IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
RBI Steps in to Ease COVID-19 Burden
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Economy
In news
- The RBI Governor has announced a series of measures to support the nation’s fight against the second wave of COVID-19 infections.
Key takeaways
- Term Liquidity Facility of Rs. 50,000 crore with tenure of up to 3 years, at repo rate, to ease access to emergency health services, for ramping up COVID-related health infrastructure & services.
- Special Long Term Repo Operations for Small Finance Banks (SFBs): In order to provide further support to micro, small and other unorganized sector entities, 3-year repo operations of Rs. 10,000 crore at repo rate, for fresh lending up to Rs 10 lakh per borrower (till 31 October, 2021)
- Lending by SFBs to MFIs to be classified as priority sector lending: In view of fresh challenges, SFBs are now permitted to regard fresh on-lending to MFIs with asset size up to Rs. 500 crore, as priority sector lending (till 31 March, 2022)
- Credit flow to MSME Entrepreneurs: To incentivize inclusion of unbanked MSMEs into banking system, exemption provided in February, 2021 wherein scheduled banks were allowed to deduct credit given to new MSME borrowers from Net Time & Demand Liabilities for calculation of CRR, is now extended to December 31, 2021.
- Rationalization of KYC norms for enhanced customer experience: Steps being proposed include –
- Extending scope to video KYC for new customer categories such as proprietorship firms,
- Conversion of limited KYC accounts to fully KYC compliant accounts,
- Introduction of more customer-friendly options in KYC updating and
- enabling the use of KYC Identifier of Centralised KYC Registry (CKYCR) for V-CIP and submission of electronic documents as identity proof
- Floating Provisions and Countercyclical Provisioning Buffer: Banks can now use 100% of floating provisions held by them, as on December 31, 2020, for making specific provisions for NPAs; (till March 31, 2022)
- Relaxation of overdraft facility for states: Maximum number of days of overdraft in a quarter for state governments has been increased from 36 to 50 days.
Initiative to waive TRIPS protection for COVID-19 vaccines
Part of: GS Prelims And GS-II – International Relations; Health
In news
- USA will support an initiative at the World Trade Organisation (WTO) to waive Trade Related Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) protection for COVID-19 vaccines.
Important value additions
The Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS)
- It is an international legal agreement between all the member nations of the World Trade Organization (WTO).
- It establishes minimum standards for the regulation by national governments of different forms of intellectual property (IP) as applied to nationals of other WTO member nations.
- TRIPS was negotiated at the end of the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) between 1989 and 1990 and is administered by the WTO.
Unique Disability ID (UDID)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – Governance; Policies and interventions
In news
- The Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD), Government of India has made it mandatory for all States/UTs to grant certificate of disability through online mode only using UDID portal from 1st June
Key takeaways
- The Central Government notified the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Rules, 2017 under RPwD Act, 2016
- Rule 18(5) mandates the Central Government to appoint a date making it mandatory for the State/UT authorities to issue certificate of disability through online mode.
- The UDID project has been under implementation since 2016.
- It will ensure complete digitization of certification of disability from 01.06.2021, besides providing a viable mechanism for cross-checking genuineness of the certificate to achieve pan-India validity, and simplifying the process for the benefit of Divyangjan.
Place in news: Dahla Dam
Part of: GS Prelims GS – I – Geography & GS-II – International Relations
In news
- The Taliban has captured Afghanistan’s second-biggest dam after months of fierce fighting in its former bastion of Kandahar.

Key takeaways
- It provides irrigation to farmers via a network of canals as well as drinking water for the provincial capital
- It is now under Taliban control.
- The dam’s capture comes after clashes erupted in neighbouring Helmand province just days after the U.S. military formally began withdrawing its remaining troops from Afghanistan.
Important value additions
Dahla Dam
- The Dahla Dam is also known as Arghandab Dam.
- It is located in the Shah Wali Kot District of Kandahar Province, Afghanistan.
- Constructed in: 1952
- It is built on the Arghandab River.
(Mains Focus)
INTERNATIONAL/ ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Intellectual property waiver for Covid-19 vaccines
Context: The United States recently announced support for waiving intellectual property protection for Covid-19 vaccines, saying extraordinary circumstances call for extraordinary measures.
All 164 WTO members must agree on the draft, and any one member can veto it. The European Union, which had earlier opposed the waiver, has now stated its intent to discuss the US-backed proposal.
What are patents and IP rights?
- A patent represents a powerful intellectual property right, and is an exclusive monopoly granted by a government to an inventor for a limited, pre-specified time.
- It provides an enforceable legal right to prevent others from copying the invention.
- Patents can be either process patents or product patents.
- A product patent ensures that the rights to the final product is protected, and anyone other than the patent holder can be restrained from manufacturing it during a specified period, even if they were to use a different process.
- A process patent enables any person other than the patent holder to manufacture the patented product by modifying certain processes in the manufacturing exercise.
- India moved from product patenting to process patenting in the 1970s, which enabled India to become a significant producer of generic drugs at global scale, and allowed companies like Cipla to provide Africa with anti-HIV drugs in the 1990s.
- But due to obligations arising out of the TRIPS Agreement, India had to amend the Patents Act in 2005, and switch to a product patents regime across the pharma, chemicals, and biotech sectors.
What does the intellectual property waiver for Covid-19 vaccines mean?
- Increased Production: Most production is currently concentrated in high-income countries. The IP waiver might open up space for production of Covid vaccines with emergency use authorisations (EUA) on a larger scale in middle-income countries. production by middle-income countries has been happening through licensing or technology transfer agreements.
- Countries including Canada, South Korea, and Bangladesh have shown interest in making Covid vaccines if they can get a patent waiver
- Role by India: The US support for an IP waiver stems from a proposal by India and South Africa in the WTO last year. That proposal had, however, called for a waiver on all Covid interventions, including testing diagnostics and novel therapeutics.
What are the deterrents for the waiver?
- Undermine R&D Investment: Pharma companies including Pfizer and AstraZeneca have opposed the proposed waiver — saying eliminating IP protections would undermine the global response to the pandemic, including the ongoing R&D efforts to tackle new variants.
- Doubts on Safety from new facilities: Pharma Companies also argued that waiving IPR & opening production facilities in developing countries could also undermine public confidence in vaccine safety and create a barrier to information sharing.
Besides patents, what are the other roadblocks to scaling up production?
- Trade barriers: Countries like the US had blocked exports of critical raw materials used in the production of some Covid-19 vaccines using regulations like the American Defence Production Act.
- Bottlenecks in supply chains
- Scarcity of raw materials and ingredients in the supply chain
- Unwillingness of rich countries to share doses with poorer nations.
Connecting the dots:
INTERNATIONAL/ ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-3: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
5G Trials in India
Context: The Department of Telecommunications allowed private telcos Airtel, Reliance Jio and Vi and well as state-run telco MTNL to start trials for 5G technology as well as its applications in various sectors. The trials will last for 6 months for now.
What is 5G?
- 5G is the fifth generation cellular technology that apart from increasing the downloading and uploading speeds (speed of 1 Gbps) over the mobile network, also reduces the latency i.e. the time taken by a network to respond.
- It also increases energy efficiency and offers more stable network connections.
- 5G is also designed to deliver signals more reliably than earlier cellular networks
- 5G will have a wider area in the frequency spectrum (range of frequencies) that will ensure no network congestion.
- In addition, it will also ensure connectivity to a full circle i.e. everything is connected to every other thing.
- 5G will help facilitate the ecosystem for the Internet of Things (IoT) and to incorporate Artificial Intelligence (AI) in our daily lives and
- To get the benefits of 5G, users will have to buy new phones, while carriers will need to install new transmission equipment to offer the faster service.
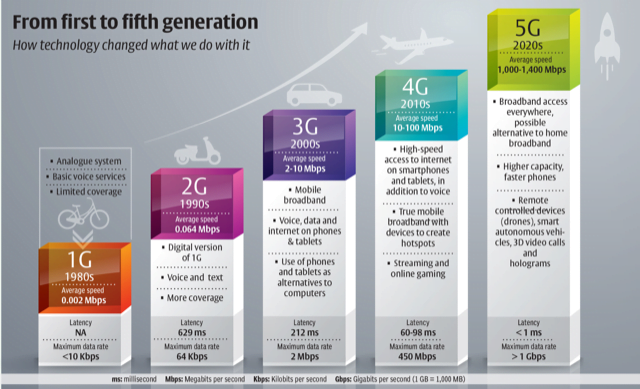
5G mainly works in 3 bands, namely low, mid and high-frequency spectrum — all of which have their uses and limitations.
- While the low band spectrum has shown great promise in terms of coverage but the maximum speed is limited to 100 Mbps. This means that while telcos can use and install it for commercial cellphone users who may not have specific demands for very high speed internet, the low band spectrum may not be optimal for specialised needs of the industry.
- The mid-band spectrum, on the other hand, offers higher speeds compared to the low band, but has limitations in terms of coverage area and penetration of signals. Telcos and companies, which have taken the lead on 5G, have indicated that this band may be used by industries and specialised factory units for building captive networks that can be moulded into the needs of that particular industry.
- The high-band spectrum offers the highest speed of all the three bands, but has extremely limited coverage and signal penetration strength. Internet speeds in the high-band spectrum of 5G has been tested to be as high as 20 Gbps (giga bits per second), while, in most cases, the maximum internet data speed in 4G has been recorded at 1 Gbps.
Why are the trials for 5G technology important for telcos?
- Cut-throat market: The telecom market in India is left with only three private telcos so in order to increase their average revenue per user, it is imperative for telcos to start offering the new 5G technology as soon as possible.
- Standing Committee’s Warning to government: A standing committee of Lok Sabha on Information Technology had submitted its report on 5G and said that India will miss the 5G bus if government doesn’t take quick steps.
What will 5G trials in India entail for now?
- In the initial phase, these trials will be for 6 months, including a 2 month period for procurement and setting up of the equipment.
- In these 6 months, telcos will be required to test their set up in urban areas, semi-urban areas as well as rural areas.
- During this period, the telcos will be provided with experimental spectrum in various bands, such as the mid-band of 3.2 GHz to 3.67 GHz, the millimeter wave band of 24.25 GHz to 28.5 GHz, and others.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding TRIPS:
- It is an international legal agreement between all the member nations of the World Trade Organization (WTO).
- TRIPS was negotiated at the end of the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Where is Dahla Dam located?
- Pakistan
- Sri Lanka
- India
- Afghanistan
ANSWERS FOR 6th May 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | B |
Must Read
On MSME Sector:
On QUAD:
About how diaspora pushed US to help in India’s COVID efforts:











