IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Increased Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Economy
In news
- There has been an increase in FDI inflows into India recently.
- Measures taken by the Government regarding Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy reforms, investment facilitation and ease of doing business have contributed to the increase.
Key takeaways
The trends in India’s FDI are:
- Highest ever total FDI inflow of US $81.72 billion during the year 2020-21.
- It is 10% higher as compared to last year (US$ 74.39 billion).
- Top investor countries: Singapore (29%), U.S.A (23%) and Mauritius (9%)
- Maximum FDI received sector-wise: Computer Software & Hardware (44%), Construction (Infrastructure) Activities (13%) and Services Sector (8%)
- Maximum FDI received state-wise: Gujarat (37%), Maharashtra (27%) and Karnataka (13%).
Related articles
Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions
In news
- The new rules for social media platforms and digital news outlets, called the Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code, came into effect recently.
Key takeaways
- The guidelines had asked all social media platforms to set up a grievances redressal and compliance mechanism, which included appointing a resident grievance officer, chief compliance officer and a nodal contact person.
- The Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology had also asked these platforms to submit monthly reports on complaints received from users and actions taken.
- A third requirement from instant messaging apps was to make provisions for tracking the first originator of a message.
- Failure to comply with any one of these requirements would take away the indemnity (security) provided to social media intermediaries under Section 79 of the Information Technology Act.
Do you know?
- Section 79 says any intermediary shall not be held legally or otherwise liable for any third party information, data, or communication link made available or hosted on its platform.
Shahi Litchi
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Trade; GI tags
In news
- Shahi litchi was in the news recently.
- Season’s first consignment of Shahi Litchi from Bihar was exported to UK.
- It is a major boost to the export of GI certified products
Key takeaways
- Shahi litchi is the fourth agricultural products to get GI certification from Bihar in 2018.
- Jardalu mango, Katarni rice and Magahi paan are other GI certified products from the state.
- India is the second largest producer of litchi (Litchi chin) in the world, after China.
- Top producer: Bihar
Important value additions
- Litchi is a sub-tropical fruit.
- It thrives best under moist sub-tropical climate.
- Ideal conditions for growth: Deep, well drained loamy soil, rich in organic matter and having pH in the range of 5 to 7
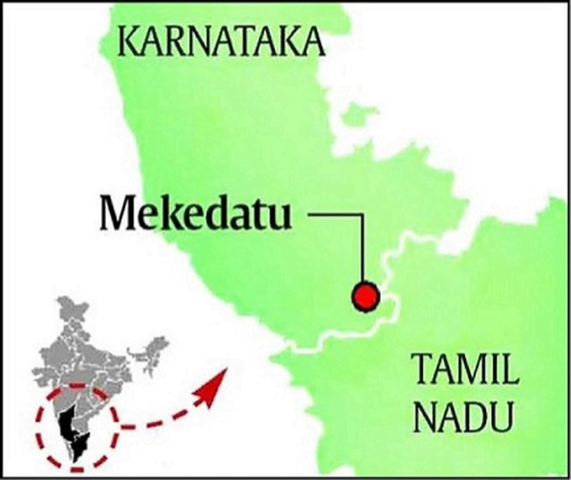
Mekedatu Multi-Purpose Project
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Infrastructure
In news
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has appointed a joint committee to look into allegations of unauthorised construction activity taking place in Mekedatu .
- The Karnataka government had proposed to construct a dam across the Cauvery River at the same place.
Important value additions
- The Mekedatu multi-purpose project involves building a balancing reservoir across the Cauvery River near Kanakapura in Ramanagaram district.
- It envisages supplying drinking water to Bengaluru and Ramanagaram districts, besides generation of power.
- However, Tamil Nadu has opposed it on the grounds that the project violates the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal award.
Miscellaneous
Vineyard Wind Project
- USA has approved the nation’s first major offshore wind farm that will help eliminate emissions from the power sector.
- It is known as Vineyard Wind project.
- It will be located off the coast of Massachusetts.
- It shall create enough electricity to power 400,000 homes by the second half of 2023.
- It shall create 3,600 jobs as well
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE/ POLITY
Topic:
- GS-2: Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Challenges ahead for India’s GST
Context: The 43rd meeting of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council is to be held on May 28. Of the 31 representatives that are expected to attend, 17 members are from the ruling BJP or its alliance partners and remaining 14 are from non-ruling alliance.
Do You Know?
- The 17 members of the ruling dispensation and the 14 members of the non-BJP dispensation in the GST Council represent exactly one half of India’s population each.
- However, the non-BJP group contributes a higher share of 60% of overall GST revenues and accounts for 63% of the country’s GDP.
Issues
- GST Meeting not held: The GST Council was mandated to meet at least once every quarter, but it had not met for two quarters, ostensibly due to the pandemic
- Increased dependency: States are dependent on GST collections for nearly half of their tax revenues. However, in the wake of economic slowdown the compensation to states have not been steady.
- Conditions for extra borrowings: Centre imposed sudden and stringent policy conditions to grant approval to States for extra borrowing in the middle of the pandemic last year.
- Differential Vaccine Pricing: There is a feeling of betrayal over how the States have been forced to pay a much higher price for COVID-19 vaccines than the Centre.
- Misuse of Cess: States are wary of the Centre’s duplicity in levying cesses that garner significant revenues for the Centre without sharing them with the States.
- Failure to deliver on early promises: GST was to deliver enormous economic efficiency gains, improve tax buoyancy and collections, boost GDP growth and usher in greater formalisation of the economy. However, 15th Finance Commission report formally acknowledges that GST has been an economic failure that did not deliver on its early promises.
- Problems underpinning GST continues: Economists point to the multiple rates structure, high tax slabs and the complexity of tax filings as the problems underpinning India’s GST.
- Uncertainty over guaranteed revenue after 2022: GST has endured so far primarily because the States were guaranteed a 14% growth in their tax revenues every year, which minimised their risks of this new experiment and compensated for their loss of fiscal sovereignty. This revenue guarantee ends in July 2022 and there is increasing demand from States to continue this compensation regime even after 2022.
Conclusion
- The phrase ‘cooperative federalism’ was introduced into India’s political lexicon to justify the transition to GST in 2017.
- Cooperative federalism has a larger meaning beyond just fiscal federalism. It also entails cooperative political, administrative and governance federalism between the States and the Centre.
Also Read
SOCIETY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-1: Indian Society & Challenges
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
COVID Orphans
Context: According to the ministry of women and child development, 577 children have been orphaned by the second wave of the pandemic in the last two months. That number might well go up.
Issues:
- Vulnerable to Trafficking: Child traffickers prey on helpless children, especially those who lost both their parents in the pandemic.
- Child Rights: Most fragile children were at the risk of being forced into marriage or child labour.
- Mental Trauma: The weight of loss of both parents will be borne by a generation of vulnerable children for many years to come.
- Access to Education Impacted: The pandemic has dealt a heavy blow to India’s children, with the closure of schools and a digital switch to education leaving a majority excluded.
Measures Taken
- Joining hands together: Communities and governments have come together to ring-fence children from any such eventuality of child falling prey to traffickers.
- Active role by Child Welfare Committees: The government has done well to entrust the task of tracking vulnerable children to child welfare committees at district level. These CWC is actively working by networking with NGOs to protect children affected by Pandemic.
- Custody of Children: The Centre had also asked the ministry of health to ask patients admitted to hospitals to specify in whose custody they would wish to leave their children in case of death.
Way Forward
- Preference to Kinship Care: It is important, as much as possible, to not uproot traumatised children and place them in institutional care, if kinship care is available. Kinship care provides better emotional support & interpersonal bonding, that is much needed for Child upbringing.
- Oversight of adopted families: Government should also make provision for oversight of families that take children in to ensure that they have a hospitable environment to grow and flourish in
- Easing Process of Adoption: The adoption process in India can sometimes run into years. The government can consider making an exception to ease the adoption of children orphaned by Covid-19, without compromising on checks and balances.
- Education: The state must make provisions for supporting the education of orphaned children.
- Mental Health Support: Finally, each child must also be provided mental health support, as unresolved trauma and grief of this scale increase the chances of producing a broken generation.
Conclusion
- Both state and society owe these most vulnerable children empathy, kindness and protection. They cannot afford to fail them.
Connecting the dots
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
- GS-3: Awareness in the field of IT
Rules and rulers: On social media curbs
Context: New Social Media Code coming into effect. It seems that most if not all global social media giants will miss complying with the new rules
- The new rules were introduced in February 2021.
- Among other things, they require the bigger social media platforms to adhere to a vastly tighter set of rules within three months, which ended on May 25.
- The new rules require these platforms to appoint
- Chief compliance officers in order to make sure the rules are followed,
- Nodal officers to coordinate with law enforcement agencies,
- Grievance officers to look into complaints from users
- Another rule requires messaging platforms such as WhatsApp to trace problematic messages to its originators (Traceability)
Issues
- Non-compliance were to trigger a further worsening of the already poor relationship between some social media players and the Government
- The latest stand-off between them, over Twitter tagging certain posts by BJP spokespeople as ‘manipulated media’, has resulted in the Delhi Police visiting the company’s offices.
- The traceability rule raises uneasy questions about how services that are end-to-end encrypted can adhere to this.
- These rules were introduced without much public consultation.
- There has also been criticism about bringing these new rules that ought to be normally triggered only via legislative action.
Way Forward
- It is important that social media companies fight the new rules in a court of law if they find them to be problematic.
- Non-compliance by companies can never be justified, even if it is to be assumed that the U.S. Government has their back.
- Five industry bodies, including the CII, FICCI and the U.S.-India Business Council have sought an extension of 6-12 months for compliance. This is an opportunity for the Government to hear out the industry, and also shed its high-handed way of rule-making.
Connecting the dots
- Dominance of Big tech
- Australia’s News Media Bargaining Code
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Jardalu mango, Katarni rice and Magahi paan are GI certified products from Which of the following state?
- Bihar
- Jharkhand
- Rajasthan
- Uttar Pradesh
Q.2 Mekedatu Multi-Purpose Project is proposed to be constructed across which of the following river?
- Cauvery
- Yamuna
- Krishna
- Godavari
ANSWERS FOR 26th May 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | B |
Must Read
On vaccination:
On political turmoil in Nepal:
About rumour amidst Pandemic:











