IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
States asked to declare Mucormycosis an epidemic
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Health; Policies and interventions
In news
- The Union government has asked the States to declare mucormycosis,, an epidemic under Epidemic Diseases Act 1897.
- Mucormycosis is the black fungal infection being reported in COVID-19 patients.
Key takeaways
- Declaring it an epidemic would lead to health facilities screening for it and reporting all such cases to the government.
- Rajasthan, Telangana and Tamil Nadu have already declared it an epidemic.
Important value additions
- Mucormycosis or black fungus is a complication caused by fungal infection.
- People catch mucormycosis by coming in contact with the fungal spores in the environment.
- The disease is being detected among patients who are recovering or have recovered from Covid-19.
Related articles
Shortage of anti-fungal injection, Amphotericin B
Money Withdrawal from online wallets through ATM permitted
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Economy
In news
- Now Money kept in various online wallets like Amazon pay, Ola money, Mobikwik, Phone pe, Delhi Metro Card etc. can be withdrawn using an ATM or Point of Sale Terminal.
Key takeaways
- RBI has permitted cash withdrawal of Rs. 2,000 per transaction with maximum limit of Rs. 10,000 per month.
- All non-bank Payment prepaid instruments can provide this service.
- Till date, RBI has permitted 37 Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs) in country.
- Maximum two lakh rupees can be kept in various wallets after completion of full KYC.
- All PPIs have to ensure interoperability by 31st March 2022
Important value additions
- PPIs help facilitate the purchase of goods and services, including financial services, remittances and fund transfers against the value stored on such instruments.
- These instruments are generally pre-loaded cards.
- Examples: Paytm and GPay (semi-closed system PPIs), gift cards (closed system PPIs) and debit or credit cards (open system PPIs).
Dahanu Gholvad Sapota
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – I – Geography
In news
- Dahanu Gholvad Sapota (Chikoo) was in news recently.
- A consignment from Palghar district of Maharashtra was shipped to the United Kingdom, giving major boost to exports of GI certified products.
Key takeaways
- GI certification of Ghovad Sapota is held by Maharashtra Rajya Chikoo Utpadak Sangh.
- The fruit is known for its sweet and unique taste.
- It is believed that the unique taste is derived from calcium rich soil of Gholvad village.
Do you know?
- Sapota-growing states- Karnataka, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, West Bengal and Andhra Pradesh.
- Highest growers: Karnataka, Maharashtra.
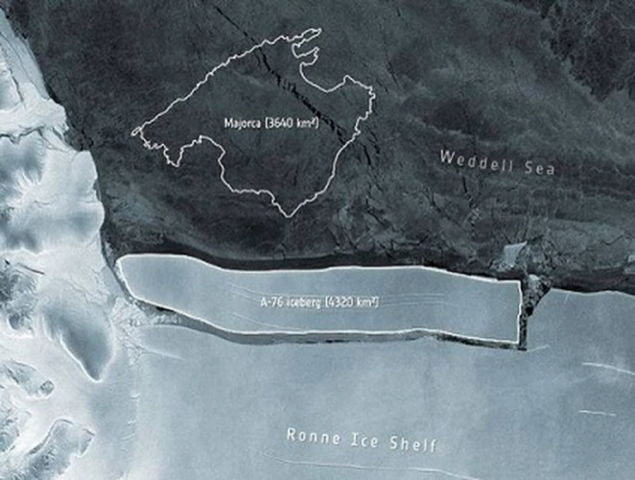
A-76 becomes World’s Largest Iceberg currently afloat in the world
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment
In news
- A giant slab of ice bigger than the Spanish island of Majorca has sheared off from the frozen edge of Antarctica into the Weddell Sea.
- It has now become the largest iceberg currently afloat in the world.
Key takeaways
- The iceberg is designated A-76 by scientists.
- A-76 broke away from Antarctica’s Ronne Ice Shelf.
- It was spotted in recent satellite images captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission.
Do you know?
- It surpassed the now second-place A-23A iceberg which is also floating in the Weddell Sea.
- Spain’s popular tourist island of Majorca lies in the Mediterranean.
- The Weddell Sea is part of the Southern Ocean and contains the Weddell Gyre.
- Its land boundaries are defined by the bay formed from the coasts of Coats Land and the Antarctic Peninsula
Airborne Transmission of SARS-COV-2 Virus
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – Health In news
- In a new advisory, the government has warned that the SARS-CoV-2 virus can be transported through air as well in the form of aerosols, and infect people up to 10 metres away.
- The general advisory on Covid-19 was issued by the office of the Principal Scientific Advisor.
Key takeaways
- The warning is in line with the latest evidence that suggests that airborne transmission of the virus, especially in enclosed spaces, cannot be ruled out.
- It was initially suggested that the virus spreads predominantly through large droplets that come out when a person is talking, sneezing or coughing.
- These droplets, because of their large size, were supposed to travel only short distances before falling on the ground.
- A person 6 feet (2 metres) away was considered safe from infection.
- However, over the months, scientists have been finding increasing evidence of the virus travelling through aerosols as well.
Do you know?
- Aerosols are small solid particles suspended in the air.
- Relatively light, aerosols can carry the virus to much larger distances.
- Also, they can remain suspended in the air for several minutes, or even hours, thereby greatly increasing the chance of the infecting a nearby person.
Related articles
Indian SARS-CoV-2 Genomic Consortia (INSACOG) launched
Virus Mutation: New SARS-CoV-2 strain
B.1.1.7 Lineage: New variant of SARS-CoV-2
Miscellaneous
FakeBuster
- Researchers at the IIT, Ropar in Punjab and Monash University, Australia have developed a unique detector named ‘FakeBuster’.
- Significance: To identify imposters attending a virtual conference without anybody’s knowledge.
- FakeBuster is a DeepFakes Detection Tool for Video Conferencing Scenarios.
- The technique will find out if some imposter is attending a Webinar or virtual meeting on behalf of one of your colleagues by morphing his image with his own.
- It can also find out faces manipulated on social media to defame or make a joke of someone.
(Mains Focus)
GOVERNANCE/ECONOMY
Topic:
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
India-Africa Relationship
Historical Background
- During early 1920s both regions fight against colonial rule and oppression.
- After India gained independence, it became a leading voice in support of African decolonisation at UN
- Independent India, though extremely poor after two centuries of colonial exploitation, strived to share its limited resources with African countries under the banner of South-South cooperation
- In 1964, India launched the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) programme to provide technical assistance through human resource development to other developing countries – Africa was biggest beneficiary
- India’s economic engagement with Africa, on the other hand, only began intensifying in the early 2000s. India’s total trade with Africa grew from US$ 6.8 billion in 2003 to US$ 76.9 billion in 2018, and India is now Africa’s third-largest trade partner
Challenges
- Government aimed to export 10 million vaccine doses to the African continent. However, due to second wave and increasing domestic demand, export prospects may be hampered.
- Indian Line of Credits(LoCs) have not been designed to achieve a larger development goal such as food security, health security, clean energy or education for all. LoCs are typically used by recipient countries to fund small development projects such as roads, bridges, railway lines.
- There is no synchronisation between different development instruments of India.
- Moreover, implementation has been a key constraint for Indian LoCs, with poor disbursal rates and project completion record.
- There has instances of violence against African students is common in India that has created unease in India-Africa relationship
- Although India has immense social capital among African nations, it has not matched this in material ties, and China’s economic and investment presence in Africa has been outstripping India’s for many years
- China is essentially trying to offer an alternative authoritarian model of development to African countries. Its message is that no longer is the liberal international path the only road for African countries to take and prosper.
With its limited resources, India can try to make its development cooperation with Africa more impactful in the following ways:
- Clear strategy for African development
- Continue the current focus on capacity building
- Harness Indian civil society organisations, NGOs, and Indian diaspora:
- Promote development-friendly private investments:
- Timely completion of projects
- Improve the experiences of Africans in India
- A thought-fully planned vaccine strategy that balances interest of India and that of Africa
Connecting the dots:
- Pandemic in Africa and opportunity for India
- Asia-Africa growth Corridor
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Business Localisation
Context: As global businesses look to diversify their supply chains, the spotlight is back on the government’s ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ (Self-Reliant India) campaign.
Benefits for Localisation
- Benefits for Customers:
- Locally produced goods are aptly suited for their home markets as they are developed and tested in local conditions
- Due to local manufacturing, customers (intermediary or end use) can expect faster deliveries.
- Local product tend be cheaper than imported goods due to differential rates of taxation
- Benefits to Companies
- Local manufacturing enables a great deal of flexibility which allows cost efficiencies, control over quality, faster turn-around times in terms of production, transportation, deliveries, etc.
- Manufacturing locally helps India’s industries grow and its talent pool to develop specialised skill sets.
- Localisation can be the gateway to further opportunities such as export growth, import substitution, and contract manufacturing.
- Benefits to Country
- India has the world’s largest population of youth at an employable age. Local manufacturing makes for a great opportunity for the country to supply a workforce to its industries.
- Localisation assists in raising the standards of the lives in the area.
- Localisation enables knowledge sharing and tech transfer with other countries, lending the home country access to the latest global technologies too
- Allows country to position itself as a manufacturing hub for other countries.
Conclusion
With greater government support and industries’ combined efforts, India will surely reap the numerous benefits of localisation in years to come
Connecting the dots:
- Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan
- Do you think the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat would be a game changer for the domestic industries? Substantiate your views.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Weddell Sea is a part of which of the following Ocean?
- Indian Ocean
- Pacific Ocean
- Southern Ocean
- Arctic Ocean
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897:
- This law enables states to ban public gatherings, ask schools and large institutions to stop functioning, and issue advisories to companies to explore work-from-home models.
- It also gives the state a right to penalise media organisations spreading misinformation.
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 20th May 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
On cyber attacks:
On Bureaucracy:
About health infrastructure: