IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Turkey- Russia Military Drill in Eastern Mediterranean announced
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- International Relations
In news
- Recently, Turkey has announced that Russia will hold live-fire naval exercises in the eastern Mediterranean.
- Already there has been escalating tensions between Turkey and its coastal neighbors Greece and Cyprus over the rights to search for energy resources in the region.
Key takeaways
- Turkey and Russia will also coordinate closely on their military presence in Syria.
- Turkey has also purchased Russia’s advanced S-400 missiles and has agreed to go with a Russian-built nuclear power plant on its southern coast.
Do you know?
- Russian exercises will take place during September 8-22 and September 17-25.
- Turkish seismic research vessels are already operating in the Mediterranean region.
- Recently, the U.S. had said that it was partially lifting a 33-year-old arms embargo against ethnically divided Cyprus.
Image source: Click here
G-20 Foreign Ministers’ Meet held
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Global Groupings; International Relations
In news
- Recently, Saudi Arabia hosted the G-20 foreign ministers’ meeting.
- Focus: Cross-border movement amid the Covid-19 pandemic.
Key takeaways
- The foreign ministers acknowledged the importance of opening borders, and promoting measures to allow the economy to thrive in light of the protective measures for the Covid-19 pandemic.
- India updated the G-20 foreign ministers about steps taken by India including Vande Bharat Mission and creation of travel bubbles for the welfare and protection of foreign citizens stranded in India as well as its own citizens abroad.
Important value additions
G-20
- It is an informal group of 19 countries and the European Union.
- Representatives of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank are also part of G-20.
- It represents about 2/3rd of the world’s population, 85% of global GDP, 80% of global investment and over 75% of global trade.

Do you know?
- It does not have any permanent secretariat or headquarters.
- Currently, Saudi Arabia holds the presidency of G-20.
- It is the first Arab nation to take over the G20 Presidency.
Indo-China Defence Ministerial Meet held
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Global Groupings; International Relations
In news
- The Indo-China Defence Minister level meet recently took place on the sidelines of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Defence Ministers’ meeting in Moscow, Russia.
Key takeaways
- India stressed upon a peaceful, stable and secure region of SCO member states.
- India also expressed concern at the security situation in Afghanistan
- India called upon the Gulf countries to resolve differences between them by “dialogue based on mutual respect.
- India unequivocally condemned terrorism in all forms and manifestations.
- It also asserted the need to build institutional capacity to deal with both traditional and non-traditional threats.
Important value additions
Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO)
- Formation: 2001
- Type: Mutual security, political, economic organisation
- Headquarters: Beijing, China.
- It is a major Eurasian organization that represents half of the world’s population.
- It is a permanent intergovernmental international organisation.
- India joined SCO in 2017.
- The organisation has two permanent bodies — the SCO Secretariat (Beijing, China) and the Executive Committee of the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) (Tashkent, Uzbekistan).
- Significance: It has the capacity to counterbalance the North Atlantic Treaty Organization.

Revised Priority Sector Lending Guidelines
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III- Banking; Economy
In news
- Recently, the RBI released revised Priority Sector Lending (PSL) guidelines.
- The guidelines align with emerging national priorities and also bring sharper focus on inclusive development.
New additions to Priority Sector Lending (PSL) sectors
- Bank finance to start-ups up to Rs. 50 crore.
- Loans to farmers for installation of solar power plants for solarisation of grid connected agriculture pumps and loans for setting up Compressed BioGas plants.
- Higher credit limit for Farmers Producers Organisations (FPOs) undertaking farming with assured marketing of their produce at a predetermined price.
- The credit limits for renewable energy, health infrastructure, including the projects under ‘Ayushman Bharat’, have been doubled.
- It seeks to address the issues concerning regional disparities in the flow of priority sector credit at district level which includes:
- Ranking districts on the basis of per capita credit flow to the priority sector.
- Building an incentive framework for districts with comparatively low flow of credit and a dis-incentive framework for districts with comparatively high flow of priority sector credit.
- Higher weightage has been assigned to priority sector credit in ‘identified districts’ where priority sector credit flow is comparatively low
Important value additions
Priority Sector Lending
- The RBI mandates banks to lend a certain portion of their funds to specified sectors, like agriculture, Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), export credit, education, housing, social infrastructure, renewable energy among others.
- All scheduled commercial banks and foreign banks (with a sizable presence in India) are mandated to set aside 40% of their Adjusted Net Bank Credit (ANDC) for lending to these sectors.
- Regional rural banks, co-operative banks and small finance banks have to allocate 75% of ANDC to PSL.
- The idea behind this is to ensure that adequate institutional credit reaches some of the vulnerable sectors of the economy, which otherwise may not be attractive for banks from the profitability point of view.
Miscellaneous
Kisan Rail
- Inaugural run of South India’s 1st and country’s 2nd Kisan Rail between Anantapur and New Delhi was flagged off recently.
- Inaugurated by: Union Minister of Agriculture & Farmer Welfare.
- The first Kisan Rail was flagged off between Devlali (Maharashtra) and Danapur (Bihar) as a weekly service.
- Objective of Kisan Rail: To provide priority to the farming sector and facilitate transportation of perishable agricultural products to various market places across the country.
- Anantapur is fast becoming the Fruit Bowl of Andhra Pradesh.
- The train service between Anantapur – New Delhi will cover a distance of 2150 kms in 40 hours.
(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNATIONAL / SECURITY
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- India and its neighborhood- relations
- Security challenges and their management in border areas
Rethinking the defence doctrine
Context: Over four months ago, the Chinese army entered territory that India has long considered its own, and never left.
Consequences of Chinese adventurism along India’s border
- Short Term Loss: In effect, the multiple incursions have changed the Line of Actual Control (LAC) and India has lost territory, at least for the time being
- Reflects India’s failure of the warning-intelligence system: Either Indian intelligence services did not collect sufficient data of Chinese intentions and early moves, or they did not interpret it correctly. Wherever the fault lay, the system apparently failed.
In the light of China’s incursion, what is the criticism of Army’s prevailing doctrine?
- Conventional Mindset: The Army’s prevailing doctrine is designed to deter and defend against major conventional invasions. This determines how the Army is organised, what equipment it operates, and where it is deployed.
- Past References: In this mindset, the Army expected that any Chinese bid to capture Indian territory would come as a major conventional invasion, as it did in 1962. The Indian response would accordingly involve large formations, with planning and command decisions made at the Corps headquarters or higher.
- Miscalculation by Security Leadership: China has no interest in launching a major conventional invasion, but this is not just a typical probe either – which Security leadership could not understand at initial stages.
- Changed Chinese Tactics: But the Chinese army’s initial forays in April and May 2020 did not look like a guns-blazing invasion. It crossed the LAC in several places nearly simultaneously, and in larger numbers than usual.
- India faced with tough choices: China’s quick land grab looks increasingly permanent, like an attempt to change the status-quo at the border without triggering war. This fait accompli leaves India with two awful choices: either start a war by launching its own reprisal attack, or do nothing and accept a new situation.
What should be the way forward w.r.t Army’s Doctrinal thinking?
- Fundamental Shift: Addressing this type of security threat requires a fundamental shift in the Army’s doctrinal thinking, from strategies revolving around punishing the adversary, to strategies that prevent its adventurism in the first place
- A new doctrinal thinking should involve
-
- Greater investment in persistent wide-area surveillance to detect and track adversary moves,
- Devolved command authority to respond to enemy aggression,
- Rehearsed procedures for an immediate local response without higher commanders’ approval.
- Speed is of essence: In countering China’s ‘grey zone’ tactics of quick land grabs, speed is of the essence. The military must be able to detect adversary action and react quickly, even pre-emptively, to stop attempted aggression from becoming a fait accompli.
- Recent Success: The late-August incident at Chushul demonstrates how this new strategy can and should work. Indian special forces troops took position on previously unoccupied heights south of Pangong Tso. In so doing they have complicated future Chinese moves to consolidate their position, and Chinese attempts to seize more ground have been foiled.
Conclusion
- The challenge for India is to learn the right lessons and be alert to similar tactics in other regions, like the Indian Ocean. It must not rely on doctrines forged in wars half a century ago.
Connecting the dots:
- India’s Nuclear Doctrine and No First Use Policy
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY/ POLITY
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
- Functions and responsibilities of various Constitutional Bodies (Election Commission)
Blockchain Technology and Voting
Context: The Election Commission in August 2020, held an online conference in collaboration with the Tamil Nadu e-Governance Agency (“TNeGA”) and IIT Madras, through which they explored the possibility of using blockchain technology for the purpose of enabling remote elections.
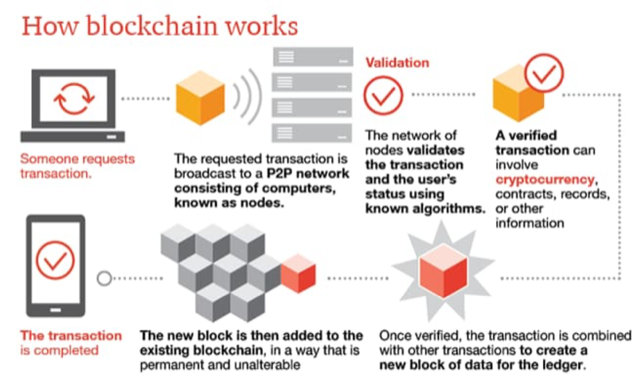
What is Blockchain Technology?
- A blockchain is a distributed ledger of information which is replicated across various nodes on a “peer-to-peer” network (P2P Network)
- The purpose of technology is of ensuring integrity and verifiability of data stored on the ledger.
- Blockchain ledgers have traditionally been used as supporting structures for cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum,however, their use in non-cryptocurrency applications too has seen a steady rise like enabling remote voting and elections.

Picture: Shows the Schematic representation of working of Blockchain Technology
What are the benefits of remote voting?
- Solved the problem of ballot portability: Remote voting would appear to benefit internal migrants and seasonal workers, who account for roughly 51 million of the populace (Census 2011).
- Useful for People in Remote Places: The envisioned solution might also be useful for some remotely-stationed members of the Indian armed forces (although that exhaustive infrastructure of Elections has helped address this)
- Helps Increase Voter Participation: Remote voting solutions may facilitate the participation in elections by specific groups of citizens, including expats, military voters, voters resident in health and care institutions, and prisoners.
- Speed and Secure: The blockchain-based voting system not only provides real-time results, but also ensures that the counting is foolproof, and with blockchain, nobody can tamper the results.
What are the Challenges associated with Blockchain Remote Voting?
- Requirement of physical presence and biometric authentication: The electors would still have to physically reach a designated venue in order to cast their vote, whereby systems would use “white-listed IP devices on dedicated internet lines”, and the system would make use of the biometric attributes of electors
- Adds Vulnerability to failure: Digitisation and interconnectivity introduce additional points of failure external to the processes which exist in the present day
- Technology not yet fully secure: Blockchain solutions rely heavily on the proper implementation of cryptographic protocols. If any shortcomings exist in an implementation, it might be misused
- Prone to targeted Denial-of-Service attacks -where an attacker would be in a position to block traffic from the system, effectively preventing, or at the very least delaying the registration of votes
- Privacy Issues: With such intrusive technology being used in elections, which when interconnected can go against the Puttaswamy judgement [on the right to privacy]
Conclusion
- It is important to note that further digitisation, in itself, does not make processes more robust.
- Any solution to electoral problems must be software independent and fault tolerable, where failure or tampering of one mechanism — or several — would not affect the integrity or transparency of the overall process.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Recently, South India’s 1st Kisan Rail was flagged off. Consider the following statements:
- The inauguration was done by Union Minister of Railways.
- The train would cover distance between Anantapur and Mumbai.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Which of the following countries have Mediterranean sea as one of their borders?
- Turkey
- Russia
- Greece
Choose the correct option:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO):
- Its headquarter is situated in Shanghai, China.
- It was Founded in 2010.
- India is one of its founders.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- None of the above
ANSWERS FOR 9th September 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | C |
| 4 | A |
Must Read
About Online learning and digital divide:
About COVID-19 Vaccine pause:
About Labour problem in South Asia:











