IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
High-level Dialogue on Desertification, Land Degradation and Drought
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – International Relations and GS III – Conservation
In news
- Recently, the Indian Prime Minister delivered a keynote address at the United Nations (UN) “High-Level Dialogue on Desertification, Land Degradation and Drought” via video conference.
Steps Taken by India to deal land degradation
- India is on track to achieve its national commitment on Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN) (Sustainable Development Goal target 15.3).
- It is working to restore 26 million hectares of degraded land by 2030.
- Over the last 10 years, around 3 million hectares of forest cover has been added.
- India is assisting fellow developing countries to develop land restoration strategies.
- A Centre of Excellence is being set up in India to promote a scientific approach towards land degradation issues.
- It is at Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education.
What is Land Degradation and its impact?
- Land degradation is caused by multiple forces, including extreme weather conditions, particularly drought and human activities that pollute or degrade the quality of soils and land utility.
- It creates arid, semi-arid and dry sub-humid areas.
- It accelerates climate change and biodiversity loss.
- It adds to droughts, wildfires, involuntary migration and the emergence of zoonotic infectious diseases.
Global Efforts to Check Land Degradation
- United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD): Sole legally binding international agreement
- The Bonn Challenge: : To bring 150 million hectares of the world’s deforested and degraded land into restoration by 2020, and 350 million hectares by 2030.
- Great Green Wall: Initiative by Global Environment Facility (GEF), where eleven countries in Sahel-Saharan Africa have focused efforts to fight against land degradation and revive native plant life to the landscape.
EU urged to consider its GSP+ status given to Sri Lanka
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – International Relations and GS -III – Economy
In news
- Recently, a resolution was adopted by the European Parliament, urging the European Union (EU) Commission to consider the temporary withdrawal of the Generalised Scheme of Preferences Plus (GSP+) status given to Sri Lanka.
- It is a set of EU rules allowing exporters from developing countries to pay less or no duties on their exports to the European Union.
- It helps developing countries to alleviate poverty and create jobs.
- The EU’s GSP is widely recognised as the most progressive in terms of coverage and benefits.
- The EU continuously monitors and reviews GSP+ beneficiary countries’ effective implementation of the international conventions on human rights, labour rights.
- The GSP was adopted at UNCTAD in New Delhi in 1968 and was instituted in 1971
- The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body.
- UNCTAD is the part of the United Nations Secretariat dealing with trade, investment, and development issues.
Generalized System of Preferences (GSP)
- Umbrella that comprises the bulk of preferential schemes granted by industrialized nations to developing countries.
- Reduced Most Favored Nations (MFN) Tariffs or duty-free entry of eligible products exported by beneficiary countries to the markets of donor countries.
Southern Ocean recognised as fifth ocean by National Geographic magazine
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -I – Geography
In news
- Recently, on the occasion of World Ocean Day (8th June), the National Geographic magazine has recognised the ‘Southern Ocean’ as the world’s fifth ocean.
- Other four Oceans are: Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, and Arctic Oceans.
About Southern Ocean
- The Southern Ocean is the only ocean ‘to touch three other oceans (Pacific, Atlantic and Indian Ocean).
- It is the only Ocean to completely embrace a continent rather than being embraced by them.
- It is also defined by its Antarctic Circumpolar Current that was formed 34 million years ago.
- The current flows from west to east around Antarctica
Significance of Recognition
- It is a step towards conservation of World’s Oceans, redirecting public awareness onto a region which needs a conservation spotlight.
- Southern Ocean is getting rapidly warmed due to global warming, industrial fishing on species like krill and Patagonian tooth fish.
Dagmara Hydro-Electric Project: Bihar
Part of: GS Prelims and GS I – Geography and GS -III – Infrastructure
In news
- Recently, a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) has been signed between National Hydro Power Corporation (NHPC) Limited and Bihar State Hydroelectric Power Corporation Limited (BSHPC) for Implementation of Dagmara Hydro-Electric Project, Supaul, Bihar
- The project is located on Kosi river.
About the Project
- It is a Run-of-the-River scheme.
- Run-of-river hydro projects use the natural downward flow of rivers and micro turbine generators to capture the kinetic energy carried by water.
- The project will have the total capacity of generating 130 MW energy,
Significance
- It will be a landmark project in the power sector scenario of Bihar as far as green power is concerned.
- It will enhance the socio-economic and infrastructure development and create employment opportunities.
About Kosi River
- The Kosi is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet, Nepal and India.
- It has its source in Tibet
- Major tributaries: Sun Kosi, Arun and Tamur
- Its unstable nature causes course changes.
- The Kosi carries the maximum amount of silt and sand after the Brahmaputra in India.
- It is also known as the “Sorrow of Bihar” due to the extreme flooding that it causes.
100% of Human Genome sequenced
Part of: GS Prelims and GS III – Sci and tech; Biotechnology
In news
- Researchers at the Telomere-to- Telomere Consortium, an international collaboration, have sequenced the first complete human reference genome.
About Genome Sequencing and genome
- Genome Sequencing means deciphering the exact order of base pairs in an individual.
- Genome is an organism’s complete set of DNA.
- Human Genome contains about 3 billion base pairs.
Benefits of Genome Sequencing
- Help in identifying genomic causes of rare diseases.
- Improving the understanding of how virus spreads.
- Identifying the genetic mutations
Various initiatives taken for genome Sequencing
- IndiGen programme: Funded by the Council for scientific and Industrial Research to undertake whole genome sequences of 1000 Indian individuals representing diverse ethnic groups from India.
- Genome India project by Department of Biotechnology which aims to collect 10,000 genetic samples from citizens across India
- Human Genome Project: An international research to determine DNA sequence of the entire Human Genome. It began in 1999 and was completed in 2003.
Miscellaneous
Raja Parba
- It is also known as Mithuna SanKranti.
- It is a three-day festival celebrating womanhood in Odisha.
- It is believed that during this period Mother Earth menstruates and prepares herself for future agricultural activities with the arrival of monsoon.
- People worship goddess Bhudevi who is the wife of Lord Jagannath
- Women are given a break from household work and people abstain from walking barefoot on the earth
(Mains Focus)
EDUCATION/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in Education sectors
- GS-2: Issues relating to development and management of Education, Human Resources
All-India Survey of Higher Education (AISHE) 2019-20
Context: The ministry of education released the findings of the All-India Survey of Higher Education (AISHE) for 2019-20 on June 10.
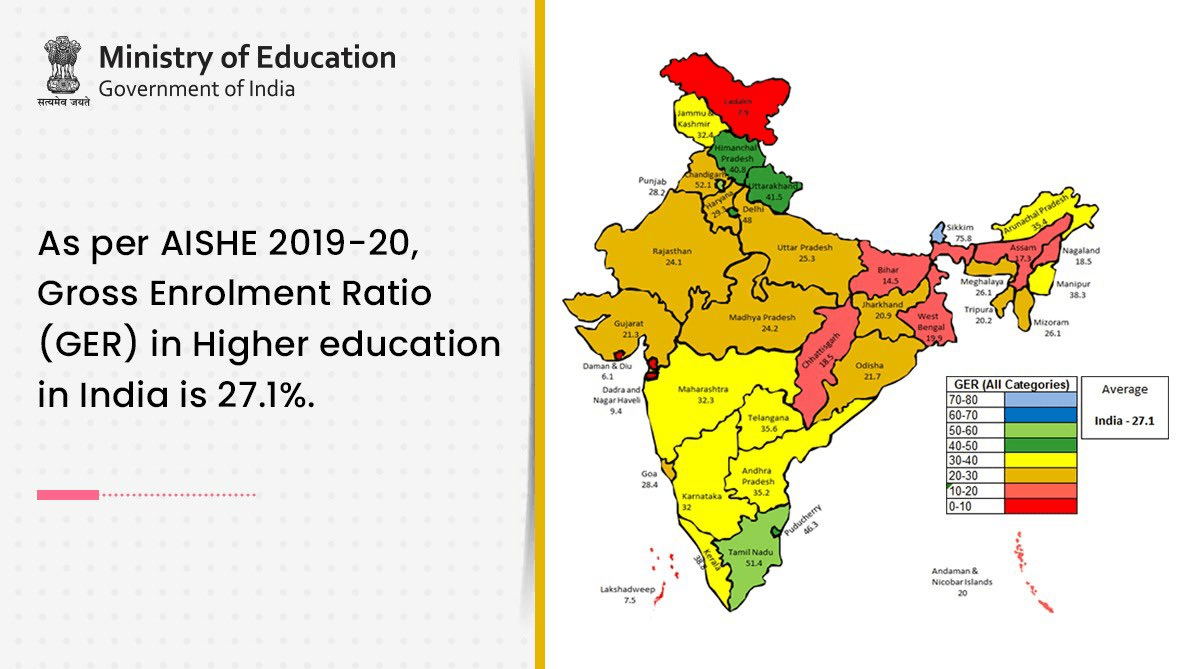
Key Highlights of the report
| Total Enrolment
In Higher Education |
Out of these, nearly 85% of the students (2.85 crore) were enrolled in the six major disciplines such as Humanities, Science, Commerce, Engineering & Technology, Medical Science and IT & Computer. |
| Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) |
GER in higher education is calculated for the 18-23 age group. It is the ratio of enrolment in higher education to the population in the eligible age group. |
| Gender Parity Index (GPI) |
|
| Students Pursuing PhD |
|
| Total Number of Teachers |
|
However, the report also contains enough evidence to suggest that India’s higher education sector confronts serious issues of inequality across the gender, caste, and regional axis.
- Headline improvement in enrolment numbers hides access to professionally rewarding courses
- When it comes to accessing professionally rewarding education, caste and gender seem to be major determinants.
- The only professional courses — among the top 10 most pursued programmes at bachelor’s and master’s level — where women do better than men are BEd and MEd, which are usually pursued by aspiring school-teachers
- Multi-layered social inequality among teachers in Higher Education
- More than 40% of the teachers in India’s higher educational institutions are non-SC-ST-OBC Hindus. Their population share, as per the findings of the 2015-16 National Family and Health Survey (NFHS), is just 17.6%.
- Even in Institutes of National Importance, which include institutes such as IITs, NITs, AIIMS, and IIMs, the share of non-SC-ST-OBC Hindu teachers is more than 70%.
- The share of women at the demonstrator/tutor position in educational institutions is 65.5%, but it falls to 27.5% at the level of associate professor/professor.
- Geography matters as much as sociology
- Access to higher education varies significantly across states.
- GER is 15.8% and 13.1% for men and women in Bihar and 44.9% and 51.8% in Delhi.
- Regional Distribution of Government Colleges
- Only 8,565 of 39,955 colleges in India or about a fifth (21.4%) were government colleges in 2019-20. But there is wide regional variation in the share of government colleges across different states.
- In poorer states in the east, government colleges make up a third to half of educational institutions, while in southern and western states government colleges are less than a fifth of all colleges.
- Government colleges are almost as big a chunk of total colleges in Delhi (55.7%) as they are in Bihar (59.8%). This should make it clear that the public sector footprint is hardly an indicator of quality of education
Connecting the dots:
- National Education Policy (NEP), 2020: It aims at increasing the GER in higher education to 50% by 2035.
EDUCATION/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- Gs-2: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Education, Human Resources
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Relearning Assessment
Context: The wait for a way to assess Class XII students after the cancellation of the board examinations has created immense anxiety in students and parents.
On this issue, there is a need to look at both the short and long-term evaluation goals.
What is assessment?
- Assessment is defined as a systematic review of learning, use of information collected from various experiences and consistent feedback.
- Assessments should have multiple rubrics in place. This will help to gauge what learners know, measure their understanding, track progress, help in planning the next step, assign remedial work and constantly give feedback to the stakeholders..
Present day assessment system
- The above definition contradicts how we assess our learners because we do not give them a variety of learning experiences.
- We assess them through a year-end standardised test of three hours in the national exams.
What measures can be taken to reform our assessment system?
- Application oriented: Questions have to be application-based. Banks of case studies, without too many knowledge and memory-based tasks, should be created.
- Innovative testing methods: Interesting testing systems, such as gamified tests, periodic midterms, project-based tests, should be attempted.
- Subject-based Evaluation techniques: It is essential to develop a framework to evaluate more autonomously. Evaluation tools need to be changed depending on the subjects. A student cannot be evaluated in science the way she is in languages.
- Interdisciplinary approach: We need to create capacity-building methods where every child is equipped with a diversity of knowledge and emphasis is given to her competencies, values and attitudes, using experiential pedagogy that integrates art, play, life skills, social and emotional learning with an interdisciplinary approach.
- Retaining the Essence of Assessment: The purpose of assessment is to understand learning outcomes. Identifying learning, aligning it to the goal, mapping skills, designing authentic tasks through which progress can be captured should be the essence of assessment
- A holistic report card should be equitable, inclusive and joyful, reflecting the learner’s diverse knowledge. A combination of self, peer, teacher and parent assessment will help create students who can reconcile tensions, take on responsibilities and shape better futures.
- Leveraging Online Assessment: Evaluating question papers physically will become a challenge. Issues of paperwork, manpower, confidentiality, and monitoring teachers in evaluation centres, will continue to pose problems. The creation of online assessment platforms has to be explored and supported by regional centres and schools
Conclusion
Unless education is more contemporary and child-centric, our children will not be able to cope with the rigours of the future. We need to have alternative learning systems that are enjoyable, inclusive, progressive and holistic. Breaking the mould of rote learning will help children realise their full potential.
Connecting the dots:
- National Education Policy mark a shift from a summative to a formative and competency-based learning system.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the following are initiatives taken for genome Sequencing by India?
- IndiGen programme
- Human Genome Project
- Genome India project
Select the correct code:
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2 Raja Parba is a festival of which of the following state of India?
- Odisha
- Tamil Nadu
- Assam
- Punjab
Q.3 Which of the following river is known as “Sorrow of Bihar’?
- Ganga
- Yamuna
- Brahmaputra
- Kosi
ANSWERS FOR 15th June 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | B |
Must Read
On Criminal Justice System:
On Electoral Bonds:
On Biodiversity:











