IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 26th June 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
India-China border dispute: 1993 India-China Agreement
Part of: GS-Prelims and Mains II – Indian and its neighbours; International Relations
In news:
- India accused the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) of violating the 1993 agreement between India and China.
- Indian government called on China to restore “peace and tranquillity” by implementing the June 6 disengagement plan agreed to by military commanders, as peace at the border is the “basis” of the India-China bilateral relationship.
Note: Aspirants should be aware of 1993 Agreement on the Maintenance of Peace and Tranquility along the LAC.
Important value additions:
1993 Agreement on the Maintenance of Peace and Tranquility along the Line of Actual Control in the India-China Border Areas
- This agreement provides the framework for border security between the parties until final determination is made regarding border demarcation.
- The parties agree to reduce troop levels compatible with friendly and good relations between them.
- They also agree to undertake confidence building measures along the line of actual control including by providing notification of troop movements.
- They agree that the India-China boundary question shall be resolved through peaceful and friendly consultations. Neither side shall use or threaten to use force against the other by any means.
Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) draft
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II and III – Govt schemes and policies; Environment and Ecosystem
In news:
- The draft of the proposed Environment Impact Assessment Notification, 2020 which seeks to amend existing EIA 2006 is open to public comments.
- The existing EIA, 2006 prescribes the procedure for industries to assess the ecological and environmental impact of their proposed activity and the mechanism whereby these would be assessed by expert committees appointed by the Ministry.
Key Prelims pointers:
Environment Impact Assessment (EIA)
- It is a process of evaluating the likely environmental impacts of a proposed project
- It is statutorily backed by the Environment Protection Act, 1986.
- Environment Impact Assessment Notification of 2006 has decentralized the environmental clearance projects by categorizing the developmental projects in two categories – Category A (national level appraisal) and Category B (state level appraisal).
- Category A projects – They require mandatory environmental clearance and thus they do not undergo the screening process.
- Category B Projects– They undergo screening process and they are classified into two types:
- Category B1 projects (Mandatorily require EIA).
- Category B2 projects (Do not require EIA).
Draft EIA Notification 2020: Criticisms
- It has inverted the logic of ‘precautionary principle’ which forms the bedrock of India’s environmental outlook.
- The new draft allows for post-facto approval for projects. It means that the clearances for projects can be awarded even if they have started construction or have been running phase without securing environmental clearances.
- The new notification comes in the wake of recent attempts to dilute environmental safeguards and follows from a tradition to widen the escape route for violators or environmental regulations.
- Polluting industries like soda-ash, acids, petroleum and petrochemical products, dyes, biomedical waste, treatment plants, synthetics, paints, chemical fertilizers, pesticides and construction industries – all of which pose threats to human health – will be exempted from the public clearance process.
- The draft notification provides for a reduction of the time period from 30 days to 20 days for the public to submit their responses during a public hearing for any application seeking environmental clearance.
India endorses the ‘polluter-pays-principle’, it cannot afford to endorse the “pollute-and-pay” sham.
Fifth anniversary of the Smart Cities Mission
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains I, II and III – Govt schemes and policies; Urbanisation and related issues; Infrastructure
In news:
- Fifth anniversary of the Smart Cities Mission was held recently.
- Housing and Urban Affairs Ministry announced initiatives like – plan to promote cycling in cities (‘Cycles4change Challenge’) and a finance portal for urban local bodies.
About Smart Cities Mission
- It is an innovative initiative under the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- The Mission covers 100 cities for the duration of five years starting from the financial year (FY) 2015-16 to 2019-20.
- It aims to drive economic growth and improve the quality of life of people by enabling local development and harnessing technology as a means to create smart outcomes for citizens.
- Objective: To promote cities that provide core infrastructure and give a decent quality of life to its citizens, a clean and sustainable environment and application of Smart Solutions.
Do you know?
- Low-cost interventions such as pop-up cycle lanes and non-motorised zones and community-led cycle rental schemes would be explored.
- The finance portal will get financial statements of all cities on a single platform. This will enable sharing and learning of best practices and helps urban local bodies in accessing market funds.
Important achievements in the five years of Smart Cities Mission
- About 31% of projects identified under the Smart Cities Mission have been completed
- About 33% of urban housing sanctioned through the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Urban) have been completed
- Under the Smart Cities Mission, 5,151 projects worth Rs. 2 lakh crore had been identified in 100 cities.
