IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Biologics offer revolutionary approach to treating diseases
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Sci & tech
In news
- A nanoparticle was recently designed by researchers from University of Massachusetts, U.S.A
- It offers a new and potentially revolutionary approach to treating diseases.
Key takeaways
- The new concept, Protein–Antibody Conjugates or PACs, combines two different approaches to drug delivery.
- One is biologics, where the idea is to target a defective protein in the system by delivering proteins to it.
- An example of this is the case of insulin treatment.
- The other approach is to use antibodies for drug delivery.
- Antibodies are something the body produces to detect a foreign substance inside the body.
- Now, PACs have a protein attached to the antibody.
- This could have an impact on incurable diseases like pancreatic cancer.
ICMR issues advisory on Plasma Therapy
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Sci & tech
In news
- According to an advisory from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), the use of convalescent plasma has been dropped from the recommended treatment guidelines for COVID-19
Key takeaways
- PLACID trial conducted last year had found no significant benefit from the use of plasma; it still continued to find a place in the recommended guidelines.
- According to some experts, the use of such plasma may have caused new mutations to the virus.
Important value additions
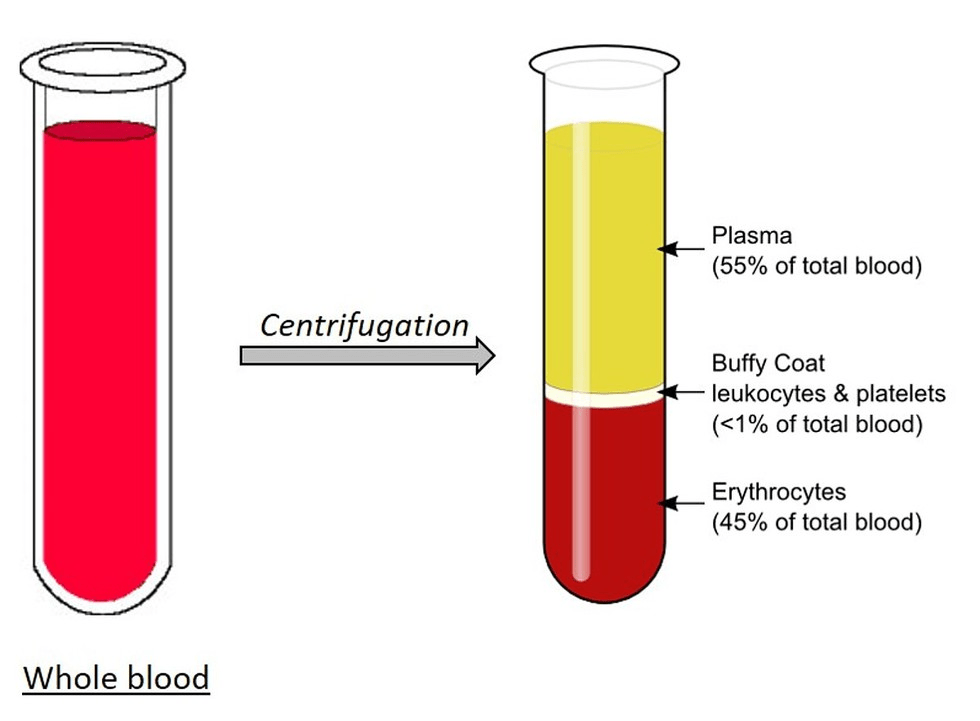
Plasma
- Blood plasma is a yellowish liquid component of blood that holds the blood cells of whole blood in suspension.
- It is the liquid part of the blood that carries cells and proteins throughout the body.
- It makes up about 55% of the body’s total blood volume.
- This plasma contains viral antibodies that have treatment potential for severe cases of the disease.
Plasma therapy
- Plasma therapy is a medical procedure that uses the blood of a recovered patient to create antibodies on those infected individuals.
- It is medically known as convalescent plasma therapy.
- This treatment uses antibodies found in the blood taken from a recovered Covid-19 patient.
- It is then used to treat those with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection to aid recovery.
Related articles
Proposed framework for Gold Exchange in India
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Economy
In news
- The Securities & Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has floated a consultation paper on the proposed framework for Gold Exchange in India.
Key takeaways
- The Gold exchange proposal was announced by the Finance Minister.
- SEBI is entrusted with the task of regulating the proposed exchange which includes vaulting, assaying the gold quality and delivery standards
- The existing stock exchanges may deal in ‘electronic gold receipt’ (EGR) through a separate segment.
- SEBI has also suggested a new exchange exclusively for EGR that would have advantages such as better liquidity and single-price reference.
- It has also been suggested that an entire transaction be divided into three tranches.
- The vault manager should have a net worth of ₹50 crore and will be required to furnish security deposits.
Species in news: Subdoluseps Nilgiriensis
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment
In news
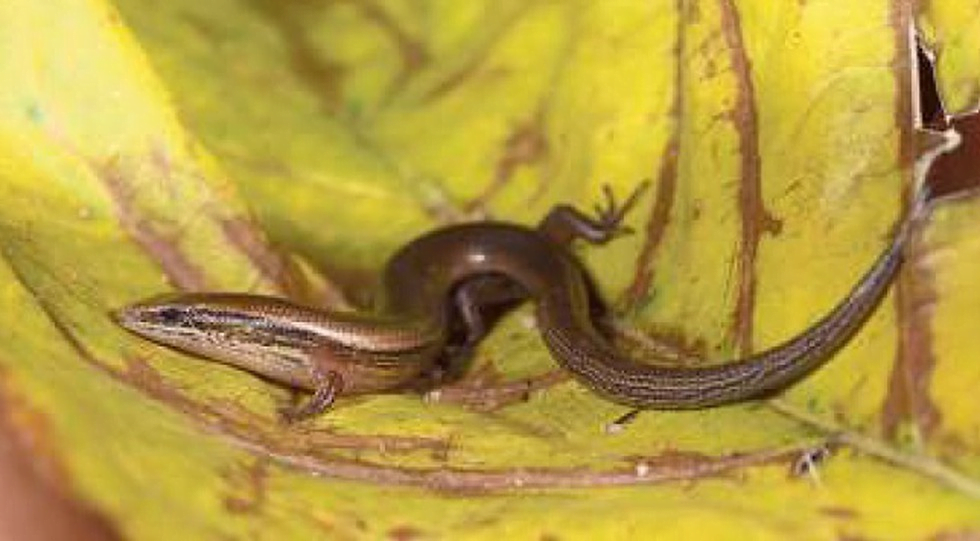
- Researchers have discovered an Asian gracile skink species from Western Ghats.
Key takeaways
- It is named Subdoluseps nilgiriensis.
- It has a slender body (7 cm)
- It is sandy brown in colour.
- It is closely related to Subdoluseps pruthi found in parts of the Eastern Ghats.
- This species is only the third skink species discovered from mainland India in the last millennium.
Do you know?
- Skinks are non-venomous.
- They resemble snakes because of the often-inconspicuous limbs and the way they move on land.
- Such resemblance often results in humans killing this harmless creature.
- It is considered a vulnerable species.
- Threats: Seasonal forest fires, housing constructions and brick kiln industries in the area.

Article 311 of the Indian Constitution
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – Constitution
In news
- Article 311 was recently in news.
Key takeaways
- Article 311 says that no government employee either of an all India service or a state government shall be dismissed or removed by an authority subordinate to the own that appointed him/her.
- Section 2 of the article says that no civil servant shall be dismissed or removed or reduced in rank except after an inquiry in which s/he has been informed of the charges and given a reasonable opportunity of being heard in respect of those charges.
- As per Article 311 (2) (a), if a government employee is convicted in a criminal case, he can be dismissed without DE.
- Under 311 (2) (c), a government employee can be dismissed when the President or the Governor, as the case may be, is satisfied that in the interest of the security of state it is not convenient to hold such an enquiry.
Do you know?
- In a departmental enquiry (DE), after an enquiry officer is appointed, the civil servant is given a formal charge sheet of the charges.
- The civil servant can represent himself/herself or choose to have a lawyer
(Mains Focus)
GOVERNANCE/ECONOMY
Topic:
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources
Prioritising the right to life
Context: The majority of India’s working population is today reeling from the impact of multiple crises: a health emergency; massive job losses, declines in incomes from work; and significantly increased mass hunger and worsening nutrition.
Survey by Hunger Watch
- Even after lockdown was lifted last year, two-third families reported eating less than they did before the lockdown, and a reduction in healthy food.
- For a quarter of the families surveyed, incomes had fallen by half.
- It also found that hunger was higher in urban India compared to rural.
Judiciary, Hunger & Right to Life
- The Supreme Court on May 13 directed the Centre and the State governments of Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh to provide free rations without insisting on ID proof to all migrant workers and to run kitchens providing free meals twice a day.
- The directive shows that the apex court acknowledged a hunger crisis in the country that needed urgent state action
Shortcomings of above direct:
- It did not extend the facility to the country as a whole;
- It did not extend the facility to cover cash payments by the state besides meals and ration;
- It made the facility a state largesse rather than a right.
- Had SC recognised a universal right to livelihood as the basis for its verdict, deriving from the right to life, the above three lacunae would have been overcome.
Vaccine Policy & Right to Life
- Being vaccinated against COVID-19 is essential for defending one’s right to life
- Government must respect everyone’s right to life and must make the vaccine equally available to all irrespective of the recipient’s capacity to pay.
- India is making people (aged 18-45 years) pay to be administered these vaccines in private clinics. Contrast this to US (most privatised medical systems) where vaccines is provided for free to all
What went wrong with India’s vaccine policy?
- Government did not ensure adequate production through compulsory licensing of more producers
- Government did not order enough vaccines.
- It reneged on its responsibility to provide these vaccines to State governments.
- It introduced differential pricing, forcing State governments to compete with each other and with private clinics to buy vaccines.
- It allowed price rise by Bharat Biotech and Serum Institute of India.
Way Ahead
State needs to take a range of measures that prioritise the right to life, which also remains the surest way of initiating assured (and equitable) economic recovery
- Monthly cash transfer, of about ₹7,000 per household for at least three months to those without regular formal employment, over and above the provision of free meals and rations.
- Expanded production and central procurement of COVID-19 vaccines, and distribution to States for free immunisation to all;
- Increased resources to the Integrated Child Development Services to enable revival and expansion of their programmes
- Making the MGNREGS purely demand-driven, with no ceilings on the number of days or the number of beneficiaries per household
- Covering urban India with a parallel MGNREGA like scheme that would also cater to the educated unemployed.
- A 1.5% wealth tax levied on only the top 1% of households will be adequate to fund the above measures of government.
Connecting the dots:
HEALTH/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Rural Areas & Second Wave
Context: The big cities battered by Covid-19 are now showing early signs of recovery from the second wave. There is growing concern now about smaller towns and rural areas where the virus has made inroads.
During the first wave, the virus did not have easy passage into rural areas. This was because
- Travel restrictions, prescribed or voluntary, prevailed even after the lockdown was lifted.
- Large gatherings were mostly avoided.
- Even where the virus entered, it had slow transmission as villages have lower population density than urban areas — people live in relatively ventilated houses and work in open fields.
- Because co-morbidities like hypertension, diabetes and cardiovascular disease are lower in rural populations, risk of severe illness and death was also less
However, during the second wave, complacency about the seriousness of COVID-19 and emergence of new strains created havoc in rural areas.
India suffered during second wave due to frail health systems in rural areas
- Inadequate health infrastructure
- Lack of trained health workforce
- Poor availability of drugs and other medical supplies,
- Poor connectivity to higher levels of care are deficient in many districts.
What measures is needed to tackle second wave in rural areas?
- Household visits by frontline health workers for symptom surveillance and case detection.
- Engagement of the local community is vital. Where available, NSS and NCC resources can be drawn upon. Community-based organisations, which have grassroots presence, can assist in the delivery of health and social services.
- Home care support and monitoring.
- Emergency transport systems that can transfer seriously ill patients to pre-determined points of advanced care and mobile laboratories must be organised with assurance of availability, affordability and equity.
- Other than for essential needs, commuting between urban and rural areas must be restricted to reduce the risk of transmission.
- Large gatherings must be prohibited for at least six months.
- Decentralised, data-driven decision making
- Essential data must be readily available locally at the block level for real-time alerts and rapid response.
- Expanded data sets can be analysed at the district level for monitoring and supportive supervision.
- More elaborate (optimal) data sets can flow to the state capital level for course corrections and resource allocation.
- At the local level, qualitative information from key informant interviews must supplement quantitative data to help in identifying roadblocks and solutions.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding Plasma:
- It is a yellowish liquid component of blood
- It carries cells and proteins throughout the body.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Under which of the following article, a government employee can be dismissed without a Departmental enquiry, when the President or the Governor, as the case may be, is satisfied that in the interest of the security of state it is not convenient to hold such an enquiry?
- Article 311
- Article 312
- Article 313
- Article 314
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding Skinks:
- They are venomous
- They resemble snakes
- They are found in both Western and Eastern ghats
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
ANSWERS FOR 17th May 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | B |
Must Read
On GST Council meeting:
On US policies on West Asia:
About Central Vista Redevelopment Project:











