IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
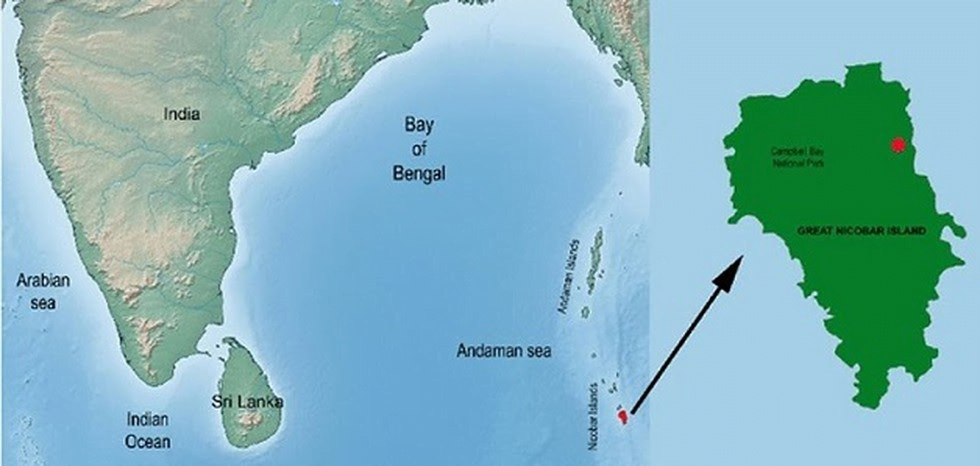
NITI Aayog’s Project for Great Nicobar Island
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Environment
In news
- The Environment Appraisal Committee (EAC) – Infrastructure I of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has flagged serious concerns about NITI Aayog’s ambitious project for Great Nicobar Island.
Key takeaways
- The committee has, however, removed the first hurdle faced by the project.
- It has “recommended” it “for grant of terms of reference (TOR)” for Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) studies, which in the first instance will include baseline studies over three months.
- The proposal includes an international container transshipment terminal, a greenfield international airport, a power plant and a township complex spread over 166 sq. km. (mainly pristine coastal systems and tropical forests), and is estimated to cost ₹75,000 crore.
Important value additions
Galathea Bay
- Galathea Bay is the site of the port and the centrepiece of the NITI Aayog proposal.
- It is an iconic nesting site in India of the enigmatic Giant Leatherback, the world’s largest marine turtle.
- A number of species are restricted to just the Galathea region.
- These include the critically endangered Nicobar shrew, the Great Nicobar crake, the Nicobar frog, the Nicobar cat snake, a new skink (Lipinia sp), a new lizard (Dibamus sp,) and a snake of the Lycodon species that is yet to be described.
Production-Linked Incentive Scheme for The Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery Storage
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- The Union Cabinet has approved the proposal of Department of Heavy Industry for implementation of the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme ‘National Programme on Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery Storage’.
Key takeaways
- Aim: To achieve a manufacturing capacity of 50 GigaWatt Hour of ACC and five Giga Watt Hour of Niche ACC with an outlay of 18,100 crore.
- ACCs are the new generation of advanced storage technologies that can store electric energy either as electrochemical or as chemical energy and convert it back to electric energy as and when required.
- It will also give a big push to electric mobility, benefiting three-wheelers, four-wheelers and heavy vehicles.
- India is currently importing Battery Storage Equipment
- The scheme will be helpful in making the country self-reliant (Atmanirbhar).
MoU between Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) and Qatar Financial Centre Authority (QFCA)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – International Relations
In news
- The Union Cabinet has approved signing of MoU between Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) and Qatar Financial Centre Authority (QFCA).
Key takeaways
- The MoU would enhance cooperation between the Institutes to work together to strengthen the Accounting profession and entrepreneurship base in Qatar.
- ICAI has an active Chapter in Doha, Qatar which was established in the year 1981 and is the oldest among the 36 overseas Chapters of the ICAI.
- Qatar (Doha) Chapter is amongst the most vibrant Chapters of ICAI.
Important value additions
The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI)
- It is a statutory body established under The Chartered Accountants Act, 1949′.
- Objective: To regulate the profession of Chartered Accountancy in India.
Aerial Passenger Ropeway System Between Dehradun and Mussoorie
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Infrastructure
In news
- The Union Cabinet gave its approval to the transfer of land of Indo-Tibetan Border Police, ITBP to Government of Uttarakhand for development of Aerial Passenger Ropeway System between Dehradun and Mussoorie.
Key takeaways
- The proposed Ropeway is a mono-cable ropeway of 5.5 Km length between Purkul Gaon, Dehradun and Library, Mussoorie being constructed at an estimated cost of Rs 285 crore.
- It will have a carrying capacity of 1,000 persons per hour per direction.
- This will considerably reduce the traffic flow on the road route from Dehradun to Mussoorie.
- This will generate direct employment of 350 and indirect employment of more than 1,500 people.
- It will also be a huge attraction for tourists which in turn will provide a boost to the tourism industry
Important value additions
Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP)
- It is India’s primary border patrol organization with its border with China’s Tibet Autonomous Region.
- It was formed in 1962 in the wake of the Sino-Indian War of 1962.
- The “Indo-Tibetan Border Police Force Act, 1992” provides for the constitution and regulation of the ITBP for ensuring the security of the borders of India and for matters connected therewith.
(Mains Focus)
INTERNATIONAL/SECURITY
Topic:
- GS-2: India and its neighborhood- relations.
- GS-3: Security challenges and their management in border areas
India-China: Lessons from Ladakh Stand-off
Context: After over a year, the stand-off between Indian and Chinese troops in eastern Ladakh shows no signs of resolution. Disengagement has stalled, China continues to reinforce its troops, and talks have been fruitless.
Implications of the border tensions
- More broadly, the India-China bilateral relationship has ruptured. India has made clear that the relationship is conditional on peace on the border.
- Political relations are marked by hostility and distrust.
- Reversing a long-held policy, India will no longer overlook the problematic border dispute for the sake of a potentially lucrative wider relationship;
- Even if disengagement continues, the relationship will remain vulnerable to destabilising disruptions.
Key Lessons to be learnt
- China is more likely to be deterred or coerced with the threat of political costs, rather than material costs.
- China’s defence budget is three to four times larger than India’s, and its Western Theatre Command boasts over 200,000 soldiers. The material burden of the crisis would not disrupt its existing priorities.
- In contrast, India successfully raised the risks of the crisis for China through its threat of a political rupture, not military punishment
- Indian Ocean Region is the key
- India should consider accepting more risk on the LAC in exchange for long-term leverage and influence in the Indian Ocean Region.
- At the land border, the difficult terrain and even balance of military force means that each side could only squeeze out modest gains at best.
- In contrast, India has traditionally been the dominant power in the Indian Ocean Region and stands to lose significant political influence and security if it fails to answer the rapid expansion of Chinese military power in the region.
- The Ladakh crisis, by prompting an increased militarisation of the LAC, should not defer long-overdue military modernisation and maritime expansion into the Indian Ocean.
Connecting the dots:
- On Pakistan’s New Map – Critical Analysis
- India-Nepal Border Dispute: Kalapani and Lipulekh
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Rural Imperative in the wake of COVID crisis
Context: The main kharif planting season will begin only from mid-June with the arrival of the monsoon rains.
Agricultural Sector in 2020-21
- The year 2020-21 was exceptional, where the farm sector expanded by 3%, even as the Indian economy as a whole contracted by 6.5&.
- Agricultural exports also grew 17.5%, despite the value of the country’s overall merchandise shipments falling by 7.2%.
- Industries like tractor, FMCG and cement companies rode high on rural demand in 2020-21.
- The end result was that rural India provided a cushion for the economy, which suffered its worst recession since Independence and the first after 1979-80.
Reasons for above scenario
- Low impact of Pandemic: Covid-19 cases being very low in rural areas last year and the government exempting agricultural activities from lockdown restrictions
- Favourable Monsoon: Another reason was excellent rains and favourable winter temperatures that helped farmers harvest a bumper crop.
- Favourable Prices: There was also a spike in global agri-commodity prices from around October, the benefits of which were reaped by soyabean, mustard, groundnut, cotton, arhar, urad and chana growers.
- Right interventions by government: Firstly, government undertook massive procurement of wheat, paddy, mustard and rabi pulses that were marketed post the lockdown. The second was the record 389.37 crore person-days of employment that got generated under MGNREGA during 2020-21. Along with these two, there was Rs 6,000-per-farmer cash transfer under PM-Kisan that ensured sizeable liquidity infusion into the rural economy.
What will be the scenario this year?
- The Indian Meteorological Department has forecast a normal southwest monsoon, while FAO’s world food price index hit an 83-month-high in April. On both these fronts — rainfall and prices — the outlook for agriculture, thus, remains favourable.
- The availability of cushion, provided by agricultural sector last year, is in doubt today, with the second wave of the pandemic not sparing rural areas
- This year, there is not much requirement for MSP procurement, barring in wheat.
- The scope of MGNREGA works is also limited when Covid has made deep inroads into rural areas.
Conclusion
- If the current wave subsides by planting season of Kharif, things shouldn’t turn out too bad.
- The focus of government should be more on cash transfers. There’s no better time to put to use the JAM (Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile) infrastructure than now.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Where is Galathea Bay located?
- Philippines
- Japan
- India
- China
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC):
- ACCs are the new generation of advanced storage technologies that can store electric energy either as electrochemical or as chemical energy
- Implementation of the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme ‘National Programme on Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery Storage’ was recently approved.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Hill station of Mussoorie is situated in the foothills of the which of the following mountain range?
- Garhwal Himalayan range
- Aravalli Range
- Kaimur Range
- MaiKal Range
ANSWERS FOR 12th May 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | A |
Must Read
On criticism of Centre’s vaccination policy:
On pandemic & hunger:
About India-EU relations:











