Land Resources (DoLR)
- On Farm Water Management (OFWM) of Department of Agriculture and Cooperation (DAC)
President Approves Promulgation of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Amendment) Ordinance, 2018: Link 1 + Link 2
Drop in Maternal Mortality Rate: According to the just released SRS bulletin (2016), India has shown impressive gains in reduction of Maternal Mortality with 22% reduction in since 2013. Nearly one thousand fewer women now die of pregnancy related complications each month in India. Maternal Mortality Ratio of India has declined from 167 in 2011-2013 to 130 in 2014-2016.
Consumer Protection Bill, 2018: The Bill provides for setting up of an executive agency to be called Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA), which will look into unfair trade practices, misleading advertisements etc., provision for ‘mediation’ as an alternate disputes resolution mechanism to facilitate quick disposal of consumer disputes, provision for product liability action arising out of injury to a consumer from a defective product and several provisions relating to simplification of the adjudication process in the consumer Commissions.
New Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) Act, 2016: The new Act has provisions of bringing under compulsory certification regime any goods or article of any scheduled industry, process, system or service which it considers necessary in the public interest or for the protection of human, animal or plant health, safety of the environment, or prevention of unfair trade practices, or national security. It also provides for notifying multiple types of conformity Assessment Schemes, including Self declaration of conformity, to facilitate ease of doing business for the manufacturers. It has provision for making hallmarking of the precious metal articles mandatory.
INGRAM under National Consumer Helpline launched to provide a common IT platform for various stake holders involved in the Consumer Grievance Redressal Mechanism and for disseminating information to consumers.












