Home Announcements

UPSC MAINS PAPER 2019 (GS 1 and GS 2): ANALYSIS, APPROACH and REFERENCES –How IASbaba was Helpful
Read GS 4 ETHICS Here
Read GS 3 Here
Dear Aspirants,
We are all engaged in some or the other activity. When there is no passion attached to the activity, we call it a ‘job’. When an activity has passion behind it, it becomes ‘joy’.
We have been doing one thing with great passion and dedication for the last 5 years. Yes! We love to guide civil servant aspirants. We have dedicated ourselves into creating an ecosystem that gives even a person sitting in the remotest corner to crack the prestigious civil services examination with Rank-1. In this process, we have developed, designed and dedicated a series of initiatives for civil services preparation.
The quality of these initiatives have been proven time and again. It has become norm to have high hit ratios in Prelims and Mains from the initiatives of IASbaba, namely Integrated Learning Programme (ILP) and Think Learn and Perform (TLP).
This article is not to boast about the HIT RATE of our initiatives in any case. It would be an injustice to say that these many questions, directly or indirectly came from our initiatives using keywords of the UPSC questions. In that way if we frame questions over the year on all keywords in UPSC syllabus our hit ratio will be 100%. However, you are smart enough to analyse the importance of our initiatives and its very close resemblance to actual UPSC papers.
Rather than numbers focus on its significance and make it a part of your preparation. You should work on smart study and smart thinking to keep your inputs minimum and maximize the output.
Below we have come up with the Analysis and Approach for each question of General Studies (GS) Paper 1 and Paper 2 that were asked by UPSC along with the links and references of IASbaba questions/ articles. Needless to say- if you are regular with the initiatives of IASbaba, your chances of clearing the most coveted examination of India is really high.
We at IASbaba are expecting bigger and better results this year!!
UPSC MAINS GENERAL STUDIES PAPER 1
DOWNLOAD THE PDFS
GENERAL STUDIES PAPER 1-2019
GENERAL STUDIES PAPER 2-2019
OVERVIEW of GENERAL STUDIES (GS) PAPER 1:
Most of the questions were of easy to moderate. However, questions were a mix of both Static and Analytical part. To fetch good marks, one must be having a comprehensive understanding of the Concepts and Historical events.
Art and Culture (Q.1): There is one question in this years paper, which is a specific question on Gandhara Art. The question is of moderate level.
Modern History (2, 3, 11, and 12): Four questions are asked which are mostly analytical in nature. The questions require a holistic understanding of each and every event. For example, the question on 1857 uprising is asking about the rebellions occurred in the preceding hundred years.
The questions are of moderate level as the themes of these questions are repetitive.
World History (13): Only one question has been asked, which is analytical in nature. The question is easy as most of the aspirants have an idea about the American and French revolution.
Geography (4, 5, 6, 7, 14, 15, 16 and 17): Eight questions are asked from Geography. The questions are a mix of both analytical and static part of the syllabus.
The questions are from easy to moderate level. Almost all the concepts are asked by UPSC in various instances.
Indian Society (8, 9, 10, 18, 19 and 20): Six questions have been asked from this part. Most of the questions are analytical in nature which requires an integrated approach while studying. For example, in question-9 women empowerment is linked to population growth.
Q1. Highlight the Central Asian and Greco -Bactrian elements in Gandhara art. (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This is a direct question. Divide the question into two parts. Influence of Central Asian elements in Gandhara art and Greek elements in Gandhara art.
Gandhara was an ancient state, a mahajanapada, in the Peshawar basin in the northwest portion of the ancient Indian subcontinent, present-day Afghanistan and Pakistan.
Central Asian features: Green phyllite and grey-blue mica schist, the basic shape has been cut out of stone, this is then plastered with lime plaster to give it a finished look,
Greco- Bactrian features: Hellenistic features of Buddha, halo in the back, anthropomorphic traditions of Roman religion and represented the Buddha with a youthful Apollo-like face, dressed in garments resembling those seen on Roman imperial statues, great detailing such as curly hair, large forehead and ears, half-closed eyes.
Q2. The 1857 Uprising was the culmination of the recurrent big and small local rebellions that had occurred in the preceding hundred years of British rule. Elucidate (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The question demands an aspirant to mention various rebellions during 1757-1857 which has led to a major uprising in 1857.
Some Rebellions:
Rangpur rebellion 1783: Peasants and Zamindars of Rangpur region in Bengal rebelled due to excessive revenue demands of British.
Paika Rebellion 1817: Paikas were essentially the peasant militias of the Gajapati rulers of Odisha who rendered military service to the king during times of war while taking up cultivation during times of peace. They unfurled the banner of rebellion against the British under the leadership of Baxi Jagandhu Bidyadhara as early as 1817 to throw off the British yoke.
Santhal Rebellion 1855: Santhals made a determined attempt to expel the outsiders (Dikus).
Sepoy Mutiny 1857: Immediate ground for the 1857 uprising.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP VALUE ADD NOTES– Modern History
- ILP Mains Mock
- https://iasbaba.com/2019/05/rstv-ias-upsc-the-revolt-of-1857/
- https://iasbaba.com/2018/12/daily-current-affairs-ias-upsc-prelims-and-mains-exam-24th-december-2018/

Q3. Examine the linkages between 19th centuries ‘Indian Renaissance’ and the emergence of national identity. (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
Here, examine the threads of 19th Centuries ‘Indian Renaissance’ that lead to the creation of national identity which hitherto was missing in India.
Indian Renaissance a cultural, social, intellectual and artistic movement in pan India during the period of the British Indian Empire, from the nineteenth century to the early twentieth century. India engaged strongly in social and cultural preparation for participation in the more “progressive” and “radical”, political programme. This created national identity.
- Bengal Renaissance: This took place from Raja Ram Mohan Roy (1775–1833) through Rabindranath Tagore (1861–1941) in Bengal region.
- Socio-religious movements: Catalyst for the emergence of nationalism. The pioneer of this movement of regeneration of India was Raja Ram Mohan Roy (1774-1833), the father of modem India who is acclaimed as the link between the fading past and dawning future, between the deep-rooted conservatism and radical reform, and between superstitious isolationism and progressive synthesis, in short, between reaction and progress.
- Social reforms: voice against polygamy, child marriage, caste system, untouchability, superstitions and use of intoxicants. Raja ram Roy encouraged inter-caste marriages, women’s education and widow re-marriages.
- Educational reforms: Roy started many learned societies and educational institutions in Bengal. He studied English language and the western education system. He also helped Lord Macaulay in starting schools and colleges in India.
Political reforms: Many freedom fighters demanded independence for India and fought for civil rights of the Indians and opposed the racial superiority of Europeans.
Other reforms: As more Indians went abroad, they reinterpreted ancient wisdom in modern idioms and likes of Vivekanada, Mrs Arundale, LokmanyaTilak, Sarvarkar, Gandhi, KaniyalalMunshi, Tata, Birla and Bose helped spark renaissance in different fields of art, crafts, dance, music, philosophy, politics, economics, science, literature etc.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP VAN- Covered in detail
Q4. Assess the impact of global warming on coral life system with examples. (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
Here, illustrate and assess with examples the impact of global warming on coral life.
Negative Impact:
- Warming ocean- thermal stress
- Sea level rise- sedimentation
- Strong and more frequent storms- the destruction of reef structure
- Changes in precipitation: algal bloom and muddy water, reduce light
- Altered ocean currents- change in connectivity and temperature regime
Example: Great Barrier Reef, Amazon reef, Miami terrace reef are under threat
Positive impact:
- Reef-building corals cannot tolerate water temperatures below 64° Fahrenheit (18° Celsius). Many grow optimally in water temperatures between 73° and 84° Fahrenheit (23°–29°Celsius).
- Due to change of ocean currents, nutrients of the location changes in the ocean.
Example: extended regions of the bay of Japan’s Tsushima Island in the Korea Strait.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Are coral reefs important to us? Examine. Also, enumerate the factors that are causing coral bleaching (C2C/TLP OFFLINE (Phase 1) Test13).
- ILP VALUE ADD NOTES– ENVIRONMENT
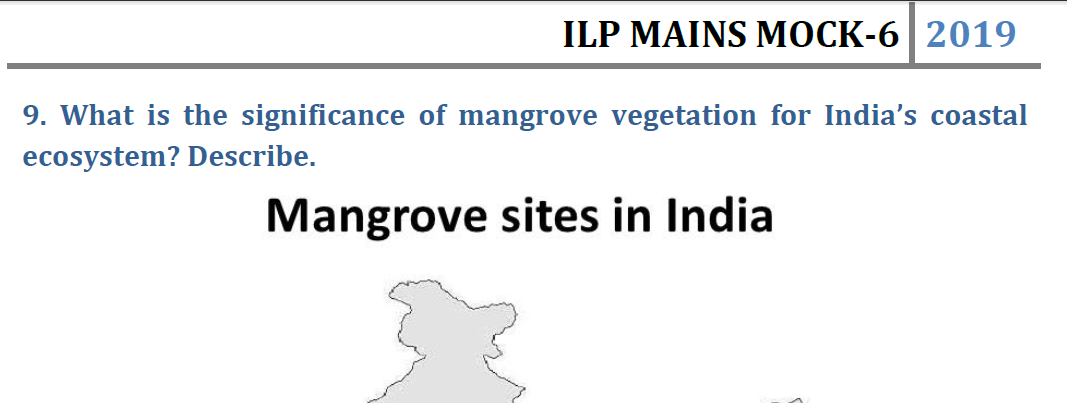
Q5. Discuss the causes of depletion of mangroves and explain their importance in maintaining coastal ecology. (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This is a direct question asking you to discuss the causes of depletion of mangroves and their importance in maintaining coastal ecology. Here you can conclude with suggestions to protect the depleting mangroves.
Causes for the depletion of mangroves:
- Clearing: Mangrove forests have often been seen as unproductive and smelly, and so cleared to make room for agricultural land, human settlements and infrastructure (such as harbours), and industrial areas.
- Overharvesting: Mangrove trees are used for firewood, construction wood, wood chip and pulp production, charcoal production, and animal fodder.
- River changes: Dams and irrigation reduce the amount of water reaching mangrove forests, changing the salinity level of water in the forest.
- Overfishing: The global overfishing crisis facing the world’s oceans has effects far beyond the directly overfished population.
- Destruction of coral reefs: Coral reefs provide the first barrier against currents and strong waves.
- Pollution: Fertilizers, pesticides, and other toxic man-made chemicals carried by river systems from sources upstream can kill animals living in mangrove forests, while oil pollution can smother mangrove roots and suffocate the trees
Importance of mangroves:
- Coastal protection: The dense root systems of mangrove forests trap sediments flowing down rivers and off the land.
- Fisheries: Mangrove forests are home to a large variety of fish, crab, shrimp, and mollusk species.
- Livelihoods: The rural communities we work with are fishers and farmers who depend on their natural environment to provide for their families.
- Water: Mangroves are essential to maintaining water quality. With their dense network of roots and surrounding vegetation, they filter and trap sediments, heavy metals, and other pollutants.
- Carbon storage: Mangroves sequester carbon at a rate two to four times greater than mature tropical forests
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Where would you find the maximum concentration of mangrove forests? What roles do mangroves play? Discuss. (TLP phase-1 2019)
- Discuss the distribution of major mangrove concentrations in the world. What roles do mangroves play in maintaining the ecological balance? What are the threats to mangroves? Discuss. (TLP phase- 2 2019)
- ILP VALUE ADD NOTES & Mock– ENVIRONMENT

Q6. Can the strategy of regional-resource based manufacturing help in promoting employment in India? (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The question is asking you whether/can the regional-resource based manufacturing generate more employment opportunities in India.
Mention some regions along with specific resources, which are helpful in manufacturing goods. Mention how employment can be generated through such manufacturing.
Examples:
- Cotton industries: Maharashtra, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu are abundant in cotton. Many cotton textiles are seen. Promotion of employment: KVIC (khadi and Village Industries Commission) plan, promote, facilitate, organise and assist in the establishment and development of khadi and village industries in the rural areas
- Jute industries: West Bengal, Assam, Orissa, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Tripura and Meghalaya are main jute growing industries. Promotion of employment -national jute policy and national textile policy
- Silk industries: Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamilnadu, Madhya Pradesh, Assam are main areas of silk industries. Promotion of employment: KSIC (Karnataka Silk Industries Corporation Limited) , central silk board are meant for expanding silk industries.
- Iron resources: Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Jharkhand, Odisha, Goa, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu are the principal Indian producers of iron ore. Promotion of employment: Jobs in Steel Plants (Visakhapatnam Steel Plant), Make in India projects in various states.
Q7. Discuss the factors for localization of agro-based food processing industries of North-West India. (Answer in 150 words).
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This question is specific to North-West India. One must discuss the factors which led to localization of agro-based food processing industries of North-West India.
Localization means the concentration of certain industries in particular areas.
Agro-based food processing is defined as a set of techno-economic activities, applied to all the products, originating from the agricultural farm, aquacultural sources, livestock and forests for their conservation, handling and value- addition to make them usable as food, feed, fibre, fuel or industrial raw materials.
Some of the factors for localization of food processing industries:
- States like Punjab, Haryana have high agricultural production (Green Revolution)
- High milk production in States like Haryana.
- Agricultural crisis and price fluctuations— Price fluctuations of agricultural produce are adversely impacting the predominantly agrarian states of North-West India. So, food processing sector can help bridging this void.
- Support by State Governments: Example-Punjab Government has formed a separate department of food processing industries.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- A similar question on North East in ILP Mock was asked.
Q.8. What makes Indian society unique in sustaining its culture? Discuss. (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
Though India is a land of diverse culture, it is able to sustain such a huge diversity. So how is India able to sustain its multi-culture society (which in itself makes our country unique) is the theme of the question.
Initially mention about the diversity of India and then bring in the unique features which have made India to sustain such wide diversity.
Examples:
- Co-existence of religions despite diversity (foreign religions and indigenous religions) from Centuries: Islam, Christianity, Judaism, Buddhism.
- Cultural tolerance: Many diverse geographical regions with various cultures co-exist even today. (Government Schemes—Ek Bharat, Shrestha Bharat)
- Propagation of culture through Socialization—Existence of Joint Family. Though the Joint Family Structure is disintegrating the familial relations still exist.
- Rulers like Ashoka, Akbar has patronized various religions and ensured that there is peaceful co-existence of religions.
- Principle of Sarva Dharma Samabhava is rooted in India’s tradition and culture—equal respect for all religions
- Indian culture in general and Hindu religion in particular have permitted and encouraged multifaceted ways of devotion, worship approaches to the understanding of world and reality.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP VAN- Culture and Society

Q9. “Empowering women is the key to control population growth”. Discuss (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The question is demanding the aspirant to establish a link between women empowerment and the control of population growth.
Firstly, one can write about the population growth rate in India and establish the need to control it.
Then data should be provided in such a way that it substantiates that, women empowerment will help to control the population growth.
The Economic Survey of 2018 mentions about son meta preference. This has resulted in 21 million “unwanted girls” in India. Such gender preferences are also contributing to the population explosion in India.
The wanted fertility rate in the country is 1.8 (NFHS-4), which means that women do not want to have more than two children. (Pressure from family)
Kerala- Female Literacy 92% Total Fertility Rate-1.8
Bihar—Female Literacy 51.5% Total Fertility Rate-3.6
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Population Control – Daily Current Affairs Analysis-26th July 2019
- https://iasbaba.com/2019/07/daily-current-affairs-ias-upsc-prelims-and-mains-exam-26th-july-2019/
Q.10. What are the challenges to our cultural practices in the name of secularism (Answer in 150 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH :
Here, you need to connect the concept of secularism with the challenges it brings to diverse cultural practices carried out in India.
The Indian concept of Secularism: equal treatment of all religions by the state and no special rights to any religion; it has to support all religion equally.
Secularism and conflicts with cultural practices:
- Religious Morality vs Constitutional Morality (Example: Sabarimala Verdict)
- Cultural traditions vs Secular traditions (Challenging the appointment of priests on the basis of Agamas)
- Triple Talaq and polygamy which is practiced by Muslims since ages is challenged.
- Cultural Practices in Hindu religion, existing from centuries are challenged (Made Snana in Coastal belt of Karnataka)
- Cow Slaughter law challenges the food habits of minority religion.
- In the name of Secularism, demand for Uniform Civil Code, though will bring in equality will subsume many cultural practices.
IASBABA’S REFERENCE:
- The fact remains that secularism is inherent in the Indian system, in the Indian ethos and culture. India cannot but be secular. Comment. (TLP plus/offline test-6)
- Do you find any contradictions in the prevalent notion, understanding and practice of secularism in India? Critically comment. (TLP 2019-phase 2)
- ILP VAN- covered in detail
Q11. Many voices had strengthened and enriched the nationalist movement during the Gandhian phase. Elaborate (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This is a direct question on Gandhian phase of freedom struggle.
Many famous personalities took part in the freedom struggle, especially during the Gandhian phase.
Here you need to mention about the various ideologies, philosophies and various personalities who brought a change through their own way in freedom struggle during Gandhian Phase i.e. from 1914 till independence.
For instance, mention about the contributions of Madan Mohan Malviya (Nationalistic education system), Aurobindo Ghosh (Spiritualism and revolutionary movement, Subhash Chandra Bose ( Socialism and extremism) , Tilak’s (Ganapati festival to bring masses into freedom struggle).
Also, you can mention the participation of:
- Women participation: thousands of women came out of their homes and participated in salt satyagraha.
- Working-class and professionals participated: lawyers, teachers, professors also joined the national movement.
- Students also boycotted class and participated in the movement in large scale.
- All religion participated: irrespective of religion and caste all people took part in mass movement.
- Business class participated: gave financial assistance and rejected imported goods.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- How did Gandhi’s arrival change the discourse of the nationalist movement? Did it make the movement more inclusive and representative? Critically comment. (TLP Phase-II 2019 GS-1 compilations).
- The phase of freedom struggle in India’s modern history witnessed intense debates over suitability of different economic ideologies to shape the country. What were the most prominent of these ideologies? Who propounded them? Also, outline the larger debates that ensued. (TLP Plus-2019 Test-1).
- ILP VAN- covered in detail
Q12. Assess the role of British imperial power in complicating the process of transfer of power during 1940s. (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH :
This is a question which asks about how British imperial power caused various troubles and hinders in transfer of powers to Indians during the 1940’s.
For example: You can talk about how in the name of transfer of power, Britisher’s involved Indian princes and Muslims to create friction between various elements. Delayed announcing border commission, formed various committees to delay transfer of power like August offer, Crips mission, Wavell plan etc.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Do you think the transfer of power from the British to the Indians was hastily handled? Critically comment. (TLP Phase-I 2019 GS-1 compilations).
Q13. Explain how the foundations of the modern world were laid by the American and French revolution. (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The question is on the contribution of American (18th century- 1775) and French revolution (18th century- 1789) to the making of the modern world (starting from the mid of 19th century – 1850 onwards)
Your answer should include how governance changed from monarchy to republican form of government, rule of law, Principles of equality, liberty and justice, separation of power, voting rights etc.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP Value Add Notes- Covered in detail (Mind Maps)
- ILP Mains Mock
- Examine the democratic principles that took a concrete shape post-American independence. (TLP Phase-I 2019 GS compilations).
- How did different European powers respond to the French revolution? Discuss. (TLP Plus 2019 Test-1).
- Why did anti-monarchy sentiments spread in 18th century Europe? Examine. (TLP Phase-I 2019 GS-1 compilations).
- What role did thinkers and philosophers play in the awakening of the conscience of the European society? What were its consequences? (TLP Phase-I 2019 GS compilations).


Q14. What is water stress? How and why does it differ regionally in India? (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This is a question which tests your knowledge about water scarcity which the world is facing and the factors which causes the scarcity in different parts of India.
In introduction define what do you mean by water stress. Then in body, you need to explain the reasons behind the water scarcity in different regions of India.
For instance, Chennai is located on Bay of Bengal but still faces water scarcity, explain how and why it faces. Same way Vidarbha region and Shimla. All three has different factors and causes. You need to identify them and explain.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP MAINS VAN- Water Stress/ Security
- Why has water become a stressed resource in many parts of the world? Analyse. (TLP Phase-I 2019 GS-1 compilations).
- Which parts of the world are suffering from acute water scarcity? It is being feared that the situation will worsen even further? Why? Analyse. (TLP Phase-II 2019 GS-1 compilations).
- How is urbanisation affecting the water bodies in the cities? What are its implications? Examine. (TLP Phase-II 2019 GS-1 compilations).
- Why is Chennai facing abnormal levels of dryness? Examine. What policy measures are needed to address the problem? Discuss. (TLP Plus/Offline 2019 test-13).
Q15. How can the mountain ecosystem be restored from the negative impact of development initiatives and tourism? (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This question is specific to mountain ecosystem, you need to first define mountain ecosystem in introduction then identify the issues with mountain ecosystem caused due development initiatives and tourism in the first part and then measures to restore them.
For instance, Mention the negative impacts like Landslides, Flash floods, Plastic wastes, invasion of alien species, monotype culture etc. Take examples of places around Himalayas like Kedarnath (floods), Shimla (Landslides), Mount Everest (Disposal of degradable and non-degradable wastes), Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats etc.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- What are some of the most serious threats to the Himalayan ecosystem today? What is the contribution of human activities in degrading the Himalayas? Discuss. (TLP Test-13)
- ILP MAINS MOCK

Q16. How is efficient and affordable urban mass transport key to the rapid economic development of India? (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The question is asked in the background of rising problems of traffic congestion in urban areas. The answer needs to primarily address the benefits of mass transport system in Urban areas.
The answer needs to highlight that mass transport system needs to be efficient w.r.t connecting different parts of Urban areas (including last-mile connectivity); efficient w.r.t time management so that these systems can be relied upon by people; efficient w.r.t energy usage so as to reduce pollution in urban areas (push for electric buses) and efficient w.r.t safety and security of transport operations. The answer should also highlight the need to make such transport systems affordable so that it is accessible by all sections of society in Urban areas.
These characteristics in Urban mass transport system will ensure people will not opt for personal vehicles for commuting in urban areas which inturn will reduce traffic burden on roads. Reduced traffic on roads will lead to savings in petrol and diesel (positively affecting our Current account deficit through reduced oil imports). Urban mass transport will also lead to reduction in travel time – thereby increasing time for productive work. The opportunity cost of commuting within Urban areas is thus reduced through efficient and affordable mass transport system. The answer can also give examples of Suburban rail system in Mumbai and Metro system in Delhi – the success of which has led to replication of same models of Urban mass transport in other cities across India.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Explain the concept of urban mobility with the help of at least two case studies. (TLP plus/Offline 2019 Test-6).
Q17. How do ocean currents and water masses differ in their impacts on marine life and coastal environment? Give suitable examples? (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The answer needs to bring out the distinction between Ocean Currents and Water masses and their impacts on marine life and costal environment.
Water mass is a body of water which has physical properties (like temperature, salinity, density) distinct from surrounding water. Ocean currents are body of water mass which flow in a well-defined path under the influence of wind, coastal features and Coriolis force.
Ocean currents impact the temperature & humidity of coastal regions for example: Warm current increases the temperature and humidity of the coastal area through which it passes, such as the Norwegian current which increase the temperature of the coastal areas of North Sea make the port workable and climate cool and moist. Also most of the cold current are found in the western margin of the continents in lower latitude which is associated with the desert landforms in these latitudes
Example: California current in western USA, Peru current in western south America etc. Ocean currents also impacts marine life and thus fish resources: In East Asia meeting of the warm Kuroshio and the cold Oyashio current provides ideal conditions for rich fishing grounds in Japan. However, navigation becomes difficult due to thick fog.
Water masses determine the hydrological conditions of the water which influence the production and the growth of plankton and fish species. For example: the growth of and survival of Corals is largely dependent on the stable conditions of water masses in which they reside. Likewise, water masses impact the humidity and pressure of air above its surface, which inturn impacts the circulation of winds affecting coastal environment Ex: Land breeze and Sea breeze.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP Value Add Notes- Covered in detail
- ILP Mains Mock- How do ocean currents alter the climate of a place? Illustrate with the help of suitable examples.
- Ocean currents have far-reaching impacts on the coastal economy. Do you agree? With the help of suitable examples, examine the ways in which ocean currents affect the coastal economy. (TLP Phase-II 2019 GS-1 compilations).
- How do ocean currents affect global climate? Illustrate by taking suitable examples. (TLP Phase-I 2019 GS-1 compilations).

Q18. Do we have cultural pockets of small India all over the nation? Elaborate with examples (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The answer should bring out the different diversities present across India and also the underlying unity.
Tribal diversity present across India have different culture compared to mainstream culture. Example: Gonds Tribes. Bhils Tribes. Santhal Tribes. Great Andamanese Tribes. Khasi Tribes. Garo Tribes.
Linguistic diversity in India – 22 official languages in VIII schedule of the Constitution
Diversity with regard to cuisine, dressing, festivals celebrated and customs observed varies from one region of India to other region. For example: Matrilineal system is observed in certain areas of Meghalaya, whereas there is strong continuance of Patriarchy and caste reflected in Haryana’s Khap Panchayats.
The can be concluded by bringing out the Cosmopolitan culture which is present Indian cities like New Delhi and Mumbai which has people from all parts of India, people belonging to all classes (billionaires and slums), all castes and all religion residing in peaceful and harmonious manner. These centres of agglomeration, in the long run have its own advantages in terms of blurring societal identity fault lines leading to better integration and acting as economic engines of the Country
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Has Indian society become intolerant in recent years? Has its religious and cultural diversity created irreparable fissures? Give your opinion. (C2C/ TLP OFFLINE (Phase 1) Test-7 2019).
- The cultural practices of India have helped in the sustenance of the ecosystem. Do you agree? Substantiate with the help of suitable examples. (C2C/TLP OFFLINE (Phase 1) comprehensive Mock-1 2019).
- India’s tribal diversity is capital. Do you agree? Substantiate. (TLP Phase-II 2019 GS-1 compilations).
- The tremendous tribal diversity of India is a socio-cultural asset. Elucidate. (C2C/ TLP OFFLINE (Phase 1) Test-7 2019).
- ILP Mains Mock- Comment upon the tribal diversity of India. Also, examine the socio-economic challenges being faced by the tribal population

Q19. What are the continued challenges for women in India against time and space? (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The answer primarily needs to bring out the problems faced by Indian Women over time (history) and space (geography)
Problems w.r.t time includes problems of Patriarchy still continuing in this modern era. The answer can expand on patriarchy present in social sector (access to education and health), in religious sector (denial of entry to temples/mosques), in economic sector (wage inequality between men and women, presence of glass ceiling) and in Political sector (low women representation in Legislatures).
The problems faced by Indian women against space can include inequality amongst women in rural and urban areas, competition in economic field from other developing countries (example of textile sector) and challenges in commuting from one place to another due to safety and security concerns.
The answer can also cite examples of recent current happenings like Sabrimala entry issue and metoo movement which highlighted the continuing challenges faced by women.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Examine the implications of adverse sex ratio for India’s future. (TLP Phase-I 2019 GS-1 compilations).
- The #metoo campaign is a reflection moral decline of Indian society. Comment. (TLP Phase-I 2019 GS-1 compilations).
- India has quite a progressive gender jurisprudence wherein women rights are protected by laws and institutions and women interests are furthered by a multitude of welfare schemes. Yet India performs poorly on major socio-economic and political indicators related to women. Why? Analyse the factors leading to this contradiction. (TLP plus/Offline 2019 Test-6).
- What is ‘sexism’? Examine its prevalence in Indian social life. Why is it harmful? Discuss. (TLP Plus/Offline comprehensive mock-1).
- The absence of women at the level of policymaking is a serious impediment to inclusive growth. Elucidate. (TLP Phase-II 2019 GS-1 compilations).
- ILP Mains Mock- Working women in India face challenges on multiple fronts. Do you agree? Illustrate
Q20. Are we losing our local identity for the global identity? Discuss. (Answer in 250 words)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The question is about the critical examination of the phenomenon of Globalisation.
Globalisation not only involves increased exchange of goods and services but also involves exchange of people, culture and Ideas. Integration and interconnectedness of economies of the world is also leading to integration of cultures. For instance: The music culture (pop music), dressing habits (western jeans wear) and value system (individualism over communitarianism) are all being impacted by globalisation.
Example of MacDonalds impacting our food habits. Thus, there is an argument that globalisation is leading to homogenisation of culture whereby people’s local identity is losing its uniqueness. The rise of protectionist measures and right-wing political parties across the world can also be attributed as backlash against the rise of global identity. The referendum results of Brexit can be cited as an example of this backlash.
The answer also needs to point out the negative fallout of such protectionism especially for India which being an emergent country needs open world to expand the scope of its exports and investment source.
The answer can conclude by highlighting the phenomenon of glocalisation – Globalisation + Localisation. This can be seen in the example of Mac Donalds avoiding pork & beef in India and instead offering Panneer Burgers so as to suit local tastes & needs. Therefore, local identity is still retained while at the same time going for more open world. Such trends show that fears of imposition of foreign values leading to loss local identity are thus misplaced.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP Mains Mock- What is glocalisation? How is it reshaping the business strategies in the 21st century? Discuss
- What do you understand by the term ‘cosmopolitanism’? Does it affect the cultural diversity of a place? Critically examine. (TLP Plus/Offline (Phase 2)2019 Test-1).
- Examine the ways in which globalisation has affected the taste for popular culture in India. (C2C/TLP OFFLINE (Phase 1) Test-7).
- Do forces of globalisation affect social mores and traditions? Substantiate with the help of suitable examples. (C2C/TLP OFFLINE (Phase 1) Test-7).
UPSC MAINS GENERAL STUDIES PAPER 2
OVERVIEW of GENERAL STUDIES (GS) PAPER 2:
This year’s question paper of GS-2 was one of the most analytical and lengthiest paper created by UPSC in the last few years. The questions were found to be on a tougher side. It was a mixture of Fundamental and Applied part.
To score high in this paper, one needs to be well aware of several important articles of Indian constitution along with current affairs, because most of the questions appearing in the GS-2 paper has direct link with recent happenings. Also one needs to include recent commissions, reports, and its recommendations in the answers.
Let us take the example in International Relation part, USA’s official pull out of UNESCO happened in December 2018, China’s increasing assertion in South china sea and USA’s Pacific doctrine has India and Japan playing a key role. So they were asked in 9th and 10th question.
Also this time the paper was such that one needs to devout at least 30-40 seconds per question to read and understand what is the basic demand and which part needs to be addressed. For instance, “From the resolution of contentious issues regarding distribution of legislative powers by the courts, ‘Principle of Federal Supremacy’ and ‘Harmonious Construction’ have emerged. Explain.” Here while reading on the first instance, there are chances of misunderstanding and explaining the distribution of legislative powers but the actual demand of the question is about the “Principle of Federal Supremacy”
The difficulty level of questions can be broken up into 3 scales i.e. Easy, Moderate and Difficult. The Difficult questions occupied the highest portion in the paper with 8 questions (4, 6, 7, 10, 16, 17, 19, & 20), the second is occupied by the moderate level with 7 questions (1, 2, 8, 9, 13, 15, & 18), the easy level occupied the last with 5 questions (3, 5, 11, 12, & 14).
There were 4 questions on International relations and 16 questions on Indian polity.
Q1. Do you think the Constitution of India does not accept the principle of strict separation of powers rather it is based on the principle of ‘checks and balances’? Explain. (10 Marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This is a direct question on Indian government system. Here you need to write about how Indian constitution even though talks about separation of power, has nowhere explicitly mentioned about it but rather has created a system of checks and balances to make sure no organ of state becomes very powerful and all 3 organ overlap/co-ordinate with each other for effective and efficient governance.
In introduction, define what you mean by separation of power doctrine. Then in main part, explain how Tasks are assigned to the different branches and their institutions in such a way that each of them can check the exercise of powers by the others. As a result, no one branch or institution can become so powerful as to control the system completely.
Also you can mention the other side by providing examples of Article 50, Articles 121 and 211 and Article 361 to explain how separation of powers are part of constitution.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- How far has the doctrine of separation of powers fared in India’s political system? Illustrate with the help of suitable examples. (C2C/TLP offline 2019 Test-1)
- Explain the concept of ‘doctrine of separation of powers’. Also examine its significance in a parliamentary democracy. (TLP Phase-1 2019)
- Covered in ILP VAN.

Q2. “The Central Administrative Tribunal which was established for redressal of grievances and complaints by or against central government employees nowadays is exercising its powers as an independent judicial authority.” Explain. (10 Marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The question is on Central administrative tribunal which was established under Art 323A of Indian constitution. You need to define in a line or two about what is CAT in Introduction along with the Article and when it was established (1985).
Then in Body, explain why it was established and its functions in 1st part, then in 2nd part explain how it has grown as an independent judicial authority over time.
End by quoting the recent verdict of Delhi HC on CAT and its powers.
Example: You can mention about how CAT rebutted the verdict of Delhi HC on its jurisdiction and asked it to swiftly decide on matters originally pending before the HC. Also, you can mention how CAT had stayed the decision of the government to retire two officers on non-performance issues.
Q3. What are the methods used by the farmer’s organizations to influence the policy-makers in India and how effective are these methods? (10 Marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This question is indirectly asking about the role of pressure groups and in particular farmers related pressure groups and how they influence the policymaking in India and how effective are they.
In the introduction, define what are pressure groups and their types. Then in the body part, list the methods used by them to influence policymakers.
Example: farmer’s protest march in Maharashtra recently, farmer’s destroying their produce over price fall issues across MP etc. Don’t forget to bring examples from various decades since independence (Agriculture Revolutions etc.)
Also, mention how effective they are in short and long terms. You can mention about Examples of remunerative prices (MSP) and sugarcane (Fair and remunerative prices). Also, you can mention about private bills being pushed in parliament for the same.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- PepsiCo versus potato growing farmers – https://iasbaba.com/2019/05/daily-current-affairs-ias-upsc-prelims-and-mains-exam-11th-may-2019/ (Daily Current Affairs Analysis-11th May 2019)
Q4. From the resolution of contentious issues regarding distribution of legislative powers by the courts, ‘Principle of Federal Supremacy’ and ‘Harmonious Construction’ have emerged. Explain. (10 Marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This is analytical questions which ask you to explain how over the years, through judicial interpretation and judgements, the legislative powers have been devolved and federal supremacy has been upheld and Doctrine of Harmonious construction have evolved.
For this question, you need to define what is the doctrine of federal supremacy and Harmonious construction in Introduction. Then in the body you need to bring out how the Principle of federal supremacy was upheld and how Harmonious construction has emerged.
Example: you need to mention with examples how some state laws were quashed which were ultra vires or against federal laws [Certain reservation bills of state like The Haryana Backward Classes (Reservation in Services and Admission in Educational Institutions) Bill 2016 and the Haryana Backward Classes Commission Bill 2016,]. Then mention the five principles laid down by the supreme court on the rule of Harmonious Construction in the landmark case of CIT v Hindustan Bulk Carriers.
Q5. What can France learn from the Indian Constitution’s approach to secularism? (10 Marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This is a direct question which asks you to compare Indian constitution with French constitution. You are aware that both India and France are constitutional democracy but follow different system of governance especially when it comes to principles of secularism.
France follows strict principle of secularism where has Indian secularism is equal respect to all religions. This question has come due to various protests in France in form of ban on Islamic dress like Burqa, veil, then raise in islamophobia, ban on halal meat, few years back Charlie Hebdo issue etc.
Your answer should contain all these examples and how France can learn from Indian secularism where multi-religions co-exist peacefully and how accommodating our constitution is in form of Fundamental rights 25-28, Education (Gurukul system, Christian convent, Islamic education), Subsidies for Pilgrimages (Haj, Amarnath) etc.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Do you find any contradictions in the prevalent notion, understanding and practice of secularism in India? Critically comment. (TLP phase-2 2019)
Q6. Despite Consistent experience of high growth, India still goes with the lowest indicators of human development. Examine the issues that make balanced and inclusive development elusive. (10 Marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This question is asking about India’s declining performance of Human development indicators even though we are experience high growth rate. Here, you can come up with facts related to human development indicators in India – India’s rank in HDI (130)
In main part of body, you need to identify those factors which are hindrance to human development and how it is impacting the country.
Then in 2nd part of body, you need to explain the issues which make balanced and inclusive development elusive. Then conclude by giving ways to address the issues like for instances, quality education to all, making healthy life a fundamental right, providing opportunity for skill development and employment etc.
Issues: Economic inequality, Poverty, Lack of awareness on government initiatives/schemes/welfare programs, etc. Prevalence of customs and traditions which act as hinders to bring about a change, for instance, women’s access to quality education (Patriarchy), access to health-related products, ( access to menstrual hygiene related products) etc
Facts that can be used in this answer – MMR 130/1L live births, Life expectancy 68.5, IMR 34/100 live births, 73% of the wealth generated in 2017 went to the richest 1% (Oxfam). 21.9% of the population is living below poverty line (2011-12) as per National poverty estimates.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- How does poverty stifle human development? Can poverty alleviation measures address the problem of stifled human development? Critically examine. (TLP phase-2 2019)
- What is Human Development Index (HDI)? Evaluate India’s overall performance with respect to the indicators constitutions the HDI. (TLP Phase-2 2019)
Q7. There is a growing divergence in the relationship between poverty and hunger in India. The shrinking of social expenditure by the government is forcing the poor to spend more on non-food essential items squeezing their food-budget – Elucidate. (10 marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
Usually poverty and hunger are related concepts. But here, you should substantiate with examples and data’s to show how there is growing divergence between the two.
In second part of question you need to explain with examples about how the government’s expenditure of social sector is decreasing and thus leading to poor spending more on non-food essentials like Health, Medicines etc.
For example: Only 3% of GDP is spent on education, 1.4% on Health, and more than 70% health expenditure are out of pocket, 22% of Indians live below poverty line.
Also include some positive, do not keep it too much negative. Mention about improvement India has made in halving poverty, reducing malnutrition, child wasting & Stunting among others.
IASBABA REFERENCE:


Q8. Implementation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) based projects/programmes usually suffers in terms of certain vital factors. Identify these factors and suggest measures for their effective implementation. (10 marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
This is a direct question on E-governance. Central government has been emphasizing too much on digital India and question on ICT was on expected line but here there is a twist. They have asked about negative sides on ICT. So you need to identify them, factors involved and suggest measures to address them.
Also include government programs in areas of ICT like Digital India, Bharat Net, NeGP etc.
For example: mention how the government has introduced ICT in PDS and issues with that (Aadhar linking, Biometric issue and how a child had to die due to hunger), Mention about issues with E-literacy, lack of access to speed internet, Privacy, Security related issues etc.
Also, give some positive aspects of ICT. For instance, how it saved revenue for exchequer by plugging leakages, weeding out ghost beneficiary, targeted delivery of services etc.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- How is the government leveraging ICT to deliver its services faster and without leakages? Illustrate with the help of suitable examples. (TLP Phase-II 2019)
- What are the impediments of e-governance in India? How can those be addressed? Discuss. (C2C/TLP offline Test-11)
Q9. ‘The time has come for India and Japan to build a strong contemporary relationship, one involving global and strategic partnership that will have a great significance for Asia and the world as a whole.’ Comment. (10 marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
Answer in two parts. Role of diplomacy between India and Japan in global partnership and strategic partnership in Asia.
In global partnership: Role of QUAD in countering the aggression of China, Tackle common challenges of terrorism and proliferation, Asia-Africa Growth Corridor or AAGC is an economic cooperation agreement between the governments of India, Japan and multiple African countries
In strategic partnership: nuclear deal, bilateral agreements, investment in north eastern countries, cultural exchange, military ‘exercise malabar’
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Indo-Japan relations not only transcend economic boundaries but also entail deep geostrategic convergence. Comment. (C2C/TLP Offline Test-11)
- The quadrilateral posturing by India, the US, Japan and Australia in the Indo-Pacific is critical to counter the aggression of China in the region. Comment. (TLP Phase-II 2019)
- Covered in VAN
Q10. ‘Too little cash, too much politics, leaves UNESCO fighting for life.’ Discuss the statement in the light of US’ withdrawal and its accusation of the cultural body as being ‘anti-Israel bias’. (10 marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The question is in reference to US pull out from UNESCO due to accusation against the organization for being Anti-Israel. Here you need to explain about UNESCO as a organization in Introduction. Then in body, firstly you need to list out the important functions and roles of UNESCO. Then explain the given quote and link it with issues plaguing the world organization.
Then explain the impact of US pull out and future of the institution in the conclusion.
Anti-Israel bias: UNESCO criticizing Israel’s occupation of East Jerusalem, then naming ancient Jewish sites as Palestinian heritage sites and granting full membership to Palestine in 2011 among others.
Example:
UNESCO is the first U.N. agency that has admitted Palestine as a full member, in 2011. As required by law, the U.S. has stopped funding the UNESCO since then. The U.S. withdrawal took effect on December 31, 2018. With US being the largest donor pulling out, its left wanting for funds. With lack of funds and donor, it is at the risk of being closed down and several initiatives like world heritage sites, Education, Cultural promotion will take a hit.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
Q11. On what grounds a people’s representative can be disqualified under the representation of people act, 1951? Also mention the remedies available to such person against his disqualification. (15 marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
It is direct question. Mention on what grounds people’s representative can be disqualified. And mention remedies to protect them from disqualification
Grounds: election offences and corrupt practices in the election, dismissal for corruption or disloyalty, failure to lodge account of election expenses, corrupt and malpractices in any type of media.
Remedies: exemption from office of profit, opinion of election commission of India
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Recent developments in Karnataka and Goa legislative assemblies prove that the political problem of defection can’t be addressed by the legal solution of the anti-defection law. Comment. (TLP Phase-II 2019)
- Polity VAN-ILP
Q12. “Parliament’s power to amend the constitution is a limited power and it cannot be enlarged into absolute power”. In the light of this statement explain whether parliament under article 368 of the constitution can destroy the Basic structure of the constitution by expanding its amending power? (15 marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The answer can begin with the explanation for the need to amend the Constitution – to make it relevant to changing times. It can cite the example of recent GST. Parliament has been vested with amending power so as to make Constitution a living and dynamic document.
The answer can then give historical examples where Parliament using this power has tried to amend Constitution which led to dilution of Fundamental rights of Citizens (25th and 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act) thus threatening the basic principles of Constitutional Democracy. The answer can then explain about SC judgement on Parliament’s power to amend constitution in Kesavananda Bharati Case which gave the doctrine of Basic Structure.
The answer can also elaborate on some of these basic structures – Independent Judiciary leading to striking down of NJAC. Therefore, along with strict procedures laid out in Article 368 for amending Constitution, Parliament is restricted its power to amend Constitution so that the soul of Constitution as envisaged by founding father of India remains intact.
Important Judgements that can be used: Minerva Mill v. Union of India (1980): the validity of 42nd amendment Act was challenged on the ground that they are destructive of the ‘basic structure’ of the Constitution. The Supreme Court by majority by 4 to 1 majority struck down clauses (4) and (5) of the article 368 inserted by 42nd Amendment, on the ground that these clauses destroyed the essential feature of the basic structure of the constitution.
Chandra Kumar v. Union of India (1997): The judgment held that every provision of the Constitution was open to amendment provided the basic foundation or structure of the Constitution was not damaged or destroyed.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Does in your opinion the basic structure doctrine undermine parliamentary sovereignty? Critically examine. (TLP Phase-I 2019)
Q13. “The reservation of seats for women in the institution of local self-government has had a limited impact on the patriarchal character of the Indian political process”. Comment. (15 marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The answer needs to provide both positive impacts as well as negatives of women reservation in India at the local governance level. The answer can start by mentioning the significance of local self-government (Democratic decentralisation, transparency & accountability) and the landmark 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment Acts which provided for Constitutional status to these institutions.
The second part of the answer can elaborate on need for reservation of seats for women in these institutions – Women are considered as largest minority, political process was confined largely to voting during elections and that too was dictated by male members of family. Through such affirmative actions, Women are empowered politically so that theirs concerns are given importance at grass root level. Due to these measures their bargaining power has not only increased in public sphere but also increased in private sphere due to enhanced socio-political awareness among women. This enhanced awareness has led to fighting Patriarchy both at home and at public places.
Other reasons – Khap Panchayats, they play a major role in restricting the empowerment of women and curtail their freedom. The low literacy level of women, lack of social encouragement due to societal norms, etc.
The answer should also elaborate on the phenomena of Pati Sarpanch- where women representatives are proxies and real power is still exercised by their male counterparts. The domination of male members in these local institution coupled with inadequate capabilities of women (administrative and educational) has led to continuance of Patriarchy.
The answer can conclude by citing examples of certain states who have increased the reservation for women up to 50% and rising demand for reservation of seats for women at State and Union legislatures.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP VAN and Mock
Q14. “The Attorney-General is the chief legal adviser and lawyer of the Government of India.” Discuss (15 Marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The question is a direct one which needs to elaborate the role and duties of Attorney-General of India. The answer can start by mentioning about Article 76 of Constitution which has provided for the office of the Attorney General for India.
The answer can elaborate on the appointment and terms of the office of Attorney-General of India and can then expand on the duties performed. Conclude the answer by highlighting the need for such office (Government is the biggest litigant in Indian courts).
Examples: AG acted as legal adviser and lawyer of Government of India: Need to link social media profiles of registered users with their Aadhaar numbers—Attorney General appeared for Tamilnadu Government in SC
The Supreme Court has fixed a deadline for the search committee on Lokpal to recommend a panel of names for appointment of the country’s first anti-graft ombudsman.—- Attorney General appeared for Centre.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP VAN and Mock
Q15. Individual parliamentarian’s role as the national lawmaker is on a decline, which in turn, has adversely impacted the quality of debates and their outcome. Discuss. (15 marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The question needs to mention the role of MLA’s, who play a significant role in law making process of the country. The reason for the decline of quality of debates and consequences of such trend.
Parliament is considered as temple of Democracy where elected representatives arrive at decision regarding governance after debates & deliberations. It is considered as the highest platform for holding the executive accountable for their actions.
The answer can then mention the reasons for its decline – Tyranny of Political Parties through instruments of Whip and Anti-defection law curbing the voice of individual lawmakers, live telecasting of Parliamentary proceeding incentivizing sensationalization of issues often neglecting meaningful discussions, use of obstructionist strategy by opposition to target ruling party, criminalization of Politics, reduction in number of sitting days of legislature and politicization of office of Speaker.
The impact is decline in credibility of the institution and thus its role in holding executive accountable for their policies & actions. This has led to poorly drafted legislations and authoritarian tendencies of executive. The answer can conclude by suggesting reforms to rectify the situation – increase the number of days of Parliamentary sittings, restrict anti-defection law only to no-confidence motions, reforms in Office of Speaker etc. as suggested in ARC 2.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- A similar question was asked in ILP Mock- The centre has a lot of dead weight in terms of ministries that are either nonfunctional or have delicate roles. Do you agree? Substantiate. How can this be addressed? Suggest
Q16. ‘In the context of the neo-liberal paradigm of developmental planning, multi-level planning is expected to make operations cost-effective and remove many implementation blockages’- Discuss (15 marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
Here, you need to explain how in the era of neo-liberal paradigm, multi-level planning has brought inefficiency in governance and made the implementation process smooth.
In introduction mention the change in developmental planning in the context of the neo-liberal era. Then in body, explain what is multi-level planning, then explain how multi-level planning is going to make operations cost-effective and remove implementation blockages.
Multi-level planning is expected to reduce regional disparities and bring more equity in development since the chief factor behind persistent regional imbalances has been diagnosed as the unstudied application of the macro plan at micro levels without necessary modifications/detailing by the local development planners to address the particular requirements of an area/target group.
Examples: Mention how expertise (subject/sector-specific) are involved in planning there by a detailed plan along with identification of bottlenecks in done and a solution is given mention how with the involvement of bottom level workers, ground-level difficulties/hindrances are taken into account. How there is going to be proper linkages between all stakeholders thereby proper flow of command and communication etc.
How in the neo-liberal phase, planning is done giving importance to local cultures and geography. Example – resource-based mobilization, job creation as we see in Punjab (wool based), West Bengal and Assam (Tea based).
Q17. The need for cooperation among various service sectors has been an inherent component of development discourse. Partnership bridges the gap among the sectors. It also sets in motion a culture of ‘collaboration’ and ‘team spirit’. In the light of statements above examine India’s development process. (15 marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
Initially mention the significance of cooperation in service sectors, which plays an important role in a country’s development. Later examine the present scenario of co-operation in India’s service sector and conclude with suggestions in overcoming the gap among various sectors.
Example:
Co-operation among Education, skill development, Health sector holds significance in India’s context. India has a huge demographic dividend and it has to be leveraged fruitfully over the next few decades. The potential of our youth has to be realized through education, skill development, elimination of gender bias, employment and good health. So the three sectors need to work in tandem to leverage the benefit of demographic dividend.
Co-operation among tourism, transport, hospitality. All these sectors need to work in co-operation which will not only generate revenue for the government but also create many employment opportunities to the people.
Q18. Performance of welfare schemes that are implemented for vulnerable sections is not so effective due to the absence of their awareness and active involvement at all stages of policy process. Discuss (15 marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The crux of the question is on low effectiveness of the welfare schemes for vulnerable sections because of lack of awareness of the schemes and participation of the vulnerable section in all the 3 stages of policy process- policy formulation, implementation, evaluation.
You can come up with case studies here.
Example:
Case 1: How central government’s minimum support price failed marginal farmers-In 2018-19, just 12% of the 33 million farmers who were growing wheat availed of the government’s minimum support price (MSP), or the price at which it promises to buy 25 crops from farmers, regardless of their prevailing market price. The rest were sold in mandis, whose access was usually controlled by middlemen and where market prices are often below government MSPs. This is a case of lack of awareness among the farmers and also price is not fixed based on the consultation with the farmers(vulnerable section)
Case 2: The Beti Bachao Beti Padhao Scheme (BBBPS) is a flagship programme run by the central government to ensure the survival, protection and education of the girl child. The programme has failed in few districts because of lack of policy implementation, diversion of funds and the failure of monitoring mechanisms. This is a case where stakeholders are not involved in policy monitoring process.
This data is for your reference: Haryana has 20 districts that are in the gender-critical district list. As per the guidelines, Rs 5 lakh were to be provided to each district for implementing the scheme. The diversion of funds has been noted in various districts of Haryana. For example, in Panipat out of the Rs 5 lakh received by the district, three were spent on the preparation of a ‘Theme Gate’ at the town’s entrance to mark the launching of the scheme. The expenditure has been categorised as ‘irregular’ and is equivalent to the diversion of funds.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- Even though entitlement based poverty alleviation measures address the symptoms of deprivation, they fail to create the enabling milieu needed for sustainability. Elucidate. (TLP plus/OFFLINE Test-7)
Q19. “The long sustained image of India as a leader of the oppressed and marginalised nations has disappeared on account of its newfound role in the emerging global order.’ Elaborate (15 Marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The question is asking you to elaborate on how the role of India has changed, as a leader of the least developed nations to the new role it has acquired being one of the leaders of the new global order. How modern India prefers to prioritize its own national interests over the collective interests of developing nation.
India, has long been hailed as a leader of the oppressed and marginalised nations (least developed nations) Example: Struggle against imperialism, formation NAM, G77.
However, post-economic liberalisation (especially in the 21st century) economic prosperity is seen as the key to a county’s attainment of great power status and has been the driving force in India’s current worldview.
Example: India has engaged in economic development in Africa, securing oil fields in Central Asia, being Israel’s biggest arms market.
Indian no longer discriminates between Israel, Palestine, US, Russia etc. Economic linkages are being seen as a means to promote ‘stability’ as in the case of China (being the largest trading partner with India). Or strategic alignment with US for nuclear cooperation.
So now, modern India prefers to prioritize its own national interests over the collective interests of developing nation.
Q20. What introduces friction into the ties between India and the United States is that Washington is still unable to find for India a position in its global strategy, which would satisfy India’s national self-esteem and ambitions’. Explain with suitable examples. (15 Marks)
LINE OF THOUGHT/APPROACH:
The question is pointing to the friction between the US and India because the US is not able to find a place for India in its global strategy/policy. India aspires to be the leader of emerging global order (Ambitions in terms of economic, political), but that does not perfectly fit in US’s strategy which is leading to friction between India and US.
Example: India wants to be the leader in the Service sector, with its abundant educated population (English speaking), but now the same is available from south-east Asian countries. And also with the Protectionism measure recently taken by the US, it is not able to satisfy India’s ambitions.
India’s relationship with Iran (for its Energy security), makes it difficult for the US to fit India in its scheme of things, as it has a strained relationship with Iran and issued sanctions recently.
India’s Make in India policy (to make India self-sufficient and a global manufacturing hub), giving importance to indigenous goods and services had created issues with US-based solar companies which also resulted in trade disputes between India and US.
IASBABA REFERENCE:
- ILP VAN and Mock

END NOTE: You can discuss and comment below to have more inputs from fellow aspirants. Paper 3 and 4 will be published soon.
TLP Connect 2020: Prelims + Mains+ Interview Mentorship Based Programme (OFFLINE and ONLINE)
Important timelines in the Video:
Initial 10 mins – about IASbaba and Team
13 minutes onwards – Philosophy behind TLP and Details about TLP Connect Mentorship programme
35mins, 30 Sec onwards – Art of Answer Writing
1:14:25 (hr:min:sec) onwards – Live Demo of Answer Writing
1:37:30 onwards – Ethics Strategy
2:19:45 onwards – Right Attitude for UPSC Preparation
DOWNLOAD THE PDFS-MAINS ANALYSIS
GENERAL STUDIES PAPER 1-2019
GENERAL STUDIES PAPER 2-2019
GENERAL STUDIES PAPER 3-2019
GENERAL STUDIES PAPER 4-2019