- So far around 4,700 projects worth Rs. 1.66 lakh crore or 81% of the total projects had been tendered and 1,638 projects worth Rs. 27,000 crore had been completed.
- Through the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT), the government had provided 79 lakh household water tap connections and 45 lakh sewer connections.
Armed gangs rule Nagaland: Governor
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II and III – Polity and Governance; Internal Security
In news:
- Nagaland Governor wrote letter to CM regarding the poor law and order situation in the state.
- The Governor’s letter said the constitutionally established State government was being challenged on a day-to-day basis by armed gangs who question the integrity and sovereignty of the nation, while the instruments of law and order remain totally unresponsive.
Do you know?
- Nagaland Governor hints at his special responsibility with respect to law and order in the State of Nagaland, enshrined in the Constitution under Article 371A (1) (b).
Important value additions:
- Article 371A deals with the special provisions with respect to the State of Nagaland.
- Article 371A (1) (b) – the Governor of Nagaland has special responsibility with respect to law and order in the state so long as internal disturbances caused by the hostile Nagas continue.
- For instance, under Article 371A (1) (b) of the Constitution, important functions like “transfer and posting of officials” entrusted with the maintenance of law and order of and above the district level will be with the approval of the Governor.
IN-SPACe to act as space industry regulator
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains – III – Science and Technology
In news:
- Union Cabinet had recently approved the creation of the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACe)
- We have already read that IN-SPACe will provide a level playing field for private companies to use Indian space infrastructure.
- The new entity of the Department of Space will also have its own chairperson and Board, and regulate and promote building of routine satellites, rockets and commercial launch services through Indian industry and start-ups.
Do you know?
- Until now, ISRO dealt with regulation and promotion of building of routine satellites, rockets and commercial launch services.
- In future, IN-SPACe will deal with such activities. It will function autonomously and parallel to ISRO.
- IN-SPACe will have its own directorates for technical, legal, safety and security, monitoring and activities promotion.
- NSIL will also be strenghtened and empowered with a larger role to work with IN-SPACe and enable it to take on some of the activities of ISRO.
- This restructuring will allow ISRO to allocate more time and resources for R&D endeavours.
Panchayats to get Rs. 10 lakh crores till 2026
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II and III – Polity – Local Self Govt; Financial Decentralisation; Economy and Development
In news:
- Panchayati Raj Ministry has pitched for a fivefold increase in Finance Commission funding for rural local bodies.
- In a meeting with the 15th Finance Commission, the Ministry asked for Rs. 10 lakh crores to be allocated for the 2020-21 to 2025-26 period.
Do you know?
- Rs. 2 lakh crore was allocated under the 14th Finance Commission.
- Allocations had tripled between the 13th and 14th Commissions as well.
- Road construction and maintenance, as well as drinking water supply have been the major projects carried out by panchayats using FC grants.
- According to the 11th schedule of the Constitution, 2.63 lakh panchayats across the country have 29 functions under their ambit.
- The new Garib Kalyan Rozgar Abhiyan will depend on panchayats to generate employment for newly returned migrant workers.
Miscellaneous
New Satellite Navigation policy soon
In news:
- A new satellite navigation policy, which has a strategic military element to it, is being proposed.
- The older ones, namely Remote Sensing Data Policy and the SatCom Policy of 2000, are being revised.
Vande Bharat mission
In news:
- The fourth round of the Vande Bharat mission, meant for the repatriation of Indians from around the world, will begin in July month.
- It will focus on bringing back Indians from the Gulf countries, Malaysia and Singapore, among others.
- Vandhe Bharat mission is the massive repatriation operation planned by the Indian government to bring back stranded Indians in different parts of the world in the wake of the coronavirus crisis.
- India has dispatched four Naval ships as part of the first phase of Vande Bharat mission.
- Indian Navy’s INS Jalashwa and INS Magar are operating to bring back Indian citizens from Maldives while INS Shardul and INS Airavat set sail to the UAE.
(MAINS FOCUS)
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY/ DEVELOPMENT/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
IN-SPACe: Growing private role
Context: The government has approved the creation of a new organisation called Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe), which is expected to be functional within six months
About IN-SPACe
- IN-SPACE will be a separate vertical within the Department of Space (DoS) that will make independent decisions for permitting and regulating activities of the private sector.
- It will have its own legal, technological, activity promotion and monitoring directorates and its Board will comprise members from the private industry, academia and government of India
- It will act as a national nodal agency for hand-holding and promoting private industry in the space sector and will even help private players build facilities within DoS premises
Why private participants?
- It is not that there is no private industry involvement in India’s space sector. In fact, a large part of manufacturing and fabrication of rockets and satellites now happens in the private sector
- However, Indian industries’ role has been mainly that of suppliers of components and sub-systems while there is huge scope for participation in satellite-based services, and ground-based systems.
- Indian industry had a barely 3% share in a rapidly growing global space economy ($360 billion). There were several Indian companies waiting for make use of these opportunities but the policy environment in India was supportive of private players
- Additionally, the demand for space-based applications and services is growing even within India, and ISRO is unable to cater to this.
Significance of the creation of IN-SPACe:
- Facilitator and regulator: IN-SPACe will act as an interface between ISRO and private parties, and assess how best to utilise India’s space resources and increase space-based activities.
- Fair Competition: IN-SPACe will provide a level playing field for private companies to use Indian space infrastructure.
- Better utilisation of space resources: Existing ISRO infrastructure, both ground- and space-based, scientific and technical resources, and even data are planned to be made accessible to interested parties to enable them to carry out their space-related activities.
- Strategic benefits: ISRO, like NASA, is essentially a scientific organisation whose main objective is exploration of space and carrying out scientific missions. The private industry will also free up ISRO to concentrate on science, R&D, interplanetary exploration and strategic launches.
- Widening the horizon of Private participation: IN-SPACe will promote private players in end-to-end space services, including building and launching rockets and satellites and providing space-based services commercially.
- Reorients space activities: IN-SPACe will reorient space sector from a ‘supply-driven’ model to a ‘demand-driven’ one, thereby ensuring optimum utilization of the nation’s space assets.
- Leveraging the potential of Young Country: So far only ISRO was doing all space related activities. Opening up of the space sector means the potential of the entire country can be leveraged
- Boost to Space Start-ups: This will not only result in an accelerated growth of the sector but also enable India to generate large scale employment in the technology sector.
- Additional revenue: ISRO can earn some money by making its facilities and data available to private players
Way Ahead
- Need for new navigation policies: India has the SatCom policy and Remote Sensing Data Policy (RSDP) but they need suitable modifications for the purpose of IN-SPACe to perform its duty in an effective manner
- Changes needed in New Space India Limited (NSIL): It needs to be recalibrated to transform its approach of a supply-driven model to being a demand-driven model for space-based services
- Enhancing ease of doing space business: Space activities are multi-layered projects which involve a lot of intricacies across domains, such as gaining access to frequencies, licensing of satellites for operation, ability to export products, imagery
Value Addition
- The SatCom policy dictates the use of Indian National Satellite (INSAT) system’s capacity by non-governmental agencies, the establishment and operation of Indian Satellite Systems and the use of foreign satellites for SatCom Services
- India’s Remote Sensing Data Policy (RSDP) is for the acquisition and distribution of remote sensing satellite data — from Indian and foreign satellites — for civilian users in India
Connecting the dots:
- UN Outer Space Treaty
- Gaganyaan Mission of ISRO
SECURITY/ GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Security challenges and their management in border areas
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors
Drug abuse amidst pandemic
Context: In Punjab, there has been 23% rise in addict registrations since Covid outbreak
Did You Know?
- Around 269 million people used drugs in 2018, up 30% from 2009, with adolescents and young adults accounting for the largest share of users
- Development assistance dedicated to drug control fell by some 90% between 2000-2017.
Why India is vulnerable to trafficking of narcotics?
- India is sandwiched between the ‘Golden Crescent’ and the ‘Golden Triangle’, the major opium production regions in the world
- The Golden Crescent region of the South Asia comprises Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan.
- The Golden Triangle is the area where the borders of Thailand, Laos and Myanmar meet at the confluence of the Ruak and Mekong rivers.
- The bumper harvests of opium in Afghanistan for the last few years have given rise to increased supply of heroin in the subcontinent
- The combination of darknet and courier/postal deliveries have made the narco/psychotropic trafficking more anonymous in nature
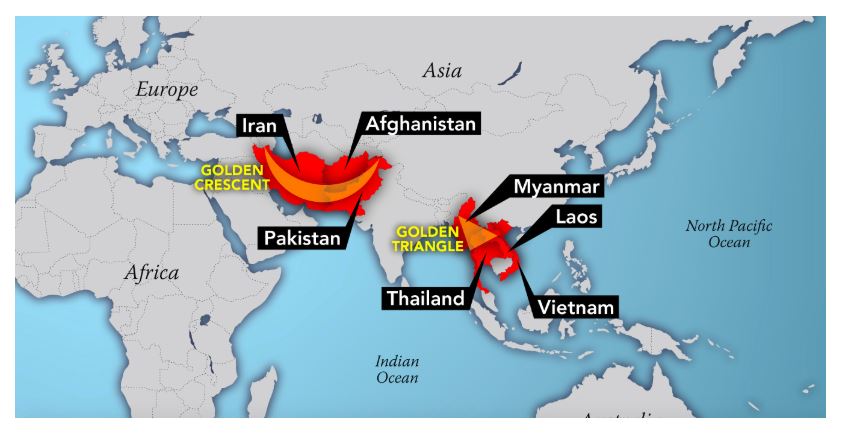
Image Source: Here
Consequences of pandemic on Drugs usage
- Increased Substance abuse: The economic downturn caused by the global pandemic may drive more people to substance abuse
- Anti-social activities: Many people will be vulnerable to involvement in drug trafficking and related crime as their incomes became dry during lockdown period
- Inattention and neglect: Governments will reduce budgets to deal with drug-related problems in the wake of reduced government revenues post-COVID-19 pandemic
- Dangers of increase in use of synthetic drugs: In the global recession that followed the 2008 financial crisis, drug users sought out cheaper synthetic substances and patterns of use shifted towards injecting drugs.
- Increase in drug use disorders: Only one out of eight people who need drug-related treatment receive it, according to the World Drug Report 2020. Some 35.6 million people suffer from drug use disorders globally.
- Prevents shift by farmers: Assistance for alternative development — creating viable, legal forms of income to enable poor farmers to stop growing illicit opium poppy or coca — will remain low.
- Increased transnational drug trafficking: National governments efforts will be focused on reviving domestic economies and this may hamper multi-lateral cooperation on cracking drug trade
- Disproportionate impact on weaker sections:
- One out of three drug users is a woman but women represent only one out of five people in treatment.
- People in prison settings, minorities, immigrants and displaced people also face barriers to treatment due to discrimination and stigma.
Way Ahead
- Greater investment in evidence-based prevention, as well as treatment and other services for drug use disorders
- International cooperation to increase access to controlled drugs for medical purposes and to strengthen law enforcement action to dismantle the transnational organised crime networks.
- Health-centred, rights-based and gender-responsive approaches to drug use and related diseases deliver better public health outcomes.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following and select the correct match:
- Article 371-A: Special provision for Nagaland
- Article 371-C: Special provision for Assam
- Article 371- G: Special provision for Mizora
Select the correct code
- 1 only
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2 Consider the following statements about IN-SPACe:
- It is an innovative program launched by Department of Science and Technology.
- It aims to provide a level playing field for private companies to use Indian space infrastructure.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Consider the following statements about Smart Cities Mission
- It is a central sector scheme.
- The Mission covers 100 cities for the duration of five years starting from the financial year (FY) 2017-2022.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4 Vande Bharat mission is associated with –
- Building cultural links with countries around the world and connecting people to people through Cultural and Educational exchanges.
- Creating sustainable model for providing adolescent girls and women an access to affordable sanitary products by leveraging Common Service Centres (CSCs)
- Boosting employment and livelihood opportunities for migrant workers returning to villages, in the wake of COVID-19 outbreak.
- Repatriation of Indians from around the world, in the wake of COVID-19 outbreak.
Q.5) Environment Impact Assessment in India is statutory backed by –
- Environment Protection Act, 1986
- Environmental Impact Assessment Act, 2006
- Biological Diversity Act, 2002
- Forest Rights Act, 2006
ANSWERS FOR 25th June 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
| 4 | B |
| 5 | B |
Must Read
An article by former foreign secretary about India’s foreign policy:
An article on whether online learning can replace school classroom:
About India-China border dispute:














