IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
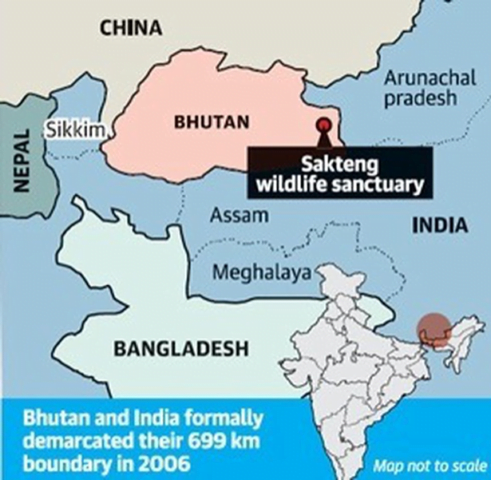
New Village in Bhutan claimed by China
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- Recently, Chinese media claimed that a new border village built by China near Bhutan was on Chinese territory.
Key takeaways
- The released images of the village show its location on territory disputed by Bhutan and China.
- The village of Pangda has been newly built and authorities in Yadong county (an administrative region) of Southwest China’s Tibet Autonomous Region have confirmed that 27 households with 124 people voluntarily moved from Shangdui village to Pangda village in September 2020.
- It is for the first time since 2017 that a Chinese residential area has been noticed near the Doklam region, which is strategically important for India.
- Bhutan has officially denied the presence of any Chinese village in its territory.
- According to China’s maps, the village is within China’s territory.
- China also blames India for the unsettled China-Bhutan border and stalled negotiations by creating the illusion that China is encroaching on Bhutanese territory.
Atal Faculty Development Programmes (FDPs)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Education
In news
- Ministry of Education recently inaugurated 46 online AICTE Training and Learning (ATAL) Academy Faculty Development Programmes (FDPs) to train teachers of higher education institutions associated with All India Council of Technical Education (AICTE) in emerging areas in technology.
Key takeaways
- The FDPs will be conducted in 22 Indian states according to the new National Education Policy (2020).
- Objective of ATAL Academy: (1) To provide quality technical education in India; (2) To promote research and entrepreneurship through training in various emerging fields. IITs, IIITs, NITs CU and research labs are organizing these ATAL FDPs.
Do you know?
- The London-based organization, Book of World Records, has recognized the FDPs as a world record, under which 1,000 online FDPs in over 100 emerging areas will benefit one lakh faculty members across premier institutions like IITs, NITs, and IIITs.
National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Disaster Management
In news
- Recently, National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC) was in news with regard to Cyclone Nivar.
Important value additions
- At the national level, Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) and National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC) are the key committees involved in the top-level decision-making wrt Disaster Management (DM).
- It deals with major crisis which have serious or national ramifications.
- Key functions: (1) Oversee the Command, Control and Coordination of the disaster response; (2) Give direction to the Crisis Management Group (CMG) as deemed necessary.
- Composition: Cabinet Secretary (Chairperson); Secretaries of Ministries / Departments and agencies with specific Disaster management responsibilities.
Sahakar Pragya launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions; E-governance
In news
- ‘Sahakar Pragya’ was recently launched.
- Launched by: Ministry of Agriculture
- Objective: To impart training to primary cooperative societies in rural areas.
Key takeaways
- There will be 45 new training modules of Sahakar Pragya.
- Training imparted by: National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) and Lakshmanrao Inamdar National Cooperative Research and Development Academy (LINAC).
- Sahakar Pragya shall enhance NCDC’s training capacity by 18-fold through an elaborate network of 18 Regional Training Centres across the country by the dedicated LINAC set up and fully funded by NCDC.
Food processing projects approved under Creation Of Infrastructure For Agro-Processing Cluster
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Food processing
In news
- The government has approved seven proposals of Food Processing Projects worth over 234 crore rupees under the Scheme for Creation of Infrastructure for Agro-Processing Cluster.
- The scheme for Creation of Infrastructure for Agro-Processing Cluster was approved in 2017 under the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana to incentivize the setting up of agro processing clusters in the country.
- This scheme aims at development of modern infrastructure to encourage entrepreneurs to set up food processing units based on cluster approach.
Important value additions
Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana
- In 2016, MoFPI introduced an umbrella Scheme for Agro-Marine Processing and Development of Agro-Processing Clusters (SAMPADA).
- It was proposed to be implemented with an allocation of ₹6,000 crores for the period of 2016-20.
- In 2017, SAMPADA was renamed as the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana (PMKSY).
- It is a Central Sector Scheme.
- Objectives: (1) To supplement agriculture; (2) To create processing and preservation capacities; (3) To modernise and expand existing food processing units with a view to increasing the level of processing; (4) To add value leading to the reduction of wastage.
- Seven component schemes under PMKSY: (1) Mega Food Parks; (2) Integrated Cold Chain and Value Addition Infrastructure; (3) Infrastructure for Agro-Processing Clusters; (4) Creation of Backward and Forward Linkages; (5) Creation/Expansion of Food Processing & Preservation Capacities; (6) Food Safety and Quality Assurance Infrastructure; (7) Human Resources and Institutions.
- Under PMKSY, capital subsidy in the form of grants-in-aid ranging from 35% to 75% of the eligible project cost subject to a maximum specified limit is provided to investors under the various schemes for undertaking infrastructure, logistic projects and setting up of food processing units in the country.
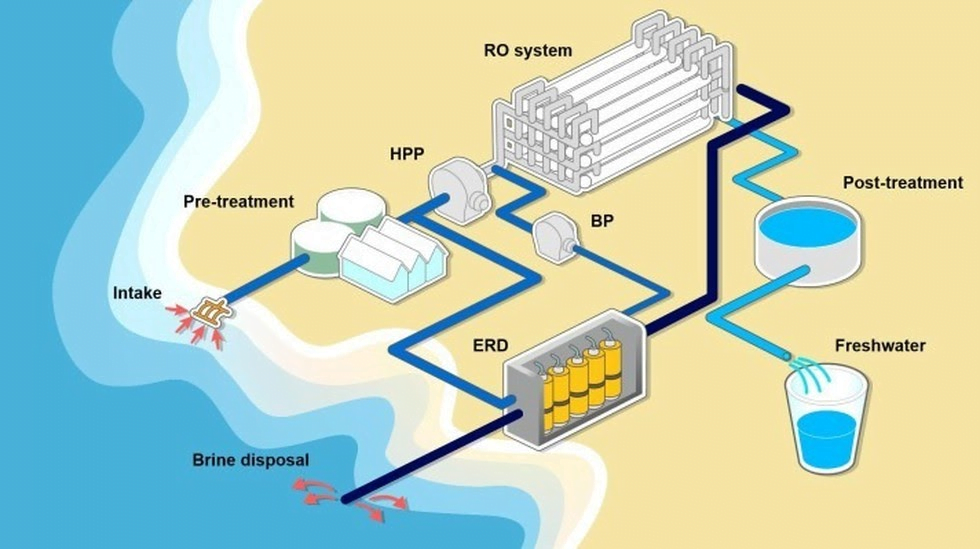
Maharashtra sets up Desalination Plants
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions & GS-III – Water resources
In news
- Maharashtra announced the setting up of a desalination plant in Mumbai.
- It is now the fourth state in India to experiment with the idea.
Key takeaways
- A desalination plant turns salt water into water that is fit to drink.
- The most commonly used technology used for the process is reverse osmosis where an external pressure is applied to push solvents from an area of high-solute concentration to an area of low-solute concentration through a membrane.
- The microscopic pores in the membranes allow water molecules through but leave salt and most other impurities behind, releasing clean water from the other side.
- Desalination is an expensive way of generating drinking water as it requires a high amount of energy.
- The other problem is the disposal of the by-product — highly concentrated brine — of the desalination process.
- While in most places brine is pumped back into the sea, there have been rising complaints that it ends up severely damaging the local ecology around the plant.
Do you know?
- Worldwide, desalination is seen as one possible answer to stave off water crisis.
- These plants are mostly set up in areas that have access to sea water.
- Desalination has largely been limited to affluent countries in the Middle East and has recently started making inroads in parts of the United States and Australia.
- In India, Tamil Nadu has been the pioneer in using this technology, setting up two desalination plants near Chennai in 2010 and then 2013.
- The other states that have proposed these plants are Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh.
Prohibition Of Unlawful Religious Conversion Ordinance, 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions; E-governance
In news
- The UP Cabinet recently cleared an ordinance to ban religious conversion for marriage.
- The new law will put the onus on the defendant to prove that conversion was not for marriage.
Key takeaways
- The Prohibition of Unlawful Religious Conversion Ordinance, 2020, recommends 1-5 years imprisonment if an accused fails to prove that the conversion of the woman was not for marriage or by use of force, allurement etc.
- The jail sentence for the offence would be 3-10 years if the woman is from the SC/ST community or is seen as part of mass conversion.
- The notice period to the district magistrate for the religious conversion has been doubled to two months from a month in an earlier draft.
Do you know?
- The ordinance comes days after the Allahabad high court said in a verdict that the right to choose a partner or live with a person of choice was part of a citizen’s fundamental right to life and liberty.
- The verdict also said earlier court rulings that ‘religious conversion for marriage was unacceptable’ was not good in law.
Report on National Nutrition Mission: NITI Aayog
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions; Health
In news
- Recently, the NITI Aayog has released “Accelerating Progress On Nutrition In India: What Will It Take”.
- It is the third progress report on the National Nutrition Mission or the Poshan Abhiyaan.
Key takeaways
- The third progress report (October 2019-April 2020) takes into account the status on the ground and implementation challenges encountered at various levels through large scale datasets.
- These datasets are the NFHS-4 and Comprehensive National Nutrition Survey (CNNS).
- According to the report, India’s targets are conservative on stunting as compared to the global target defined by the World Health Assembly (WHA). It is a prevalence rate of 5% of stunting as opposed to India’s goal of reducing stunting levels to 13.3% by 2022.
- The targets of reducing prevalence levels of anaemia among pregnant women from 50.3% (2016) to 34.4% (2022) and among adolescent girls from 52.9% (2016) to 39.66% are also considered to be conservative as compared to the WHA’s target of halving prevalence levels.
- In the wake of the pandemic, experts warn that deepening poverty and hunger may delay achieving the goals defined under the Mission.
Suggestions by the NITI Aayog:
- On Stunting: (1) To improve complementary feeding using both behaviour change interventions and complimentary food supplements in the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS); (2) To work towards investments in girls and women; (3) To improve water, sanitation, handwashing with soap and hygienic disposal of children’s stools.
- On Wasting: (1) To include interventions that go beyond the treatment of severe acute malnutrition (SAM) and also address moderate wasting; (2) To scale-up to reach facility-based treatment of SAM; (3) To urgently release a full strategy for prevention and integrated management of wasting nationally.
- On Anaemia: To scale-up scenario that focuses only on health sector interventions which will achieve modest improvements in anaemia among women of reproductive age.
Important value additions
National Nutrition Mission
- Launched in: 2018
- It is Indian Government’s flagship programme.
- Objective: To improve nutritional outcomes for children, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- It is backed by a National Nutrition Strategy prepared by the NITI Aayog with the goal of attaining “Kuposhan Mukt Bharat” or malnutrition-free India, by 2022.
- Aims: (1) To reduce stunting, undernutrition, anemia and low birth weight by 2%, 2%, 3% and 2% per annum respectively; (2) To address the problem of malnutrition in a mission-mode.
- 50% of the total budget comes from the World Bank or other multilateral development banks and the rest of the 50% is through Centre’s budgetary support.
- The Centre’s budgetary support is further divided into 60:40 between the Centre and the States, 90:10 for the north-eastern region and the Himalayan States and 100% for the Union Territories (UTs) without legislature.
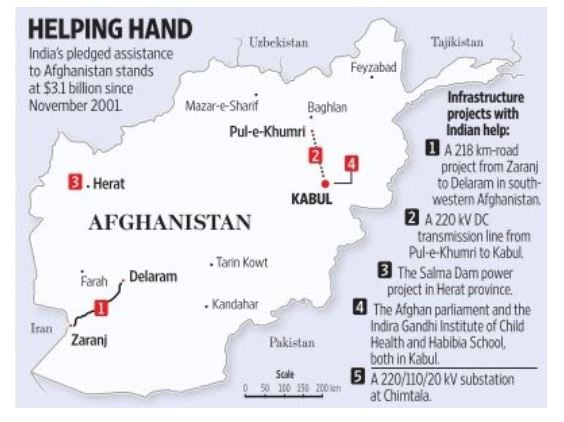
India announces 150 projects for Afghanistan
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- Recently, at the Afghanistan 2020 Conference, India has announced about 150 projects worth USD 80 million.
- The conference was attended by Afghanistan’s President, United Nations (UN) and the European Union (EU) officials and representatives of other countries.
- Also, the USA has decided to reduce its troop presence in Afghanistan to about 2,500 by January 2021.
Key takeaways
- India will launch phase-IV of high-impact community development projects, which include around 150 projects worth USD 80 million.
- It has signed an agreement for building the Shahtoot dam, which would provide safe drinking water to 2 million residents of Kabul city.
- It builds on the 202 km Pul-e-Khumri transmission line of 2009, through which India provides power to the city.
Miscellaneous
RE-INVEST 2020
- The virtual 3rd Global Renewable Energy Investment Meeting and Expo (RE-Invest 2020) shall be held in recent days which will be inaugurated by Indian PM.
- The summit is organised by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy and will be held from 26 – 28 November 2020.
- The theme for RE-Invest 2020 is ‘Innovations for Sustainable Energy Transition’.
- It will feature a 3-day conference on renewables and future energy choices, and an exhibition of manufacturers, developers, investors and innovators.
- It aims to build upon the success of the first two editions held in 2015 and 2018 and provide an international forum for investment promotion in renewable energy.

(Mains Focus)
RIGHTS/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of vulnerable sections of society.
Forest Rights Act in Jammu & Kashmir
Context: The J&K government has now decided to implement the Forest Rights Act.
Tribal politics in the erstwhile State of Jammu and Kashmir was focused on the twin issues of political reservation and enactment/extension of the Forest Rights Act (FRA) of 2006.
Brief Background of the Political Reservation Issue
- Lack of political reservation had been a major reason for the marginalization of Adivasis (Tribal people)
- The Adivasis have had to largely depend on non-tribal leadership to represent their issues and demands.
- Lack of political reservation meant that their issues were never adequately represented in the Legislative Assembly.
- The vote share of Adivasis is a major deciding factor in almost 21 Assembly constituencies, yet they remained politically marginalised.
- However, immediately after the abrogation of Article 370 (August 2019) Adivasis were provided political reservation. It was considered as step in right direction.
- The actual impact of political reservation will be seen only after elections are conducted for the Legislative Assembly of the Union Territory of J&K.
Issues of FRA
- After the abrogation of J&K’s special status, there was no delay in providing political reservation for the Adivasis. However, similar urgency wasn’t shown in the extension of the FRA
- In fact, the FRA should have been in place in J&K long time ago — nothing in Article 370 prevented the Legislative Assembly from enacting a similar law.
- The FRA would have provided Adivasis in J&K access and ownership rights, forest-based livelihood rights, and minor forest produce rights.
- Due to lack of implementation of FRA, Adivasi lands had not been protected and Adivasis, especially nomads, had neither land rights nor rehabilitation rights.
Now that FRA is being implemented, will it resolve the issues of Adivasis?
- Many Adivasi families are unlikely to benefit from the implementation of the Forest Rights Act in J&K
- Implementing the FRA is a welcome step. However, instead of alleviating fears of displacement and disempowerment, the law has only increased those fears.
- This is primarily because this is happening against the backdrop of the J&K government’s decision on October 31 to declare Roshni Act null and void. (details of Act at end of article).
- Roshni Act has been controversial due to the questionable transfer of ownership of state land to many influential people, including Ministers, legislators, bureaucrats, and police officers.
- Roshni Act also provided ownership rights to many poor and landless Adivasis but now the land will be retrieved from them (as the act will be null & void). In such a scenario, the Adivasis will fail to prove their claims of ownership under the FRA.
- Further, in the last few weeks, the eviction and demolition drives against nomads have intensified without any rehabilitation plans in place. The FRA, then, is unlikely to benefit such poor, landless Adivasis.
Conclusion
- Without a cut-off date, with land being retrieved after declaring the Roshni Act null and void, and with forceful evictions taking place, many tribal families are unlikely to benefit from the implementation of the FRA.
Jammu and Kashmir State Land (Vesting of Ownership to Occupants) Act -Roshni Act
- The Act regularised the unauthorised occupation of land.
- It granted legal ownership rights to those who had grabbed the government land in Jammu and Kashmir over several decades.
- The law provided for the collection of a fee for the legalising the illegal act of landgrab.
- The money thus raised was to be used for up-gradation of power generation in Jammu and Kashmir.
- The scheme in public view was to provide electricity, roshni in Hindi-Urdu.
- This is why this Act is called the Roshni Act and the scam Roshni scam.
- Anybody who had previously grabbed a piece of government land could approach the authorities, pay a fee and become the rightful owner of the land.
- What followed was that those who had not grabbed the land purchased such land from the poor who had erected some structure on the government and became the new legal owners of the land.
- The court held the Roshni Act as unconstitutional and directed the government to make the complete identities of influential persons who grabbed the land regularised under the law public.
- Jammu and Kashmir government issued an order to cancel all land transfers that took place under the Roshni Act.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the Indian state does not share border with Bhutan?
- Sikkim
- West Bengal
- Assam
- Bihar
Q.2 Sahakar Pragya was recently launched by which of the following Ministry?
- Ministry of Agriculture
- Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
- Ministry of Electronics and IT
- Ministry of textiles
Q.3 In which of the following states of India the technology of desalination plant has been experimented with?
- Maharashtra
- Kerala
- Andhra Pradesh
- Gujarat
- Tamil Nadu
Select the correct code:
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 2, 3 and 5 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 3, 4 and 5only
ANSWERS FOR 25th November 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
About Inter-faith marriages (controversy on “Love Jihad”):
About EdTech Control:
On refining Trade Union Strategies:














