IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 20th January 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Nearly extinct northern white rhino
Part of: GS Prelims –Environment and GS-III- Conservation
In news :
- Researchers had created the third embryo the nearly extinct northern white rhino, a remarkable success in an ongoing global mission to keep the species from going extinct.
From Prelims Point of view
The northern white rhinoceros
- The northern white rhinoceros, is one of two subspecies of the white rhinoceros (the other being the southern white rhinoceros).
- Found in several countries in East and Central Africa south of the Sahara,
- It is a grazer in grasslands and savanna woodlands.
- According to the latest International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) assessment from 2011, the subspecies is considered “Critically Endangered (Possibly Extinct in the Wild).
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
- IUCN is a membership union uniquely composed of both government and civil society organisations.
- Created in 1948, it is the global authority on the status of the natural world and the measures needed to safeguard it.
- It is headquartered in Switzerland.
- The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, is the world’s most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of plant and animal species.
- It uses a set of quantitative criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of species. These criteria are relevant to most species and all regions of the world.
- The IUCN Red List Categories define the extinction risk of species assessed. Nine categories extend from NE (Not Evaluated) to EX (Extinct). Critically Endangered (CR), Endangered (EN) and Vulnerable (VU) species are considered to be threatened with extinction.
- It is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity.
- It is also a key indicator for the SDGs and Aichi Targets.
China coronavirus: Number of cases jumps
Part of: GS Prelims –Sci & Tech and GS-III- Health
From Prelims Point of view
Coronavirus:
- Coronaviruses (CoV) are a large family of viruses that cause illness ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS-CoV) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV).
- Coronaviruses are zoonotic, meaning they are transmitted between animals and people.
Model (Agricultural) Land Leasing Act
Part of: GS Prelims –Polity and GS-II Acts
In news:
- Karnataka government’s move to amend The Karnataka Land Reforms Act, 1961 is based on the Model (Agricultural) Land Leasing Act, 2016
- Model (Agricultural) Land Leasing Act, 2016 is proposed by the Centre’s think tank NITI Aayog to increase investments in agriculture and productivity.
From Prelims Point of view
Model (Agricultural) Land Leasing Act, 2016:
- Legalise land leasing to promote agricultural efficiency, equity and power reduction. This will also help in much needed productivity improvement in agriculture as well as occupational mobility of the people and rapid rural change.
- This is very important step for land reforms through which needs of landlord as well as lease holder have been taken care.
- Through this act, the landlord can legally lease the land with mutual consent for agriculture and allied activities. In this act, it has been taken care that in any circumstances the leased holders’ claim on land will not be valid.
- Lease holder may receive institutional loan, insurance and disaster relief so that he may invest more and more in agriculture.
- Allow automatic resumption of land after the agreed lease period without requiring any minimum area of land to be left with the tenant even after termination of tenancy, as laws of some states require.
- Incentivise tenants to make investment in land improvement and also entitle them to get back the unused value of investment at the time of termination of tenancy.
- In order to resolve the dispute between the landlord and lease holder, the provision of “Special Land Tribunal” has been made in the Civil Court.
Rare migratory eagle
Part of: GS Prelims –Environment and GS-III Conservation
In news :
A lone endangered steppe eagle (Aquila nipalensis) has been sighted by a group of birdwatchers
From Prelims Point of view
Steppe eagle
- Romania east through the south Russian and Central Asian steppes to Mongolia. The European and Central Asian birds winter in Africa, and the eastern birds in India
- IUCN Endangered
- It is also the National bird (animal) of Egypt
Irrawaddy dolphins
Part of: GS Prelims –Environment and GS-III Conservation
In news :
- Irrawaddy dolphins sighted in Odisha’s Chilika lake
- India’s largest brackish water lake(Chilika) is home to their highest single lagoon population
From Prelims Point of view
Irrawaddy dolphins:
- Endangered — IUCN
- Living in brackish water near coasts, river mouths and in estuaries in South and Southeast Asia
- Found in – Ganges, Mekong and Irrawaddy river system
Chilika Lake:
- Chilika Lake It is largest coastal lagoon or brackish water lake in India and Asia and second largest lagoon in the world
Budget 2020: ”#ArthShastri” campaign
Part of: GS Prelims –Economy and GS-III Buget
In news : From Prelims Point of view
- Finance Ministry to explain economic terms through #ArthShastri social media campaign
- Through the ”#ArthShastri” campaign, the ministry would explain several economic terms through interesting animated videos to help common man and students understand budget exercise in a simple way
NBFCs to get more lending room
Part of: GS Prelims –Economy and GS-III Banking sector
In news:
- The government is debating a mechanism to get credit flowing by providing support to non-banking finance companies (NBFCs) amid a growing realisation that financial sector stress has impacted demand and stalled economic recovery.
- The options that have been deliberated ahead of the February 1 budget include a plan akin to the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) that the US put in place after the subprime mortgage crisis that sparked the financial crisis of 2007-08.
From Prelims Point of view
NBFC :
- Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) refers to a financial institution. NBFC is a type of company engaged in the business of receiving loans and advances, acquisition of stocks or shares, leasing, hire-purchase, insurance business, chit business under Companies Act 2013.
- The main business activity of the NBFCs is to raise capital funds from public depositors and investors and then lend to borrowers as per the rules and regulations prescribed by the Reserve Bank of India.
- NBFCs are becoming alternative to the banking and financial sector.
- In NBFC there is a requirement of minimum net owned fund of Rs. 2 Crore.
Read more about NBFC here : https://iasbaba.com/2019/02/daily-current-affairs-ias-upsc-prelims-and-mains-exam-04th-february-2019/#NBFCs_and_its_significance
Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) :
- TARP, expanded as the Troubled Asset Relief Program was an innovative measure launched by the U.S. Treasury in order to stabilize the financial system of the country, restore the growth of economy and prevent foreclosures during the wake of the financial crisis that struck the US in 2008.
- The Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) is a program of the United States government to purchase toxic assets and equity from financial institutions to strengthen its financial sector
Miscellaneous Topics For Prelims
Stagflation :
Stagflation is an economic scenario where an economy faces both high inflation and low growth (and high unemployment) at the same time. (Former Prime Minister Manmohan Singh had warned about the imminent risk of stagflation facing the economy)
Hong Kong Crisis :
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 20th January 2020
Niranjan Bhat committee:
- The Supreme Court has, forms committee to draft mediation law
- The panel, to be headed by mediator Niranjan Bhat, will recommend a code of conduct for mediators
Gig economy
- A labour market characterized by the prevalence of short-term contracts or freelance work as opposed to permanent jobs.
(MAINS FOCUS)
Indian Federalism
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure
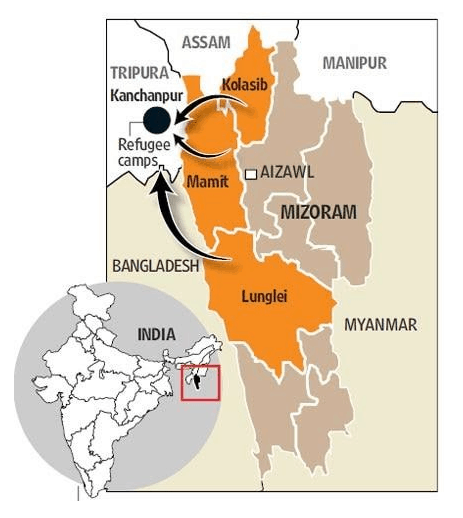
Bru Refugees

Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 20th January 2020
Context:
The quadripartite agreement signed between Centre, State government of Tripura & Mizoram and representatives of Brus Organisation to settle Brus refugees in Tripura.
Who are Brus?
- The Brus, also referred to as the Reangs, are spread across the north-eastern states of Tripura, Assam, Manipur, and Mizoram. Reangs or Brus are the second largest ethnic group in Mizoram.
- They are ethnically different from the Mizos, with their own distinct language and dialect
- In Tripura, they are recognised as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG).
Conflict in Mizoram:
- In 1995, Mizos, the majority tribe of the state of Mizoram, demanded that Brus be left out of the state’s electoral rolls as they contended that they are not indigenous to Mizoram.
- In 1997, ethnic violence forced roughly half the Bru population to flee the state in large numbers to neighbouring Tripura.
- Their exodus in 1997 was spurred by violent clashes in Mamith subdivision, a Reang-dominated area, when they demanded creation of an Autonomous District Council (ADC), under the 6th Schedule of the Constitution, in western Mizoram that was vehemently opposed by Mizo groups.
- Currently, around 35,000 (more than 5,000 families) Bru refugees living in Tripura camps.
Progress over past two decades
- The Centre and the two State governments involved made nine attempts to resettle the Brus in Mizoram. The first was in November 2010 when 1,622 Bru families with 8,573 members went back. Protests by Mizos stalled the process in subsequent years.
- In June 2018, Bru leaders (Mizoram Bru Displaced People’s Forum- MBDPF) signed an agreement in Delhi with the Centre and the two state governments, providing for repatriation to Mizoram (deadline to move back to Mizoram was set as Sep 2020) along with rehabilitation package (free ration, housing assistance, education)
- However, the camp residents said the package did not guarantee their safety in Mizoram, and were not happy with the deadline (to repatriate to Mizoram) provided by the government. Thus fear of repeat of the violence lead to the failure of agreement.
How is this agreement different from the earlier initiatives taken for the Bru?
- Allows Bru refugees to permanently settle in Tripura if they want to stay on. They will be provided voting rights in Tripura. The Bru who returned to Mizoram in the eight phases of repatriation since 2009, cannot, however, come back to Tripura.
- Fresh Survey: To ascertain the number of those settled in relief camps
- Special developmental package in addition to the Rs 600 crore fund announced for the process, including benefits for the migrants.
- Rehabilitation Package: Each family will get 0.03 acre (1.5 ganda) of land for building a home, Rs 1.5 lakh as housing assistance, and Rs 4 lakh as a one-time cash benefit for sustenance
- They will also receive a monthly allowance of Rs 5,000,(through Aadhar enabled Direct Benefit Transfer) and free rations for two years from the date of resettlement.
- Timeline provided: All Bru refugees will be moved to resettlement locations in four clusters, paving the way for the closure of the temporary camps within 180 days of the signing of the agreement and housing & payments completed with 270 days.
Role of Tripura’s erstwhile royal family
- Pradyot Kishore Debbarma, scion of Tripura’s erstwhile royal family, claimes that the Bru were originally from Tripura, and had migrated to Mizoram after their homes were flooded due to the commissioning of the Dumboor hydroelectric power project in South Tripura in 1976
- This effort by a socially respected person led to easy acceptance of Brus by Mizoram political system.
- Pradyot Deb Barman, who is also one of the signatories, committed to donate 35 acres of land for the purpos, thus easing the pressure on government in their search for land.
Concerns/Challenges:
- It could set a bad precedent and “legitimise” the ejection of minority communities by ethnocentric states.
- The displaced Brus who returned to Mizoram have already begun demanding a package equivalent to the one those who stayed behind in the Tripura relief camps
- It could fuel conflict with the locals of Tripura (between Brus and Bengali non-tribal people)
- Forests would be razed down so as to provide the land needed for settling Brus. Nearly 162 acres will be needed for the process and since Tripura is a small state, the government would look to diversion of forest land for human settlement purpose.
Connecting the dots
- Naga issues and its linkage with states of Manipur and Arunachal Pradesh
- Cooperative Federalism
- Other internal refugees in India – Kashmiri Pandits
Economy and Governance
General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
General Studies 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- Effects of liberalization on the economy, changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth.
Make In India: Is it a failure?
Context:
Impending Union Budget for FY 2020-21 in the background of fears of stagflation in economy and completion of five years of Make in India Scheme
What is Make in India Scheme?
- The Make in India initiative was launched by Government in September 2014 to transform India into a global design and manufacturing hub.
- It was launched in the backdrop of India’s growth rate falling and rising youth population who were looking for jobs (which can be absorbed in large numbers by manufacturing sector)
- It is designed to facilitate investment, foster innovation, enhance skill development, protect intellectual property and build best in class manufacturing infrastructure in the country.
- The initiative is based on four pillars:
- New Processes: Ease of doing Business is identified as important factor for promoting investment & entrepreneurship
- New Infrastructure: To develop industrial corridors and smart cities to provide infrastructure based on state-of-the-art technology with modern high-speed communication and integrated logistic arrangements
- New Sectors: Make in India’ has identified 25 sectors in manufacturing, infrastructure and service activities. These include: automobiles, aviation, chemicals, IT & BPM, pharmaceuticals, construction, defence manufacturing, electrical machinery, food processing etc.
- New Mindset: Government will act as facilitator of economic growth (partnering with private sector) and not as regulator.
The targets of the Scheme
- To increase the manufacturing sector’s growth rate to 12-14% per annum
- To increase the contribution of the manufacturing sector to 25% of the GDP by 2020 from the current 16%
- Creation of 100 million additional manufacturing jobs in the economy by 2022
Has the above targets been achieved?
- Growth of investment in the economy: Gross fixed capital formation of the private sector, a measure of aggregate investment, declined to 28.6% of GDP in 2017-18 from 31.3% in 2013-14 (Economic Survey 2018-19). This indicates weak investment by private sector in spite of flexible policies from this scheme
- Output growth: Monthly IIP pertaining to manufacturing has registered double-digit growth rates only on two occasions during the period April 2012 to November 2019.
- Employment: Unemployment leapt to a four-decade high of 6.1 per cent according to the National Sample Survey Office’s study for 2017-18 that was released in May 2019.
Way forward
- Such type of mega projects which have long gestation periods and lag effects the assessments of scheme can be premature.
- Resolving Banking Sector Crisis: Twin balance sheet problem and NBFC crisis needs to tackled aggressively so as to boost the credit outtake growth rate.
- Boosting Consumer demand: Weak monsoons along with disruption caused by demonetization & hasty implementation of GST lead to falling incomes which impacted the consumer demand. This kick-starts the investment cycle and thus manufacturing growth
- Skilling of people: It will ensure that people are equipped with necessary skills and thus reducing the training costs for firms.
Connecting the Dots
- New manufacturing Policy
- Impact on US-China trade war on Make In India Scheme
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1) Which of the following statements is/are correct?
- Viruses lack enzymes necessary for the generation of energy.
- Viruses can be cultured in any synthetic medium.
- Viruses are transmitted from one organism to another by biological vectors only
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Viruses can infect
- bacteria
- fungi
- plants
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q3. Consider the following statements:
- In tropical regions, Corona virus disease is transmitted by the same mosquito that transmits dengue.
- Sexual transmission of Corona virus disease is possible.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q4. The “Red Data Books’’ published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural resources (IUCN) contain lists of ?
- Endemic plant and animal species present in the biodiversity hotspots.
- Threatened plant and animal species.
- Protected sites for conservation of nature and natural resources in various countries.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- 1 and 3
- 2 only
- 2 and 3
- 3 only
Q5. With reference to the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) and the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES),which of the following statements is/are correct?
- IUCN is an organ of the United Nations and CITES is an international agreement between governments.
- IUCN runs thousands of field projects around the world to better manage natural environments.
- CITES is legally binding on the States that have joined it, but this Convention does not take the place of national laws.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
ANSWERS FOR 18 JAN 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | B |
MUST READ
About Bharatnet Project
About Agri food policies
About CAA and issues with Federalism











