IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 23rd May 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Rht14 & Rht18: Dwarfing genes in wheat mapped
Part of: GS-Prelims and GS-III – Science & Technology
In News:
- Scientists at Pune based Agharkar Research Institute (ARI) have mapped two alternative dwarfing genes Rht14 and Rht18 in wheat.
- ARI is an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology.
Key takeaways
- These genes have better seedling vigour and longer coleoptiles (sheath protecting the young shoot tip).
- Dwarfing genes were mapped on chromosome 6A in durum wheat.
- DNA-based markers were developed for a better selection of genes.
- Advantages of wheat lines having these genes are:
- Suitable for sowing under rice stubble-retained conditions and dry environments.
- Reduce crop residue burning
- Allow deeper sowing of wheat seeds to avail advantage of residual moisture in the soil under dry environments.
Measures announced by RBI for strengthening the economy
Part of: GS-Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In News:
- RBI announced another set of measures for strengthening the economy recently.
Key takeaways
- Repo rate: It is reduced from 4.4% to 4.0%.
- Marginal Standing Facility rate & Bank rate: Reduced from 4.65% to 4.25%.
- Reverse repo rate: Reduced from 3.75% to 3.35%.
- States have been allowed to borrow more from the Consolidated Sinking Fund. It is being maintained by state governments as a buffer for repayment of their liabilities.
- The RBI had announced a special refinance facility of ₹15,000 crore to SIDBI at RBI’s policy repo rate for a period of 90 days. This facility has now been extended by another 90 days.
- A line of credit of ₹15,000 crore will be given to the EXIM Bank, for financing India’s foreign trade.
- The loan facility has been given for a period of 90 days, with a provision to extend it by one year.
- The maximum credit which banks can extend to a particular corporate group has been increased from 25% to 30% of the bank’s eligible capital base.
Important value additions:
Repo rate
- It is also known as the benchmark interest rate.
- It is the rate at which the RBI lends money to the banks for a short term.
- When the repo rate increases, borrowing from RBI becomes more expensive.
Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) rate
- It refers to the rate at which the scheduled banks can borrow funds overnight from RBI against government securities.
- MSF is a very short term borrowing scheme for scheduled commercial banks.
Bank rate
- It is the interest rate at which a nation’s central bank lends money to domestic banks, often in the form of very short-term loans.
- Managing the bank rate is a method by which central banks affect economic activity.
Reverse repo rate
- It is the rate at which the RBI borrows money from commercial banks within the country.
- It is a monetary policy instrument which can be used to control the money supply in the country.
Consolidated Sinking Fund (CSF)
- CSF was set up in 1999-2000 by the RBI to meet redemption of market loans of the States.
- Initially, 11 States — Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Maharashtra, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Tripura, Uttaranchal and West Bengal — set up sinking funds.
- Later, the 12th Finance Commission (2005-10) recommended that all States should have sinking funds for amortisation of all loans, including loans from banks, liabilities on account of NSSF National Small Saving Fund), etc.
- The fund should be maintained outside the consolidated fund of the States and the public account.
- It should not be used for any other purpose, except for redemption of loans.
- As per the scheme, State governments could contribute 1-3% of the outstanding market loans each year to the Fund.
- The Fund is administered by the Central Accounts Section of RBI Nagpur.
Miscellaneous
Agappe Chitra Magna
- It is a magnetic nanoparticle-based RNA extraction kit for use during testing for detection of COVID-19.
- It uses an innovative technology for isolating RNA using magnetic nanoparticles to capture the RNA from the patient sample.
- The magnetic nanoparticle beads bind to the viral RNA and, when exposed to a magnetic field, give a highly purified and concentrated RNA.
- This innovation enhances the chances of identifying positive cases.
SpaceX Demo-2 Mission
- On May 27,2020, NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 test flight will lift off for the International Space Station (ISS).
- It will become the first crewed flight to launch from American soil since the conclusion of the space shuttle era in 2011.
International Day for Biological Diversity
- International Day for Biological Diversity 2020 was celebrated on 22 May with the theme “Our solutions are in nature.”
- The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) is the international legal instrument for “the conservation of biological diversity” that has been ratified by 196 nations.
Khudol
- The United Nations Secretary-General’s Envoy on Youth has listed Manipur’s ‘khudol’ (gift) among the top 10 global initiatives for an inclusive fight against the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Khudol is a crowdfunded initiative of Ya_All, an Imphal-based NGO.
- The initiative entails ensuring food supplies and health services for the LGBTQI+ community, people living with HIV, daily-wage earners, children and adolescents.
(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNATIONAL/ HISTORY
Topic: General Studies 1 & 2:
- Modern Indian history from about the middle of the eighteenth century
- India and its neighborhood- relations.
India-Nepal Border issue
Context: The inauguration of a road from Dharchula to Lipu Lekh (China border) by India’s Defence Minister over videoconferencing on May 8th 2020. This has now been followed by Nepal’s charge claiming that the stretch passes though Nepalese territory.
Did You Know?
- The Lipulekh Pass links Uttarakhand with China’s Tibetan Autonomous Region.
- The pass is near the tri-junction of India, Nepal and China
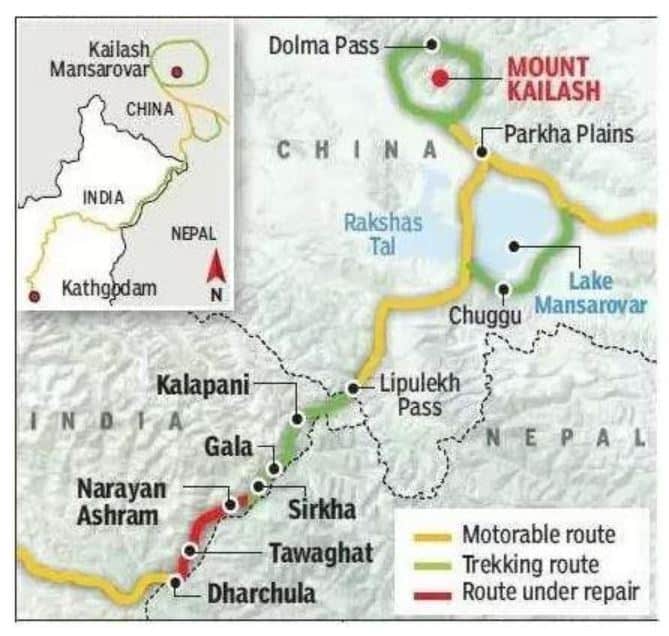
Pic Source: Eenadu
Significance of the route:
- The conversion of the trekking route to a metalled road is a boon to both pilgrims and traders.
- At present, the travel to Kailash Mansarovar takes around two to three weeks through Sikkim or Nepal routes.
- Lipulekh route had a trek of 90 Km through high altitude terrain and the elderly yartris faced lot of difficulties.
- Now, this yatra will get completed by vehicles.
- Additionally, this road follows the traditional pilgrim route for the Kailash-Mansarovar yatra.
The Sugauli Treaty
- The Nepalese kingdom had stretched from the Sutlej river in the west to the Teesta river in the East.
- However, Nepal lost the Anglo-Nepalese War and the resulting Treaty of Sugauli, 1816 limited Nepal to its present territories.
- The Sugauli Treaty stated that Nepal ceded to British the whole of the lowlands between the Rivers Kali and Rapti.
- The Survey of India maps since the 1870s showed the area of Lipu Lekh down to Kalapani as part of British India.
- Both the Rana rulers of Nepal and the Nepalese Kings accepted the boundary and did not raise any objection with the government of India after India’s Independence
What is the present controversy?
- The present controversy has arisen since the Nepalese contest that the tributary that joins the Mahakali river at Kalapani is not the Kali river.
- Therefore, Nepal now contends that the Kali river lies further west to the Lipu Lekh pass and claims both Kalapani & Susta belong to Nepal
- By 2007, the Nepal-India Technical Level Joint Boundary Working Group agreed on 182 strip maps covering almost 98% of the boundary, except the two disputed areas of Kalapani and Susta.
Nepal’s reaction has been unusually aggressive towards India
- Force Deployment: Nepal has deployed its armed police close to Kalapani. The timing and the manner in which it was deployed has raised concerns in New Delhi
- India’s passive presence: The Indo-Tibetan Border Police is also located in Kalapani since it is close to the India-China border. Indian forces are not there because of Nepal.
- New Nepalese Maps: Nepal’s actions of authorising a new map extending its territory across an area sensitive for India’s defence, has further complicated the situation
- Political Opportunism: The controversy has given Nepal’s Prime Minister K.P. Sharma Oli an opportunity to divert attention about criticism of his own government’s shortcomings
- China’s Politics: Nepal at the behest of China has objected to India’s initiative as China is bound to benefit by deteriorating India-Nepal relations
Way Ahead
- The approval of the strip maps by the respective governments (that of the Nepalese Government is still awaited),
- The resolution of the differences of opinion over Kalapani and Susta
- Speeding up the erection of damaged or missing border pillars.
Conclusion
Compared to what was accomplished between India and Bangladesh, the India-Nepal border issues appear more easily solvable
Connecting the dots:
- China’s Belt and Road Initiative & India’s Neighbourhood First Policy
- India- Bangladesh Border (maritime & land) dispute resolution
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors
An insufficient relief
Context: Union government announced a relief package of Rs 20 trillion, about 10 per cent of the country’s GDP, for the economy in crisis
Click here for details
Did You Know?
- The US has committed to the largest rescue package by any country in pure dollar terms of USD 2.7 trillion at an estimated 13% of GDP.
- Japan has announced a package equivalent to 21.1% of its GDP totalling USD 1.1 trillion
- Sweden – stimulus equal to 12 per cent of its GDP and Australia (10.8 per cent).
- Germany has announced a spending of around USD 815 billion, equal to 10.7 per cent of its GDP.
Criticism of the relief package
- The design of this relief package seeks to focus on the supply side, with an emphasis on providing liquidity through lines of credit
- This is with the aim of minimising the cost to the government.
- Even in normal circumstances, the speed of adjustment of the supply-side is slow because supply responses take time
- Also, producers would not wish to pile up inventories of unsold goods
- Rather it should have focused on the demand side by stepping up government expenditure
- Difficulties in Agricultural package implementation
- There is relief for agriculture in the form of a concessional credit line of Rs 2 trillion, but loans are neither automatic or assured
- Agri-marketing reforms and infrastructure creation are long-term promises.
- There is nothing for the corporate sector in manufacturing or services.
- The distressed sectors such as airlines, automobiles, hotels, restaurants, and tourism have been ignored.
- There is very little for public health, already in a dilapidated state.
- Structural difficulties of MSME sector
- The MSME sector, the backbone of the economy that provides 25% of employment, 32% of the GDP and 45% of exports.
- For MSMEs, lenders are not always supportive in extending loans, despite government announcement of Rs 3 trillion line of credit for loans without collateral.
- Also, buyers (central and state governments, public sector firms and the private sector) owe MSMEs as much as Rs 5 trillion.
- MSMEs just do not have the resources to pay wages or meet fixed costs on electricity, rent or interest during the lockdown period and relief package does not address this.
- There is a recycling of ideas or schemes from earlier budgets
- There is little cohesive focus on stabilisation and revival of the economy in the short-run
- Insufficient Fiscal Stimulus (government spending)
- There are 12 estimates by analysts in financial sector institutions, suggesting that the fiscal stimulus is in the range of 0.7 to 1.3% of the GDP
- Even then the fiscal stimulus’ contribution to domestic demand will be minuscule, given that private final consumer expenditure in India is about 60 per cent of the GDP.
Suggestion is Extra Fiscal Stimulus
- The extra fiscal stimulus should have been Rs 7-9 trillion (3-4 per cent of the GDP)
- This enlarged fiscal deficit cannot be financed by market borrowing, which would simply drive up interest rates and nip recovery in the bud.
- It would have to be financed by monetising the deficit – RBI buying government T-bills & printing money
- The concerns about inflation and downgrade by rating agencies are often exaggerated given that the entire world is going through similar phase
Connecting the dots:
- 1930s Great Economic Depression
- Expansionary & contractionary fiscal (or monetary) policy
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Rht14 & Rht18, often seen in news, are associated with which of the following?
- Alternative Dwarfing genes in wheat
- Newly-discovered Spike proteins of coronavirus
- Herbicide resistant gene of rice
- Genes mapped in humans that could be used for AIDS treatment
Q.2 Consider the following statements:
- Repo rate is the rate at which the RBI borrows money from the banks for a short term
- Reverse repo rate is the rate at which RBI lends money to commercial banks
- Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) rate refers to the rate at which the scheduled banks can borrow funds overnight from RBI against government securities.
- The Consolidated Sinking Fund should be maintained outside the consolidated fund of the States and the public account.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 4 only
- 3 and 4 only
Q.3 Theme for International Day for Biological Diversity 2020 was:
- Our Biodiversity, Our Food, Our Health
- Celebrating 25 years of Action for Biodiversity
- Biodiversity and Sustainable Tourism
- Our solutions are in nature
ANSWERS FOR 22nd May 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | D |
Must Read
About RBI Repo Rate Cut:
About Digital Currency Plan of China:
About PMJAY’s success:












