IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 31st October 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Chhath puja
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains I – Culture
In News
- 400 junior policemen in Bihar’s Samastipur district, a pledge of honesty is part of the application form for leave to perform Chhath puja.
- Chhath is a Hindu festival dedicated to the Sun god and his wife Usha in order to thank them for bestowing the bounties of life on earth.
- The word chhath means sixth and the festival is celebrated on the sixth day of the month Kartika of the Hindu lunar Bikram Sambat calendar.
- They rituals include holy bathing, fasting, standing in water for long periods of time, and offering prayers and food to the setting and rising sun.
- The festival is observed most elaborately in Mithila Province of Nepal, Terai-Madhesh region of Nepal, Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand and UP.
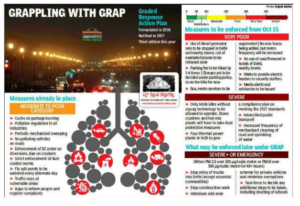
Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III –Environment
In News
-
- With air quality in Delhi nose diving to ‘severe’ levels, the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) Task Force extended the ban on construction and industrial activities dependent on coal till November 2.
- Apart from Diwali crackers and sluggish wind, the key culprit for dip in air quality in Delhi was stubble burning in Punjab and Haryana,
- The plan was prepared by the Supreme Court-mandated Environment Pollution Control Authority (EPCA), which held meetings with stakeholders from all states over several months. A graded response lays down stratified actions that are required to be taken as and when the concentration of pollutants reaches a certain level.
- This plan will be putting into action a number of anti-pollution measures and there will be specific actions for each category — moderate to poor, very poor, severe and emergency.
- Severe+ or Emergency
(PM 2.5 over 300 µg/cubic metre or PM10 over 500 µg/cu. m. for 48+ hours)
-
-
- Stop entry of trucks into Delhi (except essential commodities)
- Stop construction work
- Introduce odd/even scheme for private vehicles and minimise exemptions
- Task Force to decide any additional steps including shutting of schools
-
- Severe
(PM 2.5 over 250 µg/cu. m. or PM10 over 430 µg/cu. m.)
-
-
- Close brick kilns, hot mix plants, stone crushers
- Maximise power generation from natural gas to reduce generation from coal
- Encourage public transport, with differential rates
- More frequent mechanised cleaning of road and sprinkling of water
-
- Very Poor
(PM2.5 121-250 µg/cu. m. or PM10 351-430 µg/cu. m.)
-
-
- Stop use of diesel generator sets
- Enhance parking fee by 3-4 times
- Increase bus and Metro services
- Apartment owners to discourage burning fires in winter by providing electric heaters during winter
- Advisories to people with respiratory and cardiac conditions to restrict outdoor movement
-
- Moderate to poor
(PM2.5 61-120 µg/cu. m. or PM10 101-350 µg/cu. m.)
-
- Heavy fines for garbage burning
- Close/enforce pollution control regulations in brick kilns and industries
- Mechanised sweeping on roads with heavy traffic and water sprinkling
- Strictly enforce ban on firecrackers
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 31st October 2019
https://static.toiimg.com/photo/imgsize-113487,msid-71589359/71589359.jpg
Unnat Bharat Abhiyan
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III –Inclusive Development
In News
- President during his convocation address in Jamia millia University emphasised need to connect all sections of society with development and appreciated the University for adopting five villages under Unnat Bharat Abhiyan
- Unnat Bharat Abhiyan was launched by the Union Ministry of Human Resource Development (HRD) in April 2018.
- Under this each selected institute would adopt a cluster of villages/panchayats. Institutes will then carry out studies to assess the local problems and then use technology to improve the implementation of various government schemes.
- The Objective is to use the knowledge base of the Premier Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) of the country to ensure rural development.
- It is expected to be a two-way learning process, where institutions share their knowledge with villages and also learn from the wisdom and commonsense of rural folk.
- The key points include helping villages achieve 100% school results, creating 25 jobs each in four sectors in each village where work would take place, increasing rural incomes, providing drinking water and sanitation to villages, disposing village garbage, among other things.
- Under Unnat Bharat Abhiyan 2.0, both technical and non-technical institutions have been invited to build systems in villages as per their strengths.
Amaravati start-up area pact cancelled
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains I–Urban development
In News
- A.P government’s agreement with Singapore consortium for the development of Amaravati start-up area has been cancelled with mutual consent
- The reason given by government is that the Singapore consortium was unable to give a satisfactory explanation to doubts on the financial sustainability of the project when it was asked to reveal its exact plans.
- A.P. government had formed Amaravati Development Partners with the Singapore consortium for the development of a start-up area of nearly 1,692 acres over a period of 20 years.
- The bidding was conducted in the Swiss Challenge method in accordance with A.P. Infrastructure Development Enabling Act, 2001.
About Swiss Challenge
- It is a method of bidding, often used in public projects, in which an interested party initiates a proposal for a contract or the bid for a project.
- The government then puts the details of the project out in the public and invites proposals from others interested in executing it. On the receipt of these bids, the original contractor gets an opportunity to match the best bid.
- The Swiss Challenge allows a seller to mix-and-match the features of both an open auction and a closed tender to discover the best price for an asset.
- The method also has other uses. In its original form, a Swiss Challenge allows an infrastructure developer to come up with a suo motu proposal for a new project without waiting for the government to call for bids. This can foster innovation, as contractors or developers may initiate projects that the powers-that-be didn’t even think of.
For more viewpoints on Swiss model refer: https://iasbaba.com/2016/03/3-understand-swiss-model-public-private-partnership-discuss-features-potential-india/
Kudankulam plant&‘dtrack’ malware
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III – Energy
In News
- The Nuclear Power Corporation of India Ltd. (NPCIL) on Wednesday confirmed that a malware had indeed infected its system at the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant (KKNPP), a day after KKNPP officials had categorically asserted that the systems at the plant could not be accessed by anyone outside the network as they were all isolated.
- The matter was conveyed by CERT-In [Indian Computer Emergency Response Team] when it was noticed by them on September 4, 2019.
- The investigation had revealed that the infected computer belonged to a user who was connected “in the Internet connected network used for administrative purposes,
- However, the authorities stated that system was isolated from the critical internal network and that the networks were being “continuously monitored”.
- The cyberintrusion came to light on 28th October after the website VirusTotal uploaded a data dump that seemed to point to a data breach in the KKNPP system. The dump pointed to a ‘dtrack’ malware, which can be used as a remote administrator tool, having infected systems at the KKNPP.
About CERT-IN
- CERT-In is an acronym for ‘Indian Computer Emergency Response Team’. As per Information Technology Amendment Act 2008, CERT-In is the National Incident Response Centre for major computer security incidents in its constituency i.e. Indian cyber community.
- CERT-IN is operational since 2004
- CERT-In’s primary role is to raise security awareness among Indian cyber community and to provide technical assistance and advise them to help them recover from computer security incidents. It functions under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- Objectives of CERT-In
- Preventing cyber-attacks against the country’s cyber space.
- Responding to cyber-attacks and minimizing damage and recovery time.
- Reducing ‘national vulnerability to cyber-attacks.
- Enhancing security awareness among common citizens.
Submarine propulsion system test a success
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III- Science & Technology
In News
- The indigenous Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) system to enhance the endurance of conventional submarines being developed by DRDO reached a milestone with the successful operation of a land-based prototype.
- An AIP module enables conventional submarines to remain submerged for longer duration.Fuel cell-based AIP has merits in performance compared to other technologies
- All Scorpene submarines of the Navy are planned to be equipped with an AIP module in due course
Scorpene-class submarines
- These are a class of diesel-electric attack submarines jointly developed by the French Direction des Constructions Navales (DCN) and the Spanish company Navantia, and now by Naval Group.
- It features diesel propulsion and an additional air-independent propulsion (AIP).
Chile pulls out from hosting climate and trade summits
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II – International affairs
In News
- Chile’s President announced that his country, which has been rocked by a wave of recent protests, was not in a position to host a key UN climate change meeting and major Asia-Pacific trade summit later this year.
- The priority of Chilean government was to focus first and foremost on fully restoring public order and social peace,
- Cancelling the climate meeting, which had been scheduled for December, leaves organisers with a very tight window to find a new venue.
- Chile stepped up to host the Climate Change Conference after the initial host, Brazil, pulled out last year.Brazil’s decision came soon after the election of President Jair Bolsonaro
(MAINS FOCUS)
POLITY
TOPIC: General Studies 2
- India and its neighbourhood- relations.
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
INDIA – SAUDI ARABIA RELATIONS
Context:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi held extensive talks with the Saudi Arabia’s top leadership
- Strategic Partnership Council was established to coordinate on important issues.
- The council will be headed by Modi and the crown prince and it will meet at an interval of two years.
- India and Saudi Arabia inked dozen of agreements in several key sectors, including oil and gas, defence and civil aviation
- Saudi Arabia, known to be a key ally of Pakistan, has been siding with India in its campaign to rid the region of terrorism and pledged to extend all cooperation to effectively deal with the challenge
- The first naval exercise between the two nations will take place by end of this year or early next year.
India- Saudi relations:
- India–Saudi Arabia relations are generally strong and close, especially in commercial interests.
- Indo-Saudi bilateral trade reached US$27.48 billion in the financial year 2017–18
- Saudi Arabia’s exports to India stood at US$22.06 billion whereas India’s exports were US$5.41 billion
- the trade relations between southern India and Arabia flourished and became the backbone of the Arabian economy 1000 AD
- Arab traders held a monopoly over the spice trade between India and Europe until the rise of European imperialist empires
- Saudi Arabia is one of the largest suppliers of oil to India, who is one of the top seven trading partners and the fifth biggest investor in Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts:
- Saudi’s relations with Pakistan affected India’s strategic relations with Saudi Arabia
- Saudi Arabia supported Pakistan’s Kashmir stance
- During the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, Saudi supported Pakistan at the expense of its relations with India.
- The Russia’s close relations with India also negatively affected Indo-Saudi relations.
- During the Persian Gulf War (1990–91), India officially maintained neutrality.
Relationship since 1990s:
- Saudi Arabia has supported granting observer status to India in the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)
- Saudi has expanded its collaboration with India to fight Islamic terrorism in the Middle East
- The Saudi king and the Indian Prime Minister Manmohan Singh signed an agreement forging a strategic energy partnership that was termed the “Delhi Declaration.”
- The pact provides for a “reliable, stable and increased volume of crude oil supplies to India through long-term contracts.
- Both nations also agreed on joint ventures and the development of oil and natural gas in public and private sectors
- In 2019, Saudi Arabia increased the Hajj quota of India
Relations in 2019:
- The Saudi Crown Prince, Muhammad bin Salman, made a visit to India in February, 2019.
- The number of Indian pilgrims performing Hajj in Saudi Arabia has been increased to 200,000 every year.
- India, the world’s third-largest oil consumer, imports 83 per cent of its oil needs. Saudi Arabia is its second-biggest supplier after Iraq.
- It sold 40.33 million tonnes of crude oil to India in 2018-19 fiscal, when the country had imported 207.3 million tonnes of oil.
- India buys some 200,000 tonnes of LPG every month from Saudi Arabia.
Connecting the dots:
- India’s relations with Saudi Arabia have been on an upswing over the last few years based on burgeoning energy ties. Justify
ECONOMY
TOPIC: General Studies 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
Employment in India (Part 2)
Context:
- Since the results of the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) 2017-18 became public — they showed that unemployment in India was at a 45-year high — there has been vigorous public debate about the true state of unemployment in the country.
What fuelled debate?
- Long delays in the availability of past employment data, even though PLFS tracks employment annually.
Also read : Part 1 : https://iasbaba.com/2019/10/daily-current-affairs-ias-upsc-prelims-and-mains-exam-30th-october-2019/
Main findings:
- Total employment in the country grew by 4.5 crore in the 13 years between EUS 2004-05 and PLFS 2017-18.
- This represents a growth of just 0.8 per cent — less than half the rate at which the overall population grew, which was 1.7 per cent.
Urban and Rural:
- 4.5 crore increase in employment, 4.2 crore happened in the urban areas while rural employment either contracted (by 0.01 per cent between 2004 and 2011) or was stagnant (grew by 0.18 per cent between 2011 and 2017).
Male and female:
- Male employment grew by 6 crore but female employment fell by 1.5 crore. Women’s share in employment has fallen from an already low level of 27.08% in 2004 to 21.17 per cent in 2017.
- Youth employment (those between the ages of 15 and 24) has fallen from 8.14 crore in 2004 to 5.34 crore in 2017.
Organised and Unorganised sector:
- The rate of employment growth in the organised sector has been the fastest, and its share in the total employment has risen from 8.9 per cent in 2004 to 14 per cent in 2017.
- The pace of growth of the unorganised sector has moderated since 2011, its overall share in the economy has gone up from 37.1 per cent in 2004 to 47.7 per cent in 2017.
- The agri-cropping sector, employment has fallen from 21.9 per cent in 2004 to 17.4 per cent in 2017.
Contractual employment:
- The organised sector in India preferring to employ workers without a contract. Indeed, between 2011 and 2017, this resulted in the organised sector coming to employ more people without a contract.
- The presence of a contract makes all the difference when it comes to job security, minimum wages, equal pay for equal work, safe working conditions, etc. Without a contract, even a worker employed in the organised sector would not have any means of seeking recourse for any injustice.
Conclusion:
- Firms (organised or unorganised) preferring non-contractual employment is bad news for India’s bid to make the economy more formal.
- Firms are doing so to cut the extra costs that come with complying with inflexible and stringent labour laws.
Connecting the dots:
- Those who are poor, illiterate, and unskilled are increasingly losing out on jobs. Substantiate
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1) Swiss Challenge often seen in news is related to which of the following areas?
- Inculcating Innovation spirit among Universities
- Improvements in Urban development
- Public-Partnership Model
- None of the above
Q.2) Consider the following statements about CERT-IN
- It is the National Incident Response Centre for major computer security incidents in Indian cyber community.
- It functions under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3)Consider the following statements about Unnat Bharat Abhiyan
- It was launched by the Ministry of Skill development
- The Objective is to use the knowledge base of the Premier Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) of the country to ensure rural development
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.4)Consider the following statements about Chhath puja
- Chhath is a Hindu festival dedicated to the Sun god and his wife Usha in order to thank them for bestowing the bounties of life on earth
- The festival is observed most elaborately in Mithila Province of Nepal, Terai-Madhesh region of Nepal, Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand and UP
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
MUST READ
Visiting Kashmir: On MEP team visit
Free trade over fair trade
Upholding the ideals of fairness and rectitude
A New Kind Of Government
On the Indian economy, no one knows what to believe. This makes the uncertainty of our moment more endemic











