UPSC MAINS 2019 QUESTION PAPERS
UPSC MAINS PAPER 2019 (GENERAL STUDIES PAPER 3) : ANALYSIS, APPROACH and REFERENCES-How IASbaba was Helpful
Read GS 1 and GS 2 Here
Read GS 4 ETHICS Here
Dear Aspirants,
We are all engaged in some or the other activity. When there is no passion attached to the activity, we call it a ‘job’. When an activity has passion behind it, it becomes ‘joy’.
We have been doing one thing with great passion and dedication for the last 5 years. Yes! We love to guide civil servant aspirants. We have dedicated ourselves into creating an ecosystem that gives even a person sitting in the remotest corner to crack the prestigious civil services examination with Rank-1. In this process, we have developed, designed and dedicated a series of initiatives for civil services preparation.
The quality of these initiatives have been proven time and again. It has become the norm to have high hit ratios in Prelims and Mains from the initiatives of IASbaba, namely Integrated Learning Programme (ILP) and Think Learn and Perform (TLP).
This article is not to boast about the HIT RATE of our initiatives in any case. It would be an injustice to say that these many questions, directly or indirectly came from our initiatives using keywords of the UPSC questions. In that way, if we frame questions over the year on all keywords in UPSC syllabus our hit ratio will be 100%. However, you are smart enough to analyse the importance of our initiatives and its very close resemblance to actual UPSC papers.
Rather than numbers focus on its significance and make it a part of your preparation. You should work on the smart study and smart thinking to keep your inputs minimum and maximize the output.
Below we have come up with the Analysis and Approach for each question of General Studies (GS) Paper 3 that was asked by UPSC along with the links and references of IASbaba questions/ articles. Needless to say- if you are regular with the initiatives of IASbaba, your chances of clearing the most coveted examination of India is really high.
We at IASbaba are expecting bigger and better results this year!!
OVERVIEW of GENERAL STUDIES (GS) PAPER 3:
Overall General Studies-3 paper was easy to moderate, except for one or two technical questions which an aspirant would have found it difficult to answer in those 3 hours. Also, the questions are not lengthy, which is an added advantage to finish this paper in three hours.
Indian Economy (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 11, 12, 13 and 14): Questions 3, 4, 5 are based on agriculture which are easy to moderate.
Questions 1, 2, 11 and 12 are based on economic situation of country and are more on the analytical side.
Questions 13 and 14 are based on food grain distribution and food processing. Both these questions are about the steps taken and policy measures by Government. These questions are easy in nature.
Science and Technology (6, 15 and 16): Question 16 is on the easier side, whereas question 15 is a moderate to difficult question because of its specificity. Question number 6 can be considered an easy to moderate level question.
Environment (7 and 17): Two questions have been asked from this part. While one of them is based on static concept, the other one is based on one of the current threats (sand mining) to environment. These questions can be easily answered by the aspirants.
Disaster Management (8 and 18): Two questions have been asked from this part. The question on hazard zonation mapping is a specific question. Overall both the questions are of moderate level.
Internal Security (9, 10, 19 and 20): Four questions have been asked from this part. One of them on CyberDome project can be considered as a difficult question as it is very specific and one can answer only if they have prior knowledge about that question. The other three questions are of moderate
Q1. Enumerate the indirect taxes which have been subsumed in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. Also, comment on revenue implications of the GST introduced in India since July 2017. (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This is a direct question asking to enumerate the indirect taxes subsumed in GST. By enumeration means- provide a list of such taxes. Do not go deep explaining about each one of them (This is the first part of the question).
Second part: Revenue implications on Indian Economy after the introduction of GST. Note to mention both positive and negative sides of GST on revenue (since the question clearly says ‘implications’)
Also, this answer must be backed by reports, data and citation from government’s sources like “The growth of indirect taxes slowed to 5.80 per cent in 2017/18 compared to a growth of 21.33 per cent in 2016/17”- CAG Report on GST
- Increase in tax base- More people paying taxes- More Funds to Government.
- Streamlining of taxes that has resulted into better tax management- More money in the hands of Government
- First year of implementation of GST, revenues grew by 11.9% and the buoyancy was 1.20. A buoyancy ratio over 1shows progressiveness in the revenue growth and opens up the prospect of a rising tax-to-GDP ratio.
- The buoyancy in GST revenues is also reflected in the bump in the personal tax revenues on the direct tax side. Personal income-tax collections include the revenues of unincorporated enterprises that have tended to pay more direct tax revenues induced by their formalisation in the GST scheme.
- The first is that gross GST collections are short of expectations. Thus, as against a target of ₹1,12,000 crore a month set for 2018-19, average GST revenues fell short of ₹1 lakh crore a month in that year. The shortfall is a problem especially for the States.
- GST revenue accruing to the Central divisible pool is doing better than that received by the States from the State GST (SGST) and Integrated GST (IGST). All this enhances the dependability of States on Centre and inequality among states.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Covered in ILP VAN-Economy
- The implementation of post-independent India’s biggest tax reform i.e. the Goods and Services Tax (GST) has completed more than a year. What are your views on the impact of GST on India’s industrial growth? (TLP 2019-phase 1)
- https://tlp.iasbaba.com/2018/12/day-33-q-1-the-implementation-of-post-independent-indias-biggest-tax-reform-i-e-the-goods-and-services-tax-gst-has-completed-more-than-a-year-what-are-your-views-on-the-impact-of-gst-o/
- Daily Current Affairs Analysis 2nd July 2018
- https://iasbaba.com/2018/07/iasbabas-daily-current-affairs-prelims-mains-focus-2nd-july-2018/
Q2. Do you agree with the view that steady GDP growth and low inflation have left the Indian economy in good shape? Give reasons in support of your arguments. (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This question requires an understanding of GDP (steady) and inflation (low) and its impact on the economic growth of the country. You have to give reasons- is it good for the overall economy or not?
You can cite reports, facts and figures to support your arguments. Note not to write stories in this question as it is very much fact-oriented and asking for reasons to support your arguments, very clearly in the question itself.
Do mention the low inflation rate & GDP growth rate (present) and past trends to give clarity to steady-state of GDP growth and low inflation over previous quarters.
Divide the answer taking specific sectors and impact therein like Services, Manufacturing, Agriculture, and Infrastructure etc. Don’t miss impact on Fiscal deficit, forex reserve, FDI and share markets. You have to focus on various economic sectors only.
Points/concepts that you can use: Impact on
Per Capita Income: Given per capita monthly income of Rs 10,534 in 2018-19, an annual GDP growth of 5% means that the per capita income will go up by Rs 526 in FY20- as per one report
On Investors: If overall economic output is declining or merely holding steady, most companies will not be able to increase their profits, which is the primary driver of stock performance.
On Job Creation: over the past 20 years, annual GDP growth over 2.5% has caused a 0.5% drop in unemployment for every percentage point over 2.5%.
Inflation
- Low inflation is a sign of- Weak demand in economy. Moderately high inflation signals growing consumption and spurs investment.
- GDP deflator inflation, the relevant index of inflation, was incidentally just 2.8% in this quarter, and declined steadily over the past fiscal year.
- Inflation and growth move together and in the same direction-Philips Curve
- Low inflation means a high real interest rate that, in turn, tends to crimp investment activity.
Likewise you can answer taking specific sectors and associated sub-sectors.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP VAN- Economy-Inflation, GDP
- What inferences can be drawn regarding the health of the economy on the basis of India’s latest GDP growth trends? Analyse. (C2C 2019-phase 1 Test-2)
- Macro-economic stability is a prerequisite to sustainable growth and job creation. Comment. (TLP Phase-2 2019)
- https://tlp.iasbaba.com/2019/07/day-11-q-1-macro-economic-stability-is-a-prerequisite-to-sustainable-growth-and-job-creation-comment/
Q3. How far is Integrated Farming System (IFS) helpful in sustaining agricultural production? (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
It is a straight forward question. Crux is about sustainable agriculture through integrated farming system and its techniques.
Define Integrated Farming System and mention its importance and advantages. You have to make a correlation between IFS and agricultural production.
Sustainable agriculture means an integrated approach to increasing farm yield and managing resources in order to address all three critical aspects of sustainability: economic, environmental and social.
Integrated Farming Systems (IFS) approach stabilises income streams through natural resource management and livelihood diversification.
Sustainable development in agriculture must include integrated farming system (IFS) with efficient soil, water crop and pest management practices, which are environmentally friendly and cost effective.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP VAN- Geography
- (Yojana-Kurukshetra Gist December 2018)

Q4. Elaborate the impact of National Watershed Project in increasing agricultural production from water stressed areas. (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
You just have to establish a link between increasing agricultural production due to National Watershed Project.
Write about the aim of the project like Har Khet Ko Pani, More Crop Per Drop under Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana etc. and how it helps in increasing agricultural production.
Talk about crop intensity, better irrigation management systems, Incremental rainfed agriculture productivity, Reduce surface runoff of rainwater, increase groundwater levels and better water availability in rainfed areas etc. Provide access to global best practices in watershed management and improve the livelihood and incomes of the farmers.
WATERSHED APPROACH:
- Complementing the efforts towards soil and water conservation,
- Regeneration of ground water,
- Improvement in agricultural productivity
- Providing livelihood options
Also mention about Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP)
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP VAN- Irrigation Module- Discussed in detail under Neeranchal National Watershed Management Project and IWMP.

Q5. How was India benefitted from the contributions of Sir M.Visvesvaraya and Dr. M. S. Swaminathan in the fields of water engineering and agricultural science respectively? (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
A very straight forward question that requires specific knowledge about given personalities.
Sir M Visvesaraya suggested that India try to be at par with industrialized nations as he believed that India can become developed through industries.
- He has the credit of inventing ‘automatic sluice gates’ and ‘block irrigation system’ which are still considered to be marvels in engineering.
- Each year, his birthday 15 September is celebrated as Engineer’s Day in India.
- Since river beds were costly, he came up with an efficient way of filtering water through ‘Collector Wells’ in 1895 which was rarely seen anywhere in the world.
Dr.M S Swaminathan
- Indian geneticist and administrator- known for his role in India’s Green Revolution, a program under which high-yield varieties of wheat and rice were planted.
- Swaminathan has been called the “Father of Green Revolution in India”
- Swaminathan is an advocate of moving India to sustainable development, especially using environmentally sustainable agriculture, sustainable food security and the preservation of biodiversity.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- https://iasbaba.com/2019/09/press-information-bureau-pib-ias-upsc-8th-sep-to-15th-september-2019/ (PIB 8th to 15th September)
- https://iasbaba.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/IASbabas-Economic-Survey-2017-18-Gist.pdf (Economic Survey 2017-18 Gist)
- https://iasbaba.com/2018/12/daily-current-affairs-ias-upsc-prelims-and-mains-exam-8th-december-2018/ (Daily Current Affairs Analysis-8th December 2018)
Q6. What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
Again a straight forward question.
Mention about International Space Station and countries like US, China and Russia’s ownership/monopoly over there. India as a leading and advancing country in space development and research has to look beyond ISS. India has proved its mettle in Space Development through indigenous technologies. As a leader in South East Asia and aspiring Asian leadership role, having own Space Station is a well thought move.
Mention about upcoming programmes of ISRO like Gaganyaan Mission, Aditya Mission etc.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Programmes discussed in ILP VAN
- https://iasbaba.com/2019/06/daily-current-affairs-ias-upsc-prelims-and-mains-exam-14th-june-2019/ (Daily Current Affairs Analysis-14th June)

Q7. Coastal sand mining, whether legal or illegal, poses one of the biggest threats to our environment. Analyse the impact of sand mining along the Indian coasts, citing specific examples. (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
It is a direct question. Note to mention recent NGT judgments and incidences of illegal sand mining in various parts of the country.
National Green Tribunal imposes has imposed penalties on state governments regarding illegal sand mining. It has also made clear notifications regarding the non-compliance of NGT orders by various stakeholders.
Legal or illegal: Affects are
- It pollutes the rivers (low PH, mix of various metal oxides, reduces oxygen and thus, increased BOD). This badly affects river biota.
- In stream sand mining results in the destruction of aquatic and riparian habitat through large changes in the channel morphology. Impacts include bed degradation, bed coarsening, lowered water tables near the streambed, and channel instability.
- Sea sand – it is mined both legally and illegally, to extract minerals and for reclamation projects. It affects the terrain coastal areas.
- Salinity is affected through excessive sand mining- River, Sea.
- Large-scale sand mining also destabilises the banks and beds, affecting the natural flow of rivers and streams and increasing risks of floods, like in the case of Kerala & Assam, which experienced its worst-ever floods.
- WWF, says that mining is responsible for a 90% drop in sediment levels in major Asian rivers, including the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna, Mekong and Yangtze rivers.
- This has resulted in the shrinking of the delta regions of these rivers, leaving residents extremely vulnerable to flood, land loss, contaminated drinking water and crop damage, researchers said.
- The indiscriminate mining has also destroyed hills, eroded biodiversity spheres, denuded forests and degraded fertile soil. It has changed the physical characteristics of river basins, impacting heavily the socio-economic condition of local people.
- Sand mining generates extra vehicle traffic, which negatively impairs the environment.
This excessive mining not only impact river ecology but also affect livelihood of people living in these regions.
- Polluted water and reduced ground water levels due to sand mining lead to drinking water shortage, agrarian distress in the vicinity, which in turn has triggered an exodus of people to urban clusters, upsetting the economic and cultural balance of a society.
- Illegal sand mining also results in damage to physical infrastructure (like railways, bridges, highways etc.) nearby, resulting in further economic distress of the community.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP VAN
- What are the effects of excessive sand mining on the river ecosystem? Also discuss its long term implications for livelihood security.
- Riverbeds perform critical ecosystem services. However, rampant sand mining has severely depleted the ability of rivers to perform these services. Identify these services performed by rivers and also enumerate the factors causing their deterioration.
- https://iasbaba.com/2017/03/3-effects-excessive-sand-mining-river-ecosystem-also-discuss-long-term-implications-livelihood-security/
- https://iasbaba.com/2016/03/3-riverbeds-perform-critical-ecosystem-services-however-rampant-sand-mining-severely-depleted-ability-rivers-perform-services-identify-services-performed-rivers-al/
Q8. Vulnerability is an essential element for defining disaster impacts and its threat to people. How and in what ways can vulnerability to disasters be characterized? Discuss different types of vulnerability with reference to disasters. (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
Explain about vulnerability and establish a link between vulnerability and disasters. Discuss about various types of vulnerability and provide examples.
Physical vulnerability: Depends on its geographic proximity to the source and origin of the disasters. Example: earthquakes are common at foothills of Himalayas due to geographic structure.
Economic vulnerability: Upon the economic status of individuals, communities and nations. The poor people are more vulnerable due to economic conditions and lack of infrastructure. Example: During Kerala flood (2018) many villagers were deprived of basic amenities.
Social vulnerability: Related to levels of literacy and education, the existence of peace and security, access to basic human rights, systems of good governance, social equity, positive traditional values, customs and ideological beliefs and overall collective organizational systems. Example: Citizens passports were lost during Chennai flood (2015) which created chaos in reissuing.
Attitudinal vulnerability: About disunity and individualism in the society. Become victims of conflicts, hopelessness and pessimism which reduce their capacity of coping with a disaster. Example: Lack of cooperation from villagers to forest department during Bandipur forest fire (2019) related to investigation of the cause.
Environmental vulnerability: Due to natural resource depletion and resource degradation. Example: flash floods in Uttarakhand.
Anthropological vulnerability: Manmade disasters. Example: Bhopal gas tragedy
IASBABA REFERENCE:
This question of TLP talks about vulnerability in general and includes disaster segment also.
- What do you understand by ‘vulnerability’? How do structural vulnerabilities arise? Examine
- https://tlp.iasbaba.com/2018/11/day-18-1-what-do-you-understand-by-vulnerability-how-do-structural-vulnerabilities-arise-examine/
And this question-synopsis answers the aspects under vulnerability that was required for UPSC’s question.
- What measures both preventive and mitigative can be taken to address the ecological hazard of droughts? Suggest.
Q9. The banning of ‘Jamaat-e – islaami’ in Jammu and Kashmir brought into focus the role of over-ground workers (OGWs) in assisting terrorist organizations. Examine the role played by OGWs in assisting terrorist organizations in insurgency affected areas. Discuss measures to neutralize influence of OGWs. (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The question is of analytical nature as one should have knowledge about the difference between militant and Over-ground worker.
Try to mention few recent terrorist attacks (Pulwama, Uri) in Kashmir reflecting rising militancy in the region.
The body of the answer should bring out the characteristic of OGW –civilian who mingles in society freely and has not taken up arms to fight against Indian State, however, provides the necessary support to militants to carry on their activities.
In the second part elaborate on various role played by OGW –logistics support, funding support, ideological support, radicalization support, recruitment support and intelligence inputs to militants.
Measures to neutralize the influence of OGW
- increasing intelligence and police personnel,
- effective crackdown on funding through enhanced surveillance,
- can take help of Community leadership to counter the militant propaganda of OGW and
- ensuring that development is inclusive in nature to counter the feelings of alienation.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- https://iasbaba.com/2019/03/daily-current-affairs-ias-upsc-prelims-and-mains-exam-25th-march-2019/ (Daily Current Affairs – 25th March)
Q10. What is CyberDome Project? Explain how it can be useful in controlling internet crimes in India. (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This is a very specific question. Explain CyberDome project and its relevancy in controlling internet crimes in India.
Cyberdome project: Cyberdome is a technological research and development Centre of Kerala Police Department conceived as a Cyber Centre of excellence in cyber security as well as technology augmentation for effective policing.
It is a hightech public-private partnership Centre of collaboration for different stakeholders in the domain of cyber security and handling of cybercrimes. IT firms, ethical hackers, cyber security experts and trained volunteers work here.
Uses of cyberdome in controlling internet crimes: cyber forensic, cyber intelligence, cyber security, incidence response, internet monitoring, cybercrimes against women and children, VOIP/Skype call analysing, cyber terrorism, dark net exploring and crimes related to the social media, which will be examined through the social media analysing laboratory.
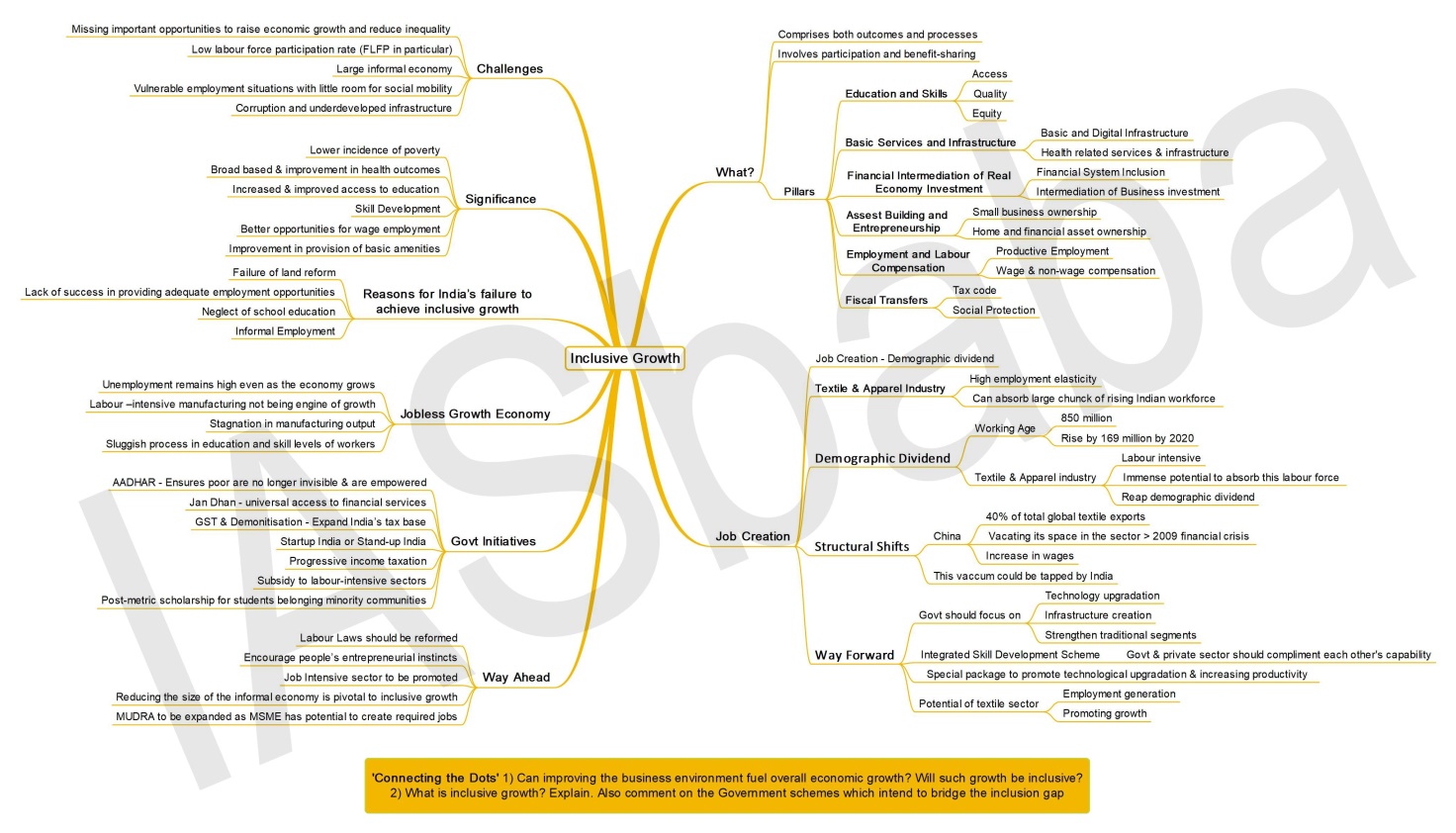
Q11. It is argued that the strategy of inclusive growth is intended to meet the objectives of inclusiveness and sustainability together. Comment on this statement. (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The QUESTION is of analytical in nature which requires understanding and inter-relation of growth, inclusiveness and sustainability.
Start by defining inclusive growth taking various sectors and aspects into consideration like economic, social, environmental correlations etc.
Inclusive economic development will include poor, vulnerable, marginalized, women, youth and people from every stratum of society in economic activity for a sustainable future.
Growth (GDP growth), inclusive development (distribution of growth & reduction of inequality) and sustainability (inter-generational equity)- Provide facts and reports on these parameters.
The inter-relationship between these three: inclusiveness w.r.t women, Dalits, tribals and weaker sections of society, fiscal sustainability (CAD and Fiscal deficit), and environmental sustainability (water conservation, air pollution, sustainable forestry and plastic usage).
Measures towards such a path – rectifying our economic structure (boost to labour intensive manufacturing sector), affirmative actions of government, better targeting of welfare measures and adoption of recycling & cleaner technologies.
Example of Greta Thunberg – 16-year-old Swedish girl (CAN BE QUOTED) who is demanding increased actions from government with regard to Climate Change. This shows that Sweden even though high on HDI and low on inequality is having issues w.r.t its developmental model.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- What do you understand by ‘inclusive growth’? What are its dimensions? Discuss. (TLP Phase-1 2019)
- https://tlp.iasbaba.com/2018/12/day-29-q-1-what-do-you-understand-by-inclusive-growth-what-are-its-dimensions-discuss/
- Why is inclusive economic growth imperative for a sustainable future? Analyse. (TLP Phase-2 2019)
- https://tlp.iasbaba.com/2019/07/day-12-q-4-why-is-inclusive-economic-growth-imperative-for-a-sustainable-future-analyse/
- Inclusive Growth Mind Map – (ILP 2019)
Q12. The public expenditure management is a challenge to the government of India in the context of budget making during the post-liberalization period. Clarify it. (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The question is analytical in nature which needs critical examination of budgeting exercise.
Mention the evolving role of government, post 1991, where government role has changed from being the driver of economic growth to that of facilitator of growth process.
Elaborate the three pillars of Public Expenditure Management –
- Aggregate fiscal discipline (Fiscal deficit, CAD),
- Allocative efficiency (fund allocation between different priority sectors), and
- Operational efficiency (to reduce leakages).
The answer needs to give primacy to first aspect by explaining Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, FRBM Act. (To institutionalize financial discipline, reduce India’s fiscal deficit, improve macroeconomic management and the overall management of the public funds by moving towards a balanced budget and strengthen fiscal prudence.)
Mention about the challenges faced by government on each of these three aspects–
- Low tax base,
- Populist measures (farm loan waiver, free electricity),
- External factors (global slowdown impacting export, oil prices),
- Leakages and corruption etc.
Answer can be concluded by brief mention of N.K.Singh panel recommendations – Fiscal Council, range of Fiscal Deficit and debt-to-GDP ratio etc.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP VAN- Polity and Economy- Budgeting
- What budgeting reforms have been taken in the latest budget? Discuss.
- https://iasbaba.com/2017/02/5-budgeting-reforms-taken-latest-budget-discuss/
Q13. What are the reformative steps taken by the government to make food grain distribution system more effective? (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
Mention major Reforms in Public Distribution System (PDS) for better Targeting, Transparency & Accountability in procuring and distribution.
Automation of Fair Price Shops: use of PoS at FPS
Direct Benefit Transfer (Cash): food subsidy is directly credited to the account of the beneficiaries.
Aadhaar Seeding in PDS: To weed out duplicate/in-eligible/bogus ration cards and to enable rightful targeting.
Deletion of ration cards: As an outcome of digitization of Ration Cards/beneficiary records, de-duplication due to Aadhaar seeding, transfer/migration/deaths, change in economic status of beneficiaries.
Digital/Cashless/Less-cash Payments in PDS: To promote the use of less-cash/digital payment mechanisms, the Department has issued detailed guidelines for use of AePS, UPI, USSD, Debit/Rupay Cards and e-Wallets.
Food procuring: cold storage and strengthening food supply chain.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- How can revamping the PDS in India ensure food security? What measures should be taken in this direction? Suggest. (TLP phase-I GS-3 compilations)
- https://tlp.iasbaba.com/2019/01/day-44-q-3-how-can-revamping-the-pds-in-india-ensure-food-security-what-measures-should-be-taken-in-this-direction-suggest/
- Does India’s Public Distribution System (PDS) address food security concerns and malnutrition effectively? Critically examine. (C2C Test-2)
- ILP VAN & MOCK

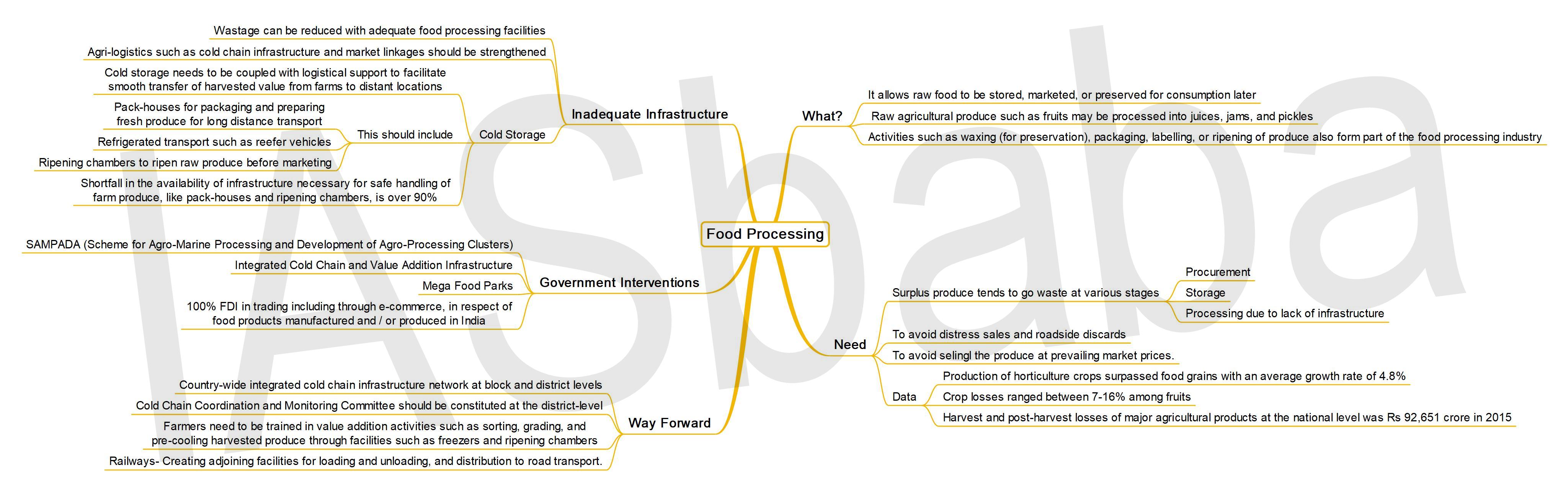
Q14. Elaborate the policy taken by the government of India to meet the challenges of the food processing sector. (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
Explain about food processing sectors: It is the transformation of raw ingredients, by physical or chemical means into food, or of food into other forms. It is very direct question asking about government of India’s initiatives to meet the challenges of the food processing sectors.
First, mention the challenges and then provide its solution through policy/initiatives of GoI
FICCI through its internal research identified 15 major factors hampering the growth of food processing sector and holding it back. (Mentioned below)
- Comprehensive national level policy on food processing sector
- Availability of trained manpower
- Processing plants with cost effective technologies
- Cost effective food machinery & packaging technologies
- Constraints in raw material production
- Inadequate infrastructural facilities
- Access to Credit
- Market Intelligence
- Inconsistency in central and state policies
- Lack of Applied research
- Adequate value addition
- Lack of specific plan to attract private sector investment across the value chain
- Food safety Laws
- Weights & measures Act & Packaging commodity rules
- Taxation
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP VAN and Mock
- What are the supply chain constraints of India’s food processing sector? What steps have been taken to address those? Examine. (TLP phase-II GS-3 compilations)
- Food Processing Mind Map – (ILP 2019)
- https://tlp.iasbaba.com/2019/07/day-15-q-2-what-are-the-supply-chain-constraints-of-indias-food-processing-sector-what-steps-have-been-taken-to-address-those-examine/


Q15. How is the government of India protecting traditional knowledge of medicine from patenting by pharmaceutical companies? (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
Start with your understanding of ‘Traditional Knowledge’-Define it. Write about Traditional Knowledge Digital Library-India, Creation of Ministry of Ayush by GoI, CSIR etc.
Traditional Knowledge Digital Library: A repository of 1200 formulations of various systems of Indian medicine, such as Ayurveda, Unani and Siddha and 1500 Yoga postures (asanas), translated into five languages English, German, French, Spanish and Japanese.
- India has also signed agreements with the European Patent Office (EPO), United Kingdom Intellectual Property Office (UKIPO) and the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) to prevent the grant of invalid patents by giving patent examiners at International Patent Offices access to the TKDL database for patent search and examination.
- With patent examiners getting access to the TKDL database, legal cases regarding unethical patent claims, which had taken years and vast expenditure for each case, could be avoided
- Intellectual Property Rights- TRIPS
- Convention on Biodiversity- As a future project, a people’s Register of Biodiversity, is being set up by the government, to document and protect, traditional knowledge passed down through the oral tradition, under India’s National Biodiversity Act of 2002.
To date the TKDL has enabled the cancellation or withdrawal of a large number of patent applications attempting to claim rights over the use of various medicinal plants.
Example- Neem Case, Turmeric Case, Basmati Case- all won by India against other countries.
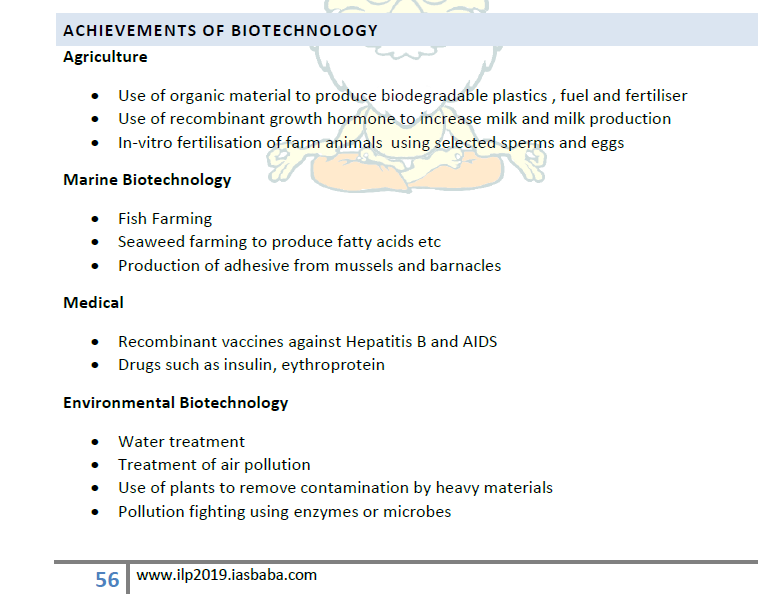
Q16. How can biotechnology improve the living standards of farmers? (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
In this question answer how biotechnology can improve the living standards of farmers. Do not write anything not related or asked.
You have to mention GM Crops, Organic farming techniques, Innovation in the field of agriculture Molecular farming etc. Also, mention that with scientific understanding, farmers are becoming better in terms of awareness and technical understanding.
Discuss few government schemes and programmes in this regard like Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana: To promote bio-farming in the country, research institutions innovation in the field of agriculture for better agricultural practices, w.r.t seeds and various varieties, farming techniques etc.
Areas to touch:
- Use of organic material to produce biodegradable plastics , fuel and fertiliser
- Use of recombinant growth hormone to increase milk and milk production
- In-vitro fertilisation of farm animals using selected sperms and eggs
- Genetically Modified Organisms and Gene Editing Techniques.
- Fish Farming
- Seaweed farming to produce fatty acids etc.
- Organic farming techniques
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP VAN- Covered in Science and Environment VAN and Mains Mock
- Innovations in the field of infotech and biotech hold the potential to transform the agricultural landscape. Comment. (TLP phase-I GS-3 compilations)
- https://tlp.iasbaba.com/2019/01/day-43-q-4-innovations-in-the-field-of-infotech-and-biotech-hold-the-potential-to-transform-the-agricultural-landscape-comment/
- Farming in India must move up the technology ladder, with the government setting out clear and progressive policies on GM crops and IPR. Comment. (TLP Plus test-3)
Q17. Define the concept of carrying capacity of an ecosystem as relevant to an environment. Explain how understanding this concept is vital while planning for sustainable development of a region. (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
Define Carrying Capacity w.r.t Environment
Concept of “carrying capacity”
- The concept of “carrying capacity” addresses the question as to how many people can be permitted into any area without the risk of degrading the environment there.
- The carrying capacity of a biological species in an environment is the maximum population size of the species that the environment can sustain indefinitely, given the food, habitat, water, and other necessities available in the environment.
There is a certain carrying capacity of the environment. When the rate of extraction of resources exceeds the rate of their regeneration, the environment fails to perform its activities. The resulting phenomenon is called environmental degradation. Relate the given dimensions with sustainable development. While discussing the vitality of sustainable planning and development focus on resources to be used since it is about carrying capacity.
For example: When talking about Pollution-Air/Water, give facts and reports where overuse or improper management has worsen the situation. Like in Delhi Air Pollution. Similarly for other aspects.
Dimensions to be discussed are
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP VAN- Economy and Environment
- Is it possible to strike a balance between developmental imperatives of a growing economy like India and the limits to growth imposed by environmental degradation? Critically analyse. (TLP phase-II GS-3 compilations)
- https://tlp.iasbaba.com/2019/08/day-51-q-2-is-it-possible-to-strike-a-balance-between-developmental-imperatives-of-a-growing-economy-like-india-and-the-limits-to-growth-imposed-by-environmental-degradation-critically-analyse/
Q18. Disaster preparedness is the first step in any disaster management process. Explain how hazard zonation mapping will help in disaster mitigation in the case of landslides. (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This is a direct question on disaster management.
The 1st part of the question asks you to explain the importance/significance of Disaster preparedness as the 1st step of any disaster management process. And the 2nd part on how hazard zonation mapping will help in disaster mitigation specific to landslides
Disasters affect millions of people each year on a personal, business, local community or national level. The golden rule for successful disaster management at all levels is to increase awareness, develop actions plans and practice them.
Mitigation -Minimizing the effects of disaster. Example: building codes and zoning; vulnerability analyses; public education. Preparedness – Planning how to respond. Example: preparedness plans; emergency exercises/training; warning systems.
Landslide hazard zonation refers to the division of land into homogeneous areas and ranking of these areas according to their degrees of actual or potential hazard caused by landslides and mass movements. The landslide hazard zonation maps display the spatial distribution of hazard classes.
Example: the regional landslide hazard zonation maps of Srinagar-Rudraprayag area of Garhwal Himalaya in the state of Uttarakhand. The hazard zonation map produced by using this technique classifies the area into relative hazard classes in which the high hazard zones well correspond with high frequency of landslides.
Q19. Indian government has recently strengthened the anti-terrorism laws by amending the unlawful activities (Prevention) act (UAPA), 1967 and the NIA Act. Analyze the changes in the context of prevailing security environment while discussing the scope and reasons for opposing the UAPA by human rights organizations. (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
Taking note of features of respective amendments under the UAPA Act, analyse the issues under required headings:
Amendments of UAPA Act:
- Approval for seizure of property by NIA:Under the Act, an investigating officer is required to obtain the prior approval of the Director General of Police to seize properties that may be connected with terrorism. The Bill adds that if the investigation is conducted by an officer of the National Investigation Agency (NIA), the approval of the Director General of NIA would be required for seizure of such property.
- Investigation by NIA: Under the Act, investigation of cases may be conducted by officers of the rank of Deputy Superintendent or Assistant Commissioner of Police or above. The Bill additionally empowers the officers of the NIA, of the rank of Inspector or above, to investigate cases.
- Insertion to schedule of treaties: The Act defines terrorist acts to include acts committed within the scope of any of the treaties listed in a schedule to the Act. The Schedule lists nine treaties, including the Convention for the Suppression of Terrorist Bombings (1997), and the Convention against Taking of Hostages (1979). The Bill adds another treaty to the list. This is the International Convention for Suppression of Acts of Nuclear Terrorism (2005).
Issues with the amendment:
- An organization: the Centre may designate an organisation as a terrorist organisation if it commits or participates in acts of terrorism, prepares for terrorism, promotes terrorism, or is otherwise involved in terrorism. The rules are ambiguous.
- Not effective: The government said the new law would be used “sparsely” — for example only in such cases as dreaded militants like Yasin Bhatkal and Masood Azhar, to name a few.
- Unlawful’ detention: Provisions in the UAPA are stricter than the domestic criminal law. Under the law, the police are allowed a time period of 180 days for investigation as opposed to 60 to 90 days under criminal law.
- Violation of rights: The Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Amendment Act, 2019 is violation of fundamental rights as enshrined under Article 14 (Right to Equality), 19 (Right to Free Speech and Expression) and 21 (Right to Life) of the Constitution of India.
- Against federalism: NIA seizing property in any state is against the federalism.
- More power to central government: The Act assigns absolute power to the central government, by way of which if the Centre deems an activity as unlawful then it can vary.
- Societal attitude: Once an individual is designated as a terrorist, he will lose his job, family will be biased.
- Trivial reasons: UAPA has been used to file an utterly flimsy case against selfless, dedicated human rights activists and NGOs.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Will the amendments to the UAPA Act control terrorism in India? Critically examine. (TLP Plus test-13)
- What are the most striking features of the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Amendment Act? Are these changes justified? Share your viewpoint. (TLP Plus test-13)
- UAPA Mind Map – (ILP 2019)
- ILP Mains Mock

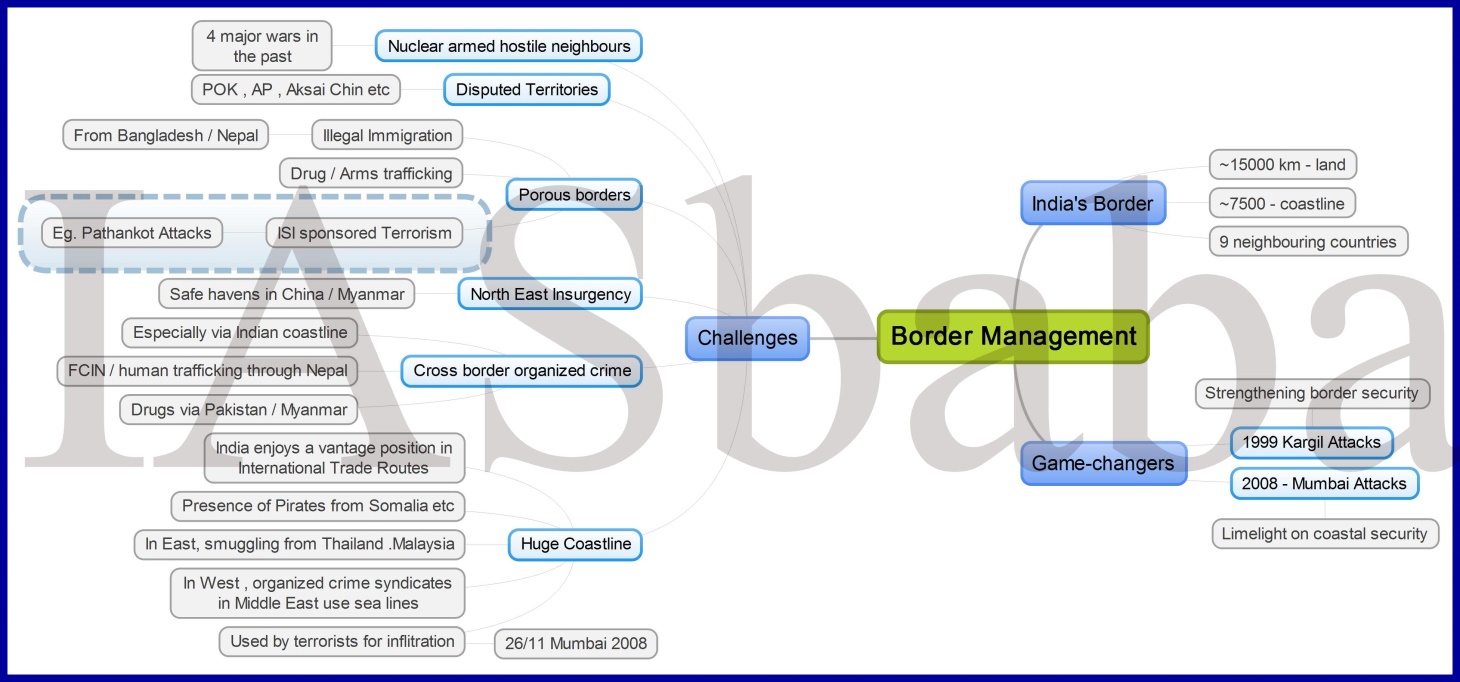
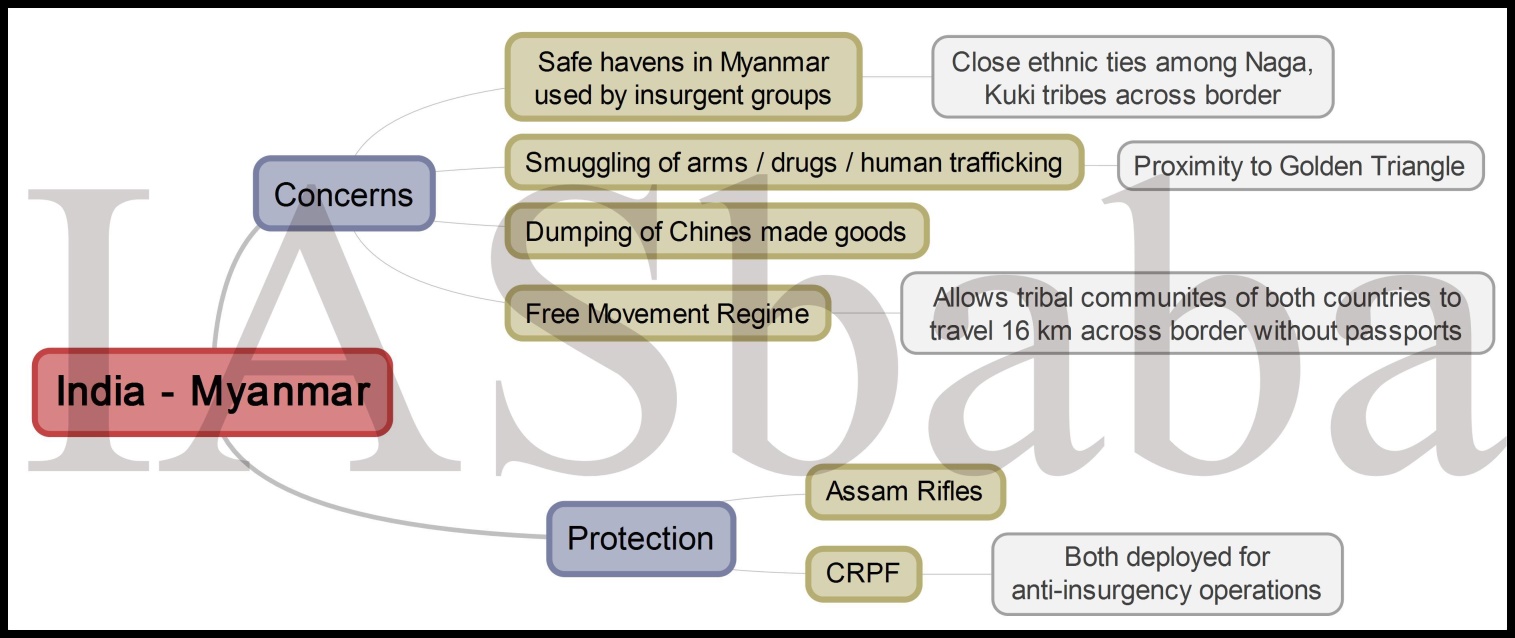
Q20. Cross-border movement of insurgents is only one of the several security challenges facing the policing of the border in North-East India. Examine the various challenges currently emanating across the India-Myanmar border. Also discuss the steps to counter the challenges. (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
It is a straight forward question on security related challenges w.r.t India-Myanmar border. Since it is asking to ‘EXAMINE’ the various challenges, you are supposed to not only write/list out the challenges but also mention why or why not the issue is resolved yet with few facts/reports etc.
For example
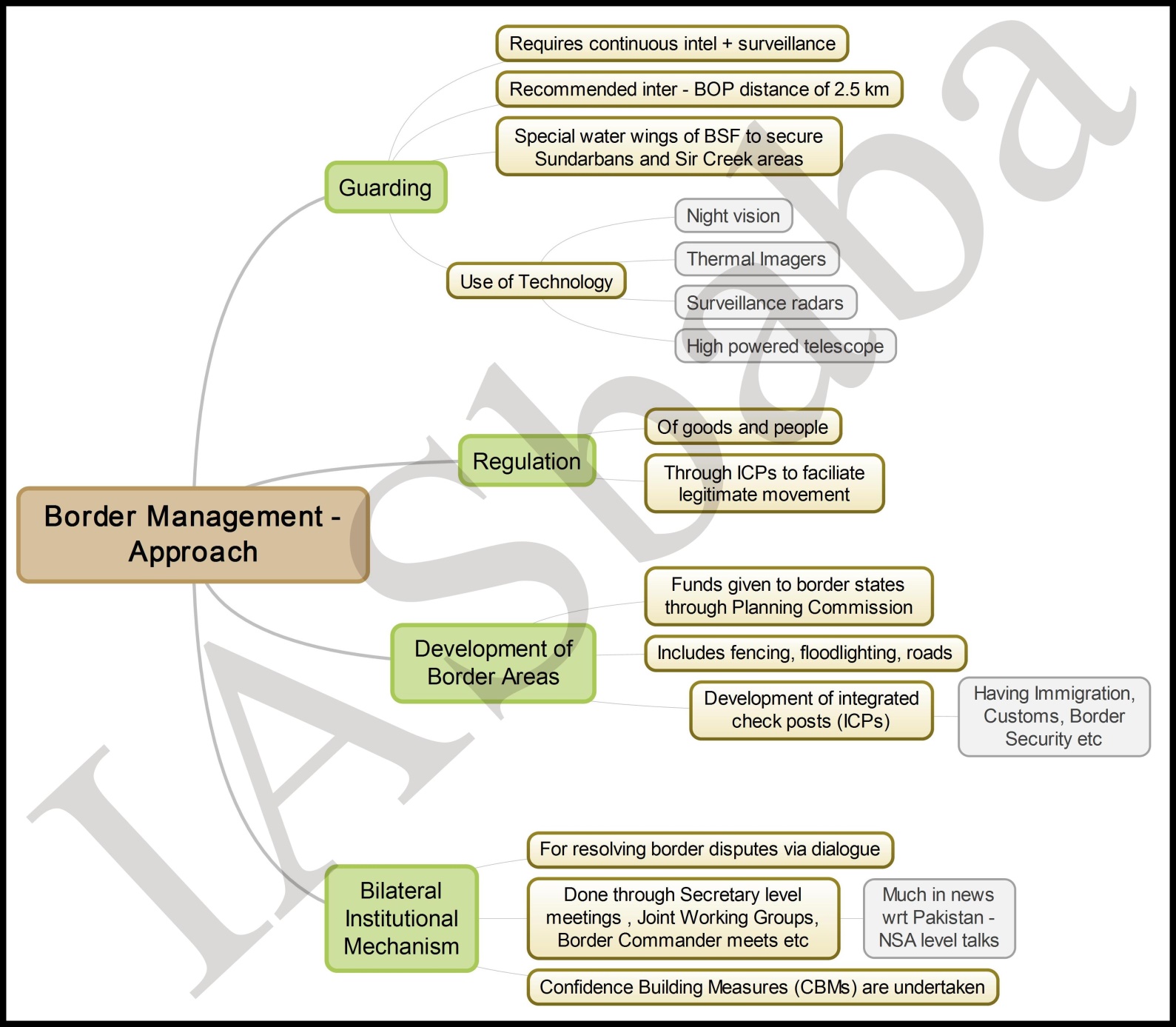
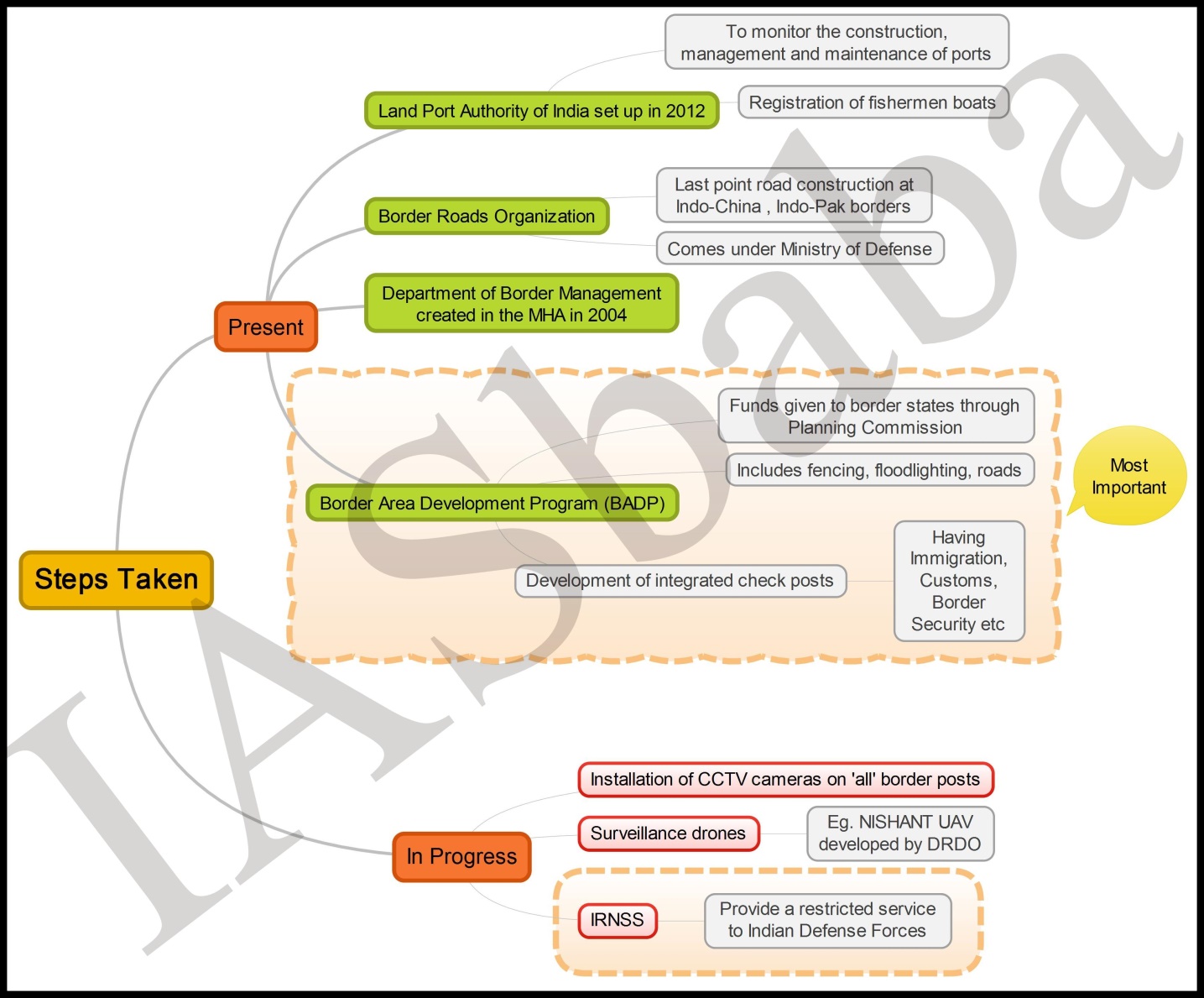
- Mention about porous border (basically border management), boundary agreements between India-Myanmar, Movement Regime between two countries, lack of infrastructural support and development (mention the difficult geographical terrain and lack of funds from government), golden triangle, drug trafficking, human trafficking, illegal migrants etc. and associated challenges in its management from government. You must mention the mutual programmes and initiatives of India-Myanmar Governments regarding the same. Like, Operation Sunrise.
Second part of the question: You have to discuss about the steps to counter those challenges.
Here, make sure to streamline your answer by using structured content: Say if in the first part, you mentioned about drug trafficking, then surely you need to mention the steps to counter drug trafficking in second part too. Similarly, you should be very careful in understanding the correlation between first and second part.
This will conclude and make sure that your answer doesn’t lack flow, structure and content at the same time.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP 2019 VAN
- How is ethno-nationalism in the North East a serious internal security threat to India? How is it being tackled? Discuss. (TLP Plus Test-13)
- ILP Mind Maps
TLP Connect 2020: Prelims + Mains+ Interview Mentorship Based Programme (OFFLINE and ONLINE)
Important timelines in the Video:
Initial 10 mins – about IASbaba and Team
13 minutes onwards – Philosophy behind TLP and Details about TLP Connect Mentorship programme
35mins, 30 Sec onwards – Art of Answer Writing
1:14:25 (hr:min:sec) onwards – Live Demo of Answer Writing
1:37:30 onwards – Ethics Strategy
2:19:45 onwards – Right Attitude for UPSC Preparation
DOWNLOAD THE PDFS
GENERAL STUDIES PAPER 1-2019
GENERAL STUDIES PAPER 2-2019
GENERAL STUDIES PAPER 3-2019
GENERAL STUDIES PAPER 4-2019














