IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
SAKSHAM (Shramik Shakti Manch) launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II –Welfare schemes; Policies and interventions & GS-III – Employment
In news
- Technology Information, Forecasting and Assessment Council (TIFAC) has launched SAKSHAM (Shramik Shakti Manch).
- TIFAC is an autonomous organization under the Department of Science & Technology, Government of India
Key takeaways
- It is a job portal for mapping the skills of Shramiks with regard to requirements of MSMEs.
- Objective: To directly connect Shramiks with MSMEs and facilitate their placement
- The portal will help eliminate labour contractors.
- It shall help identification of skill proficiency level and development of Skill Cards for Shramiks.
- The portal uses algorithm and Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools for availability of Shramiks.
- The portal was initially launched in two districts and is now being launched as an all India portal.
Seaweeds Mission launched for commercial farming of seaweeds
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Agriculture; Economy
In news
- Technology Information, Forecasting and Assessment Council (TIFAC) has launched a Seaweed Mission.
- Objective: Commercial farming of seaweeds and its processing for value addition towards boosting national economy.
The Mission shall undertake following activities:
- Establishing model demonstration farms over one hectare for cultivation of economically important seaweeds in nearshore and onshore along the Indian coasts.
- Establishment of seaweed nurseries for supplying seed material for large scale farming
- Onshore cultivation for (i) Seedling supply facility (ii) Seaweed cultivation for processing
- Setting up of processing plant for production of plant growth stimulants (sap) and industrially important cell wall polysaccharides such as agar, agarose, carrageenan and alginates from fresh seaweeds
Advantages of the Mission:
- By an estimate, if cultivation is done in 5% of the EEZ area of India, it can: (1) provide employment to ~ 50 million people; (2) set up new seaweed industry; (3) contribute to national GDP; (4) increase ocean productivity; (5) reduce algal blooms, (6) increase Carbon sequestration; (7) provide bio-ethanol of 6.6 billion litres.
Do you know?
- Out of the global seaweed production of around 32 million tons, fresh weight is valued around 12 billion USD.
- China produces ~57 %, Indonesia ~28%, whereas India is having a mere share of ~0.01-0.02%.
India-Australia Circular Economy (I-ACE) Hackathon, 2021
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – International Relations
In news
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) and Australia’s national science agency (CSIRO) kick started the India-Australia Circular Economy (I-ACE) Hackathon, 2021.
- Goal: To enable talented innovative students and start-ups from Australia and India to address common national issues through innovative technology solutions
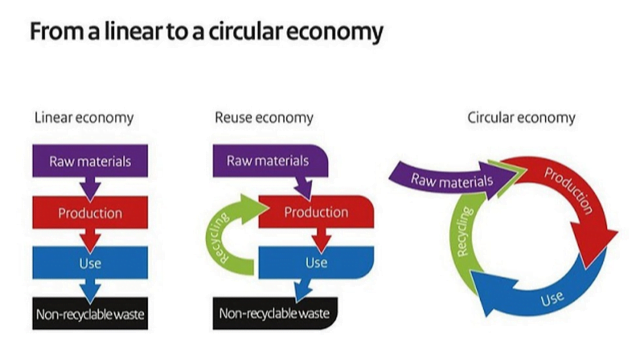
Key themes for the hackathon:
- Innovation in packaging reducing packaging waste
- Innovation in food supply chains avoiding waste
- Creating opportunities for plastic waste reduction
- Recycling critical energy metals and e-waste
Do you know?
- A ‘circular economy’ model employs waste management and focuses on reusing, recycling and responsible manufacture.
- It can support the development of new industries and jobs, reducing emissions and increasing efficient use of natural resources.
Steps taken by the Government for Child Beggars
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – I – Social Issues & GS- II – Welfare schemes
In news
- Lok Sabha recently informed about the steps related to Child Beggars.
- Ministry: Ministry of Women and Child Development
Key takeaways
- The Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015 (JJ Act) is the primary law for children in the country.
- As per Section 2 of the Act,2015, a child who is found working in contravention of labour laws or is found begging is included as a “child in need of care and protection”.
- As per Section 76, whoever employs any child for the purpose of begging shall be punishable with imprisonment upto five years and fine of one lakh rupees.
- Child Protection Services (CPS) under Integrated Child Development Services scheme supports the children in difficult circumstances including child beggars and destitute children.
- Institutional care is provided through Child Care Institutions (CCIs), as a rehabilitative measure.
- The scheme supports 24×7 emergency helpline service for children in distress conditions (toll free number, 1098 from anywhere in India.
- A pilot project is undertaken for Comprehensive Rehabilitation of Persons engaged in the act of begging in 10 cities.
- It includes education of children engaged in begging/children of persons engaged in the begging.
Arbitration And Conciliation (Amendment) Bill 2021
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Economy
In news
- Arbitration and Conciliation (Amendment) Bill 2021 was passed recently in the Lok Sabha.
Key takeaways
- It seeks to amend the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996.
- It contains provisions to deal with domestic and international arbitration.
- It defines the law for conducting conciliation proceedings.
- It specifies that a stay on the arbitral award can be provided if the court is satisfied th atthe relevant arbitration agreement was induced by fraud or corruption.
- This change will be effective from October 23, 2015
- It removes the Schedule for arbitrators.
- The qualifications, experience, and norms for accreditation of arbitrations will be specified under the regulations.
Tholpavakoothu
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – I – Culture
In news
- For the first time, Tholpavakkoothu, the famous shadow leather puppets will tell stories of the epic Ramayana with the help of robots.
Important value additions
- Tholpavakoothu is a form of shadow puppetry.
- Practiced in: Kerala, India.
- It is performed using leather puppets as a ritual dedicated to Bhadrakali.
- It is performed in Devi temples in specially built theatres called koothumadams.
- It is believed to have originated in the ninth century AD.
- It uses Kamba Ramayana as its basic text.
Miscellaneous
Tapovan Dam
-
Rescue operations resumed at the NTPC’s Tapovan hydel project tunnel where many workers are trapped after a snow avalanche triggered flash floods
- It is being constructed on Dhauliganga River in Chamoli District, Uttarakhand.
- The plant is expected to generate over 2.5 TWh of electricity annually.
Related articles:
- RSTV- Floods and Dam Management: Click here
- Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs): Click here
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment; Infrastructure: Ports
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
How tech can transform law enforcement
Context: There is an urgent need for law enforcement agencies (LEAs) to adopt technology in their operations as it can act as a force multiplier. This is especially true in India where the police to population ratio is less than 150 per 100,000 (UN recommended number is 222)
Following are the ways in which LEAs can use technology to increase their efficiency and effectiveness:
- Digitising Citizen-Facing Services: By providing digital access to the police, citizens can avail services from the comfort of their home. For instance: The Punjab Police has a citizen-facing portal, Saanjh, which provides online services for downloading FIRS and searching for stolen vehicles and lost mobiles, among other services
- Departmental Monitoring: Technology can also be used to provide senior police officials dashboard views for their areas of jurisdiction, identify trends, patterns, outliers and take corrective action.
- Citizen Awareness: Digital portals, social media can be used by LEAs to reach out directly to citizens — providing information on traffic jams, how to protect against cybercrime, dispelling rumours, countering fake news.
- Crime Detection: Due to increasing usage of phones, it will difficult to analyse the records of Call Detail Records (CDRs) manually. CDR analysis tools can be used to identify call patterns, most frequently called numbers, geo-location, and help in tracking missing persons, lost mobiles, movement, and establish relationships between criminal associates.
- Leveraging AI and Big Data: Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be used to match fingerprints, facial images, analyse CCTV footage and recognise vehicle number plates. Big Data can be used to integrate data from multiple sources such as social media tools, financial institutions, travel records, hotel stays, CDRs and criminal records. This helps in creating 360-degree view of the criminal and draw linkages between criminal associates.
- Crime Prevention: Big Data can play a major role as it can be used to identify crime patterns and hot spots. AI can be used to draw correlations between the type of crime, time, location. Given the high number of postings and transfers in the police, these dashboards can help the newly transferred officer to get up to speed quickly.
- Riot Control: Sentiment analysis of social media chatter can be used to identify potential riots (including location and time) as well as track the source of rumours designed to create communal disharmony. Social media can also be used to provide authentic information to public to dispel rumours.
- Human Resource Management: Key performance indicators such as the time taken to file a charge-sheet, types of crimes solved, time taken to address complaints, citizen feedback scores can be used to determine an officer’s performance in a more objective manner.
- Integrating Criminal Justice System: The five pillars of the criminal justice system are police, courts, prosecution, jails and forensics. Countless man-years are lost in taking physical files from one place to another. Real-time integration between the information technology systems of these pillars will help in reducing duplicate data entry and errors.
Conclusion
Technology integration will significantly increase the efficiency of our LEAs and, at the same time, drastically reduce the time taken to provide justice. It can be a win-win for all the key stakeholders
Connecting the dots:
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-3: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Parliamentary Committee and 5G
Context: A standing committee of Lok Sabha on Information Technology has submitted its report on 5G and said that India will miss the 5G bus.
What are the findings of the parliamentary standing committee on IT?
- Little Progress on ground: Despite the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) having submitted a report on the steps to make India 5G ready as early as August 2018, there was very little progress on the ground.
- High Spectrum Prices: the reserve price for auction of 5G was one of the highest in the world. It needed to be rationalised, taking into account the per capita income of the country and also by comparing it with reserve price mandated by other countries.
- Inadequate and poor development of test cases: Globally, as many as 118 telecom service providers across 59 countries have started deploying 5G networks. India is yet to give formal approvals for 5G testing despite all the three major private telecom players having submitted their applications as early as January 2020.
- Delayed rollout of 5G: Comparing it to the deployment of other older technologies such as 2G, on which it was late by four years, 3G on which India was as much as a decade late, and 4G on which India missed by the bus by 7 years, the committee concluded that “sufficient preparatory work had not been undertaken for launching of 5G services in India.”
- Low reach of optical fibre across India, and deficient back-haul capacity are other factors which is delaying the deployment of 5G in India.
Conclusion
- Not all hope is lost as far as the roll out of 5G in India is concerned
- Even before the findings of the parliamentary committee were made public, the DoT had, in a bid to facilitate faster roll out of new services, reduced the notice period for telcos to six months from one year.
- A reduced time would mean that telcos could as soon as September this year start testing the 5G network for commercial purposes in all three bands, namely low, mid and high frequency spectrum
- Apart from this, the parliamentary committee also hoped that the DoT would reach an understanding with the Department of Space and Ministry of Defence at the earliest to earmark the allocation of spectrum waves.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Tapovan Dam is being constructed on which of the following river?
- Dhauliganga
- Rishiganga
- Ganga
- Yamuna
Q.2 Tholpavakoothu, a form of shadow puppetry, is practiced in:
- Kerala
- Tamil Nadu
- Andhra pradesh
- Telangana
Q.3 Which of the following is incorrect?
- Comprehensive Rehabilitation of Persons includes education of children engaged in begging
- Institutional care is provided through Child Care Institutions (CCIs) under Child Protection Services (CPS) of Integrated Child Development Services scheme.
- As per Section 2 of the JJ Act, 2015, a child who is found begging is included as a “child in need of care and protection”.
- As per Section 76, whoever employs any child for the purpose of begging shall be punishable with imprisonment up to 10 years and fine of one lakh rupees.
ANSWERS FOR 12th February 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | B |
Must Read
On possible continuity of US foreign policies despite change in regime:
On US President making first call to Indian PM Modi:
About criticism of developmental in context of Uttarakhand Floods:











