IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs (Prelims + Mains Focus)- 28th June 2018
Archives
(PRELIMS+MAINS FOCUS)
U.S. postpones 2+2 dialogue with India
Part of: GS Mains Paper II- International relations; India and the World
In News:
- 2+2 dialogue involving the defence and foreign ministers of India and the United States has been postponed.
- This was the second time that USA has postponed the maiden 2+2 dialogue with India.
Rift between India and US: Fast recap
- On Iran Sanctions: India had refused to cut down on all oil supplies from Iran. In other words, India is unwilling to accept US diktat on stopping all oil imports from Iran
- On India’s plans to acquire the Russian S-400 missile system: Indo-US ties are also being tested over defence supplies from Russia including S-400 missile defence system and impending sanctions if India went ahead with the purchase.
- Trade protectionism of Trump administration has forced India to impose retaliatory measures. We recently read that India has notified higher tariffs on several items imported from the U.S.
- Several issues/disputes in World Trade Organisation (WTO); Trade protectionism; Disputes on the new American steel and aluminium tariffs; disputes on Indian price reductions on medical devices
- Harley-Davidson motorcycles row – US calling for India to scrap its 75-100% tariffs
Article link: U.S. postpones 2+2 dialogue with India – The Hindu
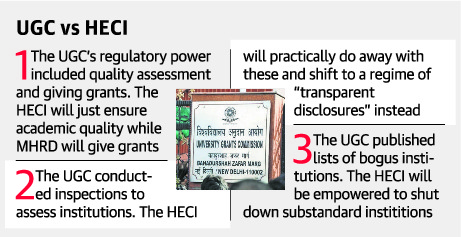
Centre may scrap University Grants Commission (UGC)
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Government policies and schemes; Education Reforms
In news:
- Government is set to replace UGC with a higher education commission by repealing the UGC Act, 1951.
- Government proposes to introduce new regulator – Higher Education Commission of India (HECI)
- The focus of HECI will be on improving academic standards and the quality of Higher Education.
- The proposed commission will have 12 members appointed by the Central Government, apart from the chairperson and vice-chairperson.
What does the draft Higher Education Commission of India (Repeal of University Grants Commission Act) Act, 2018 contain?
- HECI Bill 2018 seeks to repeal UGC Act and provides for setting up of Higher Education Commission of India.
- The draft HECI bill takes away funding powers from the proposed regulator and gives it powers to ensure academic quality.
- In other words, unlike UGC, HECI will not have grant functions and would focus only on academic matters. The ministry will deal with the grant functions.
- HECI will also be backed with penal powers to order closure of institutes that violate set norms, imposition of fines where necessary and provisions for imprisonment up to three years where necessary.
Pic: https://d39gegkjaqduz9.cloudfront.net/TH/2018/06/28/DEL/Delhi/TH/5_01/7b5a094b_2205129_101_mr.jpg
Article link:Centre may scrap UGC, proposes new regulator – Today’s Paper
Hayabusa2 probe: Ryugu asteroid
Part of: GS Prelims – Science and Technology; Space missions
In news:
- A Japanese probe called Hayabusa2 successfully settled above the Ryugu asteroid.
- Hayabusa2 probe to collect information about the birth of the solar system and the origin of life after a more than three-year voyage through deep space.

Pic: Ryugu asteroid (https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/szvi4w/article24273216.ece/alternates/FREE_660/THJC-SPACE-JAPANPROBE)
Do you know?
- UN’s International Asteroid Day on June 30, a global event to raise awareness about the hazards of an asteroid impact and technological progress to counter such a threat.
(MAINS FOCUS)
GOVERNMENT POLICY/SCHEME
TOPIC: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, institutions and bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Ujjwala Revolution
Introduction:
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana is a scheme of the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas for providing LPG connections to women from Below Poverty Line (BPL) households.
- Last month, the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) completed two years of operation.
About PMUY
- Under the scheme, five crore (now 8 crores) LPG connections are to be provided to BPL households. The identification of eligible BPL families will be made in consultation with the State Governments and the Union Territories.
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) aims to safeguard the health of women & children by providing them with a clean cooking fuel – LPG, so that they don’t have to compromise their health in smoky kitchens or wander in unsafe areas collecting firewood.
- The ambitious scheme also laid down a condition — that the LPG connections will be issued in the name of the women of the households.
- Encouraged by the rapid release of connections, the central government revised the target and scope of the scheme to eight crore connections by March 2020.
- Under the scheme, the union government bears the connection cost of ₹1,600 per connection, and each household pays about ₹1,500 for the stove and the first LPG cylinder. Centre to raise allocation for the project to ₹4,800 crore
Key highlights:
- Number of LPG connections has crossed 4 crore
- LPG penetration in India has risen from 56% in 2014 to 80%
- However, greater challenge for the mission lies in refills
Studying the usage of gas by PMUY customers and visiting multiple villages across the country, the following features of the programme are evident.
- One, interactions with PMUY subscribers suggest that they focus on the value that LPG generates for them and not on its cost.
- Two, the programme has also witnessed the emergence of a peer learning platform: the Pradhan Mantri LPG Panchayat. LPG Panchayats being held at village levels across India are helping more and more people appreciate the advantages of clean fuel.
- The adoption of LPG has received a boost with supplies ramping up and service improving.
Conclusion:
PMUY is a bold new initiative that aspires to fundamentally address one of the pressing energy–access, health and gender challenges in the country.
The programme has been successful in introducing a sense of urgency into the transition to modern cooking fuels and disbursing connections. But it has been less successful in introducing a sustained change because of issues around affordability and reliability of LPG supply.
Government needs to re-look at their connection focused approach, and should ensure adequate provisions for affordability, availability, and accountability.
This will propel PMUY to achieve the desired objective of not only disbursing connections but making the LPG sector a real contributor to overcoming this deep-rooted challenge affecting energy access, health, and gender disparity.
There needs to be a synergy in the Gas connection with the Electricity connection.
Connecting the dots:
- Why having an LPG connection important for woman empowerment? In this regard, do you think Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana can make a difference? Examine. Also discuss its other advantages.
ECONOMY
TOPIC: General Studies 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
- Inclusive growth and development; Commercial disputes
United Nations Commission on International Trade Law on Commercial Disputes
Introduction:
- India to participate in deliberations at the United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) in New York
- UNCITRAL deliberation deals with an important issue concerning resolution of commercial disputes.
Dispute redressal mechanisms:
Commercial disputes are resolved not only through courts and arbitration but also through mediation.
- Arbitration:- It consists of hearing and determining of a dispute between parties by persons chosen by them.
- Conciliation:- It is the process of facilitating amicable settlement between parties. It can’t be forced on a party not intending for conciliation.
- Mediation:- It is devised to assist disputants in reaching an agreement on their terms and conditions in arriving at a settlement. A “process whereby parties attempt to reach an amicable settlement of their dispute with the assistance of a third person (the mediator).
UNCITRAL deliberations will consider how these settlement agreements in disputes in international commercial transactions will be implemented by courts in different countries.
Key pointers:
- Mandatory pre-litigation mediation has been introduced in commercial disputes.
- Right now there are policy gaps with regard to mediation process involving cross-border disputes. Therefore adoption of the convention will address those gaps and eases mediation process which in turn helps in managing and resolving disputes that arise in their commercial transactions.
Why is this UNCITRAL important for India?
- India has lost substantial earnings as a result of international disputes being taken for resolution outside the country.
- Strengthening the dispute resolution policies will encourage dispute resolution in India, where the commercial relationship once began.
- The convention will link laws adopted by countries to recognise domestic mediation and extend them beyond their boundaries.
- Once UNCITRAL formulates principles, countries will have a consistent framework for enforcing mediation agreements made in other countries.
- The convention is opportune and will facilitate legal reform to ease dispute resolution.
Connecting the dots:
- Why having an international convention law on commercial disputes imperative for the Indian legal scenario? Discuss. Can you identify the existing alternative institutional arrangements for dispute resolution? Also discuss their merits and limitations.
- The pendency of huge number of commercial disputes cases in different courts of India demands a revolution in the field of alternate dispute resolution. Comment. What steps have been taken in this direction? Discuss.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Q.1) Japan’s HAYABUSA-2 is associated with
- Mission to explore exoplanets
- Spacecraft to observe atmosphere of Pluto
- Spacecraft powered by plutonium
- Mission to explore asteroid
Q.2) Which of the following statements are correct regarding Ujjawala scheme?
- It is a comprehensive scheme to prevent trafficking of women and children for commercial/sexual exploitation.
- The aim is to facilitate the rescue of victims and place them in safe custody.
- To facilitate the repatriation of cross border trafficking victims
Select the code from following:
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- None
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.3) The aim of Ujjwala Yojana is to
- Electrify all rural villages by 2030
- Provide free primary education to girl child
- Provide free LPG Connection to women below poverty line
- None of the above
MUST READ
Reality check: On bank NPAs
From little to zero tolerance
Citizens, non-citizens, minorities
The skew in education
The amalgamation of regional rural banks is poorly planned











